easyexcel读和写excel
请直接看原文:
JAVA使用easyexcel操作Excel-CSDN博客
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
之前写过一篇《JAVA操作Excel》,介绍了jxl和poi读写Excel的实现,今天为大家介绍一下使用easyexcel对Excel进行读写,项目主页地址:GitHub - alibaba/easyexcel: 快速、简洁、解决大文件内存溢出的java处理Excel工具
作者对easyexcel的介绍是:
Java解析、生成Excel比较有名的框架有Apache poi、jxl。但他们都存在一个严重的问题就是非常的耗内存,poi有一套SAX模式的API可以一定程度的解决一些内存溢出的问题,但POI还是有一些缺陷,比如07版Excel解压缩以及解压后存储都是在内存中完成的,内存消耗依然很大。easyexcel重写了poi对07版Excel的解析,能够原本一个3M的excel用POI sax依然需要100M左右内存降低到KB级别,并且再大的excel不会出现内存溢出,03版依赖POI的sax模式。在上层做了模型转换的封装,让使用者更加简单方便
使用easyexcel,首先我们需要添加maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>1.0.1</version>
</dependency>一.写入excle无表头
首先,我们先来看看如何写Excel,写入Excel,我们可以通过com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter类实现,下面我们来看一下最简单的无表头的实现
package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
/**
* 每行数据是List<String>无表头
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void writeWithoutHead() throws IOException {
try (OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("withoutHead.xlsx");) {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX, false);
Sheet sheet1 = new Sheet(1, 0);
sheet1.setSheetName("sheet1");
List<List<String>> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
List<String> item = new ArrayList<>();
item.add("item0" + i);
item.add("item1" + i);
item.add("item2" + i);
data.add(item);
}
writer.write0(data, sheet1);
writer.finish();
}
}
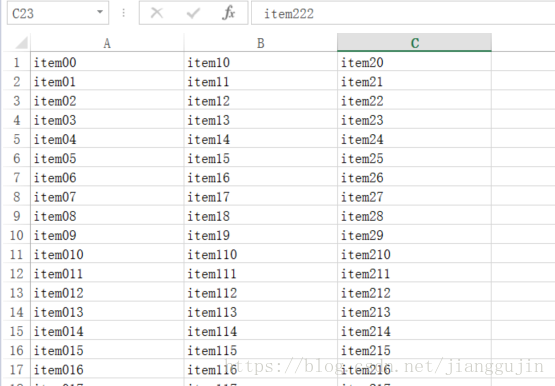
}生成的Excel样式如下:
二.写入excle有表头
很多时候,我们在生成Excel的时候都是需要添加表头的,使用easyexcel可以很容易的实现,我们可以对上面的例子进行简单的改造,为其添加表头
package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Table;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
@Test
public void writeWithoutHead() throws IOException {
try (OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("withHead.xlsx");) {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
Sheet sheet1 = new Sheet(1, 0);
sheet1.setSheetName("sheet1");
List<List<String>> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
List<String> item = new ArrayList<>();
item.add("item0" + i);
item.add("item1" + i);
item.add("item2" + i);
data.add(item);
}
List<List<String>> head = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
List<String> headCoulumn1 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn2 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn3 = new ArrayList<String>();
headCoulumn1.add("第一列");
headCoulumn2.add("第二列");
headCoulumn3.add("第三列");
head.add(headCoulumn1);
head.add(headCoulumn2);
head.add(headCoulumn3);
Table table = new Table(1);
table.setHead(head);
writer.write0(data, sheet1, table);
writer.finish();
}
}
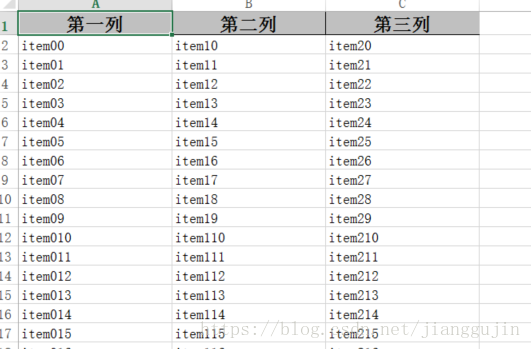
}效果如下:
三.实体类写入excle有表头
除了上面添加表头的方式,我们还可以使用实体类,为其添加com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty注解来生成表头,实体类数据作为Excel数据
package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Table;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
@Test
public void writeWithHead() throws IOException {
try (OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("withHead.xlsx");) {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
