Bean的作用域和生命周期
目录
1.作⽤域定义
1.1Bean的6个作用域
1.singleton:单例作用域
2.prototype:多例作用域
3.request:请求作用域
4.session:会话作用域
5.application:全局作用域
6.websocket:HTTP WebSocket作用域
单例作⽤域(singleton) VS 全局作⽤域(application)
1.2设置作用域
1.直接设置值@Scope("potptype")
2.用枚举设置:@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
2.Spring 执⾏流程和 Bean 的⽣命周期
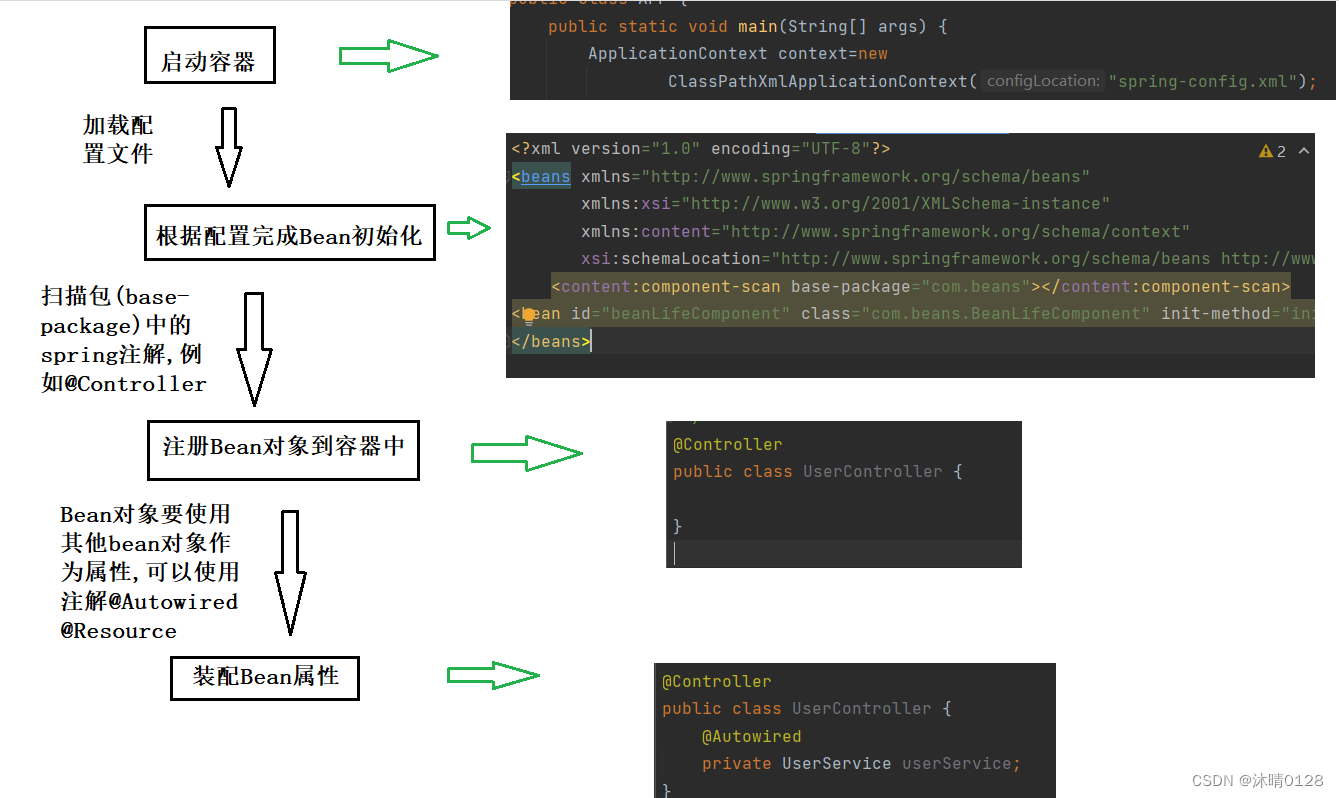
2.1Spring 执⾏流程
2.2Bean 的⽣命周期
1.作⽤域定义
Bean的作用域是指Bean在Spring整个框架中的某种行为模式
例如单例作用域,表示Bean在整个Spring只有一份,是全局共享的,有人修改了这个值,那么另一个人读取到的是被修改的值
1.1Bean的6个作用域
1.singleton:单例作用域
- 描述:该作⽤域下的Bean在IoC容器中只存在⼀个实例:获取Bean(即通applicationContext.getBean等⽅法获取)和装配Bean(即通过@Autowired注⼊)都是一个对象
- 场景:Bean对象的属性状态不用更新
2.prototype:多例作用域
- 描述:该作用域的Bean的请求都会创建新的实例:获取Bean(即通applicationContext.getBean等⽅法获取)和装配Bean(即通过@Autowired注⼊)都是新的对象
- 场景:Bean对象的属性状态要更新
3.request:请求作用域
- 描述:每次HTP请求都会创建新的Bean实例
- 场景:一个http请求和响应的共享Bean
4.session:会话作用域
- 描述:在⼀个http session中,定义⼀个Bean实例
- 场景:⽤户回话的共享Bean, ⽐如:记录⼀个⽤户的登陆信息
5.application:全局作用域
- 描述:在一个http servlet context中,定义一个Bean实例
- 场景:Web应用的上下文信息,例如:记录一个应用的共享信息
6.websocket:HTTP WebSocket作用域
- 描述:在一个Http websocket的生命周期中,定义一个Bean实例
- 场景:websoket的每次会话中,保存一个Map结果的头信息,将⽤来包裹客户端消息头。第⼀次初始化后,直到WebSocket结束都是同⼀个Bean。
单例作⽤域(singleton) VS 全局作⽤域(application)
- singleton 是 Spring Core 的作⽤域;application 是 Spring Web 中的作⽤域;
- singleton 作⽤于 IoC 的容器,⽽ application 作⽤于 Servlet 容器。
1.2设置作用域
使⽤ @Scope 标签就可以⽤来声明 Bean 的作⽤域
1.直接设置值@Scope("potptype")
对象存入容器中
@Component
public class UserBean {
@Bean(name = "user2")
@Scope("prototype")
public User user2(){
User user2=new User();
user2.setUserId(2);
user2.setUsername("张三");
return user2;
}
}把user对象注入当前类: 修改名字
@Component
public class BeanScope1 {
@Autowired
private User user2;
public User getUser(){
User user=user2;
user.setUsername("悟空");
return user;
}
}把user对象注入当前类:不修改,直接返回
@Component
public class BeanScope2 {
@Autowired
private User user2;
public User getUser2() {
return user2;
}
}启动类:
创建上下文,获取bean,使用bean
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
