2016 ICPC合肥站 传递 HDU-5961(拓扑排序 / bitset / 暴力(可hack))
题目链接:HDU-5961 传递
中文题面就不解释题目意思,解释一下名词的意思
完全图:对于一个无向图
G
G
G 而言,设点集为
V
V
V,点集中任意不相同两点
u
,
v
u, v
u,v 间都有且仅有一条边叫做完全图。
竞赛图:在一个完全图的基础上给所有边定向,就变成了竞赛图。
可传递:在一个有向图中若存在边
(
a
→
b
)
(a\rightarrow b)
(a→b)(代表一条由
a
a
a 指向
b
b
b 的边,下同),和
(
b
→
c
)
(b\rightarrow c)
(b→c)。则一定要存在边
(
a
→
c
)
(a\rightarrow c)
(a→c) 若不存在即不合法。
拓扑排序
思路
我认为的正解,很妙的反向建图的思路,一直思考暴力没往这方面想。
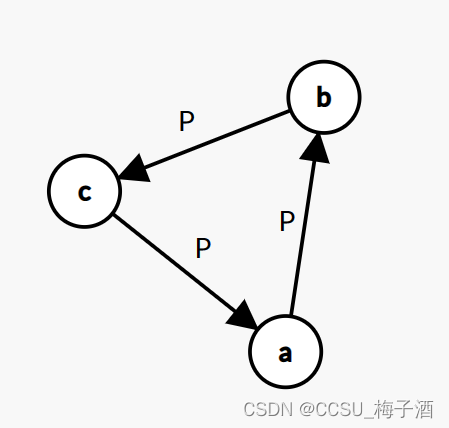
考虑任意图不合法的情况
-
有环存在同一图中: ( a → b ) ( b → c ) ( c → a ) (a\rightarrow b) (b\rightarrow c) (c\rightarrow a) (a→b)(b→c)(c→a)。
-
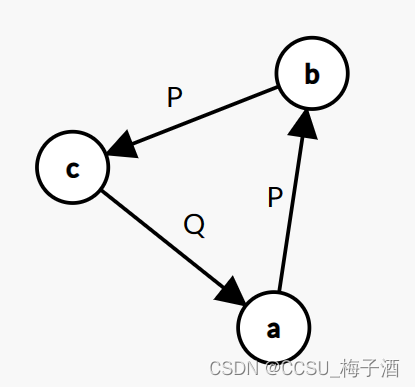
存在需要满足可传递的前置情况,却少了边
P P P 图: ( a → b ) ( b → c ) (a\rightarrow b) (b\rightarrow c) (a→b)(b→c) (理应要有 ( a → c ) (a\rightarrow c) (a→c) 才合法,但这条边却存在与另一图中)
Q Q Q 图: ( a → c ) / ( c → a ) (a\rightarrow c) / (c\rightarrow a) (a→c)/(c→a)
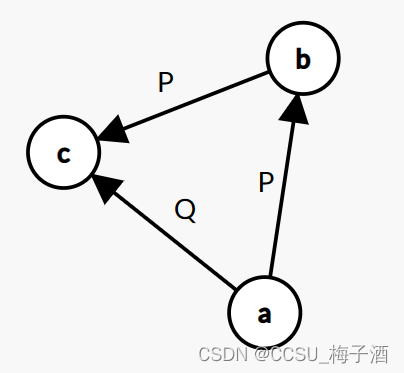
情况1:只需要对图跑一遍拓扑排序判环即可解决。
情况2:因为竞赛图是在完全图基础上定向而来,那么如果一个图P仅有
(
a
→
b
)
(
b
→
c
)
(a\rightarrow b) (b\rightarrow c)
(a→b)(b→c),没有
(
a
→
c
)
/
(
c
→
a
)
(a\rightarrow c) / (c\rightarrow a)
(a→c)/(c→a)。
不是情况1的环但也不合法, 但
(
a
→
c
)
/
(
c
→
a
)
(a\rightarrow c) / (c\rightarrow a)
(a→c)/(c→a) 一定会存在另一张图
Q
Q
Q 中。
如果
Q
Q
Q 图中存在的是
(
c
→
a
)
(c \rightarrow a)
(c→a),那么我们如果将两个图合并起来,就会形成
(
a
→
b
)
(
b
→
c
)
(
c
→
a
)
(a\rightarrow b) (b\rightarrow c) (c\rightarrow a)
(a→b)(b→c)(c→a) 的环。
如果存在的是
(
a
→
c
)
(a \rightarrow c)
(a→c),那么我们将
Q
Q
Q 图的边反向再与图
P
P
P 合并那么也将构成环。
于是得出结论:将
P
,
Q
P,Q
P,Q 图中任意一个反向记为
Q
′
Q'
Q′(不妨假设将
Q
Q
Q 反向)
将图
P
,
Q
P, Q
P,Q 合并拓扑排序判环,再将图
P
,
Q
′
P,Q'
P,Q′ 合并拓扑排序判环 任意情况有环即不合法。
网上很多题解都仅仅是将图 Q Q Q 反向与 P P P 合并判环,而没有将原图 Q Q Q 与 P P P 反向判环这是错误的,两者都需要才能正确判断,这里提供一个hack样例。
input:
2
3
-P-
--P
Q--
3
-PQ
--P
---
output:
N
N
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2023;
char mp[N][N];
int n, head[N], in[N], tot;
struct edge{
int to, nex;
}e[N * N];
void add(int from, int to){
in[to] ++;
e[++ tot].to = to;
e[tot].nex = head[from];
head[from] = tot;
}
void build(int op){ // 建图
tot = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
in[i] = head[i] = 0;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++){
if(mp[i][j] == 'P') add(i, j);
if(mp[i][j] == 'Q'){
if(op == 1) add(i, j); // 正
else add(j, i); // 反
}
}
}
}
queue<int>q;
bool topsort(int op){
build(op);
vector<int>cnt;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
if(!in[i]) q.push(i);
}
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
cnt.push_back(u);
for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].nex){
int v = e[i].to; in[v] --;
if(!in[v]) q.push(v);
}
}
return (int)cnt.size() == n;
}
void solve(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
scanf("%s", mp[i] + 1);
}
if(!topsort(1) || !topsort(0)) puts("N");
else puts("T");
}
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
暴力
思路
将图用邻接表存(vector / 链式前向星)对两个图分别三重for循环暴力判断。注意这种方法是可以被hack掉的,但是不知道是赛时数据弱还是怎么回事,能成功AC。
接下来给出hack样例和构造方法:其实就是让所有边都只存在一张图
P
P
P 中并且该图合法,任意点都指向编号大于自己的其他点,然后将数据拉满
T
=
8
,
n
=
2000
T = 8, n = 2000
T=8,n=2000 即可。
hack样例
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2023;
char mp[N][N];
int vis[N], n;
bool flag;
vector<int>g[2][N];
bool check(int op){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
for(int j = 0; j < g[op][i].size(); j ++){
int u = g[op][i][j];
for(int k = 0; k < g[op][u].size(); k ++){
int v = g[op][u][k];
if(op == 0 && mp[i][v] != 'Q') return true;
if(op == 1 && mp[i][v] != 'P') return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void solve(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
scanf("%s", mp[i] + 1);
g[0][i].clear();
g[1][i].clear();
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++){
if(mp[i][j] == '-') continue ;
g[mp[i][j] == 'P'][i].push_back(j);
}
}
if(check(1) || check(0)) puts("N");
else puts("T");
}
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t --){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
bitset优化暴力
可以看这位老哥的 WA是一笔财富
