Redis从简单使用到底层原理与分布式缓存
文章目录
- ==[Redis参考手册](https://redis.io/docs/latest/commands/)==
- 1 基础认识
- 1.1 安装配置
- 1.2 通用命令
- 1.3 数据类型
- 1.3.1 数据结构与内部编码
- string
- key的结构
- hash
- list
- set
- sorted_set
- 1.4 单线程模型
- 2 redis客户端
- 2.1 RESP协议(Redis serialization protocol)
- 2.2 基础案例
- 3 分布式缓存 —— redis集群
- 3.1 持久化
- 3.1.1 RDB
- 3.1.2 RDB底层原理
- 3.1.3 AOF持久化
- 3.1.4 AOF与RDB的对比
- 3.2 Redis主从
- 3.2.1 搭建主从集群
- 3.2.2 数据同步原理
- 3.3 Redis哨兵
- Sentinel监控原理
- 选择新的master
- 如何实现故障转移
- 3.3.1 搭建哨兵集群
- 3.3.2 Redis客户端状态感知
- 3.4 Redis分片集群
- 3.4.1 搭建分片集群
- 3.4.2 散列插槽
- 3.4.3 集群伸缩
- 3.4.4 故障转移
- 4 多级缓存
- 4.1 JVM进程缓存
- 4.2 OpenResty
- 4.3 缓存同步
- 4.3.1 Canel
- 5 Redis实践优化
- 5.1 key的设计
- 5.2 批处理优化
- 5.2.1 集群模式下的批处理
- 5.3 服务端优化
- 5.3.1 持久化配置
- 5.3.2 慢查询
- 外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传
- 5.3.3 服务器安全配置
- 5.3.4 内存配置
- 5.3.5 集群相关问题
- 6 Redis底层原理
- 6.1 底层数据结构
- 6.1.1 SDS动态数组
- 6.1.2 Intset
- 6.1.3 Dict
- 6.1.4 ZipList
- 6.1.5 QuickList
- 6.1.5 SkipList
- 6.1.6 RedisObject
- 6.2 五种数据结构
- 6.2.1 String
- 6.2.2 List
- 6.2.3 Set
- 6.2.4 ZSet
- 6.2.5 Hash
- 6.3 Redis网络模型
- 6.3.1 selecct
- 6.3.2 poll
- 6.3.3 epoll
- 6.3.4 Redis网络模型
- 6.4 Redis通信协议
- 7 Redis实战
- 7.1 短信登录
- 7.2 商户查询缓存
- 6.2.4 ZSet
- 6.2.5 Hash
- 6.3 Redis网络模型
- 6.3.1 selecct
- 6.3.2 poll
- 6.3.3 epoll
- 6.3.4 Redis网络模型
- 6.4 Redis通信协议
- 7 Redis实战
- 7.1 短信登录
- 7.2 商户查询缓存
Redis参考手册
1 基础认识
-
NoSQL与SQL
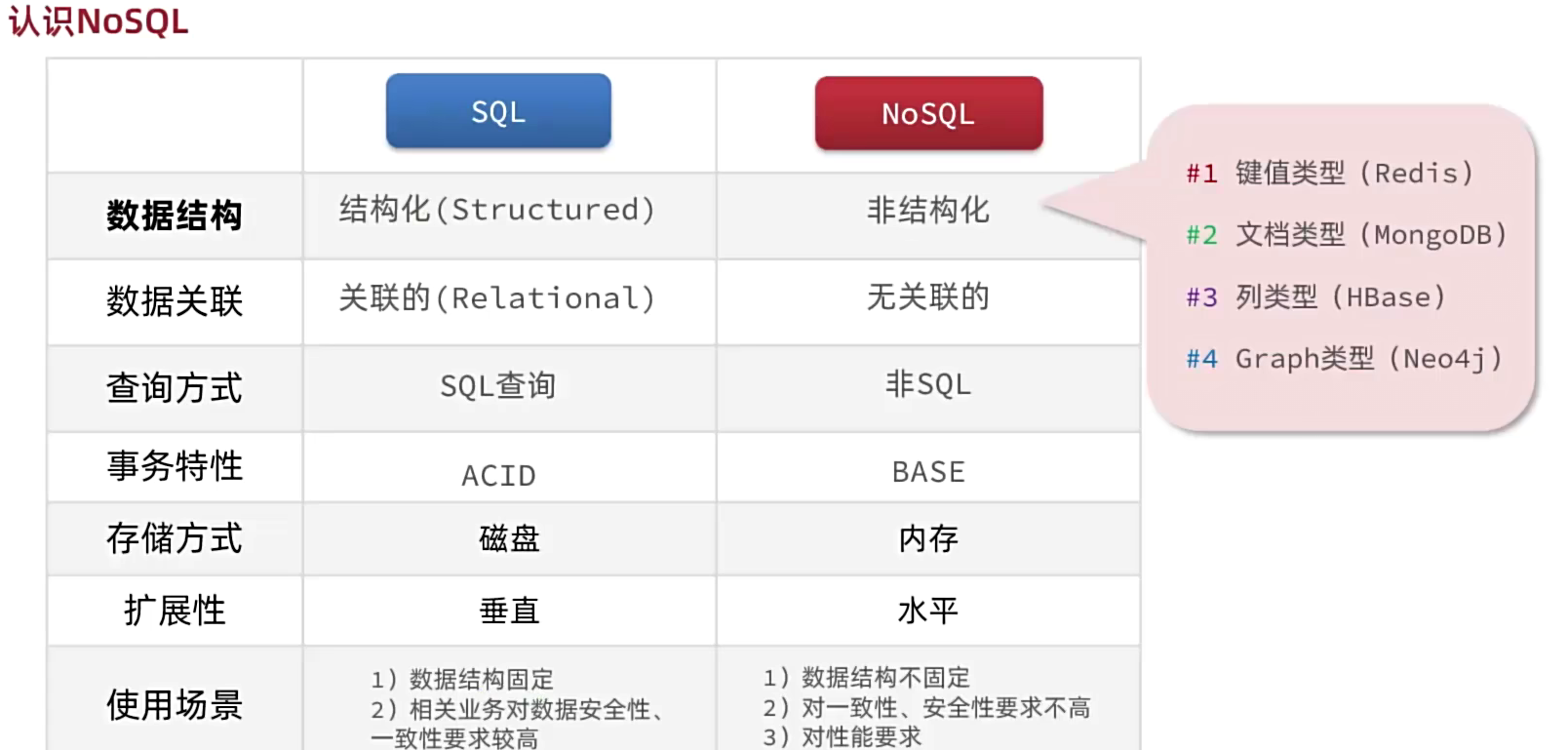
-
特征

1.1 安装配置
-
安装:
sudo apt install redis -
配置文件
etc/redis/redis.confbind 0.0.0.0 ::1 #将本地环回改为任意ip daemonize yes #守护进程启动 requirepass 123123 #设置密码为123123 protected-mode no #开启后其他主机才能访问 logfile "xxx.log" #开启日志,并记录到xxx.log中配置完后重启服务器:
service redis-sever restart查看运行状态:
service redis-server status
-
链接
redis-cli #--raw 将二进制编码 -
退出:
quit或ctrl + d
1.2 通用命令
help @generic #查看通用命令文档
- 类型
- key:字符串
- value:字符串、哈希表、列表、集合…
get
GET key
set
SET key value
exists
EXISTS key [key ...] #判断多个key,返回key存在 的个数
del
DEL key [key ...] #返回删除key的个数
expire:设置过期时间
EXPIRE key [seconds]
PEXPIRE key [millisecond]
ttl:(time to live)获取key的过期时间
TTL key #返回-2表示key已经删除了
- 过期策略
定期删除 与 惰性删除 相结合
type: 查看key对应的value的值
redis> SET key1 "value"
"OK"
redis> LPUSH key2 "value"
(integer) 1
redis> SADD key3 "value"
(integer) 1
redis> TYPE key1
"string"
redis> TYPE key2
"list"
redis> TYPE key3
"set"
redis>
keys
KEYS pattern
-
pattern

-
flushall:清除所有数据库中的key -
scan——渐进式遍历 -
select dbIndex—— 切换数据库
dbIndex范围为0-15
1.3 数据类型
1.3.1 数据结构与内部编码
-
raw:原始字符串(C语言中的字符数组)
-
embstr:对于短字符串的优化
-
ziplist:对于键值对少的时候,通过压缩列表进行优化
-
quicklist:从redis3.2开始用quicklist实现list
-
skiplist:跳表
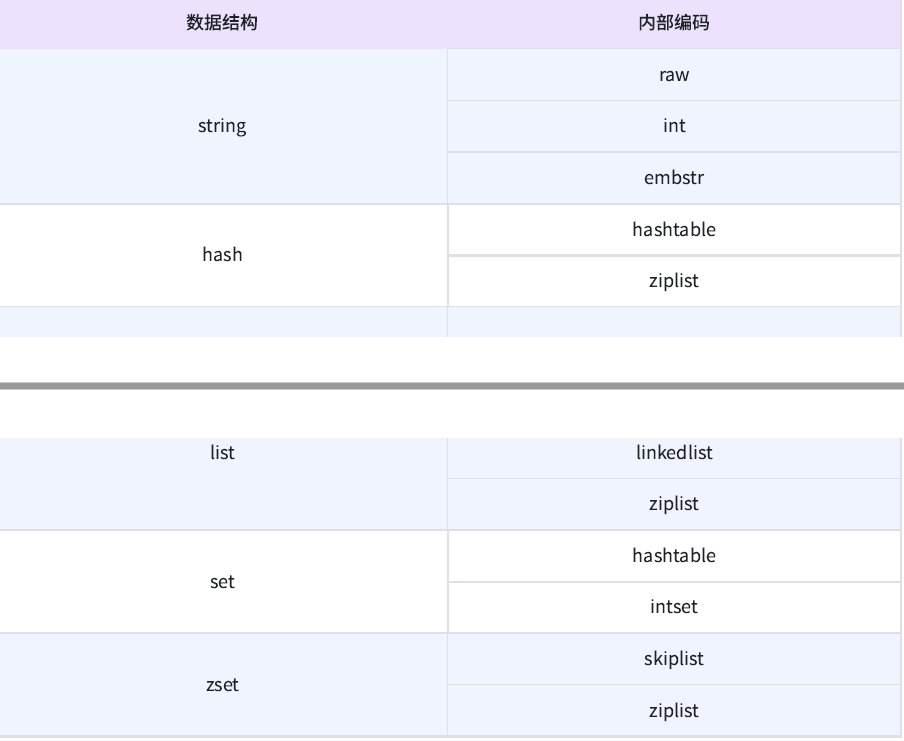
-
查看实际编码方式
OBJECT encoding key
string
set
SET key value [NX | XX] [GET] [EX seconds | PX milliseconds | EXAT unix-time-seconds | PXAT unix-time-milliseconds | KEEPTTL]

