图解算法数据结构-LeetBook-栈和队列04_望远镜中最高的海拔_滑动窗口
科技馆内有一台虚拟观景望远镜,它可以用来观测特定纬度地区的地形情况。该纬度的海拔数据记于数组 heights ,其中 heights[i] 表示对应位置的海拔高度。请找出并返回望远镜视野范围 limit 内,可以观测到的最高海拔值。
示例 1:
输入:heights = [14,2,27,-5,28,13,39], limit = 3
输出:[27,27,28,28,39]
解释:
滑动窗口的位置 最大值
[14 2 27] -5 28 13 39 27
14 [2 27 -5] 28 13 39 27
14 2 [27 -5 28] 13 39 28
14 2 27 [-5 28 13] 39 28
14 2 27 -5 [28 13 39] 39
提示:
你可以假设输入总是有效的,在输入数组不为空的情况下:
1 <= limit <= heights.length
-10000 <= heights[i] <= 10000
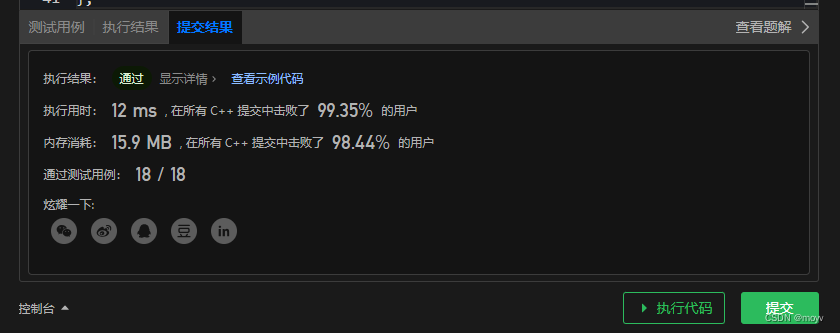
解法一
从头到尾遍历每个状态的窗口
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxAltitude(vector<int>& heights, int limit) {
vector<int> res;
if(heights.empty()) return res;
int max_;
for(int i = 0;i <= int(heights.size())-limit;i++){
max_ = heights[i];
for(int j = 1;j < limit;j++){
if(heights[i+j] > max_) max_ = heights[i+j];
}
res.push_back(max_);
}
return res;
}
};
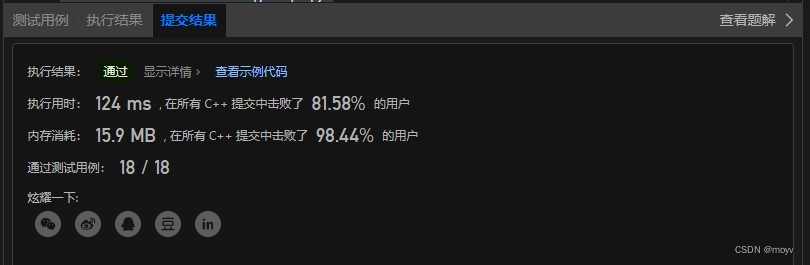
解法二
上一个方法显然有很多冗余的比较,比如
7 2 8 10
3
滑动到第二个状态的时候,因为8所在的位置在窗口左侧的右边,所以只需要将新加入的10和8(之前的最大值)比较
8 2 6 4
3
滑动到第二个状态的时候,因为8所在的位置在窗口左侧,所以需要重新在新窗口中找最大值
基于以上思想
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxAltitude(vector<int>& heights, int limit) {
vector<int> res;
if(heights.empty()) return res;
if(limit == 1) return heights;
int len = heights.size(), pre_max_index = 0, max_ = heights[0];
//计算第一个max
for(int i = 0;i < limit;i++){
if(heights[i] > max_){
max_ = heights[i];
pre_max_index = i;
}
}
res.push_back(max_);
for(int i = 1;i <= len-limit;i++){
if(i < pre_max_index){
//如果这次窗口左侧在之前最大值的索引左侧(不包括之前最大值的索引)
//只需要比较新加入的值和之前最大值
if(heights[i+limit-1] > max_){
max_ = heights[i+limit-1];
pre_max_index = i+limit-1;
}
res.push_back(max_);
} else {//重新开始一个最大值,默认值为heights[i]
int temp = limit;
max_ = heights[i];
pre_max_index = i;
while(temp--){
if(heights[i+temp] > max_){
pre_max_index = i+temp;
max_ = heights[i+temp];
}
}
res.push_back(max_);
}
}
return res;
}
};
当然,如果limit为1,根本就不需要计算直接返回就行。
新加入的值:
h
e
i
g
h
t
s
[
i
+
l
i
m
i
t
−
1
]
heights[i+limit-1]
heights[i+limit−1]