【算法题】机试指南-数据结构进阶篇
本文仅供个人学习使用,免费分享。每日更新,建议关注收藏!
目前[机试指南]本系列已经达到字数10w+,所以按原每个章节拆开发布,点击目录跳转。
本站友情链接:
- c/c++算法题指南
严书代码
c/c++大复习1
c/c++大复习2 - python算法题指南
牛客华为机试103精华
python输入输出大全
python语法
PAT甲级真题刷题笔记 共179道 - python官方文档
python官方文档 - 机试指南系列
基础篇
贪心篇
递归分治搜索篇
数据结构进阶篇(树/图/优先队列)
数学问题篇
动态规划篇
STL篇
目录
- 数据结构进阶
- 二叉树
- 二叉排序树
- 优先队列priority queue
- 散列表
- 图论
- 并查集Union Find
- 最小生成树MST(minimum spanning tree)
- 最短路径
- 拓扑排序
- 关键路径
数据结构进阶
满足是一棵树的条件:
(1)有一个节点入度为0,其它节点入度均为1;
(2)从度数为零的节点(树根)能够便利到所有的节点。
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/178
注意读题 是无向边,不知道哪个是父节点,所以上述考入度判断的条件(1)就不适用了
from typing import (
List,
)
import collections
class Solution:
def validTree(self, n, edges):
if len(edges) != n - 1: #先用边数判断
return False
neighbors = collections.defaultdict(list)
for k, v in edges:
neighbors[k].append(v)
neighbors[v].append(k)
visited = []
queue = [0]
while queue:#bfs
cur = queue.pop()
visited.append(cur)
queue += [node for node in neighbors[cur] if node not in visited]
return len(visited) == n #最后用访问点数判断
#方法:并查集
from typing import (
List,
)
class UnionFind:
""" With Path Compression, beats 93.60%
"""
def __init__(self, N):
self.components = N
self.id = [i for i in range(N)]
self.sz = [1 for _ in range(N)]
def root(self, p):
while self.id[p] != p:
self.id[p] = self.id[self.id[p]] #此句删掉就没有Path Compression
p = self.id[p]
return p
def find(self, p, q):
i = self.root(p)
j = self.root(q)
return i == j
def union(self, p, q):
i = self.root(p)
j = self.root(q)
if i == j:
return
elif i < j:
self.id[i] = j
self.sz[j] += self.sz[i]
else:
self.id[j] = i
self.sz[i] += self.sz[j]
self.components -= 1
class Solution:
def validTree(self, n, edges):
if len(edges) != n - 1: return False
unionFind = UnionFind(n) # weighted union find with path compression
for edge in edges:
unionFind.union(edge[0], edge[1])
return unionFind.components == 1
二叉树
例题10.1 二叉树遍历(清华大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiKuUTlX
给出先序遍历(空节点用#表示),建立二叉树,输出中序遍历
import sys
def creat(node,string,index):
if(index==len(string)):
return -1
if(index>-1):
char=string[index]
if(char !='#'):
node.val=char
index+=1
if(index<len(string)):
if(string[index]!='#'):
node.left=TreeNode()
index = creat(node.left,string,index)
else: index+=1
if(index>-1 and index<len(string)):
if(string[index]!='#'):
node.right=TreeNode()
index = creat(node.right,string,index)
else: index+=1
else: index+=1
return index
def inorder(node):
if(node!=None):
inorder(node.left)
print(node.val,end=' ')
inorder(node.right)
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=''):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
for line in sys.stdin:
string = list(line)
#print(string)
Tree = TreeNode() #实例化
creat(Tree,string,0)
#print(Tree)
inorder(Tree)
例题10.2 二叉树遍历(华中科技大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiKgDfLU
给出先序遍历和中序遍历,建立二叉树,输出后序遍历(后序遍历递归版)
import sys
def creat(node,preorder,inorder,index):
j=0
node.val=preorder[index]
left=[]
for j in range(len(inorder)):
if(inorder[j]==node.val):
break
else: left.append(inorder[j])
if(j+1<len(inorder)):right=inorder[j+1:]
else:right=[]
if(len(left)):
node.left=TreeNode()
index=creat(node.left,preorder,left,index+1)
if(len(right)):
node.right=TreeNode()
index=creat(node.right,preorder,right,index+1)
return index
def postorder(Tree):
if(Tree):
postorder(Tree.left)
postorder(Tree.right)
print(Tree.val,end='')
