声音响度、声压级计权(A B C)实现
声压 sound pressure
声压就是大气压受到声波扰动后产生的变化,即为大气压强的余压,它相当于在大气压强上的叠加一个声波扰动引起的压强变化。由于声压的测量比较容易实现,通过声压的测量也可以间接求得质点速度等其它物理量,所以声学中常用这个物理量来描述声波
我们知道大气压强单位 1Pa = 1 pascal = 1N/m
实际计算可以参考http://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-soundlevel.htm
由于人对不同的声音频段 听感大小不一致,所以要对声音进行计权处理
如下实现 A B C 计权的实现,计权的实现参考标准,用于逼近实际的等响度曲线
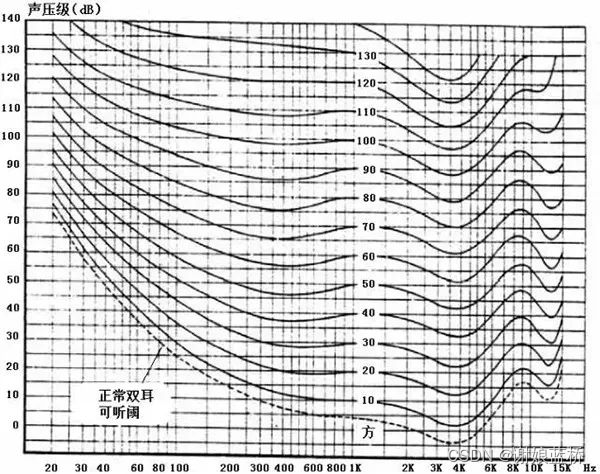
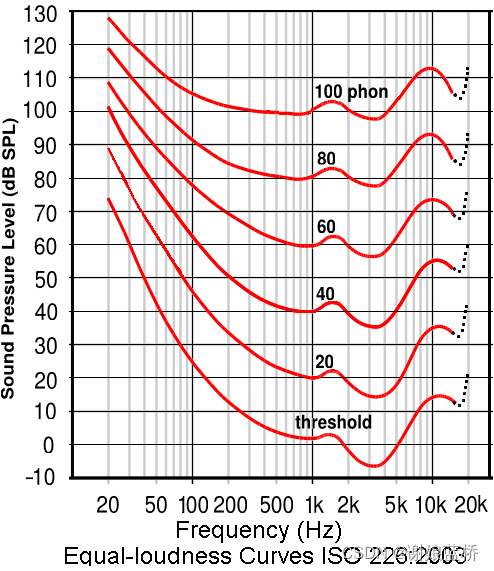
ISO 226-2003标准
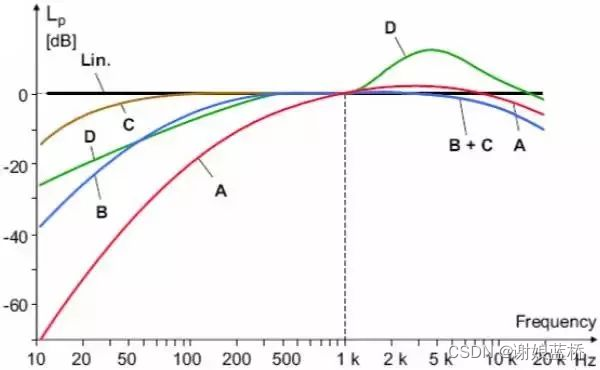
A、B、C三种计权网络特性,分别对应于倒置的40、70、100Phon等响曲线(1000Hz归一化到0dB),其作用是分别反应人耳对低、中、高声压级的响度感觉。A计权被证实是人耳对声压级主观反应的极好校正。对由A计权测量的声级称为A声级,记作LPA 或dB(A)。近来B计权、C计权已很少采用。
-
A计权:40Phon等响曲线的翻转,模拟55dB以下低强度噪声特性。
-
B计权:70Phon等响曲线的翻转,模拟55~85dB中等强度噪声特性。
-
C计权:100Phon等响曲线的翻转,模拟高强度噪声特性。
-
D计权:专用于飞机噪声的测量。

target_folder='audio/'
audio_targets = '.wav'
spl_folder = '/c_audio'
from librosa import load
from os import listdir,path
from scipy.signal import lfilter,bilinear
from numpy import pi, convolve,log10,sqrt,sum,power
from csv import writer
def a_weighting_coeffs_design(sample_rate):
"""Returns b and a coeff of a A-weighting filter.
Parameters
----------
sample_rate : scalar
Sample rate of the signals that well be filtered.
