深入源码理解redis数据结构(一)
文章目录
- 一. 动态字符串SDS
- 二. IntSet
- 三. Dict
一. 动态字符串SDS
我们都知道Redis中保存的Key是字符串,value往往是字符串或者字符串的集合。可见字符串是Redis中最常用的一种数据结构。不过Redis没有直接使用C语言的字符串,因为C语言字符串存在着很多问题:
- 获取字符串长度需要运算
- 非二进制安全(不能包含特殊字符)
- 不可修改
针对以上问题,Redis构建了一种新的字符串结构,称为动态字符串,简称SDS
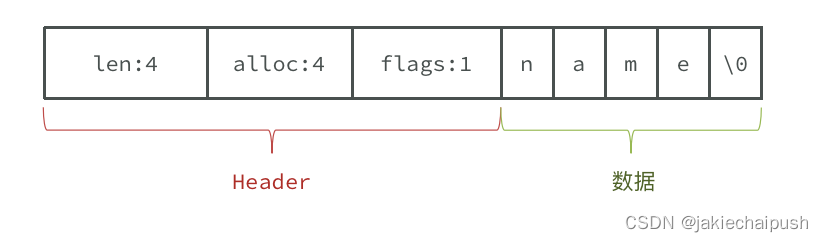
SDS的源码定义
typedef char *sds;
/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
// __attribute__ ((packed))的作用就是告诉编译器取消结构在编译过程中的优化对齐,按照实际占用字节数进行对齐,是GCC特有的语法
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
len:buf已经保存字符串的数量,不包含结束标志(C语言字符的结束标志是’\0’)
alloc:bug申请的总的字节数,不包含结束标志(解决了二进制安全问题)
flags:不同的SDS头类型,不用控制SDS的头大小
char buf[]:字符数组本体,保存最终SDS字符串
SDS之所以叫做动态字符串,是因为它具备动态扩容能力:假如我们现在要在已经定义的字符串上面进行追加字符串操作,这里首先会申请新的内存空间:
- 如果新字符串小于1M,则新空间为扩展后字符串长度的2倍+1
- 如果新字符串大于1M,则新空间为扩展后字符串长度的+1M+1,称为内存预分配
优点:
- 获取字符串长度的时间复杂度为O(1)
- 支持动态扩容
- 减少内存分配次数
- 二进制安全
二. IntSet
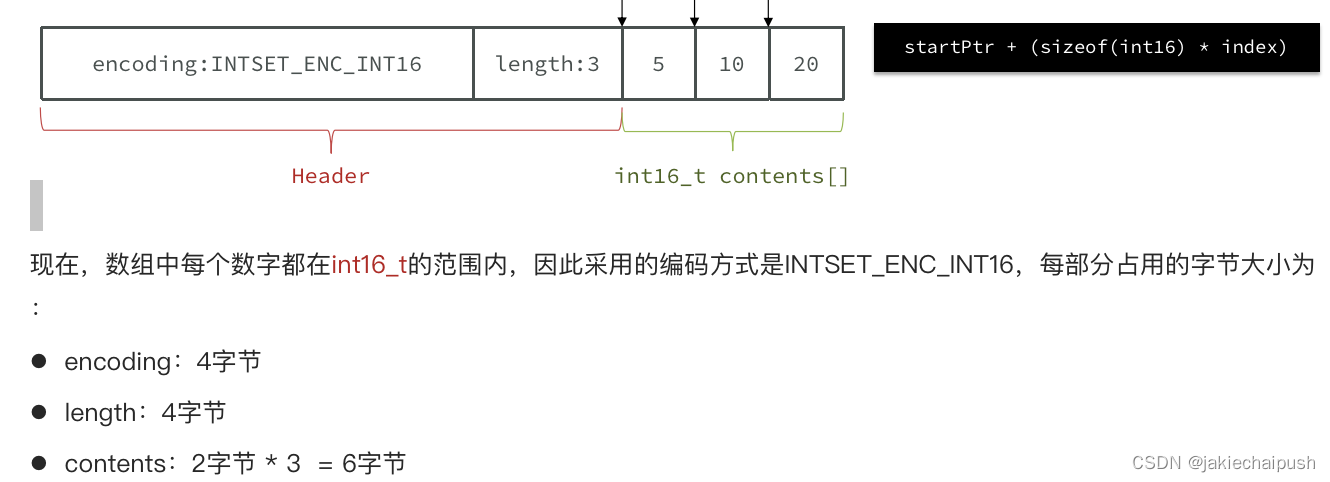
IntSet是redis中set集合的一种实现方式。基于整数数组实现,并且具备长度可变、有序等特征,源码定义如下
typedef struct intset {
uint32_t encoding;
uint32_t length;
int8_t contents[];
} intset;
contents:8比特整数位数组
length:元素个数
encoding:编码方式,支持存放16位、32位、64位整数
注意:虽然contents数组存储的整数类型为int8_t,但实际上的存储类型是由encoding指定的,contents的元素相当于只做一个内存指针的作用
其中encoding包含三种模式,表示存储的整数大小不同:
#define INTSET_ENC_INT16 (sizeof(int16_t))
#define INTSET_ENC_INT32 (sizeof(int32_t))
#define INTSET_ENC_INT64 (sizeof(int64_t))
为了方便查找,Redis会将intset中所有的整数按照升序依次保存在contents数组中,结构如图:
Intset会根据数组元素的大小对数组进行升级,也就是编码方式的升级,例如我现在数组中都是16位的元素,突然来了个32位的元素,Redis可以自动将Intset升级到32位(对数组还需要扩容)。倒序依次将数组中的元素拷贝到扩容后的正确位置。
Intset新增函数
intset *intsetAdd(intset *is, int64_t value, uint8_t *success) {
uint8_t valenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);
uint32_t pos;//指定要插入的位置
if (success) *success = 1;
if (valenc > intrev32ifbe(is->encoding)) {
/* This always succeeds, so we don't need to curry *success. */
return intsetUpgradeAndAdd(is,value);
} else {
/* Abort if the value is already present in the set.