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=''):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
for line in sys.stdin:
preorder = list(line)
preorder.pop()
inorder= list(input())
#print(preorder,inorder)
Tree = TreeNode() #实例化
creat(Tree,preorder,inorder,0)
postorder(Tree)
print('\r')#注意不是\n \n会在两个输出之间多夹一个空行
二叉排序树
中序遍历可得到升序序列
例题10.3 二叉排序树(华中科技大学复试上机题 http://t.cn/Ai9PAkkv
初始为空树,建立二叉排序树。
import sys
def creat(Tree,inputs,index):
if(index>=len(inputs)):
return
num=inputs[index]
point=Tree
parent=Tree
direction='left' #默认左孩子
while(point!=None):
if(point.val<num):
parent=point
direction='right'
point=point.right
elif(point.val>num):
parent=point
direction='left'
point=point.left
if(direction=='left'):
parent.left=TreeNode(num)
else:
parent.right=TreeNode(num)
print(parent.val)
creat(Tree,inputs,index+1)
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self,val='') -> None:
self.val=val
self.left=None
self.right=None
for line in sys.stdin:
n = line
inputs=[int(i) for i in input().split()]
Tree = TreeNode(inputs[0])
print(-1)
creat(Tree,inputs,1)
习题10.1 二叉搜索树(浙江大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/Ai9PUJtK
判断两序列是否为同一二叉搜索树序列
import sys
def creat(Tree,inputs,index):
if(index>=len(inputs)):
return
num=inputs[index]
point=Tree
parent=Tree
direction='left' #默认左孩子
while(point!=None):
if(point.val<num):
parent=point
direction='right'
point=point.right
elif(point.val>num):
parent=point
direction='left'
point=point.left
if(direction=='left'):
parent.left=TreeNode(num)
else:
parent.right=TreeNode(num)
#print(parent.val)
creat(Tree,inputs,index+1)
def preorder(node,string):
if(node!=None):
string+=node.val
string=preorder(node.left,string)
string=preorder(node.right,string)
return string
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self,val='') -> None:
self.val=val
self.left=None
self.right=None
for line in sys.stdin:
a = int(line)
if (a==0):break
list1=list(input())
Tree1 = TreeNode(list1[0])
creat(Tree1,list1,1)
string1=preorder(Tree1,"")
for i in range(a):
new_list=list(input())
Tree2 = TreeNode(new_list[0])
creat(Tree2,new_list,1)
string2=preorder(Tree2,"")
if(string1== string2):print('YES')
else:print('NO')
优先队列priority queue
队列按照优先级顺序排列,最高级先出first in greatest out
使用STL priority_queue(底层实现:二叉堆)
一看到哈夫曼树(树的带权路径长度最小的二叉树,又叫最优树,可能不唯一),就知道考察优先队列。带权路径长度=所有叶子节点的带权路径长度之和(带权路径长度=根节点到达该节点路径长度*该节点权值)
哈夫曼树的求法:
- 所有节点放入集合k
- 若k中节点多于1个,取出其中权值最小的两个节点,构造成某个新节点的左右子节点,新节点的权值为两个子节点的权值和,并将新节点放入k,删除两个已构造过的节点
- 若k中仅剩一个节点,即为该哈夫曼树的根节点,构造过程中所有中间节点的权值和=该哈夫曼树的带权路径和,即在构造函数中answer+=a+b;最终输出answer即可。
- 使用优先队列可高效求出k中权值最小的两个元素
#include<queue>
priority_queue<typename> name;//大顶堆的定义,注意比较优先级需要在typename结构体中重载<小于号
//若需要优先级低的先输出,小顶堆,则需要如下定义
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> name;
// 定义复数结构
struct Complex {
int real; // 实部
int imag; // 虚部
Complex(int a, int b) : real(a), imag(b) {} // 构造函数
// 重载小于运算符,用于优先队列的比较
bool operator<(Complex c) const {
return real * real + imag * imag < c.real * c.real + c.imag * c.imag;
}
};
name.empty()
name.size()
.push() .pop()
.top()//访问最高优先级的元素
'''
Python内置库中的queue.PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue(iterable):括号可以为空,即创建了一个空对象。若用可迭代对象初始化必须要 优先级 + 元素 的方式来初始化。
put(item):向优先级队列中插入元素 item,item 是一个元组,第一个元素为优先级。
get():从优先级队列中获取元素,返回值是一个元组 (priority, data),其中 priority 是优先级,data 是实际的数据。
qsize():返回优先级队列的大小,即队列中当前的元素个数。
empty():如果优先级队列为空,返回 True;否则返回 False。
而对象之间的大小比较,可以基于类定义的__lt__魔术方法实现,__lt__魔术方法可以实现同一个类的两个对象基于比较运算符进行大小比较。
'''