Sheet sheet1 = new Sheet(1, 0, ExcelPropertyIndexModel.class);
sheet1.setSheetName("sheet1");
List<ExcelPropertyIndexModel> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
ExcelPropertyIndexModel item = new ExcelPropertyIndexModel();
item.name = "name" + i;
item.age = "age" + i;
item.email = "email" + i;
item.address = "address" + i;
item.sax = "sax" + i;
item.heigh = "heigh" + i;
item.last = "last" + i;
data.add(item);
}
writer.write(data, sheet1);
writer.finish();
}
}
public static class ExcelPropertyIndexModel extends BaseRowModel {
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名", index = 0)
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(value = "年龄", index = 1)
private String age;
@ExcelProperty(value = "邮箱", index = 2)
private String email;
@ExcelProperty(value = "地址", index = 3)
private String address;
@ExcelProperty(value = "性别", index = 4)
private String sax;
@ExcelProperty(value = "高度", index = 5)
private String heigh;
@ExcelProperty(value = "备注", index = 6)
private String last;
}
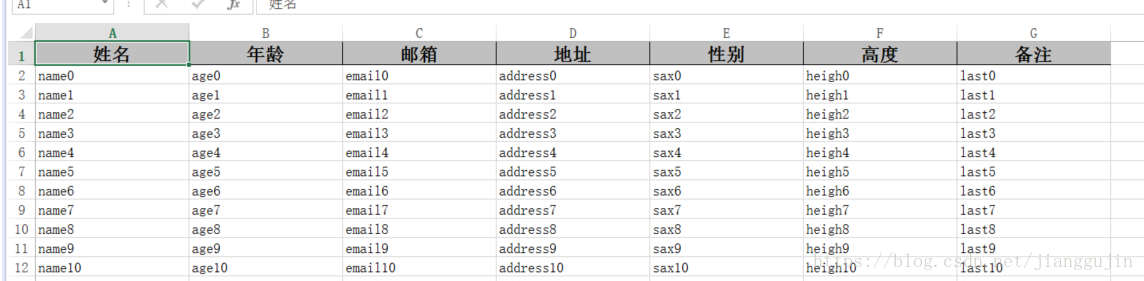
}效果如下:
四.实体类写入excle有多行表头
如果单行表头表头还不满足需求,没关系,还可以使用多行复杂的表头
package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Table;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
@Test
public void writeWithMultiHead() throws IOException {
try (OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("withMultiHead.xlsx");) {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
Sheet sheet1 = new Sheet(1, 0, MultiLineHeadExcelModel.class);
sheet1.setSheetName("sheet1");
List<MultiLineHeadExcelModel> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
MultiLineHeadExcelModel item = new MultiLineHeadExcelModel();
item.p1 = "p1" + i;
item.p2 = "p2" + i;
item.p3 = "p3" + i;
item.p4 = "p4" + i;
item.p5 = "p5" + i;
item.p6 = "p6" + i;
item.p7 = "p7" + i;
item.p8 = "p8" + i;
item.p9 = "p9" + i;
data.add(item);
}
writer.write(data, sheet1);
writer.finish();
}
}
public static class MultiLineHeadExcelModel extends BaseRowModel {
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头1", "表头1", "表头31" }, index = 0)
private String p1;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头1", "表头1", "表头32" }, index = 1)
private String p2;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头3", "表头3", "表头3" }, index = 2)
private String p3;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头4", "表头4", "表头4" }, index = 3)
private String p4;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头5", "表头51", "表头52" }, index = 4)
private String p5;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头6", "表头61", "表头611" }, index = 5)
private String p6;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头6", "表头61", "表头612" }, index = 6)
private String p7;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头6", "表头62", "表头621" }, index = 7)
private String p8;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头6", "表头62", "表头622" }, index = 8)
private String p9;
}
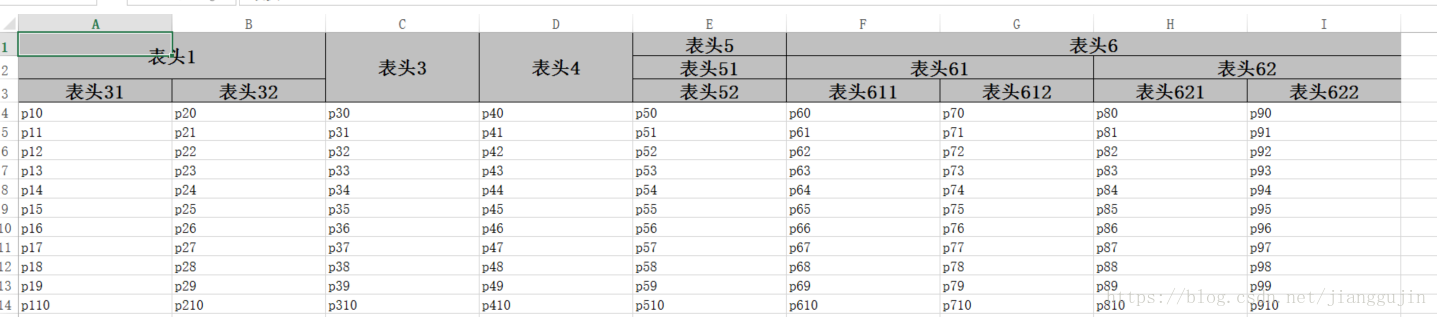
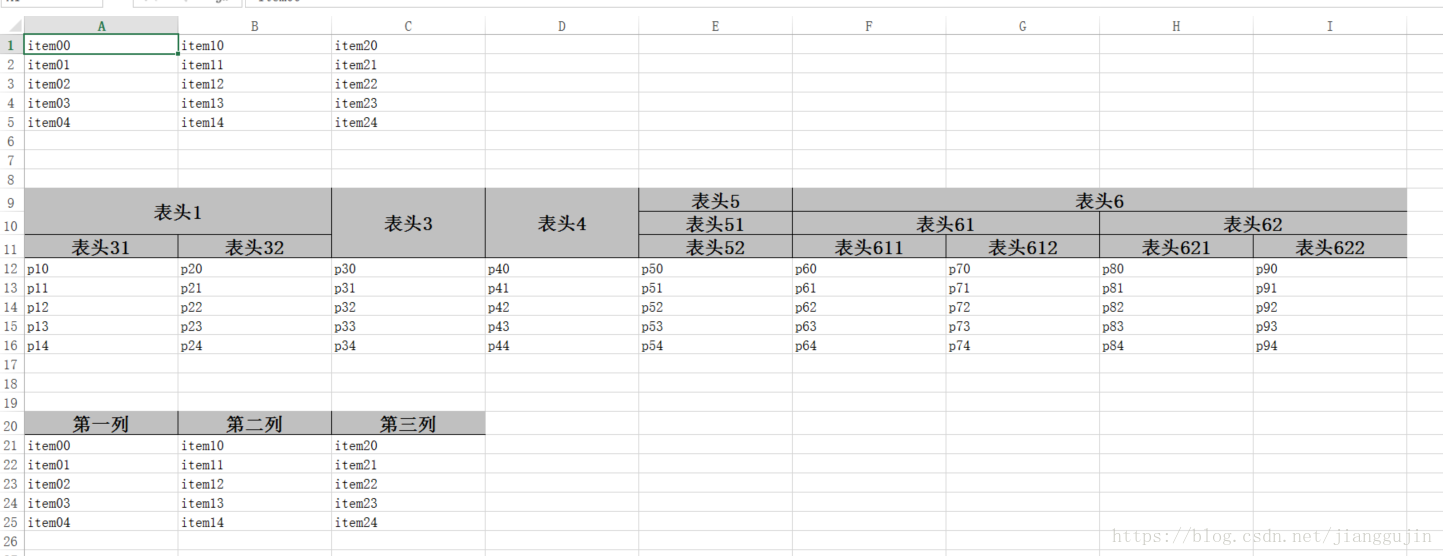
}效果如下:
五.写入excle一个sheet有多个表
怎么样,这些已经基本满足我们的日常需求了,easyexcel不仅支持上述几种形式,还支持在一个sheet中添加多个表