* This call will populate "pos" with the right position to insert
* the value when it cannot be found. */
if (intsetSearch(is,value,&pos)) {
if (success) *success = 0;
return is;
}
is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
if (pos < intrev32ifbe(is->length)) intsetMoveTail(is,pos,pos+1);
}
_intsetSet(is,pos,value);
is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
return is;
}
- 参数说明:
is为我们要操作的Intset,value为我们要插入的值,success用来存储操作结果- 过程说明:
- 获取要插入元素的编码:
uint8_t valenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);- 如果要插入元素的编码值要大于Intset本身存储的元素是的编码值则调用
intsetUpgradeAndAdd函数执行升级操作if (valenc > intrev32ifbe(is->encoding))- 否则直接调用
intsetSearch函数直接插入元素- 最后更新
length即可
升级函数的源代码如下
static intset *intsetUpgradeAndAdd(intset *is, int64_t value) {
//获取intset当前编码
uint8_t curenc = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);
uint8_t newenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);
int length = intrev32ifbe(is->length);
int prepend = value < 0 ? 1 : 0;
/* First set new encoding and resize */
is->encoding = intrev32ifbe(newenc);
is = intsetResize(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
/* Upgrade back-to-front so we don't overwrite values.
* Note that the "prepend" variable is used to make sure we have an empty
* space at either the beginning or the end of the intset. */
while(length--)
_intsetSet(is,length+prepend,_intsetGetEncoded(is,length,curenc));
/* Set the value at the beginning or the end. */
if (prepend)
_intsetSet(is,0,value);
else
_intsetSet(is,intrev32ifbe(is->length),value);
is->length = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(is->length)+1);
return is;
}
- 参数说明:
is为我们要操作的Intset对象,value为我们要插入的值- 流程说明:
- 首先获取
Intset中原始的编码方式uint8_t curenc = intrev32ifbe(is->encoding);和value的原始编码方式uint8_t newenc = _intsetValueEncoding(value);- 然后获取Intset中元素的个数
int length = intrev32ifbe(is->length);- 判断插入值是否小于0
int prepend = value < 0 ? 1 : 0;- 将要插入的元素的编码赋值给Intset对象
is->encoding = intrev32ifbe(newenc);- 然后调用
intsetResize方法重置Intset大小- 使用while循环执行倒序遍历,将元素搬运到新的位置
- 最后插入新元素即可
intsetSearch查找元素源码
static uint8_t intsetSearch(intset *is, int64_t value, uint32_t *pos) {
int min = 0, max = intrev32ifbe(is->length)-1, mid = -1;
int64_t cur = -1;
/* The value can never be found when the set is empty */
if (intrev32ifbe(is->length) == 0) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
} else {
/* Check for the case where we know we cannot find the value,
* but do know the insert position. */
if (value > _intsetGet(is,max)) {
if (pos) *pos = intrev32ifbe(is->length);
return 0;
} else if (value < _intsetGet(is,0)) {
if (pos) *pos = 0;
return 0;
}
}
while(max >= min) {
mid = ((unsigned int)min + (unsigned int)max) >> 1;
cur = _intsetGet(is,mid);
if (value > cur) {
min = mid+1;
} else if (value < cur) {
max = mid-1;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (value == cur) {
if (pos) *pos = mid;
return 1;
} else {
if (pos) *pos = min;
return 0;
}
}
可以看到它底层使用二分查找实现的
总结
- Redis会确保IntSet中的元素唯一且有序
- 具备类型升级机制,可以节省内存空间
- 底层采用二分查找方式来查询
三. Dict
Redis是一个键值型数据库,我们可以根据键实现快速的增删改查,而键与值的映射关系正是通过Dict实现的
Dict的实现和Java中HashMap的实现非常类似,它由三部分组成:哈希表、哈希节点和字典
哈希表源码
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
dictEntry **table:用一个二维数组来实现hash表的
size:hash表的长度
sizemask:哈希表的掩码,总等于size-1(用来进行hash运算)
used:dictEntry个数
哈希节点源码
struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {//c语言中的联合体
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next; /* Next entry in the same hash bucket. */
void *metadata[]; /* An arbitrary number of bytes (starting at a
};
- key :表示哈希节点的键
- v:表示值(用一个联合体指定值的类型可以是多种)
- next:这个地方的意思是,在哈希表这个数据结构中,我们是通过指定的hash算法将元素映射到数组指定位置,我们将数组中存储元素的每个位置看成一个桶,而一个桶中可能有多个元素(因为元素的hash值可能相等),而在一个桶中元素的组织方式就是链表,所以next在这里是指向该链表的下一个元素
