C++ 实现 matlab 的 buttap 函数
文章目录
- 1. matlab buttap 函数的功能
- 2. matlab buttap 函数的使用方法
- 3. C++实现
- 4. 测试
1. matlab buttap 函数的功能
输入模拟低通巴特沃斯滤波器的最低阶数,输出对应模拟低通巴特沃斯滤波器的传递函数的零点、极点、增益
其中,零点都为0,增益为1
也就是说设计的是全极点的模拟巴特沃斯滤波器
2. matlab buttap 函数的使用方法
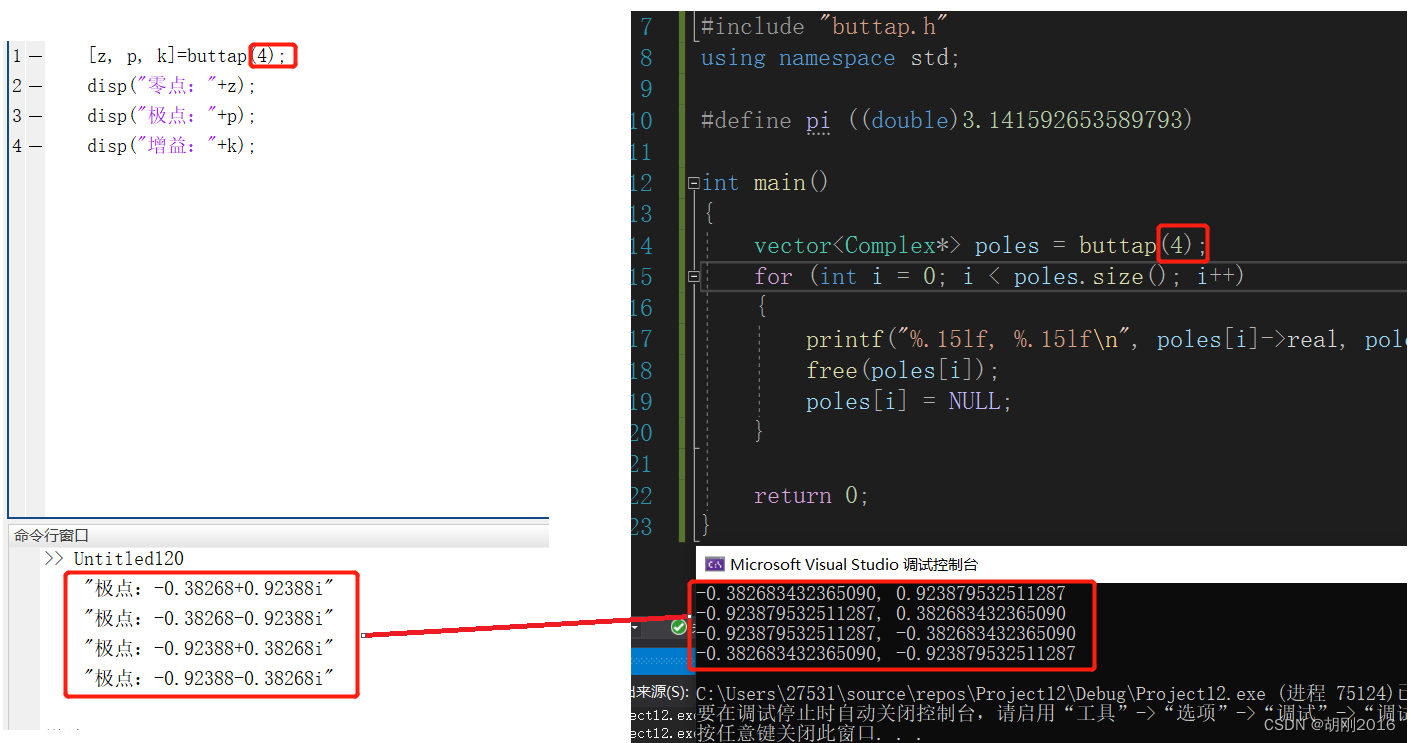
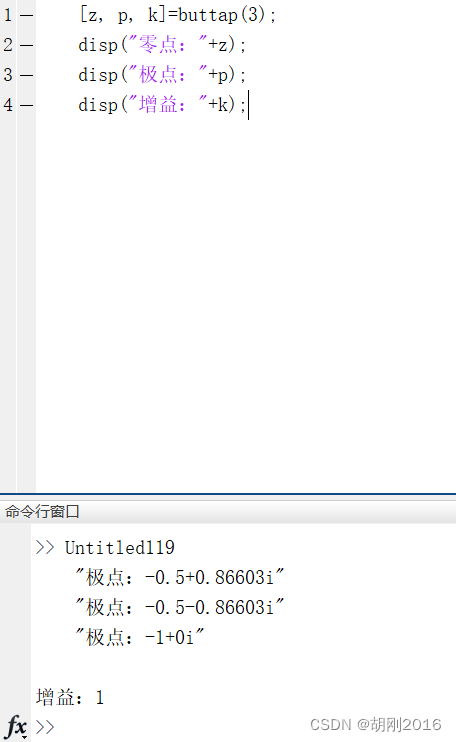
[z, p, k]=buttap(3);
disp("零点:"+z);
disp("极点:"+p);
disp("增益:"+k);
3. C++实现
#pragma once
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include "complex.h"