BeanScope1 beanScope1=context.getBean(BeanScope1.class);
User user1= beanScope1.getUser();
System.out.println("BeanScope1:"+user1);
BeanScope2 beanScope2=context.getBean(BeanScope2.class);
User user2= beanScope2.getUser2();
System.out.println("BeanScope2:"+user2);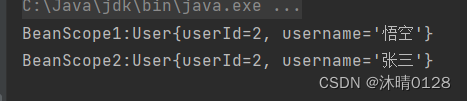
两个结果不同,说明@Scope把bean从单例作用域变成了多例作用域
2.用枚举设置:@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
@Component
public class UserBean {
@Bean(name = "user2")
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public User user2(){
User user2=new User();
user2.setUserId(2);
user2.setUsername("张三");
return user2;
}
}2.Spring 执⾏流程和 Bean 的⽣命周期
2.1Spring 执⾏流程
2.2Bean 的⽣命周期
1.实例化Bean(为Bean分配内存)
2.设置属性(Bean注入和装配)
3.Bean初始化
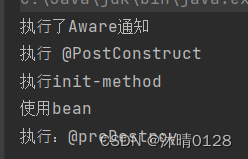
- 实现各种Aware方法
- 执行BeanPostProcesser初始化前置方法
- 执行构造方法,两种执行方式,一种是执行 @PostConstruct 初始化⽅法,依赖注⼊操作之后被执⾏(注解时代的方法);第二种执⾏⾃⼰指定的 init-method ⽅法(如果有指定的话)(xml时代的方法);
- 执行BeanPostProcessor 初始化后置⽅法。
4.使用Bean
5.销毁Bean
销毁容器的各种⽅法,如 @PreDestroy、重写DisposableBean 接⼝⽅法、destroy-method。
public class BeanLifeComponent implements BeanNameAware {
//初始化
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("执⾏ @PostConstruct");
}
//普通方法,bean中调用 要配置
public void init() {
System.out.println("执⾏init-method");
}
public void use(){
System.out.println("使用bean");
}
//销毁方法
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
System.out.println("执⾏:@preDestroy");
}
//执行通知
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println("执⾏了Aware通知");
}
}xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:content="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<content:component-scan base-package="com.beans"></content:component-scan>
<bean id="beanLifeComponent" class="com.beans.BeanLifeComponent" init-method="init"></bean>
</beans>调用类
public class APP2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
BeanLifeComponent beanLifeComponent=context.getBean("beanLifeComponent",BeanLifeComponent.class);
beanLifeComponent.use();
context.destroy();
}
}