from queue import PriorityQueue
# 创建一个空的优先级队列
my_priority_queue = PriorityQueue()
# 通过可迭代对象初始化优先级队列
data = [(1, "Task 1"), (3, "Task 3"), (2, "Task 2")]
my_priority_queue = PriorityQueue(data)
例题10.5 复数集合(北京邮电大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/Ai98yYlt
import sys
from queue import PriorityQueue
class plural(object):
def __init__(self,string):
index1=string.find('+')
self.real=string[:index1]
self.virtual=string[index1+2:]
self.size=(int(self.real)**2+int(self.virtual)**2)**0.5
def __lt__(self,other):
if(self.size == other.size):
return self.real > other.size
else:
return self.size > other.size
for line in sys.stdin:
a = int(line)
# 创建一个空的优先级队列
pp_queue = PriorityQueue()
while(a):
command=input()
if(command=='Pop'):
if(pp_queue.empty()):print('empty')
else:
data= pp_queue.get()
print(data.real+'+i'+data.virtual)
print('SIZE =',pp_queue.qsize())
else:
command2,p= command.split()
new_p=plural(p)
pp_queue.put(new_p)
print('SIZE =',pp_queue.qsize())
a-=1
例题10.6 哈夫曼树(北京邮电大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiCuGMki
import sys
import copy
from queue import PriorityQueue
def preorder(node,layer,total):
if(node.left!=None):
total=preorder(node.left,layer+1,total)
if(node.right!=None):
total=preorder(node.right,layer+1,total)
if(node.left==None and node.right==None):total+=node.val*layer
return total
class node(object):
def __init__(self,val) -> None:
self.val=val
self.left=None
self.right=None
def __lt__(self,other):
return self.val<other.val
for line in sys.stdin:
n = int(line)
leafs=input().split()
leafs.sort()
#print(leafs)
pp_queue=PriorityQueue()
for i in range(len(leafs)):
pp_queue.put(node(int(leafs[i])))
total=0
leafs=[]
while(pp_queue.qsize()>1):
data1=pp_queue.get()
data2=pp_queue.get()
sum=data1.val+data2.val
parent=node(sum)
parent.left=data1
parent.right=data2
pp_queue.put(parent)
root=pp_queue.get()
total=preorder(root,0,0)
#total+=item.val*(max_layer-item.layer)
print(total)
习题10.2 查找第K小的数(北京邮电大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiCu5hcK
import sys
from queue import PriorityQueue
for line in sys.stdin:
n = int(line)
inputs=input().split()
pp_queue=PriorityQueue()
for i in inputs:
pp_queue.put(int(i))
j=0
k=int(input())
res=0
last=0
while(j<k):
last=res
res=pp_queue.get()
if(res==last):
j-=1
j+=1
print(res)
习题10.3 搬水果(吉林大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiCu5nsQ
import sys
from queue import PriorityQueue
for line in sys.stdin:
pp_queue=PriorityQueue()
a = int(line)
dp=[]
if(a):
f= [int(x) for x in input().split()]
#print(f)
for i in f:
pp_queue.put(i)
total=0
i=0
while(pp_queue.qsize()>1):
f1=pp_queue.get()
f2=pp_queue.get()
pp_queue.put(f1+f2)
dp.append(f1+f2)
print(sum(dp))
散列表
应用场景:查找,而线性查找会超时,典型映射题目
使用STL -map(底层实现:红黑树)会按照key排序,还有一种unordered_map无序,使用方法相同。
#include<map>
map<type1,type2>name;//key-value
name.empty()
name.size()
.insert() .erase()
//访问方法:
name[key]
name.at(key)
map<type1,type2>::iterator it;//迭代器it
.find()//返回迭代器,若未找到返回迭代器end()
.clear()
.begin() .end()
当需要双向映射时,可以用两个map,也可以都放在一个map中(当key与value不出现重复时)
例题10.7 查找学生信息(清华大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiCuVIuY
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
a = int(line)
d={}
for i in range(a):
data=input()
key=data.split()[0] #data[:2]是错的,因为key可能不止两位数
d[key]=data
b=int(input())
for i in range(b):
check=input()
if(check in d):
print(d[check])
else:
print('No Answer!')