package test;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelWriter;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Table;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
public class ExcelWriteTest {
@Test
public void writeWithMultiTable() throws IOException {
try (OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("withMultiTable.xlsx");) {
ExcelWriter writer = new ExcelWriter(out, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
Sheet sheet1 = new Sheet(1, 0);
sheet1.setSheetName("sheet1");
// 数据全是List<String> 无模型映射关系
Table table1 = new Table(1);
List<List<String>> data1 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
List<String> item = new ArrayList<>();
item.add("item0" + i);
item.add("item1" + i);
item.add("item2" + i);
data1.add(item);
}
writer.write0(data1, sheet1, table1);
// 模型上有表头的注解
Table table2 = new Table(2);
table2.setClazz(MultiLineHeadExcelModel.class);
List<MultiLineHeadExcelModel> data2 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
MultiLineHeadExcelModel item = new MultiLineHeadExcelModel();
item.p1 = "p1" + i;
item.p2 = "p2" + i;
item.p3 = "p3" + i;
item.p4 = "p4" + i;
item.p5 = "p5" + i;
item.p6 = "p6" + i;
item.p7 = "p7" + i;
item.p8 = "p8" + i;
item.p9 = "p9" + i;
data2.add(item);
}
writer.write(data2, sheet1, table2);
// 模型上没有注解,表头数据动态传入,此情况下模型field顺序与excel现实顺序一致
List<List<String>> head = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
List<String> headCoulumn1 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn2 = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> headCoulumn3 = new ArrayList<String>();
headCoulumn1.add("第一列");
headCoulumn2.add("第二列");
headCoulumn3.add("第三列");
head.add(headCoulumn1);
head.add(headCoulumn2);
head.add(headCoulumn3);
Table table3 = new Table(3);
table3.setHead(head);
writer.write0(data1, sheet1, table3);
writer.finish();
}
}
public static class MultiLineHeadExcelModel extends BaseRowModel {
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头1", "表头1", "表头31" }, index = 0)
private String p1;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头1", "表头1", "表头32" }, index = 1)
private String p2;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头3", "表头3", "表头3" }, index = 2)
private String p3;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头4", "表头4", "表头4" }, index = 3)
private String p4;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头5", "表头51", "表头52" }, index = 4)
private String p5;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头6", "表头61", "表头611" }, index = 5)
private String p6;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头6", "表头61", "表头612" }, index = 6)
private String p7;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头6", "表头62", "表头621" }, index = 7)
private String p8;
@ExcelProperty(value = { "表头6", "表头62", "表头622" }, index = 8)
private String p9;
}
}效果如下:
如果表头的样式不满足我们的需求,需要调整,我们可以使用com.alibaba.excel.metadata.TableStyle定义我们需要的样式,然后调用table对象的setTableStyle方法进行设置。
六.读取excel内容(不建议用下面的方法,自己百度一下easyexcel读的简单示例方法就够用了)
好了,到这里写入excel就基本介绍完了,下面我们就来看看如何读取excel,实际上现在的这个版本(1.0.1)在读取的时候是有BUG的,读取03版的.xls格式的excel正常,但是读取07版的.xlsx版的excel就会出异常,原因是在解析的时候sheet临时文件路径拼装有误,下面是我针对这个版本修复后的实现,大家可以替换掉原包中的实现
