Linux 串口应用编程
1 串口 API
Linux串口通信:
在
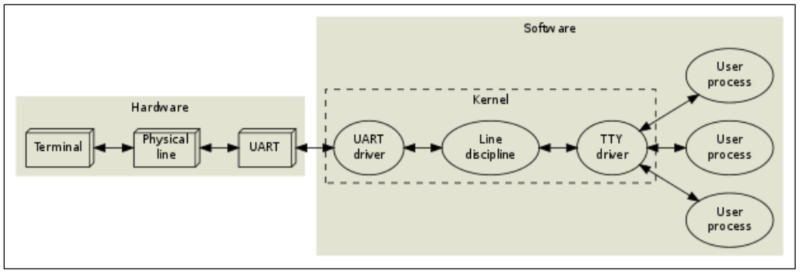
Linux
系统中,操作设备的统一接口就是:
open/ioctl/read/write
。
对于
UART
,又在
ioctl
之上封装了很多函数,主要是用来设置行规程。所以对于 UART
,编程的套路就是:
⚫
open
;
⚫
设置行规程,比如波特率、数据位、停止位、检验位、
RAW
模式、一有数据就返回;
⚫
read/write
;
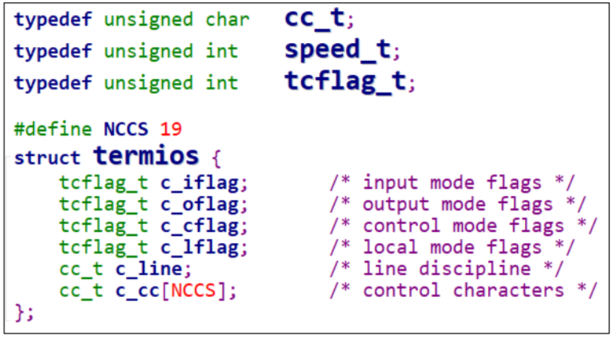
怎么设置行规程?行规程的参数用结构体
termios
来表示,可以参考
Linux串口—struct termios
结构体:
这些函数在名称上有一些惯例:
⚫
tc
:
terminal contorl
⚫
cf: control flag
下面列出一些函数:
函数名 作用
tcgetattr get terminal attributes,
获得终端的属性
tcsetattr set terminal attributes,
修改终端参数
tcflush
清空终端未完成的输入/输出请求及数据
cfsetispeed sets the input baud rate,
设置输入波特率
cfsetospeed sets the output baud rate,
设置输出波特率
cfsetspeed
同时设置输入、输出波特率
函数不多,主要是需要设置好 termios
中的参数,这些参数很复杂,可以参考 Linux 串口—
struct termios
结构体。
2 串口收发实验
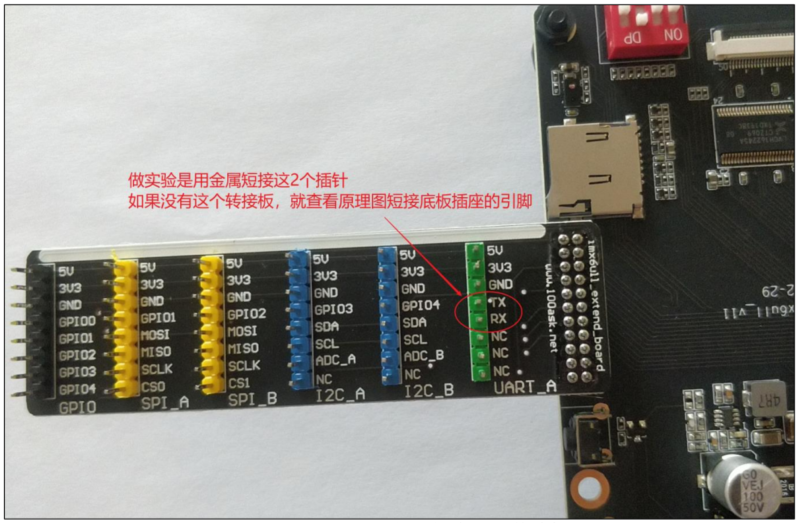
本实验通过把串口的发送、接收引脚短接,实现自发自收:使用 write
函数发出字符,使用 read
函数读取字符。
2.1 上机实验
2.1.1 设置工具链
vim ~/.bashrc
export ARCH=arm
export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihfexport PATH=$PATH:/home/book/100ask_imx6ull-sdk/ToolChain/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf_sdk-buildroot/bin2.1.2 编译、执行程序
1. Ubuntu 上
arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -o serial_send_recv serial_send_recv.c
2. 板子上
/mnt/serial_send_recv /dev/ttymxc52.2 GPS 模块实验
2.2.1 GPS 简介
全球定位系统(Global Positioning System
,
GPS)
是一种以空中卫星为基础的高精度无线电导航的定位系统,它在全球任何地方以及近地空间都能够提供准确的地理位置、车行速度及精确的时间信息。GPS
主要由三大组成部分:空间部分、地面监控部分和用户设备部分。GPS
系统具有高精度、全天候、用广泛等特点。
太空卫星部分由多颗卫星组成,分成多个轨道,绕行地球一周约 12
小时。每个卫星均持续发射载有卫星轨道数据及时间的无线电波,提供地球上的各种接收机来应用。
地面管制部分,这是为了追踪及控制太空卫星运行所设置的地面管制站,主要工作为负责修正与维护每个卫星能够正常运转的各项参数数据,以确保每个卫星都能够提供正确的讯息给使用者接收机来接收
使用者接收机(即用户设备),追踪所有的 GPS 卫星,并实时的计算出接收机所在位置的坐标、移动速度及时间。我们日常接触到的是用户设备部分,这里使用到的 GPS
模块即为用户设备接收机部分。
2.2.2 GPS 模块硬件
GPS 模块与外部控制器的通讯接口有多种方式,这里我们使用串口进行通讯,波特率为 9600bps,1bit
停止位,无校验位,无流控,默认每秒输出一次标准格式数据。
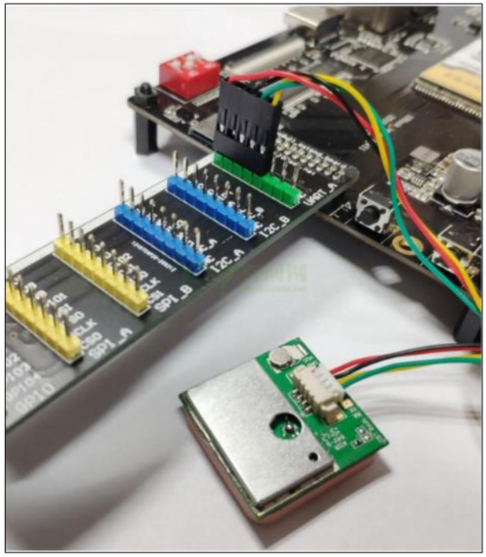
GPS 模块外观如下图所示,通过排线与控制器进行供电和通讯。该模块为集成模块,没有相关原理图。

2.2.3 GPS 模块数据格式
GPS 使用多种标准数据格式,目前最通用的
GNSS
格式是
NMEA0183
格式。NMEA0183 是最终定位格式,即将二进制定位格式转为统一标准定位格式,与卫星类型无关。这是一套定义接收机输出的标准信息,有几种不同的格式,每种都是独立相关的 ASCII