例题10.8 魔咒词典(浙江大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiCufczt
import sys
dic={}
for line in sys.stdin:
if(line=='@END@\n'):break
else:
line=line.lstrip('[')
line=line.rstrip('\n')
a = line.split(']')
dic[a[0]]=a[1][1:]
#print(dic)
num=int(input())
for i in range(num):
inputs=input()
if(inputs.find('[')==0 and inputs.find(']')==len(inputs)-1):
check=inputs.lstrip('[')
check=check.rstrip(']')
if(check in dic.keys()):
print(dic[check])
continue
elif(inputs in dic.values()):
for key,value in dic.items():
if(value==inputs):
print(key)
break
continue
print('what?')
例题10.9 字串计算(北京大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiCuJtI5
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
string=line
dic={}
if(string):
for i in range(len(string)):
for j in range(i+1,len(string)):
temp=string[i:j]
try:
dic[temp]+=1
except:
dic[temp]=0
dic[temp]+=1
dic=sorted(dic.items())
#print(dic)
for item in dic:
if(item[1]>1):
print(item[0],item[1])
习题10.4 统计同成绩学生人数(浙江大学复试上机题) https://www.nowcoder.com/share/jump/19131511723814164917
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
n = int(line)
if(n==0):break
scores=input().split()
check=input()
print(scores.count(check))
习题10.5 开门人和关门人(浙江大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiCuM09f
import sys
import copy
class person(object):
def __init__(self,id,start,end) -> None:
self.id=id
self.start=start
self.end=end
for line in sys.stdin:
n = int(line)
people=[]
min_p=0
max_p=0
min_time='24:00:00'
max_time='00:00:00'
for i in range(n):
inputs=input().split()
new=person(inputs[0],inputs[1],inputs[2])
if(inputs[1]<min_time):
min_time=inputs[1]
min_p=i
if(inputs[2]>max_time):
max_time=inputs[2]
max_p=i
people.append(copy.deepcopy(new))
print(people[min_p].id,people[max_p].id)
习题10.6 谁是你的潜在朋友(北京大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiCux4f7
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
inputs= [int(i) for i in line.split()]
n,m=inputs[0],inputs[-1]
books=[[]for i in range(m)]
for i in range(n):
p=int(input())
books[p].append(i)
#print(books)
for i in range(n):
flag=0
for item in books:
if(i in item and len(item)>1):
print(len(item)-1)
flag=1
if(flag==0):
print('BeiJu')
www.lintcode.com/problem/124/
模版:用set
from typing import (
List,
)
class Solution:
def longestConsecutive(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
longest_streak = 0
num_set = set(nums)
for num in num_set:
if num - 1 not in num_set:
current_num = num
current_streak = 1
while current_num + 1 in num_set:
current_num += 1
current_streak += 1
