UVA1368 DNA Consensus String
DNA Consensus String
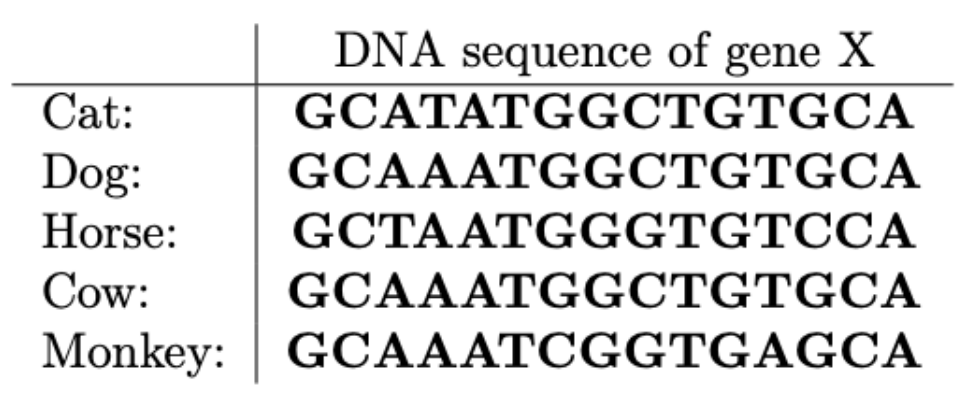
The Hamming distance is the number of different characters at each position from two strings of equal length. For example, assume we are given the two strings “AGCAT” and “GGAAT.” The Hamming distance of these two strings is 2 because the 1st and the 3rd characters of the two strings are different. Using the Hamming distance, we can define a representative string for a set of multiple strings of equal length. Given a set of strings S = {s1, …, sm} of length n, the consensus error between a string y of length n and the set S is the sum of the Hamming distances between y and each si in S. If the consensus error between y and S is the minimum among all possible strings y of length n, y is called a consensus string of S. For example, given the three strings “AGCAT” 、“AGACT” and “GGAAT” the consensus string of the given strings is “AGAAT” because the sum of the Hamming distances between “AGAAT” and the three strings is 3 which is minimal. (In this case, the consensus string is unique, but in general, there can be more than one consensus string.) We use the consensus string as a representative of the DNA sequence. For the example of Figure 1 above, a consensus string of gene X is “GCAAATGGCTGTGCA” and the consensus error is 7.
Input: Your program is to read from standard input. The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases T is given in the first line of the input. Each test case starts with a line containing two integers m and n which are separated by a single space. The integer m(4 ≤ m ≤ 50) represents the number of DNA sequences and n(4 ≤ n ≤ 1000) represents the length of the DNA sequences, respectively. In each of the next m lines, each DNA sequence is given.
Output: Your program is to write to standard output. Print the consensus string in the first line of each case and the consensus error in the second line of each case. If there exists more than one consensus string, print the lexicographically smallest consensus string.
DNA序列 DNA Consensus String
题面翻译
输入 m m m个长度均为 n n n的 DNA \text{DNA} DNA序列,求一个 DNA \text{DNA} DNA序列,到所有序列的总 Hamming \text{Hamming} Hamming距离尽量小。两个等长字符串的 Hamming \text{Hamming} Hamming距离等于字符不同的位置个数,如 ACGT \text{ACGT} ACGT和 GCGA \text{GCGA} GCGA的 Hamming \text{Hamming} Hamming距离为 2 2 2(左数第 1 1 1、 4 4 4个字符不同)。
输入整数 m m m和 n n n( 4 ≤ m ≤ 50 4\leq m \leq 50 4≤m≤50, 4 ≤ n ≤ 1000 4\leq n \leq 1000 4≤n≤1000),以及 m m m个长度为 n n n的 DNA \text{DNA} DNA序列,(只包含字母 A A A、 C C C、 G G G、 T T T),输出到 m m m个序列的 H a m m i n g Hamming Hamming距离和最小的 DNA \text{DNA} DNA序列和对应的距离。如有多解,要求字典序最小的解。
题目描述
输入格式
输出格式
Solution
采用贪心策略
设str[i][j]为第i个字符串的第j个元素,因为字符串序列是等长的首先比较相同位置的字符,并记录其A、G、C、T的个数,当所有m个字符串的第i个位置遍历完毕,计算A、G、C、T个数最大,当数目相同时使用字典序最小的的并作为std_s[i]
//
// Created by Gowi on 2023/12/2.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define N 55
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str[N];
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
int m, n;
string std_s;
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
cin >> str[i];
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int a = 0, c = 0, g = 0, t = 0, index_n = 0;
char index_c = 'Z';
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (str[j][i] == 'A') {
a++;
} else if (str[j][i] == 'C') {
c++;
} else if (str[j][i] == 'G') {
g++;
} else {
t++;
}
index_n = max(a, max(c, max(g, t)));
}
if (t == index_n && 'T' < index_c) {
index_c = 'T';
}
if (g == index_n && 'G' < index_c) {
index_c = 'G';
}
if (c == index_n && 'C' < index_c) {
index_c = 'C';
}
if (a == index_n && 'A' < index_c) {
index_c = 'A';
}
std_s += index_c;
if (index_c != 'A') {
sum += a;
}
if (index_c != 'G') {
sum += g;
}
if (index_c != 'C') {
sum += c;
}
if (index_c != 'T') {
sum += t;
}
}
std_s[n] = '\0';
cout << std_s << endl;
cout << sum << endl;
}
}