package com.alibaba.excel.read;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.v07.RowHandler;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.v07.XmlParserFactory;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.v07.XMLTempFile;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.exception.ExcelAnalysisException;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.util.FileUtil;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.model.SharedStringsTable;
import org.apache.xmlbeans.XmlException;
import org.openxmlformats.schemas.spreadsheetml.x2006.main.CTWorkbook;
import org.openxmlformats.schemas.spreadsheetml.x2006.main.CTWorkbookPr;
import org.openxmlformats.schemas.spreadsheetml.x2006.main.WorkbookDocument;
import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.ContentHandler;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
public class SaxAnalyserV07 extends BaseSaxAnalyser {
private SharedStringsTable sharedStringsTable;
private List<String> sharedStringList = new LinkedList<String>();
private List<SheetSource> sheetSourceList = new ArrayList<SheetSource>();
private boolean use1904WindowDate = false;
private final String path;
private File tmpFile;
private String workBookXMLFilePath;
private String sharedStringXMLFilePath;
public SaxAnalyserV07(AnalysisContext analysisContext) throws Exception {
this.analysisContext = analysisContext;
this.path = XMLTempFile.createPath();
this.tmpFile = new File(XMLTempFile.getTmpFilePath(path));
this.workBookXMLFilePath = XMLTempFile.getWorkBookFilePath(path);
this.sharedStringXMLFilePath = XMLTempFile.getSharedStringFilePath(path);
start();
}
@Override
protected void execute() {
try {
Sheet sheet = analysisContext.getCurrentSheet();
if (!isAnalysisAllSheets(sheet)) {
if (this.sheetSourceList.size() < sheet.getSheetNo() || sheet.getSheetNo() == 0) {
return;
}
InputStream sheetInputStream = this.sheetSourceList.get(sheet.getSheetNo() - 1).getInputStream();
parseXmlSource(sheetInputStream);
return;
}
int i = 0;
for (SheetSource sheetSource : this.sheetSourceList) {
i++;
this.analysisContext.setCurrentSheet(new Sheet(i));
parseXmlSource(sheetSource.getInputStream());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
stop();
throw new ExcelAnalysisException(e);
} finally {
}
}
private boolean isAnalysisAllSheets(Sheet sheet) {
if (sheet == null) {
return true;
}
if (sheet.getSheetNo() < 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void stop() {
FileUtil.deletefile(path);
}
private void parseXmlSource(InputStream inputStream) {
try {
ContentHandler handler = new RowHandler(this, this.sharedStringsTable, this.analysisContext,
sharedStringList);
XmlParserFactory.parse(inputStream, handler);
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
throw new ExcelAnalysisException(e);
}
}
public List<Sheet> getSheets() {
List<Sheet> sheets = new ArrayList<Sheet>();
try {
int i = 1;
for (SheetSource sheetSource : this.sheetSourceList) {
Sheet sheet = new Sheet(i, 0);
sheet.setSheetName(sheetSource.getSheetName());
i++;
sheets.add(sheet);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