longest_streak = max(longest_streak, current_streak)
return longest_streak
图论
邻接矩阵adjacency matrix用二维数组实现,邻接表adjacency list用vector实现。
graph[from].push_back(edge(to,length));
并查集Union Find
两个基本操作:查找、合并(+路径压缩)。
应用:例如可达、可联通、判断是否是连通图、求连通分量、还需要加多少边联通、是否是树
#并查集 python 模版
class UnionFind:
""" With Path Compression, beats 93.60%
"""
def __init__(self, N):
self.components = N
self.id = [i for i in range(N)]
self.sz = [1 for _ in range(N)]
def root(self, p):
while self.id[p] != p:
self.id[p] = self.id[self.id[p]] #此句删掉就没有Path Compression
p = self.id[p]
return p
def find(self, p, q):
i = self.root(p)
j = self.root(q)
return i == j
def union(self, p, q):
i = self.root(p)
j = self.root(q)
if i == j:
return
elif i < j:#注意都是合并两个点的最终父母
self.id[i] = j
self.sz[j] += self.sz[i]
else:
self.id[j] = i
self.sz[i] += self.sz[j]
self.components -= 1
例题11.1 畅通工程(浙江大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiOvBHj9
import sys
class UnionFind(object):
def __init__(self,n) -> None:
self.component=n
self.id=[i for i in range(n+1)]
self.size=[1 for _ in range(n+1)]
def root(self,a):
p=a
while(self.id[p]!=p):
self.id[p]=self.id[self.id[p]]
p=self.id[p]
return p
def union(self,a,b):
a_p=self.root(a)
b_p=self.root(b)
if(a_p == b_p):
return
elif(a_p>b_p):#小号合并到大号
self.id[b_p]=a_p
self.size[a_p]+=self.size[b_p]
else:
self.id[a_p]=b_p
self.size[b_p]+=self.size[a_p]
#print(a,a_p,b,b_p,'--1')
self.component-=1
for line in sys.stdin:
try:
cn,rn =line.split()
cn=int(cn)
u=UnionFind(cn)
cnt=0
for i in range(int(rn)):
a,b=input().split()
a=int(a)
b=int(b)
#print('old parent',u.root(a),u.root(b))
u.union(a,b)
if(u.component==0):print(0)
else:print(u.component-1)
except:
break
例题11.2 连通图(吉林大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiO77VoA
import sys
class UnionFind(object):
def __init__(self,n) -> None:
self.component=n
self.id=[i for i in range(n+1)]
self.size=[1 for _ in range(n+1)]
def root(self,a):
p=a
while(self.id[p]!=p):
self.id[p]=self.id[self.id[p]]
p=self.id[p]
return p
def union(self,a,b):
a_p=self.root(a)
b_p=self.root(b)
if(a_p == b_p):
return
elif(a_p>b_p):#小号合并到大号
self.id[b_p]=a_p
self.size[a_p]+=self.size[b_p]
else:
self.id[a_p]=b_p
self.size[b_p]+=self.size[a_p]
#print(a,a_p,b,b_p,'--1')
self.component-=1
for line in sys.stdin:
cn,rn =line.split()
cn=int(cn)
u=UnionFind(cn)
cnt=0
if(cn==0):break
for i in range(int(rn)):
a,b=input().split()
a=int(a)
b=int(b)
#print('old parent',u.root(a),u.root(b))
u.union(a,b)
if(u.component==0 or u.component==1):
print('YES')
else:print('NO')