#define pi ((double)3.141592653589793)
using namespace std;
vector<Complex*> buttap(int n)
{
vector<Complex*> poles;
if (n <= 0)
{
return poles;
}
poles.resize(n);
for (int k = 0, i = 0; k <= ((2 * n) - 1); k++)
{
if (1.0 * cos(pi * 0.5 + pi * (2 * k + 1) / (2 * n)) < 0)
{
poles[i] = (Complex*)malloc(sizeof(Complex));
poles[i]->real = 1.0 * cos(pi * 0.5 + pi * (2 * k + 1) / (2 * n));
poles[i]->img = 1.0 * sin(pi * 0.5 + pi * (2 * k + 1) / (2 * n));
i++;
if (i == n) break;
}
}
return poles;
}
4. 测试
测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include "buttap.h"
using namespace std;
#define pi ((double)3.141592653589793)
int main()
{
vector<Complex*> poles = buttap(*N);
for (int i = 0; i < poles.size(); i++)
{
printf("%.15lf, %.15lf\n", poles[i]->real, poles[i]->img);
free(poles[i]);
poles[i] = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
测试结果
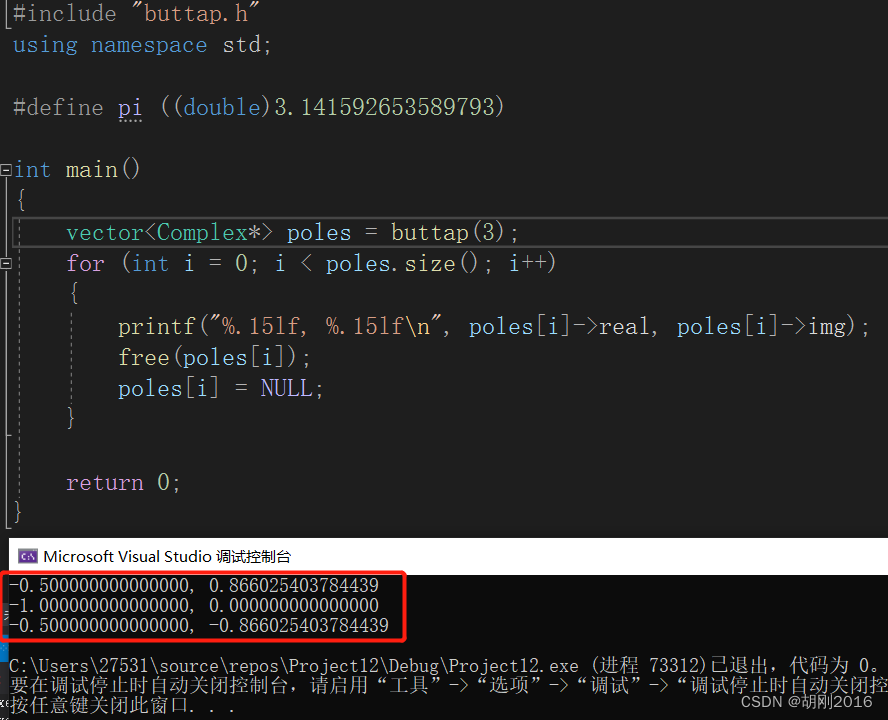
可以看出和matlab 的结果一致
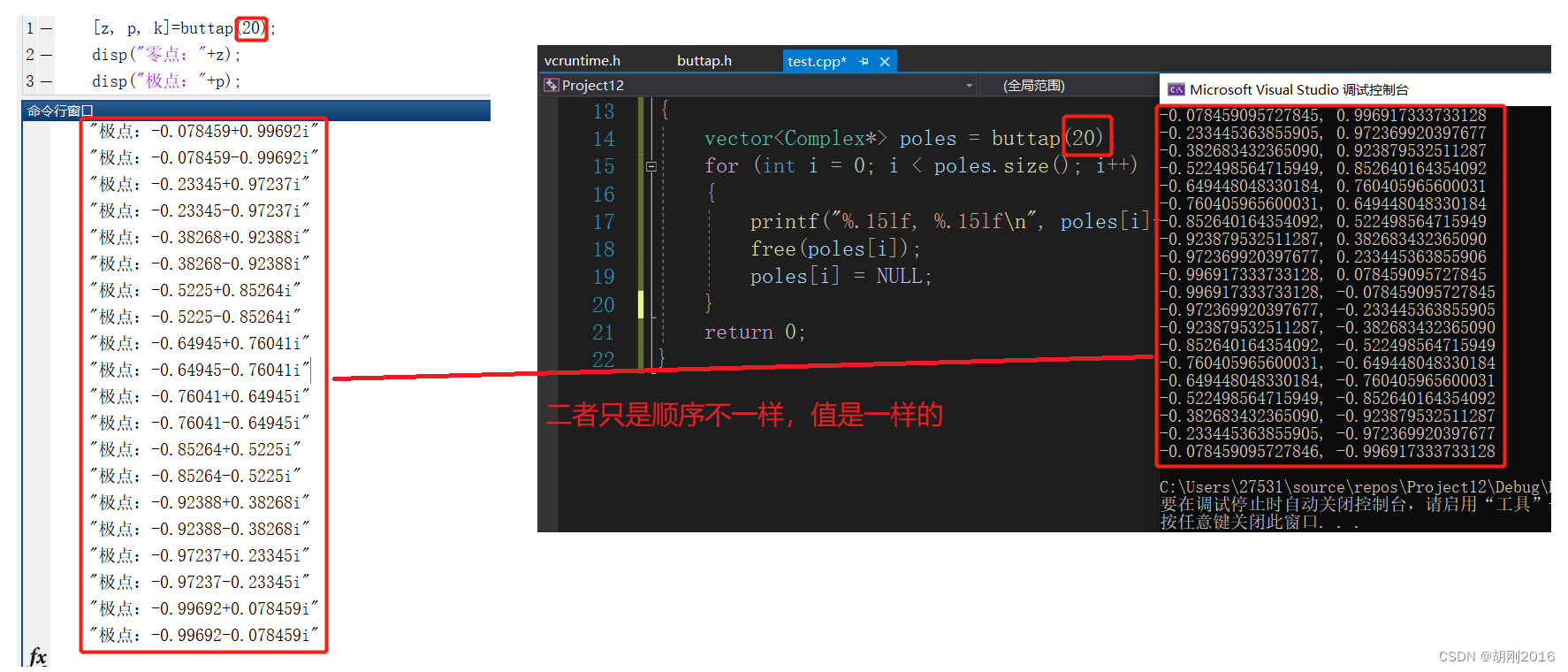
下面再给出几组测试结果