Returns
-------
b, a : ndarray
Filter coefficients for a digital weighting filter.
Examples
--------
>>> b, a = a_weighting_coeff_design(sample_rate)
To Filter a signal use scipy lfilter:
>>> from scipy.signal import lfilter
>>> y = lfilter(b, a, x)
See Also
--------
b_weighting_coeffs_design : B-Weighting coefficients.
c_weighting_coeffs_design : C-Weighting coefficients.
weight_signal : Apply a weighting filter to a signal.
scipy.lfilter : Filtering signal with `b` and `a` coefficients.
"""
f1 = 20.598997
f2 = 107.65265
f3 = 737.86223
f4 = 12194.217
A1000 = 1.9997
numerators = [(2 * pi * f4)**2 * (10**(A1000 / 20.0)), 0., 0., 0., 0.]
denominators = convolve([1., +4 * pi * f4, (2 * pi * f4)**2],
[1., +4 * pi * f1, (2 * pi * f1)**2])
denominators = convolve(convolve(denominators, [1., 2 * pi * f3]),
[1., 2 * pi * f2])
return bilinear(numerators, denominators, sample_rate)
def b_weighting_coeffs_design(sample_rate):
"""Returns `b` and `a` coeff of a B-weighting filter.
B-Weighting is no longer described in DIN61672.
Parameters
----------
sample_rate : scalar
Sample rate of the signals that well be filtered.
Returns
-------
b, a : ndarray
Filter coefficients for a digital weighting filter.
Examples
--------
>>> b, a = b_weighting_coeff_design(sample_rate)
To Filter a signal use :function: scipy.lfilter:
>>> from scipy.signal import lfilter
>>> y = lfilter(b, a, x)
See Also
--------
a_weighting_coeffs_design : A-Weighting coefficients.
c_weighting_coeffs_design : C-Weighting coefficients.
weight_signal : Apply a weighting filter to a signal.
"""
f1 = 20.598997
f2 = 158.5
f4 = 12194.217
B1000 = 0.17
numerators = [(2 * pi * f4)**2 * (10**(B1000 / 20)), 0, 0, 0]
denominators = convolve([1, +4 * pi * f4, (2 * pi * f4)**2],
[1, +4 * pi * f1, (2 * pi * f1)**2])
denominators = convolve(denominators, [1, 2 * pi * f2])
return bilinear(numerators, denominators, sample_rate)
def c_weighting_coeffs_design(sample_rate):
"""Returns b and a coeff of a C-weighting filter.
Parameters
----------
sample_rate : scalar
Sample rate of the signals that well be filtered.
Returns
-------
b, a : ndarray
Filter coefficients for a digital weighting filter.
Examples
--------
b, a = c_weighting_coeffs_design(sample_rate)
To Filter a signal use scipy lfilter:
from scipy.signal import lfilter
y = lfilter(b, a, x)
See Also
--------
a_weighting_coeffs_design : A-Weighting coefficients.
b_weighting_coeffs_design : B-Weighting coefficients.
weight_signal : Apply a weighting filter to a signal.
"""
f1 = 20.598997
f4 = 12194.217
C1000 = 0.0619
numerators = [(2 * pi * f4)**2 * (10**(C1000 / 20)), 0, 0]
denominators = convolve([1, +4 * pi * f4, (2 * pi * f4)**2],
[1, +4 * pi * f1, (2 * pi * f1)**2])
return bilinear(numerators, denominators, sample_rate)
def SPLCal(x):
Leng = len(x)
pa = sqrt(sum(power(x, 2))/Leng)
p0 = 2e-5
spl = 20 * log10(pa / p0)
return spl
def preprocess_spl(name,spl):
"""Main logic for SPL weighting"""
n = 1
##at = find_recordings(target_folder, audio_targets)
at =listdir(target_folder)
for f in at:
filename = path.join(target_folder, f)
x, Fs = load(filename)
b, a = c_weighting_coeffs_design(Fs)
y = lfilter(b, a, x)
out = SPLCal(y)
spl.append(out)
name.append(f[:-4])
print(filename[6:-4]+" spl:"+str(out))
'''print("--- Preprocessing SPLs: " + str(round(n / len(at) * 100, 2)) +
"% done. ---\t\t",
end='\r\r\r\n\n')'''
n += 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
name =[]
spl= []
preprocess_spl(name,spl)
header =['name', 'spl(dbc)']
with open('save.csv', 'w') as file:
# 2. Create a CSV writer
mywrite = writer(file)
# 3. Write data to the file
mywrite.writerow(header)
tmp = zip(name,spl)
mywrite.writerows(tmp)
file.close()
