Java 多线程(抢CPU)
哈哈哈
什么是多线程:可以让程序同时做多件事情。
多线程的作用:提高效率。
多线程的应用场景:想让多个事情同时运行。
并发(多个指令在单个CPU交替执行)和并行(多个指令在多个CPU交替执行)
多线程的实现方式:
1.继承Thread类的方式实现(简单,扩展性差)
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.自己定义一个类继承Thread
//2.重写run方法
//3.创建子类的对象,并启动线程
MyThread t1=new MyThread();
MyThread t2=new MyThread();
t1.setName("1");
t2.setName("2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"hello");
}
}
}
2.实现Runnable接口的方式进行实现(复杂,扩展性强)
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.自己定义一个类实现Runnable接口
//2.重写里面的run方法
//3.创建自己的类的对象
//4.创建一个Thread类的对象,并开启线程
MyRun mr=new MyRun();
Thread t=new Thread(mr);
Thread t2=new Thread(mr);
t.setName("1");
t2.setName("2");
t.start();
t2.start();
}
}public class MyRun implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Thread t=Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(t.getName()+"hello");
}
}
}
3.利用Callable接口和Future接口方式实现(可以获取结果)
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//1.创建一个类MyCallable实现Callable接口
//2.重写call
//3.创建MyCallable对象
//4.创建FutureTask的对象
//5.创建Thread类对象并启动
MyCallable mc=new MyCallable();
FutureTask<Integer> ft=new FutureTask<>(mc);
Thread t1=new Thread(ft);
t1.start();
Integer result=ft.get();
System.out.println(result);
}
}import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception{
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum=sum+i;
}
return sum;
}
}
多线程的常用成员方法
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//getName
MyThread mt=new MyThread("111");
MyThread t2=new MyThread();
mt.start();
t2.start();
//setName
//....
//currentThread
Thread t=Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(t.getName());
//sleep(long time)毫秒 睡眠时间
System.out.println("11111");
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("22222");
}
}
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public MyThread() {
}
public MyThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
}
}
}
线程的优先级
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnable mr=new MyRunnable();
Thread t1=new Thread(mr,"1");
Thread t2=new Thread(mr,"2");
System.out.println(t1.getPriority());//默认优先级5
System.out.println(t2.getPriority());//默认优先级5//最小1//最大10
t1.setPriority(1);
t2.setPriority(10);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"@"+i);
}
}
}
守护线程(起码有2个线程)
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread t1=new MyThread();
MyThread2 t2=new MyThread2();
t1.setName("1");
t2.setName("2");
t2.setDaemon(true);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
}
}
}
public class MyThread2 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
}
}
}
礼让线程
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread2 t1=new MyThread2();
MyThread2 t2=new MyThread2();
t1.setName("1");
t2.setName("2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
public class MyThread2 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
Thread.yield();//礼让一下,再重新抢夺CPU的执行权
}
}
}
插入线程/插队线程
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread t1=new MyThread();
t1.setName("1");
t1.start();
t1.join();//把t线程插入到当前线程(main)之前
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main"+i);
}
}
}
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(getName()+"@"+i);
}
}
}
线程的生命周期:
一个线程从创建,到结束。
线程的安全问题
(下面这个代码存在问题)
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread t1=new MyThread();
MyThread t2=new MyThread();
MyThread t3=new MyThread();
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
public class MyThread extends Thread{
static int ticket=0;//这个类所有对象共享ticket数据(加了static)
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if(ticket<100){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket++;
System.out.println(getName()+"正在卖第"+ticket+"张票");
}else break;
}
}
}同步代码块
(可以解决问题)
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread t1=new MyThread();
MyThread t2=new MyThread();
MyThread t3=new MyThread();