stop();
throw new ExcelAnalysisException(e);
} finally {
}
return sheets;
}
private void start() throws IOException, XmlException, ParserConfigurationException, SAXException {
createTmpFile();
unZipTempFile();
initSharedStringsTable();
initUse1904WindowDate();
initSheetSourceList();
}
private void createTmpFile() throws FileNotFoundException {
FileUtil.writeFile(tmpFile, analysisContext.getInputStream());
}
private void unZipTempFile() throws IOException {
FileUtil.doUnZip(path, tmpFile);
}
private void initSheetSourceList() throws IOException, ParserConfigurationException, SAXException {
this.sheetSourceList = new ArrayList<SheetSource>();
InputStream workbookXml = new FileInputStream(this.workBookXMLFilePath);
XmlParserFactory.parse(workbookXml, new DefaultHandler() {
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String qName, Attributes attrs) throws SAXException {
if (qName.toLowerCase(Locale.US).equals("sheet")) {
String name = null;
int id = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < attrs.getLength(); i++) {
if (attrs.getLocalName(i).toLowerCase(Locale.US).equals("name")) {
name = attrs.getValue(i);
}/** else if (attrs.getLocalName(i).toLowerCase(Locale.US).equals("r:id")) {
id = Integer.parseInt(attrs.getValue(i).replaceAll("rId", ""));
try {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(XMLTempFile.getSheetFilePath(path, id));
sheetSourceList.add(new SheetSource(id, name, inputStream));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} **/
//应该使用sheetId属性
else if (attrs.getLocalName(i).toLowerCase(Locale.US).equals("sheetid")) {
id = Integer.parseInt(attrs.getValue(i));
try {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(XMLTempFile.getSheetFilePath(path, id));
sheetSourceList.add(new SheetSource(id, name, inputStream));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
});
workbookXml.close();
// 排序后是倒序,不符合实际要求
// Collections.sort(sheetSourceList);
Collections.sort(sheetSourceList, new Comparator<SheetSource>() {
@Override
public int compare(SheetSource o1, SheetSource o2) {
return o1.id - o2.id;
}
});
}
private void initUse1904WindowDate() throws IOException, XmlException {
InputStream workbookXml = new FileInputStream(workBookXMLFilePath);
WorkbookDocument ctWorkbook = WorkbookDocument.Factory.parse(workbookXml);
CTWorkbook wb = ctWorkbook.getWorkbook();
CTWorkbookPr prefix = wb.getWorkbookPr();
if (prefix != null) {
this.use1904WindowDate = prefix.getDate1904();
}
this.analysisContext.setUse1904WindowDate(use1904WindowDate);
workbookXml.close();
}
private void initSharedStringsTable() throws IOException, ParserConfigurationException, SAXException {
//因为sharedStrings.xml文件不一定存在,所以在处理之前增加判断
File sharedStringXMLFile = new File(this.sharedStringXMLFilePath);
if (!sharedStringXMLFile.exists()) {
return;
}
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(this.sharedStringXMLFilePath);
//this.sharedStringsTable = new SharedStringsTable();
//this.sharedStringsTable.readFrom(inputStream);
XmlParserFactory.parse(inputStream, new DefaultHandler() {
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length) {