get
get只能查询字符串类型的value
mget/mset
设置/获取多组键值对
setnx/setex/psetex
不存在则设置/另外设置过期时间(单位s)/(单位ms)
-
#将value视为整数,对其+- incr incrby decr decrby incrbyfloat #前面四个只能算整数,incrbyfloat可以算浮点数 -
函数 例子 效果 appendappend key value追加fvalue getrangegetrange key start end截取value的[start, end]区间部分,负数下标表示倒数 setrangesetrange key offset valueoffset表示从第几个开始 strlenstrlen key获取value的长度(字符为单位),若不是string类型则报错
key的结构
- 让redis像mysql一样存储
- key:
数据库:表 - value:
{字段:值, 字段:值...}

hash

list

set

sorted_set
- 默认按score升序排列,在
Z后面加上REV倒序排列

1.4 单线程模型
redis虽然是单线程模型,为什么效率却这么高
- 访问内存,MySQL则多是访问硬盘
- 核心功能简单
- 单线程模型,避免了多线程带来的开销
- 底层使用epoll
2 redis客户端
- redis自定义应用层协议
2.1 RESP协议(Redis serialization protocol)
2.2 基础案例
#include <sw/redis++/redis++.h>
using namespace sw::redis;
try {
// Create an Redis object, which is movable but NOT copyable.
auto redis = Redis("tcp://127.0.0.1:6379");
// ***** STRING commands *****
redis.set("key", "val");
auto val = redis.get("key"); // val is of type OptionalString. See 'API Reference' section for details.
if (val) {
// Dereference val to get the returned value of std::string type.
std::cout << *val << std::endl;
} // else key doesn't exist.
// ***** LIST commands *****
// std::vector<std::string> to Redis LIST.
std::vector<std::string> vec = {"a", "b", "c"};
redis.rpush("list", vec.begin(), vec.end());
// std::initializer_list to Redis LIST.
redis.rpush("list", {"a", "b", "c"});
// Redis LIST to std::vector<std::string>.
vec.clear();
redis.lrange("list", 0, -1, std::back_inserter(vec));
// ***** HASH commands *****
redis.hset("hash", "field", "val");
// Another way to do the same job.
redis.hset("hash", std::make_pair("field", "val"));
// std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> to Redis HASH.
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> m = {
{"field1", "val1"},
{"field2", "val2"}
};
redis.hmset("hash", m.begin(), m.end());
// Redis HASH to std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string>.
m.clear();
redis.hgetall("hash", std::inserter(m, m.begin()));
// Get value only.
// NOTE: since field might NOT exist, so we need to parse it to OptionalString.
std::vector<OptionalString> vals;
redis.hmget("hash", {"field1", "field2"}, std::back_inserter(vals));
// ***** SET commands *****
redis.sadd("set", "m1");
// std::unordered_set<std::string> to Redis SET.
std::unordered_set<std::string> set = {"m2", "m3"};
redis.sadd("set", set.begin(), set.end());
// std::initializer_list to Redis SET.
redis.sadd("set", {"m2", "m3"});
// Redis SET to std::unordered_set<std::string>.
set.clear();
redis.smembers("set", std::inserter(set, set.begin()));
if (redis.sismember("set", "m1")) {
std::cout << "m1 exists" << std::endl;
} // else NOT exist.
// ***** SORTED SET commands *****
redis.zadd("sorted_set", "m1", 1.3);
// std::unordered_map<std::string, double> to Redis SORTED SET.
std::unordered_map<std::string, double> scores = {
{"m2", 2.3},
{"m3", 4.5}
};
redis.zadd("sorted_set", scores.begin(), scores.end());
// Redis SORTED SET to std::vector<std::pair<std::string, double>>.
// NOTE: The return results of zrangebyscore are ordered, if you save the results
// in to `std::unordered_map<std::string, double>`, you'll lose the order.
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, double>> zset_result;
redis.zrangebyscore("sorted_set",
UnboundedInterval<double>{}, // (-inf, +inf)
std::back_inserter(zset_result));
// Only get member names:
// pass an inserter of std::vector<std::string> type as output parameter.
std::vector<std::string> without_score;
redis.zrangebyscore("sorted_set",
BoundedInterval<double>(1.5, 3.4, BoundType::CLOSED), // [1.5, 3.4]
std::back_inserter(without_score));
// Get both member names and scores:
// pass an back_inserter of std::vector<std::pair<std::string, double>> as output parameter.
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, double>> with_score;
redis.zrangebyscore("sorted_set",
BoundedInterval<double>(1.5, 3.4, BoundType::LEFT_OPEN), // (1.5, 3.4]
std::back_inserter(with_score));
// ***** SCRIPTING commands *****
// Script returns a single element.
auto num = redis.eval<long long>("return 1", {}, {});
// Script returns an array of elements.
std::vector<std::string> nums;
redis.eval("return {ARGV[1], ARGV[2]}", {}, {"1", "2"}, std::back_inserter(nums));
// mset with TTL
auto mset_with_ttl_script = R"(
local len = #KEYS
if (len == 0 or len + 1 ~= #ARGV) then return 0 end
local ttl = tonumber(ARGV[len + 1])
if (not ttl or ttl <= 0) then return 0 end
for i = 1, len do redis.call("SET", KEYS[i], ARGV[i], "EX", ttl) end
return 1
)";
// Set multiple key-value pairs with TTL of 60 seconds.
auto keys = {"key1", "key2", "key3"};
std::vector<std::string> args = {"val1", "val2", "val3", "60"};
redis.eval<long long>(mset_with_ttl_script, keys.begin(), keys.end(), args.begin(), args.end());
// ***** Pipeline *****
// Create a pipeline.
auto pipe = redis.pipeline();
// Send mulitple commands and get all replies.
auto pipe_replies = pipe.set("key", "value")
.get("key")
.rename("key", "new-key")
.rpush("list", {"a", "b", "c"})
.lrange("list", 0, -1)
.exec();
// Parse reply with reply type and index.
auto set_cmd_result = pipe_replies.get<bool>(0);
auto get_cmd_result = pipe_replies.get<OptionalString>(1);
// rename command result
pipe_replies.get<void>(2);
auto rpush_cmd_result = pipe_replies.get<long long>(3);
std::vector<std::string> lrange_cmd_result;
pipe_replies.get(4, back_inserter(lrange_cmd_result));
// ***** Transaction *****
// Create a transaction.
auto tx = redis.transaction();
// Run multiple commands in a transaction, and get all replies.
auto tx_replies = tx.incr("num0")
.incr("num1")
.mget({"num0", "num1"})
.exec();
// Parse reply with reply type and index.
auto incr_result0 = tx_replies.get<long long>(0);
auto incr_result1 = tx_replies.get<long long>(1);
std::vector<OptionalString> mget_cmd_result;
tx_replies.get(2, back_inserter(mget_cmd_result));
// ***** Generic Command Interface *****
// There's no *Redis::client_getname* interface.
// But you can use *Redis::command* to get the client name.
val = redis.command<OptionalString>("client", "getname");
if (val) {
std::cout << *val << std::endl;
}
// Same as above.
auto getname_cmd_str = {"client", "getname"};
val = redis.command<OptionalString>(getname_cmd_str.begin(), getname_cmd_str.end());
// There's no *Redis::sort* interface.
// But you can use *Redis::command* to send sort the list.
std::vector<std::string> sorted_list;
redis.command("sort", "list", "ALPHA", std::back_inserter(sorted_list));
// Another *Redis::command* to do the same work.
auto sort_cmd_str = {"sort", "list", "ALPHA"};
redis.command(sort_cmd_str.begin(), sort_cmd_str.end(), std::back_inserter(sorted_list));
// ***** Redis Cluster *****
// Create a RedisCluster object, which is movable but NOT copyable.
auto redis_cluster = RedisCluster("tcp://127.0.0.1:7000");
// RedisCluster has similar interfaces as Redis.
redis_cluster.set("key", "value");
val = redis_cluster.get("key");
if (val) {
std::cout << *val << std::endl;
} // else key doesn't exist.
// Keys with hash-tag.
redis_cluster.set("key{tag}1", "val1");
redis_cluster.set("key{tag}2", "val2");
redis_cluster.set("key{tag}3", "val3");
std::vector<OptionalString> hash_tag_res;
redis_cluster.mget({"key{tag}1", "key{tag}2", "key{tag}3"},
std::back_inserter(hash_tag_res));
} catch (const Error &e) {
// Error handling.
}
3 分布式缓存 —— redis集群
3.1 持久化
- 单节点Redis的问题:1. 数据丢失 2. 并发能力 3. 存储能力 4. 故障恢复
3.1.1 RDB