当我们向Dict添加元素的时候,Redis首先会根据key计算出hash值(h),然后利用h & sizemask来计算元素应该存储到数组中哪个索引的位置
字典源码
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
int16_t pauserehash; /* If >0 rehashing is paused (<0 indicates coding error) */
} dict;
type:type表示字典的类型,不同的类型具有不同的hash函数
privdata:私有数据,在做特殊hash时使用
dictht ht[2]:一个Dict包含两个hash表,其中一个是当前数据,另一个一般为空,rehash时使用
rehashidx:rehash的进度,-1表示未进行
pauserehash:
不管是扩容还是收缩,必定会创建新的hash表,导致hash表的size和sizemask变化,而key的查询与sizemask有段,因此必须对hash表的每一个key重新计算索引值,插入新的hash表,这个过程就叫做rehash
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d)
{
/*如果正在做rehash,则返回ok*/
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
/* 如果hash表为空,则初始化哈希表为默认大小4 */
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
/* 当负载因子(used/size)达到1以上,并且当前没有进行bgrewrite操作 */
/* 或者当负载因子大于5时。则进行扩容 */
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio) &&
dictTypeExpandAllowed(d))
{
//扩容大小为used+1,底层会对扩容大小做判断,实际上是找的第一个大于等于used+1的2^n
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used + 1);
}
return DICT_OK;
}
dict收缩
Dict除了扩容以外,每次删除元素时也会对负载因子做检查,当负载因子小雨0.1时,会做hash收缩操作:
//server.c文件
int htNeedsResize(dict *dict) {
long long size, used;
//哈希表大小
size = dictSlots(dict);
//entry数量
used = dictSize(dict);
//size>4(hash表初始大小)并且,负载因子低于0.1
return (size > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(used*100/size < HASHTABLE_MIN_FILL));
}
int dictResize(dict *d)
{
unsigned long minimal;
//如果正在做bgsave或bgrewriteof或rehash,则返回错误
if (!dict_can_resize || dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_ERR;
//获取used,也就是entry个数
minimal = d->ht[0].used;
//如果used小于4,则重置为4
if (minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)
minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
//重置大小为minimal,其实就是第一个大于等于nimimal的2^n的数
return dictExpand(d, minimal);
}
上面我们看到dictExpand的这个函数不管是在哈希表的初始化、扩容还是收缩都用到了这个函数,下面来详细解释一下这个函数
int _dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size, int* malloc_failed)
{
if (malloc_failed) *malloc_failed = 0;
//如果当前entry数量超过了要申请的size大小,或者正在rehash,直接报错
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
//声明新的hashtable
dictht n; /* the new hash table */
//实际大小,大小为传入的大于size的第一个2^n
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
/* Detect overflows */
if (realsize < size || realsize * sizeof(dictEntry*) < realsize)
return DICT_ERR;
/* Rehashing to the same table size is not useful. */
if (realsize == d->ht[0].size) return DICT_ERR;
/* Allocate the new hash table and initialize all pointers to NULL */
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
if (malloc_failed) {
n.table = ztrycalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
*malloc_failed = n.table == NULL;
if (*malloc_failed)
return DICT_ERR;
} else
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
/* Is this the first initialization? If so it's not really a rehashing
* we just set the first hash table so that it can accept keys. */
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Prepare a second hash table for incremental rehashing */
d->ht[1] = n;
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
设想一下,如果hash表中的数据有数百万,那么做rehash的过程因为需要将所有原来hash表的元素rehash到新的hash表中,那么线程阻塞时间特别长,所以dict的rehash操作并不是一次性完成的,而是分多次,渐进式的rehash,流程如下:
- 计算新的hash表的size,值取决于当前要做的事扩容还是搜索
如果是扩容,则新size为第一个大于等于dict.ht[0].used+1的2^n
如果是收缩,则新size为第一个大于等于dict.ht[0].used的2^n
- 按照新的size申请内存空间,创建dictht,并赋值给dict.ht[1]
- 设置dict.rehashidx=0,标示开始rehash过程
- 每次做增删查操作时,都检查一下dict.rehashidx是否大于-1,如果是则将dict.ht[0].table[rehashidx]的entry练表表rehash到dict.ht[1],并且将rehashidx++。直至dict.ht[0]的所有数据都rehash到dict.ht[1]
- 将dict.ht[1]赋值给dict.ht[0],给dict.ht[1]初始化为空hash表,释放原来的dict.ht[0]的内容
- 将reahshidx赋值为-1,代表rehash结束
- 在rehash过程中,新增 操作,则直接写入ht[1],查询、修改和删除则会在dict.ht[0]和dict.ht[1]依次查找并执行,这样可以确保ht[0]的数据只减不增,随着rehash最终为空