sharedStringList.add(new String(ch, start, length));
}
});
inputStream.close();
}
private class SheetSource implements Comparable<SheetSource> {
private int id;
private String sheetName;
private InputStream inputStream;
public SheetSource(int id, String sheetName, InputStream inputStream) {
this.id = id;
this.sheetName = sheetName;
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
public String getSheetName() {
return sheetName;
}
public void setSheetName(String sheetName) {
this.sheetName = sheetName;
}
public InputStream getInputStream() {
return inputStream;
}
public void setInputStream(InputStream inputStream) {
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int compareTo(SheetSource o) {
if (o.id == this.id) {
return 0;
} else if (o.id > this.id) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
}另外,使用easyexcel读取excel的时候需要设置excel的版本,但是有些时候我们无法预知excel的版本,所以个人感觉这样不是太好,所以模仿poi写了一个用于获取com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader对象的工具类
package com.alibaba.excel.read;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.PushbackInputStream;
import org.apache.poi.EmptyFileException;
import org.apache.poi.openxml4j.exceptions.InvalidFormatException;
import org.apache.poi.poifs.filesystem.DocumentFactoryHelper;
import org.apache.poi.poifs.filesystem.NPOIFSFileSystem;
import org.apache.poi.util.IOUtils;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.alibaba.excel.support.ExcelTypeEnum;
public class ExcelReaderFactory {
/**
* @param in
* 文件输入流
* @param customContent
* 自定义模型可以在
* {@link AnalysisEventListener#invoke(Object, AnalysisContext) }
* AnalysisContext中获取用于监听者回调使用
* @param eventListener
* 用户监听
* @throws IOException
* @throws EmptyFileException
* @throws InvalidFormatException
*/
public static ExcelReader getExcelReader(InputStream in, Object customContent,
AnalysisEventListener<?> eventListener) throws EmptyFileException, IOException, InvalidFormatException {
// 如果输入流不支持mark/reset,需要对其进行包裹
if (!in.markSupported()) {
in = new PushbackInputStream(in, 8);
}
// 确保至少有一些数据
byte[] header8 = IOUtils.peekFirst8Bytes(in);
ExcelTypeEnum excelTypeEnum = null;
if (NPOIFSFileSystem.hasPOIFSHeader(header8)) {
excelTypeEnum = ExcelTypeEnum.XLS;
}
if (DocumentFactoryHelper.hasOOXMLHeader(in)) {
excelTypeEnum = ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX;
}
if (excelTypeEnum != null) {
return new ExcelReader(in, excelTypeEnum, customContent, eventListener);
}
throw new InvalidFormatException("Your InputStream was neither an OLE2 stream, nor an OOXML stream");
}
/**
* @param in
* 文件输入流
* @param customContent
* 自定义模型可以在
* {@link AnalysisEventListener#invoke(Object, AnalysisContext) }
* AnalysisContext中获取用于监听者回调使用
* @param eventListener
* 用户监听
* @param trim
* 是否对解析的String做trim()默认true,用于防止 excel中空格引起的装换报错。
* @throws IOException
* @throws EmptyFileException
* @throws InvalidFormatException
*/
public static ExcelReader getExcelReader(InputStream in, Object customContent,
AnalysisEventListener<?> eventListener, boolean trim)
throws EmptyFileException, IOException, InvalidFormatException {
// 如果输入流不支持mark/reset,需要对其进行包裹