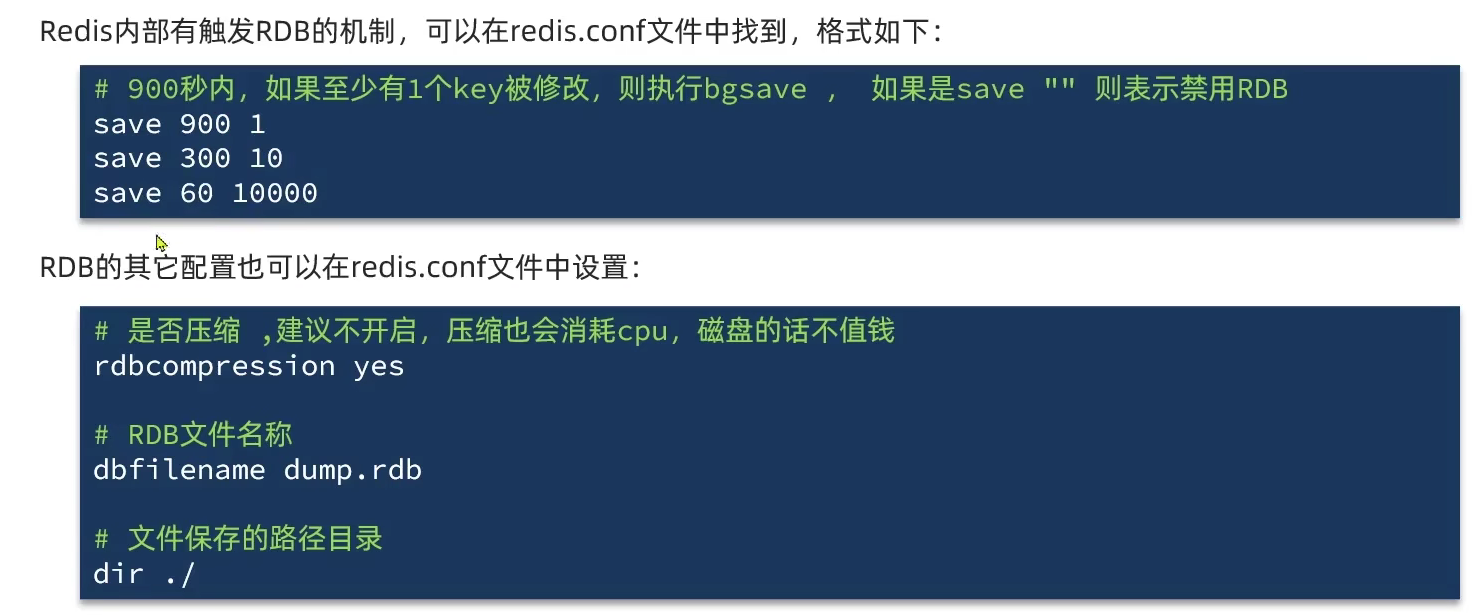
3.1.2 RDB底层原理
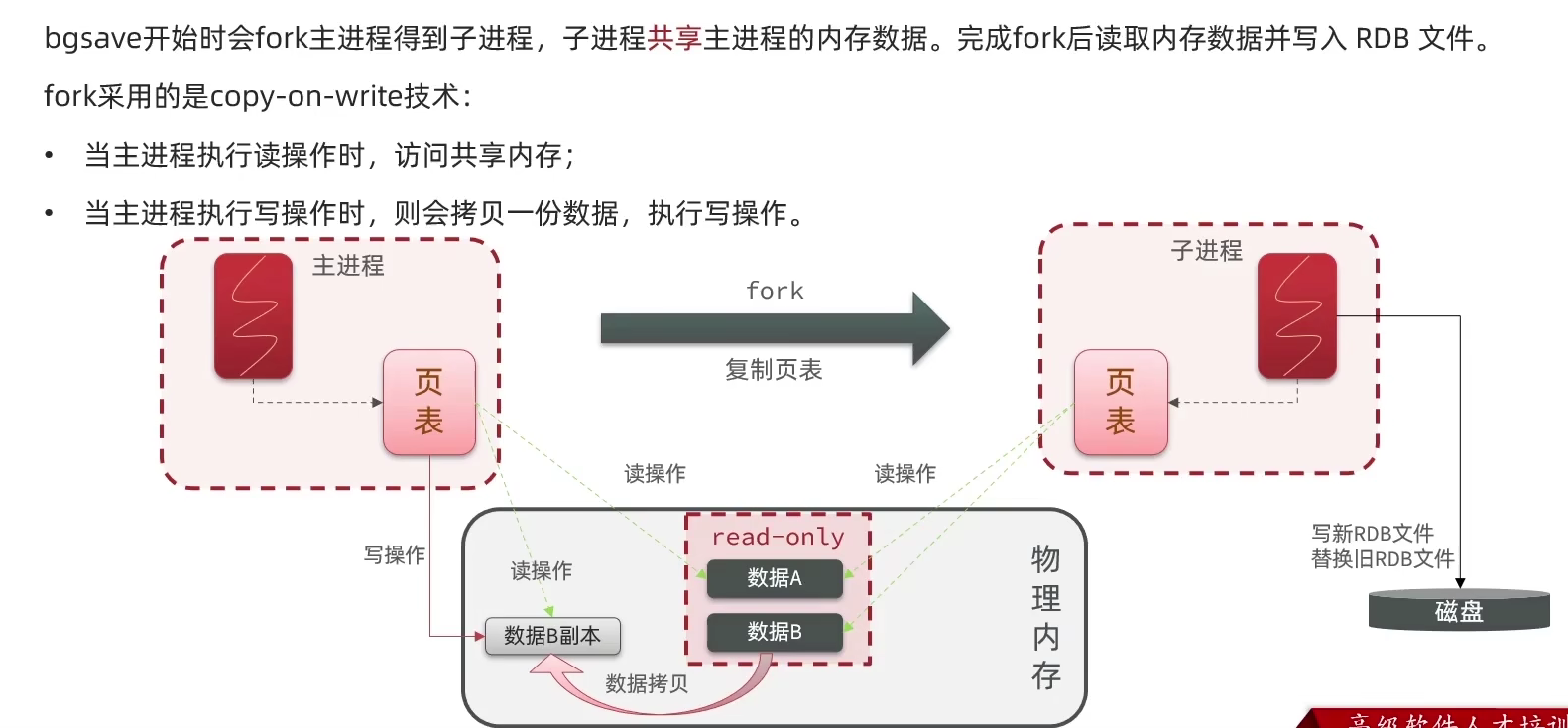
3.1.3 AOF持久化
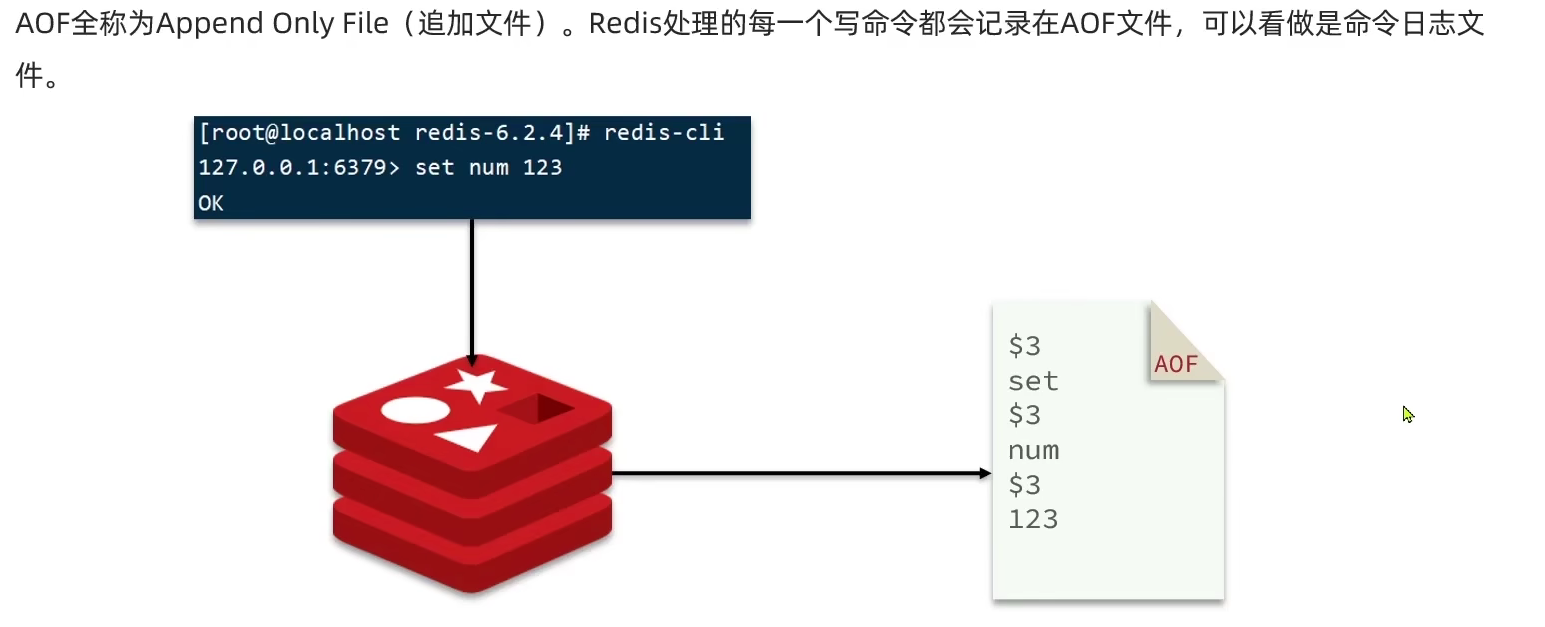
- 默认选择
appendfsync everysec