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
public class MyThread extends Thread{
static int ticket=0;//这个类所有对象共享ticket数据(加了static)
static Object obj=new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
synchronized (obj){
if(ticket<100){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket++;
System.out.println(getName()+"正在卖第"+ticket+"张票");
}else break;
}
}
}
}
同步方法:
就是把synchronized关键字加到方法上
public class ss {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnable mr=new MyRunnable();
Thread t1=new Thread(mr);
Thread t2=new Thread(mr);
Thread t3=new Thread(mr);
t1.setName("窗口1");
t2.setName("窗口2");
t3.setName("窗口3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
int ticket=0;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if (method()) break;
}
}
private synchronized boolean method() {
if(ticket==100){
return true;
}else{
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"在卖第"+ticket+"张票");
}
return false;
}
}
lock锁
死锁
等待唤醒机制
1.消费者
2.生产者
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cook c=new Cook();
Foodie f=new Foodie();
// c.setName("厨师");
// f.setName("吃货");
c.start();
f.start();
}
}
public class Foodie extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
synchronized (Desk.lock){
if(Desk.count==0){
break;
}else{
if(Desk.foodFlag==0){
try {
Desk.lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
else{
Desk.count--;
System.out.println("吃货还能吃"+Desk.count+"碗");
Desk.lock.notifyAll();
Desk.foodFlag=0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
public class Cook extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
synchronized (Desk.lock){
if(Desk.count==0){
break;
}else {
if (Desk.foodFlag==1){
try {
Desk.lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}else {
System.out.println("厨师做了一碗面条");
Desk.foodFlag=1;
Desk.lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
}
}
public class Desk {
public static int foodFlag=0;//桌上是否有食物
public static int count=10;
public static Object lock=new Object();
}
利用阻塞队列方式实现
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1);
Cook c=new Cook(queue);
Foodie f=new Foodie(queue);
c.start();
f.start();
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Foodie extends Thread{
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue;
public Foodie(ArrayBlockingQueue<String>queue){
this.queue=queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
String food=queue.take();
System.out.println(food);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public class Desk {
public static int foodFlag=0;//桌上是否有食物
public static int count=10;
public static Object lock=new Object();
}
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Cook extends Thread{
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue;
public Cook(ArrayBlockingQueue<String>queue){
this.queue=queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
queue.put("面条");
System.out.println("厨师做了一碗面条");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}多线程的6种状态

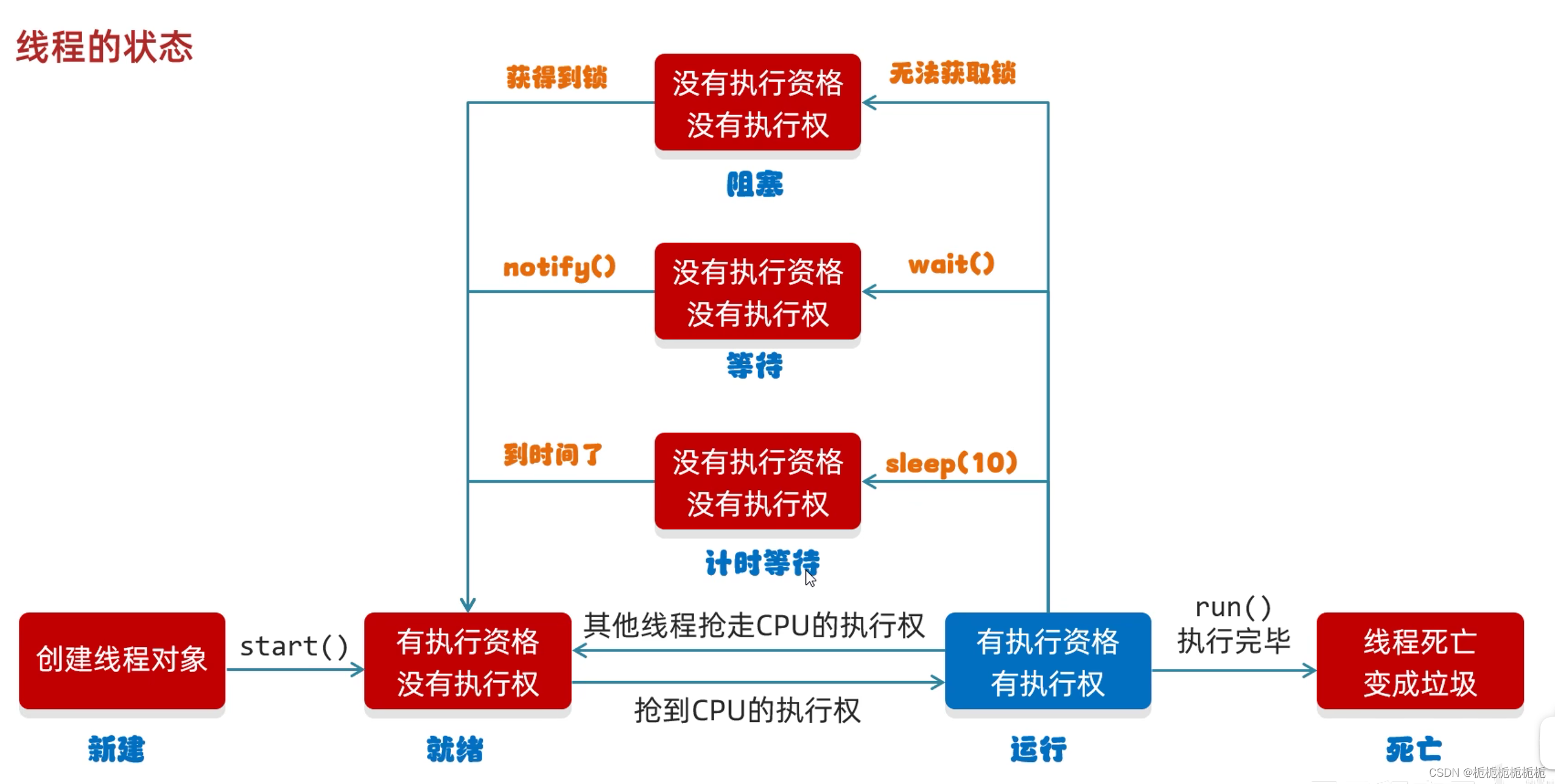
线程池:
1.创建线程池
2.提交任务
3.所有任务全部执行完毕,关闭线程池
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class n {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.获取线程池对象
// ExecutorService pool1=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//无上限
ExecutorService pool1=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);//有上限
// 2.提交任务
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
pool1.submit(new MyRunnable());
// 3.销毁线程池
pool1.shutdown();
}
}
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---"+i);
}
}
}
自定义线程池
回头再看
最大并行数
4核8线程:最大并行数8
public class sa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count=Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
System.out.println(count);
}
}
线程池多大合适
CPU密集型运算 最大并行数+1
I/O密集型运算 最大并行数*期望CPU利用率*(总时间(CPU计算时间+等待时间)/CPU计算时间)
多线程的额外扩展内容
回头再看