例题11.3 Is It A Tree?(北京大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiO7FyDO
同pat 2024夏压轴题目
树需要满足条件:
- 根节点入度为0,其余节点入度为1
- 只有一个根节点,其余节点均属于一个并查集
习题11.1 找出直系亲属(浙江大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiOzTX5c
import sys
import collections
#这里要介绍一种可以当list操作的字典 neighbors = collections.defaultdict(value_type)
class UnionFind(object):
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.child=collections.defaultdict(str)
def root(self,a,b):
flag='parent'
for i in range(2):
if(i==0):
p=a
elif(p!=b):
p=b
a,b=b,a
flag='child'
else:break
cnt=1
out='-'
while(self.child[p]!=p):
p=self.child[p]
cnt+=1
if(p=='-' or p==''):
out='-'
cnt=1
break
if(p==b):
break
if(p==b):
if(cnt==2):
out=flag
if(cnt>=3):
out='grand'+flag
if(cnt>3):
out='great-'*(cnt-3)+out
return out
u=UnionFind()
for line in sys.stdin:
try:
a,b=line.split()
a=int(a)
b=int(b)
for i in range(a):
string=input()
u.child[string[1]]=string[0]
u.child[string[2]]=string[0]
if(u.child[string[0]]==''):
u.child[string[0]]=string[0]
for j in range(b):
string=input()
print(u.root(string[0],string[1]))
except:
break
习题11.2 第一题(上海交通大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiOhkgMJ
import sys
import collections
#这里要介绍一种可以当list操作的字典 neighbors = collections.defaultdict(value_type)
class UnionFind(object):
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.id=collections.defaultdict(int)
def root(self,a):
p=a
while(self.id[p]!=p):
self.id[p]=self.id[self.id[p]]
p=self.id[p]
return p
def union(self,a,b):
a_p=self.root(a)
b_p=self.root(b)
if(a_p == b_p):
return
elif(a_p>b_p):#小号合并到大号
self.id[b_p]=a_p
else:
self.id[a_p]=b_p
#print(a,self.root(a),b,self.root(b),'--1')
u=UnionFind()
for line in sys.stdin:
try:
a,b=line.split()
a=int(a)
b=int(b)
if(u.id[a]==0):
u.id[a]=a
if(u.id[b]==0):
u.id[b]=b
if(a!=b):
u.union(a,b)
except:
break
cnt=0
for key,value in u.id.items():
#print(key,value)
if(key==value):
cnt+=1
print(cnt)
习题11.3 Head of a Gang(浙江大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiOzQMBH
import sys
import collections
class UnionFind(object):
def __init__(self,n) -> None:
self.component=n
self.id=collections.defaultdict(str)
self.size=collections.defaultdict(int)
self.alltime=collections.defaultdict(int)
def root(self,a):
p=a
while(self.id[p]!=p):
self.id[p]=self.id[self.id[p]]
p=self.id[p]
return p
def union(self,a,b):
a_p=self.root(a)
b_p=self.root(b)
if(a_p == b_p):
return
elif(u.alltime[b_p]<=u.alltime[a_p]):#小号合并到大号
self.id[b_p]=a_p
self.size[a_p]+=self.size[b_p]
self.alltime[a_p]+=self.alltime[b_p]