- 解决AOF文件过大的问题(清除无效数据) —— 执行
bgrewriteaof命令

3.1.4 AOF与RDB的对比
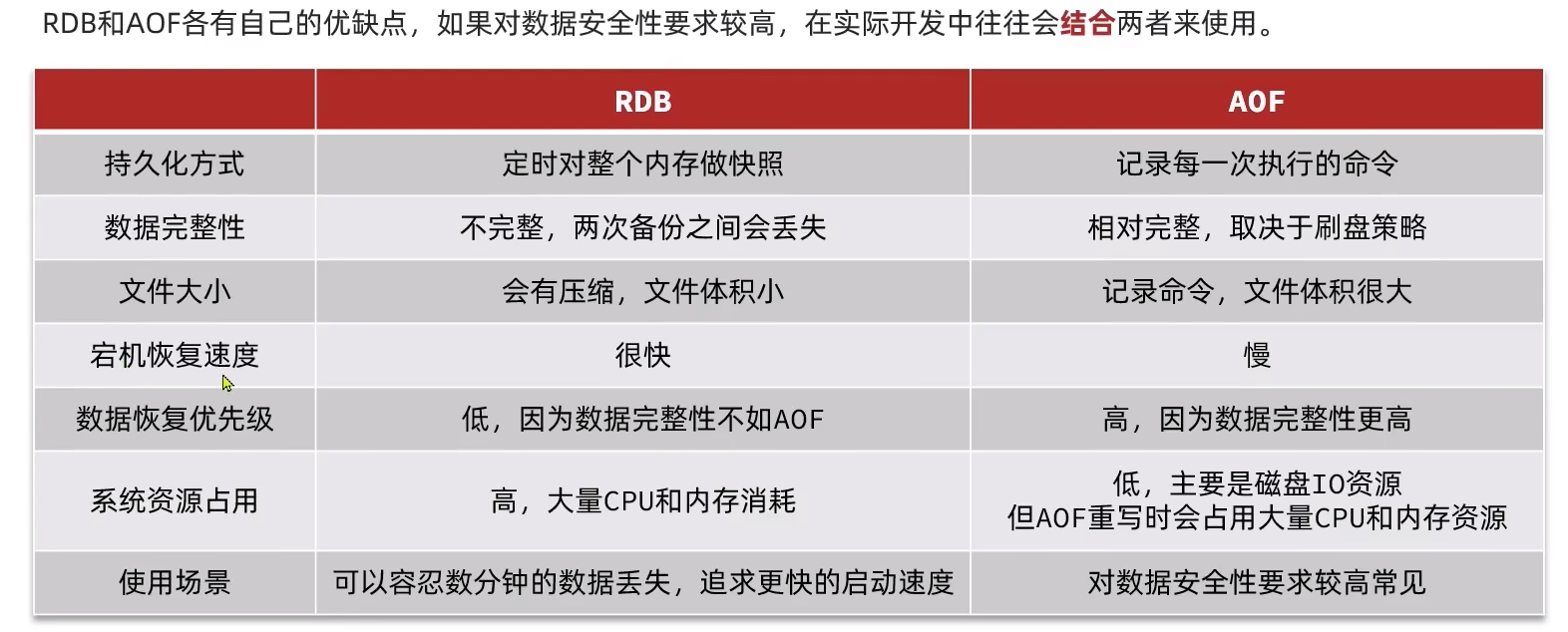
3.2 Redis主从
3.2.1 搭建主从集群
(转Redis集群.md)
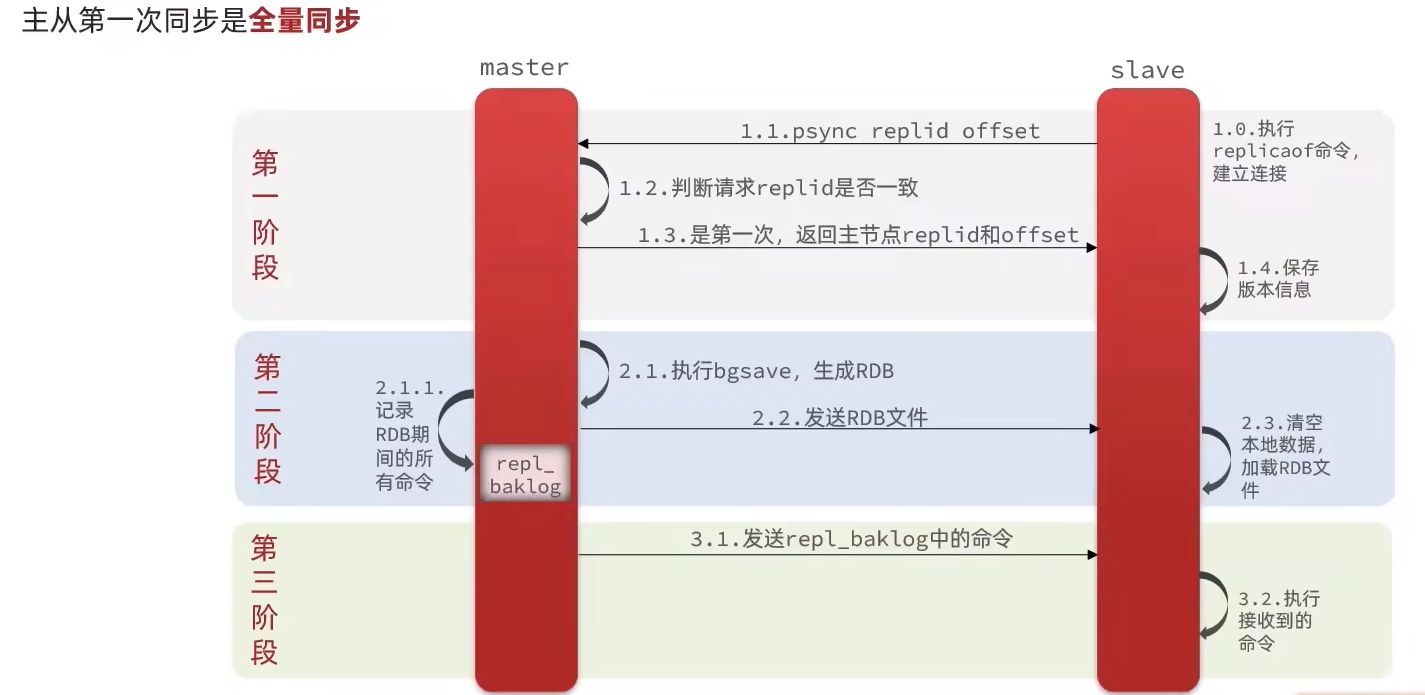
3.2.2 数据同步原理
- 全量同步
- id不同- > 生成RDB做全量同步
- id相同 -> 通过offset做增量同步

- 增量同步
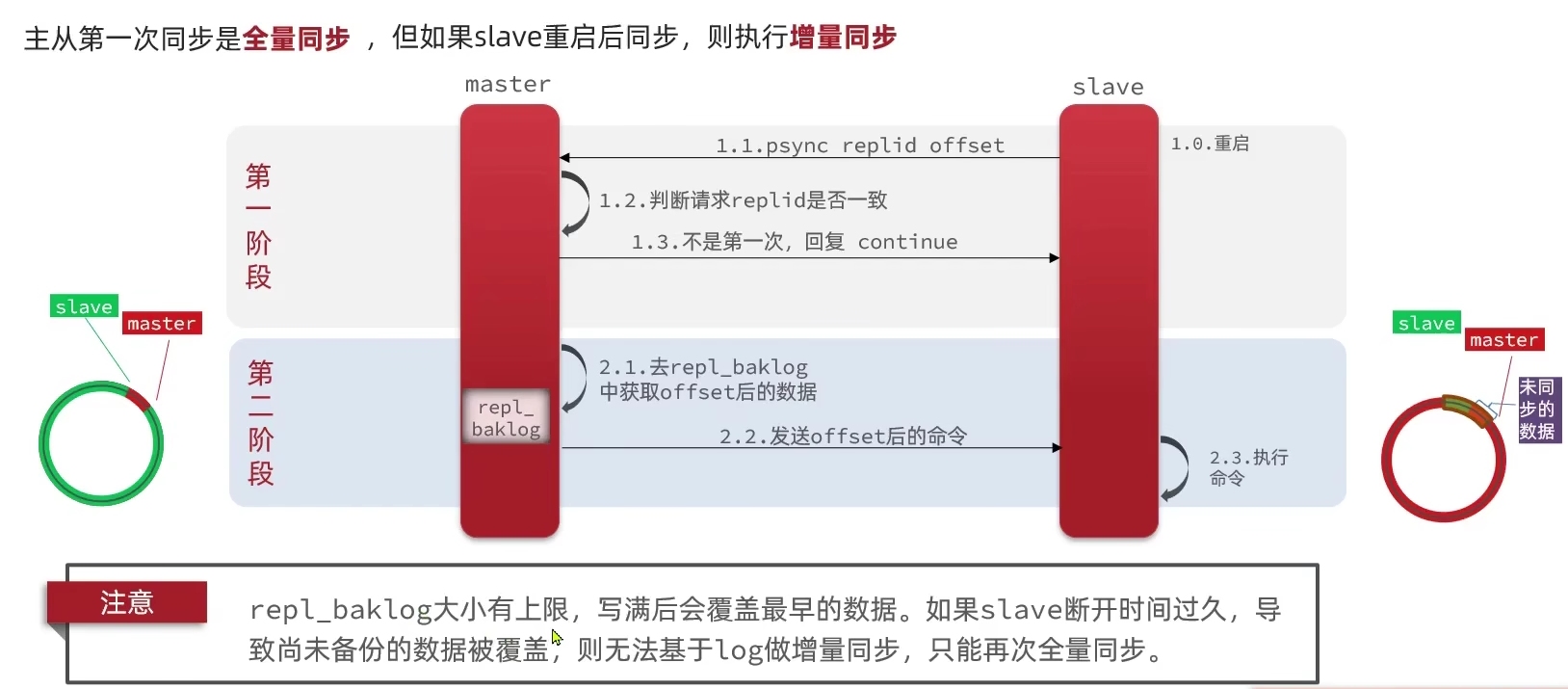
- 如何优化主从集群同步
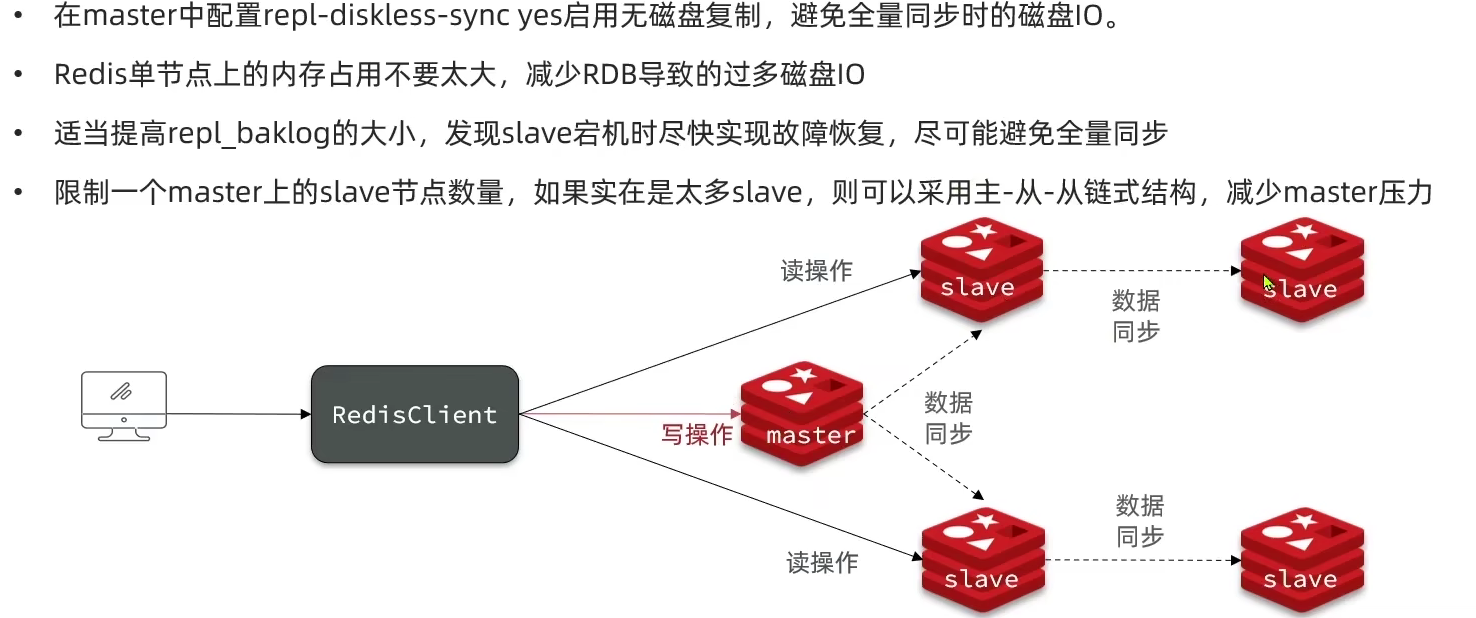
3.3 Redis哨兵
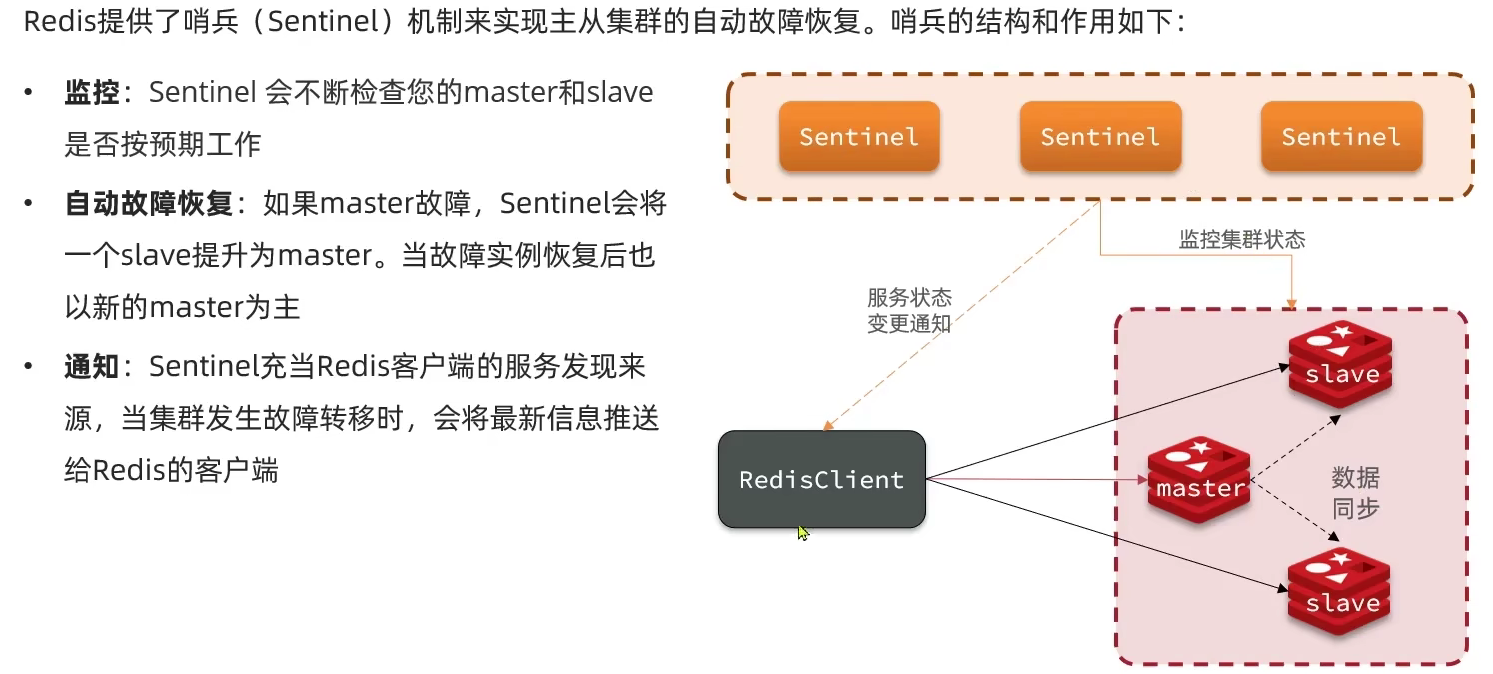
Sentinel监控原理
Sentinel基于心跳机制监测服务状态,每隔1秒向集群的每个实例发送ping命令
主观下线:如果某sentinel节点发现某实例未在规定时间响应,则认为该实例主观下线。
客观下线:若超过指定数量(quorum)的sentinel都认为该实例主观下线,则该实例客观下线。quorum值最好超过Sentinel实例数量的一半。
选择新的master

