C/C++,优化算法——双离子推销员问题(Bitonic Travelling Salesman Problem)的计算方法与源代码
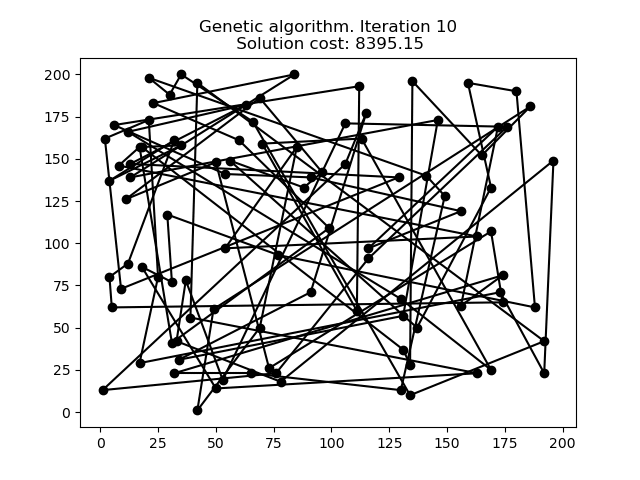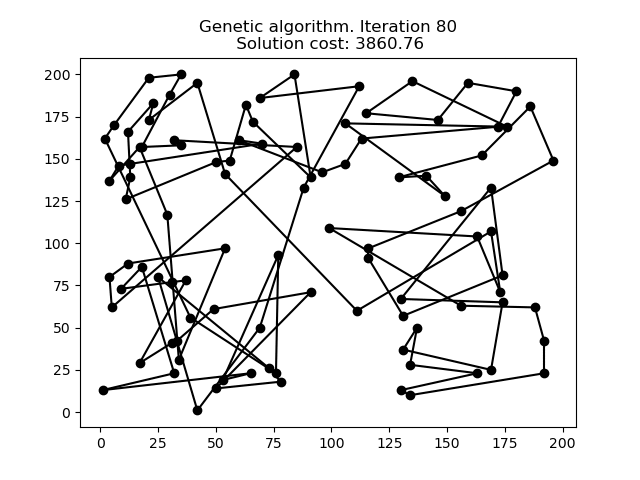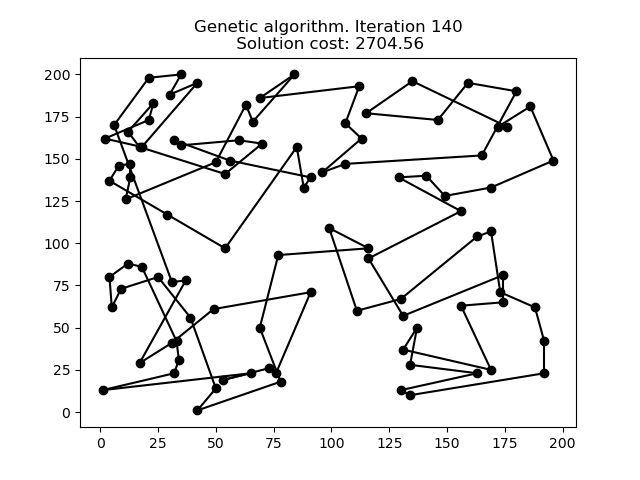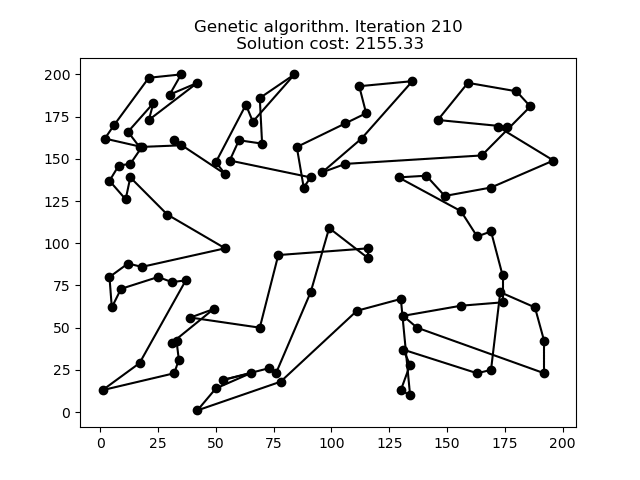
1 文本格式
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Size of the array a[]
const int mxN = 1005;
// Structure to store the x and
// y coordinates of a point
struct Coordinates {
double x, y;
} a[mxN];
// Declare a 2-D dp array
float dp[mxN][mxN];
// Function to calculate the
// distance between two points
// in a Euclidian plane
float distance(int i, int j)
{
// Return the distance
return sqrt(
(a[i].x - a[j].x) * (a[i].x - a[j].x)
+ (a[i].y - a[j].y) * (a[i].y - a[j].y));
}
// Utility recursive function to find
// the bitonic tour distance
float findTourDistance(int i, int j)
{
// Memoization
if (dp[i][j] > 0)
return dp[i][j];
// Update dp[i][j]
dp[i][j] = min(
findTourDistance(i + 1, j) + distance(i, i + 1),
findTourDistance(i + 1, i) + distance(j, i + 1));
return dp[i][j];
}
// Function to find the
// bitonic tour distance
void bitonicTSP(int N)
{
// Initialize the dp array
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
// Base Case
for (int j = 1; j < N - 1; j++)
dp[N - 1][j] = distance(N - 1, N)
+ distance(j, N);
// Print the answer
printf("%.2f\n", findTourDistance(1, 1));
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int N = 3;
a[1].x = 1, a[1].y = 1;
a[2].x = 2, a[2].y = 3;
a[3].x = 3, a[3].y = 1;
// Function Call
bitonicTSP(N);
}
2 代码格式
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Size of the array a[]
const int mxN = 1005;
// Structure to store the x and
// y coordinates of a point
struct Coordinates {
double x, y;
} a[mxN];
// Declare a 2-D dp array
float dp[mxN][mxN];
// Function to calculate the
// distance between two points
// in a Euclidian plane
float distance(int i, int j)
{
// Return the distance
return sqrt(
(a[i].x - a[j].x) * (a[i].x - a[j].x)
+ (a[i].y - a[j].y) * (a[i].y - a[j].y));
}
// Utility recursive function to find
// the bitonic tour distance
float findTourDistance(int i, int j)
{
// Memoization
if (dp[i][j] > 0)
return dp[i][j];
// Update dp[i][j]
dp[i][j] = min(
findTourDistance(i + 1, j) + distance(i, i + 1),
findTourDistance(i + 1, i) + distance(j, i + 1));
return dp[i][j];
}
// Function to find the
// bitonic tour distance
void bitonicTSP(int N)
{
// Initialize the dp array
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
// Base Case
for (int j = 1; j < N - 1; j++)
dp[N - 1][j] = distance(N - 1, N)
+ distance(j, N);
// Print the answer
printf("%.2f\n", findTourDistance(1, 1));
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Input
int N = 3;
a[1].x = 1, a[1].y = 1;
a[2].x = 2, a[2].y = 3;
a[3].x = 3, a[3].y = 1;
// Function Call
bitonicTSP(N);
}