格式,逗点隔开数据流,数据流长度从
30-100
字符不等,通常以每秒间隔持续输出。
NVMEA0183 格式主要针对民用定位导航,与专业
RTCM2.3/3.0
和
CMR+
的GNSS 数据格式不同。通过
NMEA0183
格式,可以实现
GNSS
接收机与
PC
或
PDA 之间的数据交换,可以通过 USB
和
COM
口等通用数据接口进行数据传输,其兼容性高,数据传输稳定。这里我们使用串口进行是通讯,通信框图如下图所示。
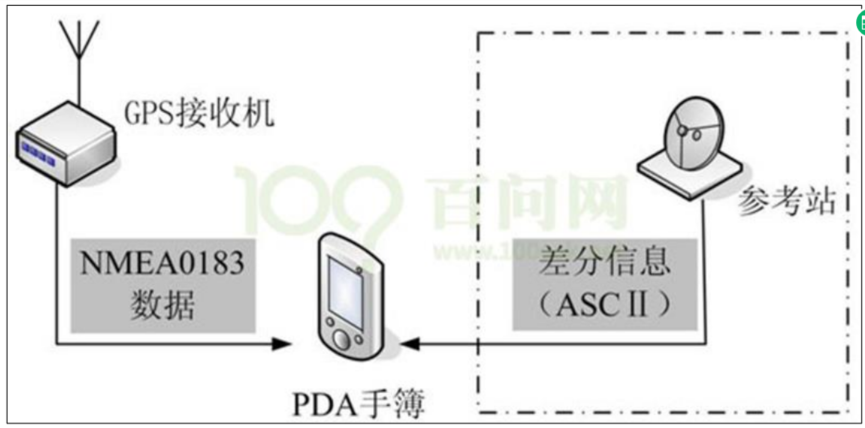
我们使用串口接收数据,收到的数据包含:$GPGGA
(
GPS
定位数据)、
$GPGLL(地理定位信息)、$GPGSA
(当前卫星信息)、
$GPGSV
(可见卫星状态信息)、$GPRMC(推荐最小定位信息)、
$GPVTG
(地面速度信息)。
这里我们只分析$GPGGA (Global Positioning System Fix Data)
即可,它包含了 GPS
定位经纬度、质量因子、
HDOP
、高程、参考站号等字段。其标准格式如下:
$GPGGA,<1>,<2>,<3>,<4>,<5>,<6>,<7>,<8>,<9>,M,<10>,M,<11>,<12>*hh<CR><LF>
$XXGGA 语句各字段的含义和取值范围各字段的含义和取值范围见下表所示,XX 取值有:
◼
GPGGA
:单
GPS
◼
BDGGA
:单北斗
◼
GLGGA
:单
GLONASS
◼
GNGGA
:多星联合定位
$XXGGA 字段
<1> UTC 时间 hhmmss.ss 000000.00~235959.99
<2> 纬度,格式:ddmm.mmmm 000.00000~8959.9999
<3> 南北半球 N 北纬 S 南纬
<4> 经度格式 dddmm.mmmm 00000.0000~17959.9999
<5> 东西半球 E 表示东经 W 表示西经
<6> GPS 状态 0=未定位
1=GPS 单点定位固定解
2=差分定位
3=PPS 解
4=RTK 固定解
5=RTK 浮点解
6=估计值
7=手工输入模式
8=模拟模式
<7> 应用解算位置的卫星数 00~12
<8> HDOP 水平图形强度因子 0.500~99.000(大于 6
不可用
)
<9> 海拔高度 -9999.9~99999.9
<l0> 地球椭球面相对大地水准面的高度(高程异常) -9999.9~99999.9
<11> 差分时间 从最近一次接收到差分信号开始的秒数,如果不是差分定位将为空
<12> 参考站号 0000~1023;不使用 DGPS 时为空
例子:
$GPGGA
,
074529.82
,
2429.6717
,
N
,
11804.6973
,
E
,
1
,
8
,
1.098
, 42.110,,,
M
,,
*76
。
2.3 编程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* set_opt(fd,115200,8,'N',1) */
int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop)
{
struct termios newtio,oldtio;
if ( tcgetattr( fd,&oldtio) != 0) {
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return -1;
}
bzero( &newtio, sizeof( newtio ) );
newtio.c_cflag |= CLOCAL | CREAD;
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
newtio.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG); /*Input*/
newtio.c_oflag &= ~OPOST; /*Output*/
switch( nBits )
{
case 7:
newtio.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
newtio.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
}
switch( nEvent )
{
case 'O':
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;
newtio.c_cflag |= PARODD;
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