如何实现故障转移

3.3.1 搭建哨兵集群
(转Redis集群.md)
3.3.2 Redis客户端状态感知
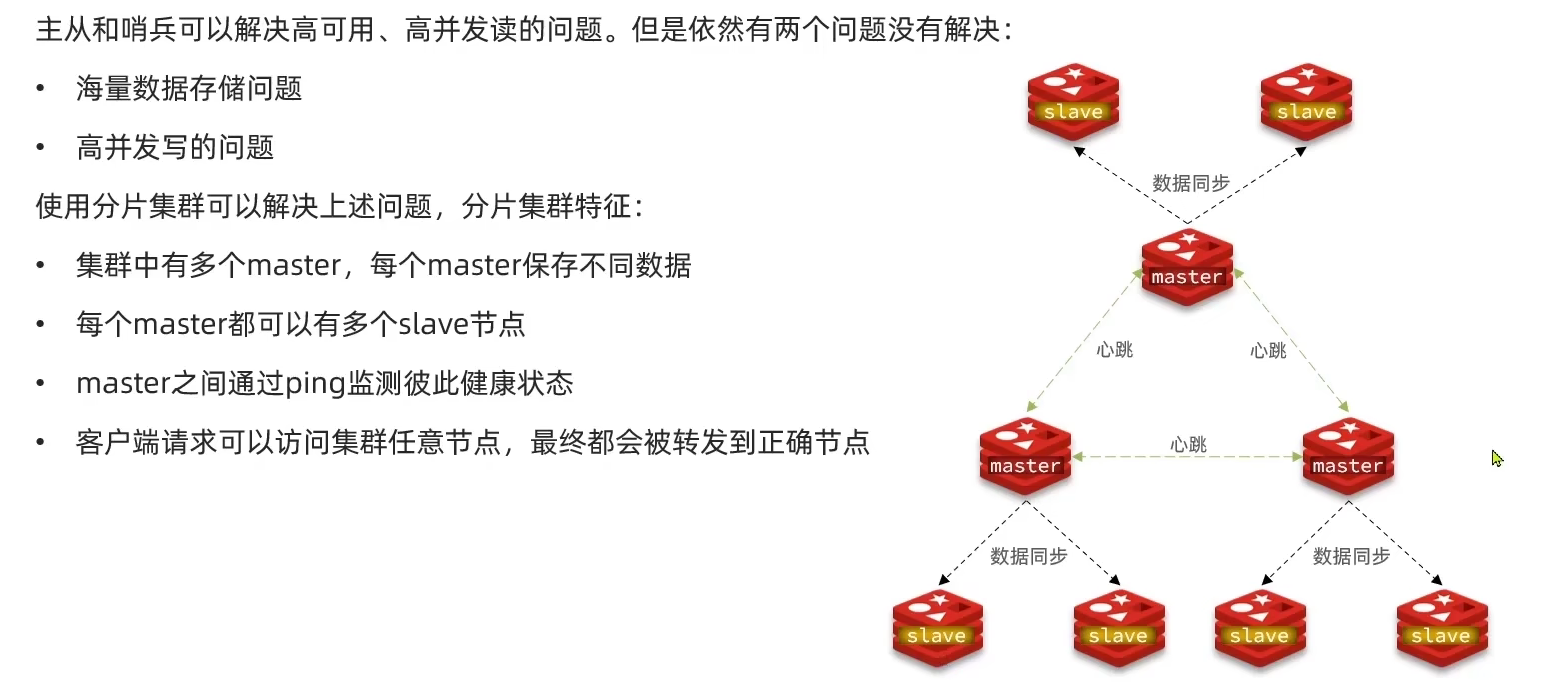
3.4 Redis分片集群
3.4.1 搭建分片集群
(转Redis集群.md)
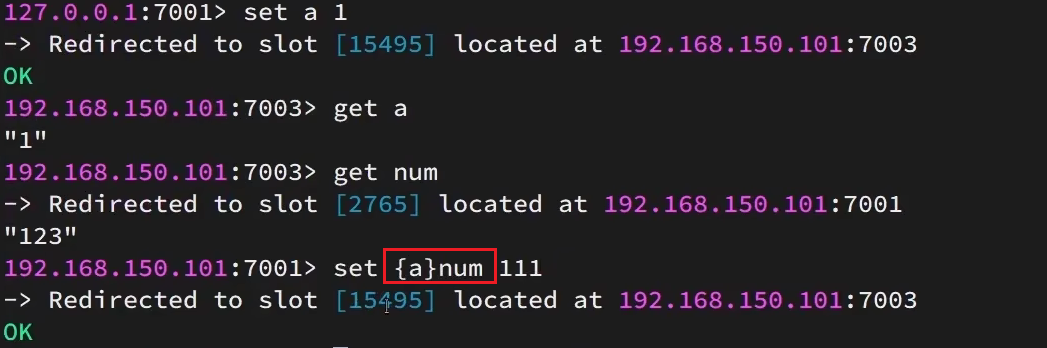
3.4.2 散列插槽
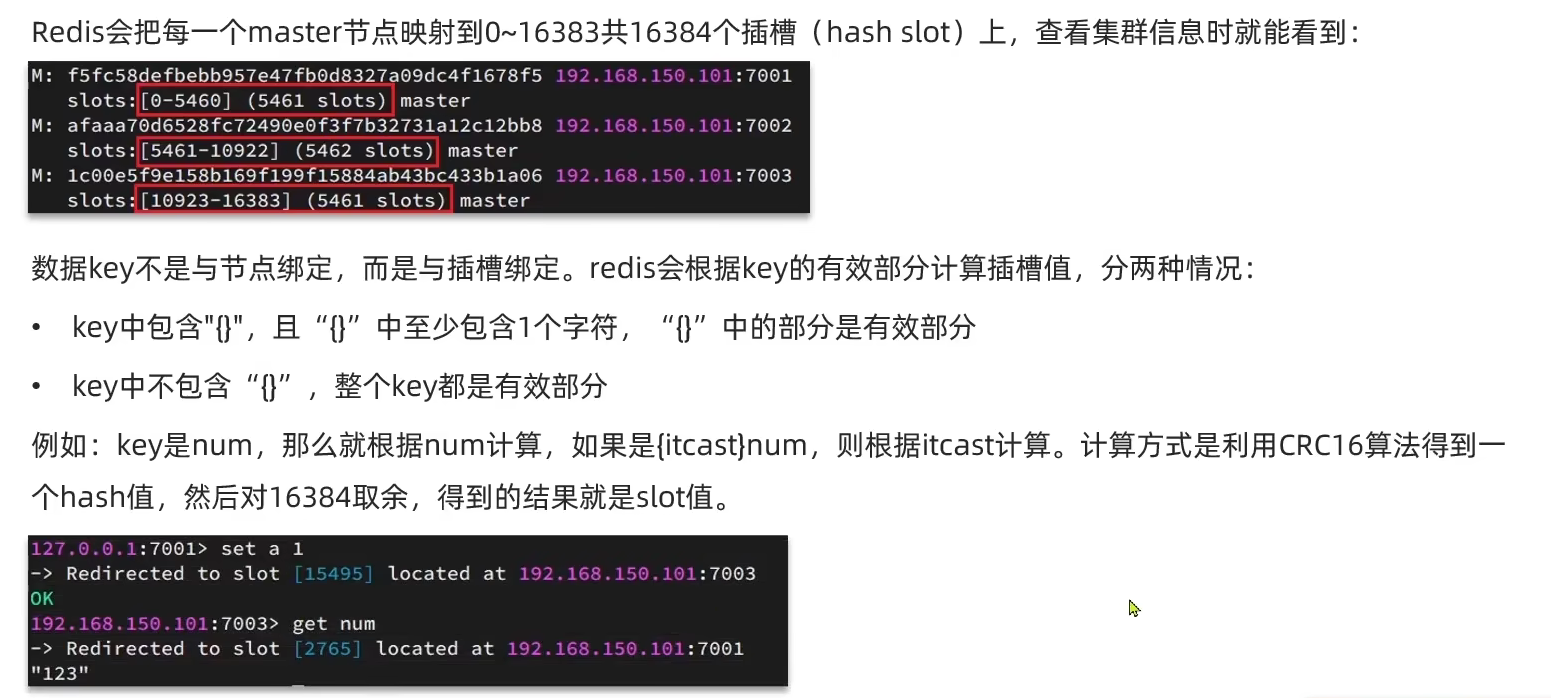
- 如何将同一类数据固定的保存在同一个Redis实例中