elif(u.alltime[b_p]>u.alltime[a_p]):
self.id[a_p]=b_p
self.size[b_p]+=self.size[a_p]
self.alltime[b_p]+=self.alltime[a_p]
self.component-=1
for line in sys.stdin:
cn,k =line.split()
cn=int(cn)
k=int(k)
u=UnionFind(cn)
cnt=0
people=[]
for i in range(cn):
a,b,time=input().split()
time=int(time)
if(u.id[a]==''):
u.id[a]=a
u.size[a]=1
if(u.id[b]==''):
u.id[b]=b
u.size[b]=1
u.alltime[a]+=time
u.alltime[b]+=time
#注意1 要在union函数之前加好对话双方的time,全部加完之后再从头union
people.append([a,b])
people=sorted(people,key=lambda x:-max(u.alltime[x[0]],u.alltime[x[1]]))
#注意2 需要将其排序成最大的alltime先合并,不然会出现前面合并后某个节点alltime大过本来的最大alltime节点
#导致的父节点不正确
for item in people:
a=item[0]
b=item[1]
u.union(a,b)
flag=0
people=[]
for key,value in u.id.items():
if(key==value and u.alltime[key]>k*2 and u.size[key]>2):
cnt+=1
people.append(str(key)+' '+str(u.size[key]))
flag=1
people=sorted(people,key=lambda x:x[0])
if(flag==0):
print(0)
else:
print(cnt)
for item in people:
print(item)
最小生成树MST(minimum spanning tree)
优先使用kruskal
步骤:
- 初始所有顶点均孤立
- 按边权升序排列,若遍历到的边两个顶点分属不同集合,则确定该边属于MST,并将该边分属集合合并
- 遍历完所有边后若连通,则被选的边和所有顶点构成MST;否则MST不存在。
例题11.4 还是畅通工程(浙江大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiWud0C6
例题11.5 继续畅通工程(浙江大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiW3fcfp
习题11.4 Freckles(北京大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiW3Hbqr
习题11.5 Jungle Roads(北京大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AiW33P91
最短路径
分两类,
- 单源【边都是正数】、
- 朴素dijkstra o(n^2) 只与节点数n有关,与边m无关,适用于稠密图
- 堆优化版dijkstra o(mlogn)
- 单源【含负边】
- 多源最短路径。
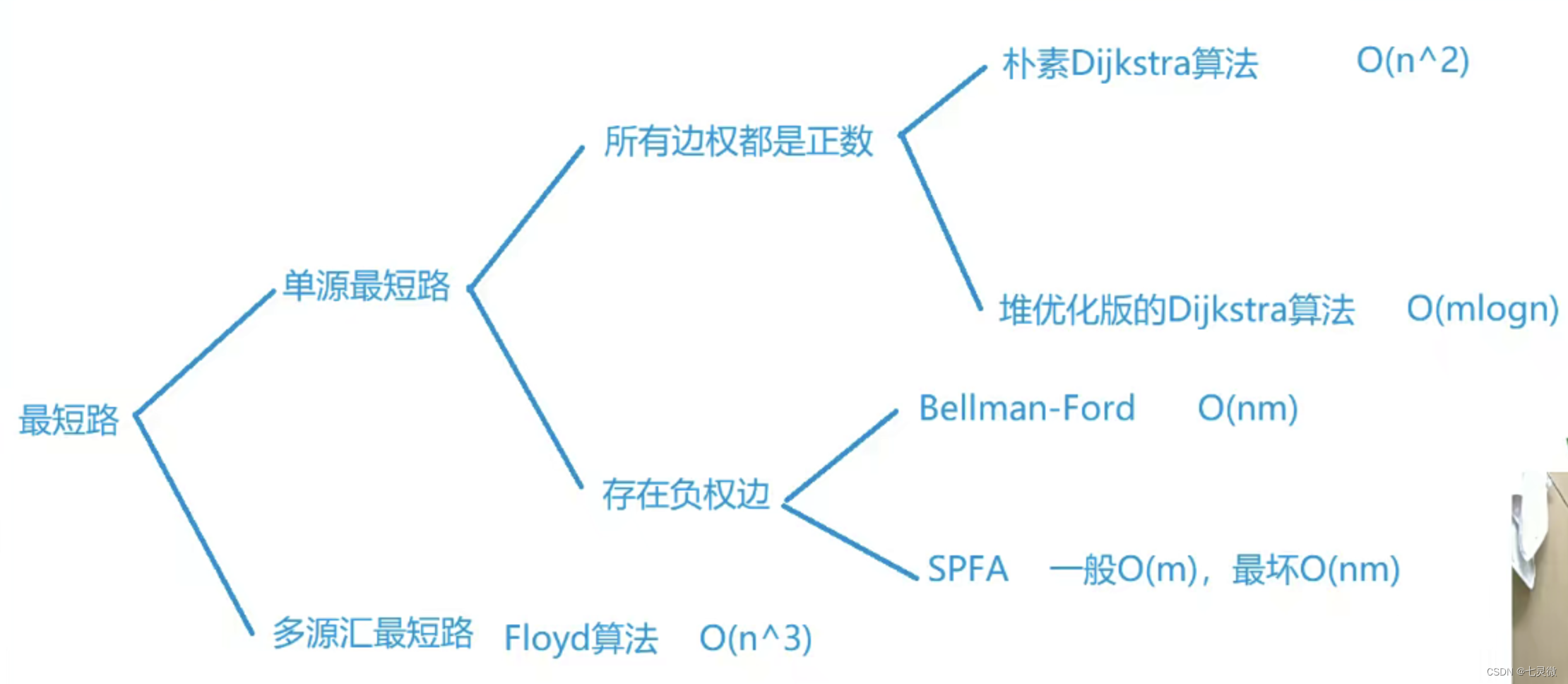
dijkstra【遵循贪心策略】也是将顶点v划分成两个集合s,t;
s是已确定的顶点集合,初始只包含起点
t=v-s,是未确定的顶点集合。
反复从集合t中选择当前到起点最近的顶点u(这里可以维护一个优先队列),将u加入s,并对所有从u发出的边进行松弛操作。
例题11.6 畅通工程续(浙江大学复试上机题) http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1874
略
例题11.7 最短路径问题(浙江大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AilPbME2
习题11.6 最短路径(上海交通大学复试上机题) http://t.cn/AilPCAuL
拓扑排序
拓扑排序就是将有向无环图的图节点排序成一条序列。
如果有向图中有环,就不存在拓扑排序。可以通过拓扑排序算法来得到拓扑排序,以及判断是否存在环。
拓扑排序步骤:
- 建图并记录所有节点的入度。
- 将所有入度为0的节点加入队列。
- 取出队首的元素now,将其加入拓扑序列。
- 访问所有now的邻接点nxt,将nxt的入度减1,当减到0后,将nxt加入队列。
- 重复步骤3、4,直到队列为空。
- 如果拓扑序列个数等于节点数,代表该有向图无环,且存在拓扑序。
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/615/
from typing import (
List,
)
class Solution:
"""
@param num_courses: a total of n courses
@param prerequisites: a list of prerequisite pairs
@return: true if can finish all courses or false
"""
def can_finish(self, num_courses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
# write your code here
queue=[]
res=[]