break;
case 'E':
newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);
newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
break;
case 'N':
newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
break;
}
switch( nSpeed )
{
case 2400:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2400);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2400);
break;
case 4800:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B4800);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B4800);
break;
case 9600:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);
break;
case 115200:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B115200);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B115200);
break;
default:
cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);
cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);
break;
}
if( nStop == 1 )
newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
else if ( nStop == 2 )
newtio.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
newtio.c_cc[VMIN] = 1; /* 读数据时的最小字节数: 没读到这些数据我就不返回! */
newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0; /* 等待第1个数据的时间:
* 比如VMIN设为10表示至少读到10个数据才返回,
* 但是没有数据总不能一直等吧? 可以设置VTIME(单位是10秒)
* 假设VTIME=1,表示:
* 10秒内一个数据都没有的话就返回
* 如果10秒内至少读到了1个字节,那就继续等待,完全读到VMIN个数据再返回
*/
tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH);
if((tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio))!=0)
{
perror("com set error");
return -1;
}
//printf("set done!\n");
return 0;
}
int open_port(char *com)
{
int fd;
//fd = open(com, O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_NDELAY);
fd = open(com, O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY);
if (-1 == fd){
return(-1);
}
if(fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, 0)<0) /* 设置串口为阻塞状态*/
{
printf("fcntl failed!\n");
return -1;
}
return fd;
}
int read_gps_raw_data(int fd, char *buf)
{
int i = 0;
int iRet;
char c;
int start = 0;
while (1)
{
iRet = read(fd, &c, 1);
if (iRet == 1)
{
if (c == '$')
start = 1;