3.4.3 集群伸缩
- 创建新Redis,加入到集群中
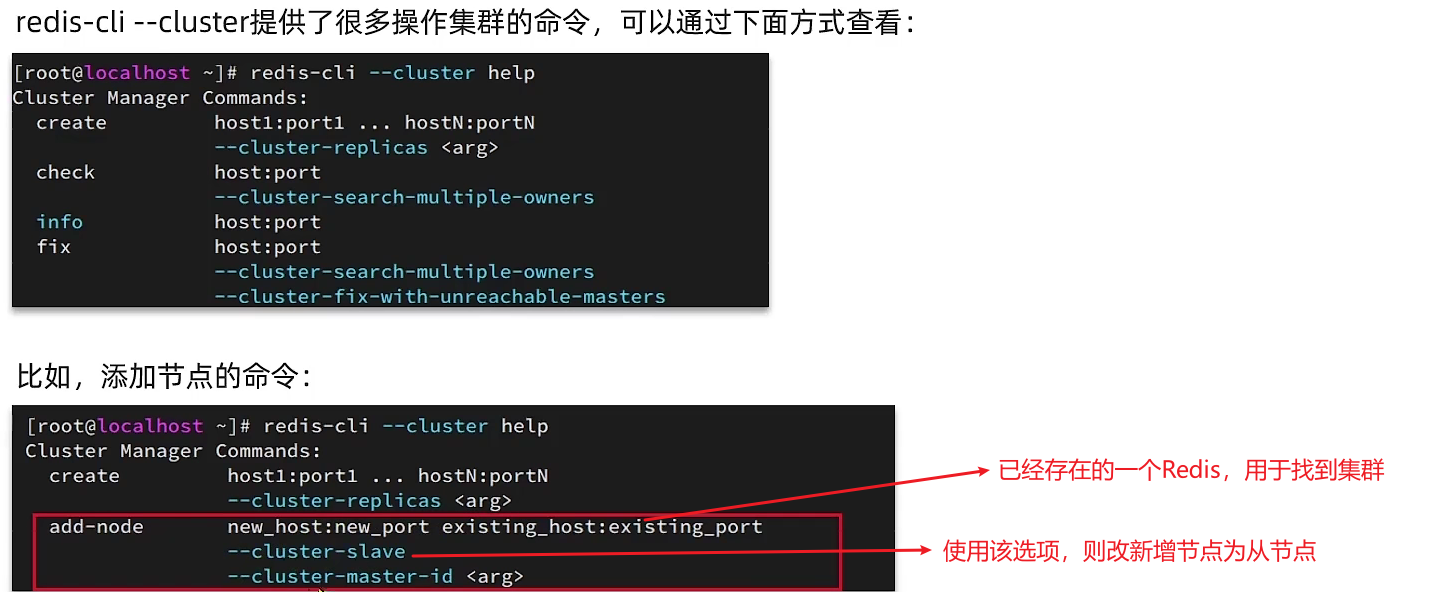
- 分配插槽
redis-cli --cluster reshard ip:port
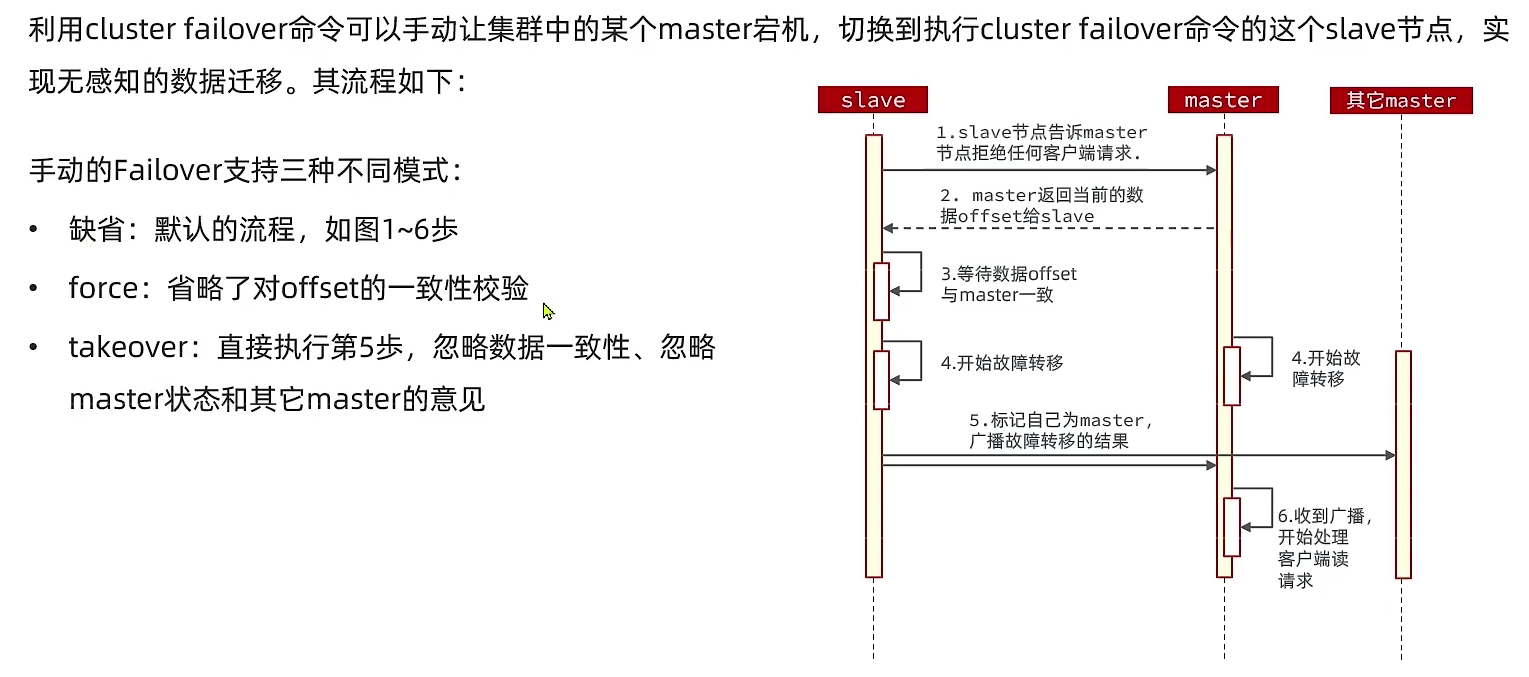
3.4.4 故障转移
- 自动转移
- 一个服务突然宕机,slave节点自动转移成master
- 手动转移
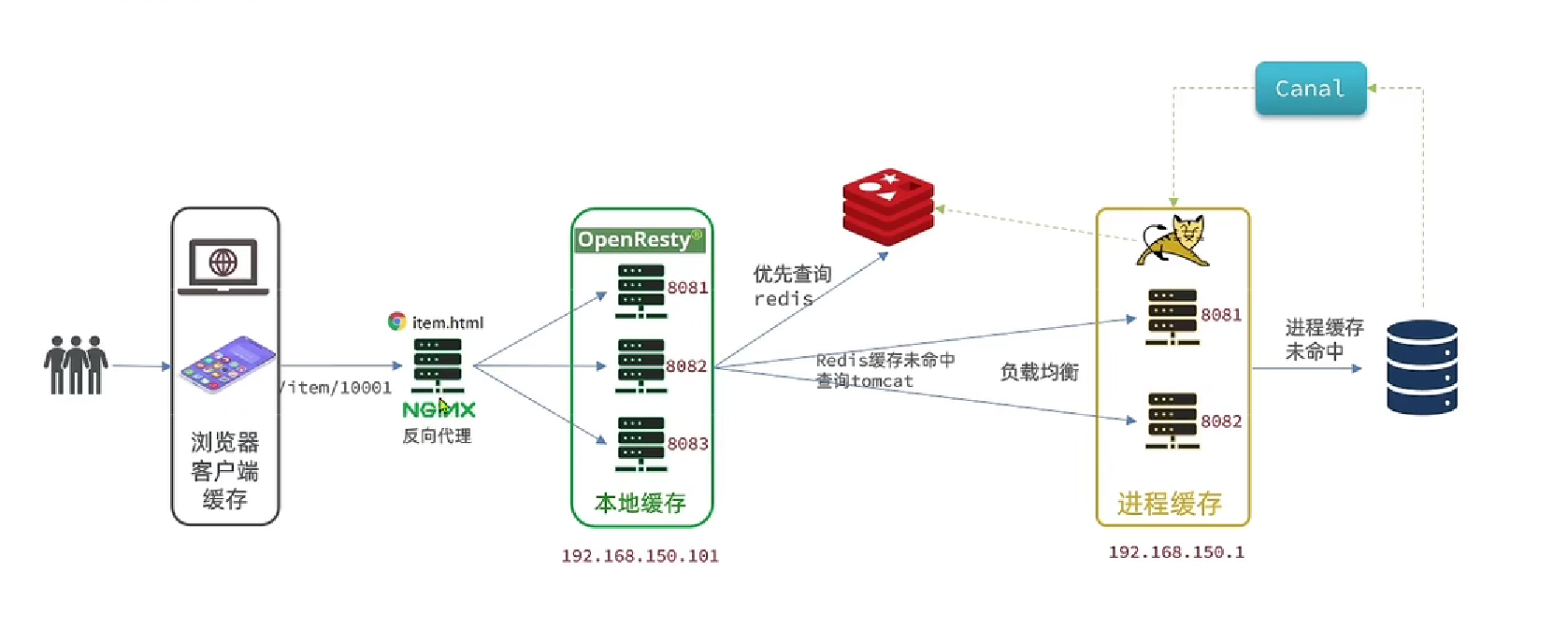
4 多级缓存