if (!in.markSupported()) {
in = new PushbackInputStream(in, 8);
}
// 确保至少有一些数据
byte[] header8 = IOUtils.peekFirst8Bytes(in);
ExcelTypeEnum excelTypeEnum = null;
if (NPOIFSFileSystem.hasPOIFSHeader(header8)) {
excelTypeEnum = ExcelTypeEnum.XLS;
}
if (DocumentFactoryHelper.hasOOXMLHeader(in)) {
excelTypeEnum = ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX;
}
if (excelTypeEnum != null) {
return new ExcelReader(in, excelTypeEnum, customContent, eventListener, trim);
}
throw new InvalidFormatException("Your InputStream was neither an OLE2 stream, nor an OOXML stream");
}
}下面我们就来写一个简单的读取Excel的示例:
package test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.ExcelReaderFactory;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.event.AnalysisEventListener;
public class ExcelReadTest {
@Test
public void read() throws Exception {
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream("withoutHead.xlsx");) {
AnalysisEventListener<List<String>> listener = new AnalysisEventListener<List<String>>() {
@Override
public void invoke(List<String> object, AnalysisContext context) {
System.err.println("Row:" + context.getCurrentRowNum() + " Data:" + object);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
System.err.println("doAfterAllAnalysed...");
}
};
ExcelReader excelReader = ExcelReaderFactory.getExcelReader(in, null, listener);
excelReader.read();
}
}
}正如写入Excel的时候可以使用数据模型一样,在读取Excel的时候也可以直接将数据映射为模型对象,区别在于要使用ExcelReader #read的重载方法。
package test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader;
import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.BaseRowModel;
import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.Sheet;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.ExcelReaderFactory;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.read.event.AnalysisEventListener;
public class ExcelReadTest {
@Test
public void read() throws Exception {
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream("withHead.xlsx");) {
AnalysisEventListener<ExcelPropertyIndexModel> listener = new AnalysisEventListener<ExcelPropertyIndexModel>() {
@Override
public void invoke(ExcelPropertyIndexModel object, AnalysisContext context) {
System.err.println("Row:" + context.getCurrentRowNum() + " Data:" + object);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
System.err.println("doAfterAllAnalysed...");
}
};
ExcelReader excelReader = ExcelReaderFactory.getExcelReader(in, null, listener);
// 第二个参数为表头行数,按照实际设置
excelReader.read(new Sheet(1, 1, ExcelPropertyIndexModel.class));
}
}
public static class ExcelPropertyIndexModel extends BaseRowModel {
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名", index = 0)
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(value = "年龄", index = 1)
private String age;
@ExcelProperty(value = "邮箱", index = 2)
private String email;
@ExcelProperty(value = "地址", index = 3)
private String address;
@ExcelProperty(value = "性别", index = 4)
private String sax;
@ExcelProperty(value = "高度", index = 5)
private String heigh;
@ExcelProperty(value = "备注", index = 6)
private String last;
}
}以上就是关于easyexcel的使用方法介绍,如有疑问,欢迎交流指正。