if (start)
{
buf[i++] = c;
}
if (c == '\n' || c == '\r')
return 0;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
}
/* eg. $GPGGA,082559.00,4005.22599,N,11632.58234,E,1,04,3.08,14.6,M,-5.6,M,,*76"<CR><LF> */
int parse_gps_raw_data(char *buf, char *time, char *lat, char *ns, char *lng, char *ew)
{
char tmp[10];
if (buf[0] != '$')
return -1;
else if (strncmp(buf+3, "GGA", 3) != 0)
return -1;
else if (strstr(buf, ",,,,,"))
{
printf("Place the GPS to open area\n");
return -1;
}
else {
//printf("raw data: %s\n", buf);
sscanf(buf, "%[^,],%[^,],%[^,],%[^,],%[^,],%[^,]", tmp, time, lat, ns, lng, ew);
return 0;
}
}
/*
* ./serial_send_recv <dev>
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int iRet;
char c;
char buf[1000];
char time[100];
char Lat[100];
char ns[100];
char Lng[100];
char ew[100];
float fLat, fLng;
/* 1. open */
/* 2. setup
* 115200,8N1
* RAW mode
* return data immediately
*/
/* 3. write and read */
if (argc != 2)
{
printf("Usage: \n");
printf("%s </dev/ttySAC1 or other>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fd = open_port(argv[1]);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s err!\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
iRet = set_opt(fd, 9600, 8, 'N', 1);
if (iRet)
{
printf("set port err!\n");
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
/* eg. $GPGGA,082559.00,4005.22599,N,11632.58234,E,1,04,3.08,14.6,M,-5.6,M,,*76"<CR><LF>*/
/* read line */
iRet = read_gps_raw_data(fd, buf);
/* parse line */
if (iRet == 0)
{
iRet = parse_gps_raw_data(buf, time, Lat, ns, Lng, ew);
}
/* printf */
if (iRet == 0)
{
printf("Time : %s\n", time);
printf("ns : %s\n", ns);
printf("ew : %s\n", ew);
printf("Lat : %s\n", Lat);
printf("Lng : %s\n", Lng);
/* 纬度格式: ddmm.mmmm */
sscanf(Lat+2, "%f", &fLat);
fLat = fLat / 60;
fLat += (Lat[0] - '0')*10 + (Lat[1] - '0');
/* 经度格式: dddmm.mmmm */
sscanf(Lng+3, "%f", &fLng);
fLng = fLng / 60;
fLng += (Lng[0] - '0')*100 + (Lng[1] - '0')*10 + (Lng[2] - '0');
printf("Lng,Lat: %.06f,%.06f\n", fLng, fLat);
}
}
return 0;
}
2.4 接线