4.1 JVM进程缓存
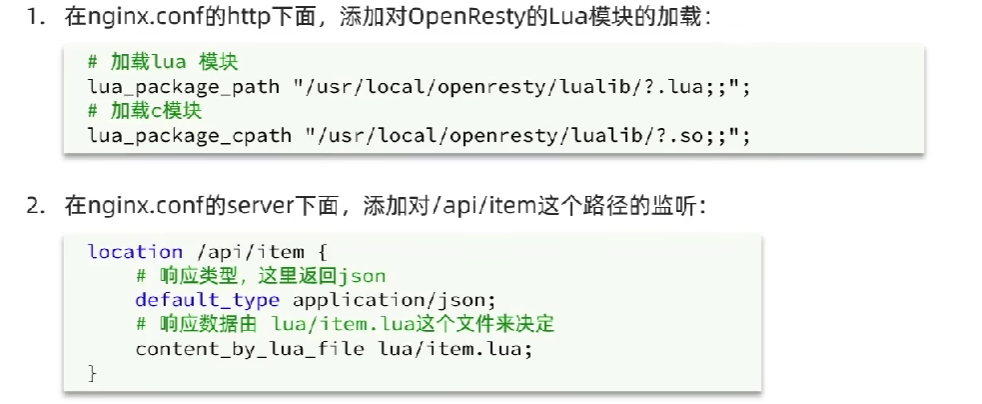
4.2 OpenResty


- 修改nginx.conf文件
- 编写item.lua文件

- 获取请求参数
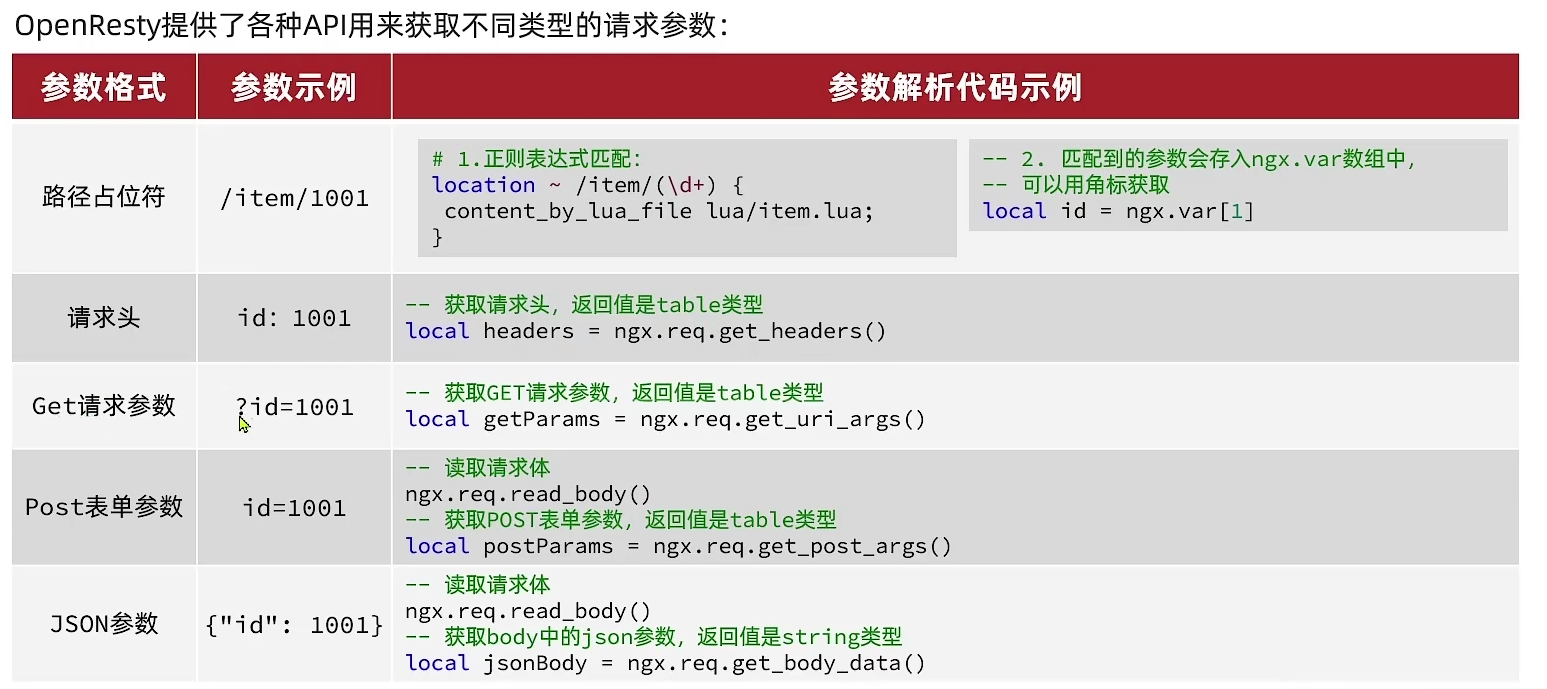
- 封装http请求,由OpenResty发送给后端
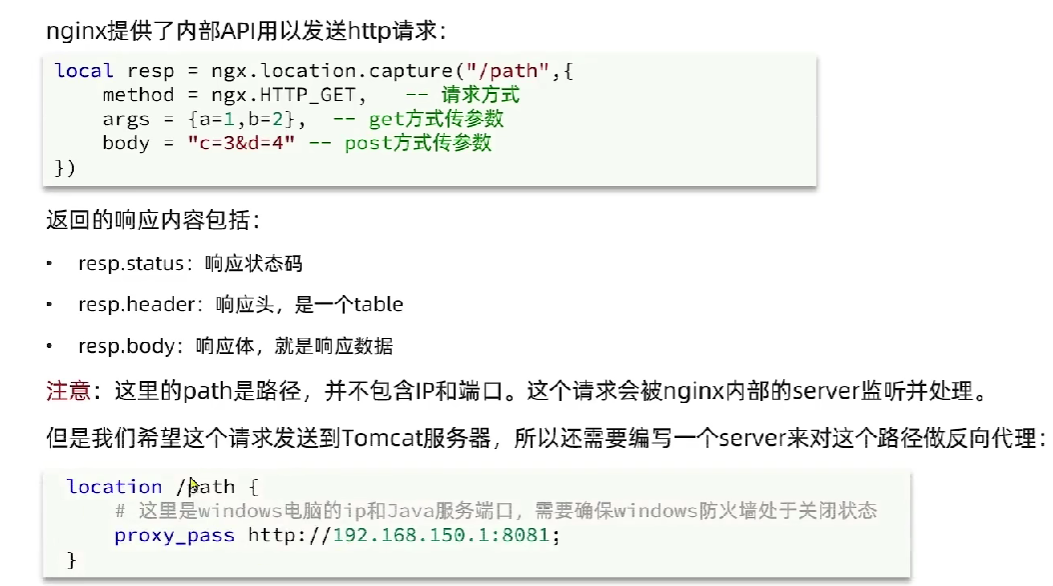
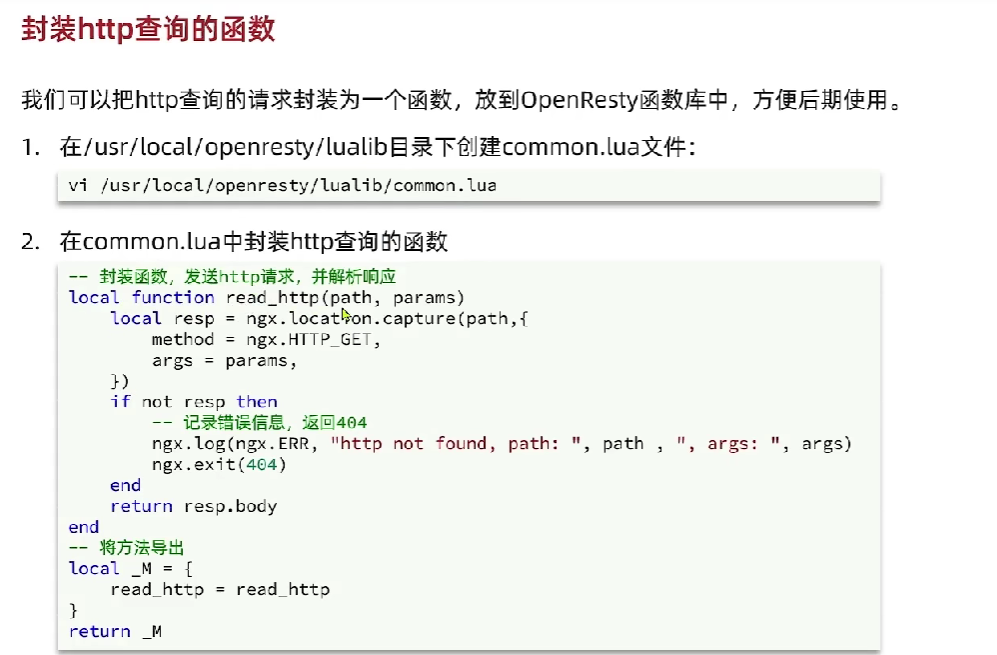
- 使用common.lua,通过item.lua发送请求到后端
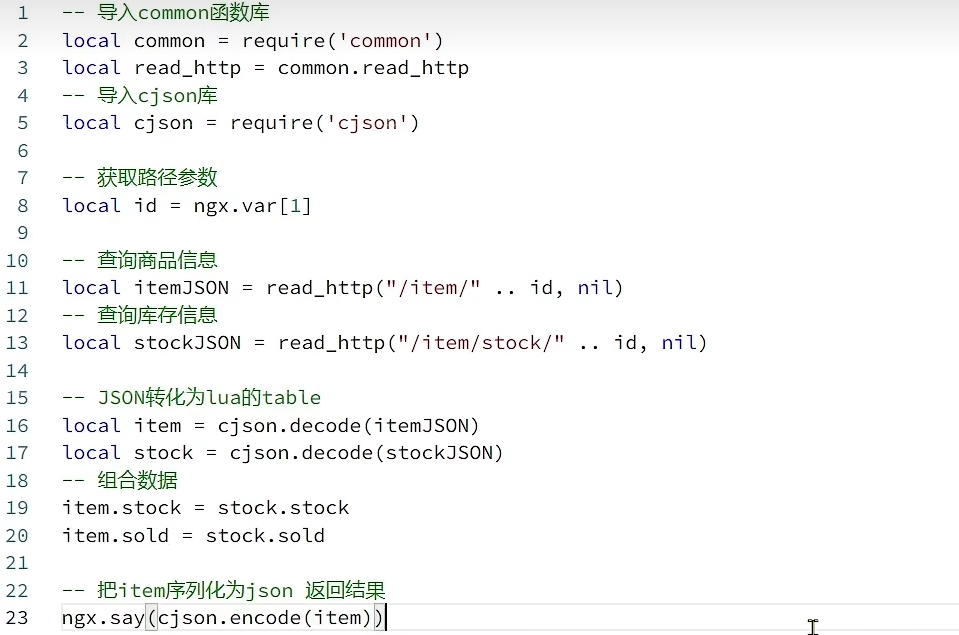
-
Redis预热
-
OpenResty访问Redis缓存