edges=[[]for i in range(num_courses)]#这个是拿空间换时间,否则会超时
indegree=[0 for i in range(num_courses)]
for item in prerequisites:
s=item[0]
e=item[1]
edges[s].append(e)
indegree[e]+=1
#print(indegree)
for i in range(num_courses):
if(indegree[i]==0):
queue.append(i)
while(len(queue)):
front=queue[0]
res.append(front)
for item in edges[front]:
indegree[item]-=1
if(indegree[item]==0):
queue.append(item)
queue.pop(0)
return len(res)==num_courses
例题11.8 Legal or Not http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3342
略
例题11.9 确定比赛名次 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1285
略
难以想到用拓扑排序的题目!!难
https://www.lintcode.com/problem/892/
有一个很容易想到拓扑排序的方法是:凡是题目要求把一个复杂的节点按顺序输出时,要想到拓扑排序。
Input:[“wrt”,“wrf”,“er”,“ett”,“rftt”]
Output:“wertf”
Explanation:
from “wrt"and"wrf” ,we can get ‘t’<‘f’
from “wrt"and"er” ,we can get ‘w’<‘e’
from “er"and"ett” ,we can get ‘r’<‘t’
from “ett"and"rftt” ,we can get ‘e’<‘r’
So return “wertf”
从这里可以知道,可以将前后两个串第一个开始不同的地方看作一条边,如
from “wrt"and"wrf” ,we can get ‘t’<‘f’ :so this is edge ’ t-f’
from “wrt"and"er” ,we can get ‘w’<‘e’ : so this is edge ‘w-e’
from “er"and"ett” ,we can get ‘r’<‘t’: so this is edge ‘r-t’
from “ett"and"rftt” ,we can get ‘e’<‘r’:so this is edge ‘e-r’
class Solution:
"""
@param words: a list of words
@return: a string which is correct order
"""
def alienOrder(self, words):
# Write your code here
from collections import defaultdict
#这种dict可以当list用,与传统list不同的是 其index可以是字符串等
from collections import deque
import heapq #堆,默认为小顶堆
graph = {}
# initial graph
for w in words:
for c in w:
graph[c] = set() #建立空set
for i in range(1, len(words)):
for j in range(min(len(words[i]), len(words[i-1]))):
if words[i-1][j] != words[i][j]:
graph[words[i-1][j]].add(words[i][j])#得到一条边
break
j=min(len(words[i]), len(words[i-1]))
print(j,words[i-1][:j],words[i][:j])
if(words[i-1][:j]==words[i][:j] and len(words[i-1])>len(words[i])):
return ''
'''
上述return 为了防止出现'abc','ab'这种顺序失效的情况
'''
indegree = defaultdict(int)
for g in graph:
for ne in graph[g]:
indegree[ne] += 1
q = [w for w in graph if indegree[w] == 0]
heapq.heapify(q) #将这个q堆进行从小到大的排序,可以看成一个排好序的list
order = []
visited = set()#放重复
while q:
# n = q.pop()
n = heapq.heappop(q)
if n in visited:
continue
visited.add(n) #set添加元素是add
order.append(n)
for ne in graph[n]:
indegree[ne] -= 1
if indegree[ne] == 0:
# q.appendleft(ne)
heapq.heappush(q, ne)
return ''.join(order) if len(order) == len(graph) else ''
#如果生成顺序所包含的元素数目与一开始输入中包含的不同字符种数不同,则属于顺序失效
关键路径
例题11.10 Instructions Arrangement http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4109
略