- nginx本地缓存
4.3 缓存同步


4.3.1 Canel
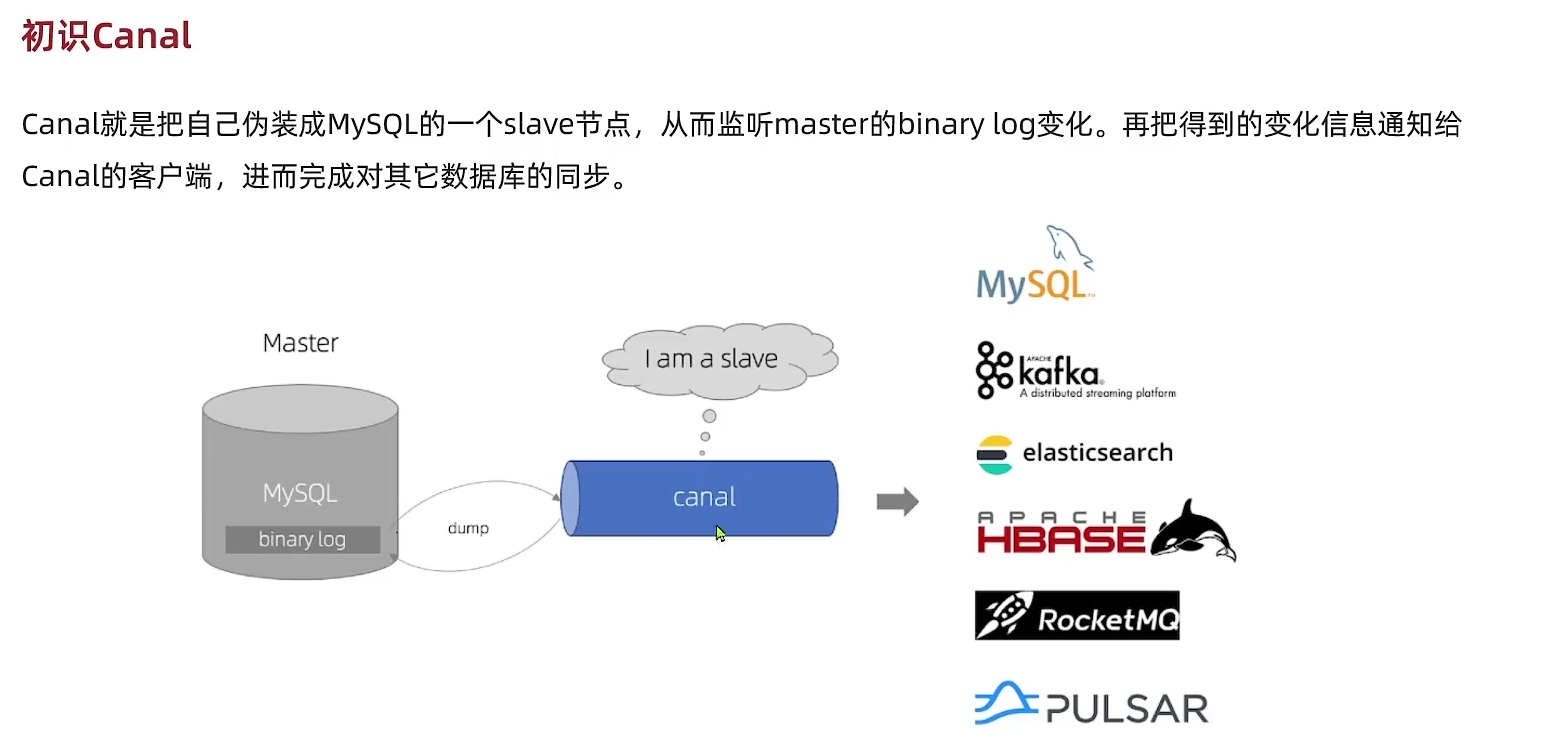
5 Redis实践优化
5.1 key的设计

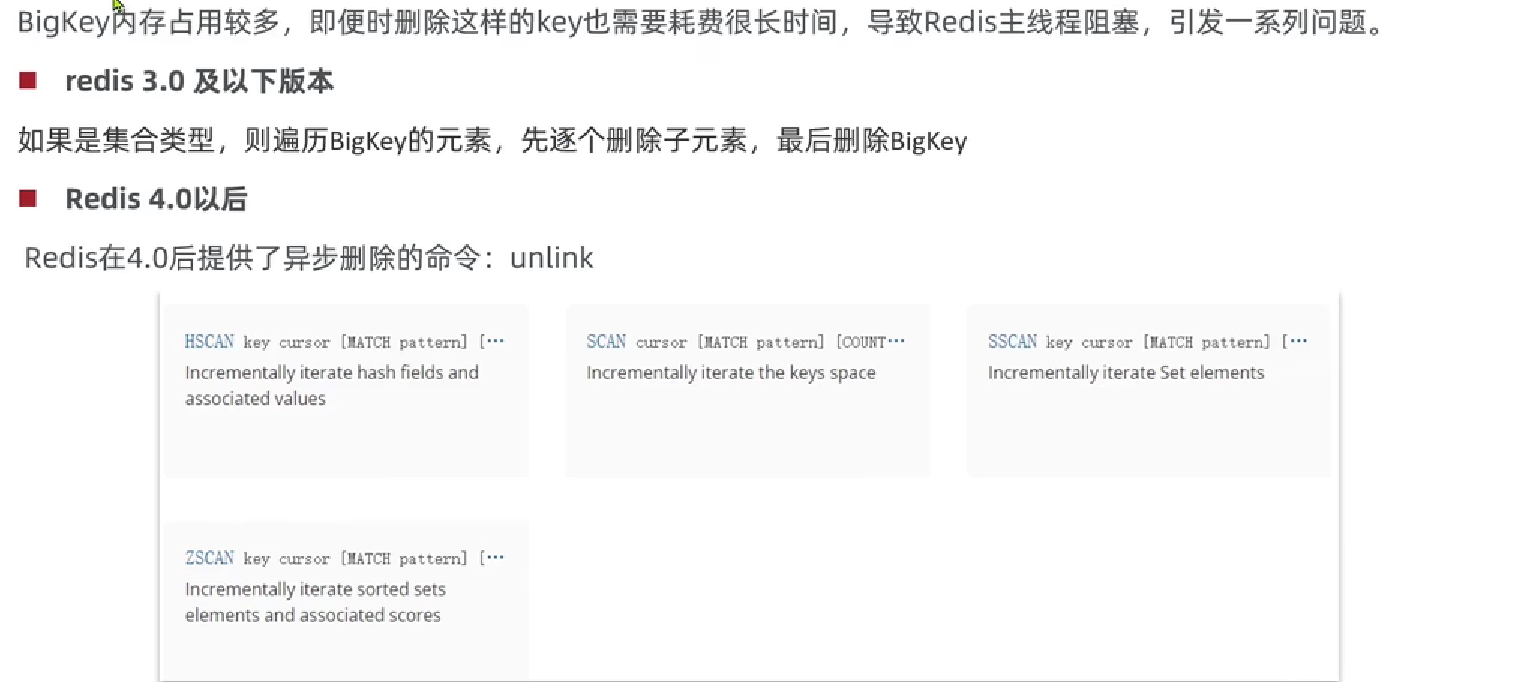
- 什么是Big Key
单个key的value小于10KB
对于集合类型的key,建议元素数量小于1000
- Big Key的危害

- 删除Big Key
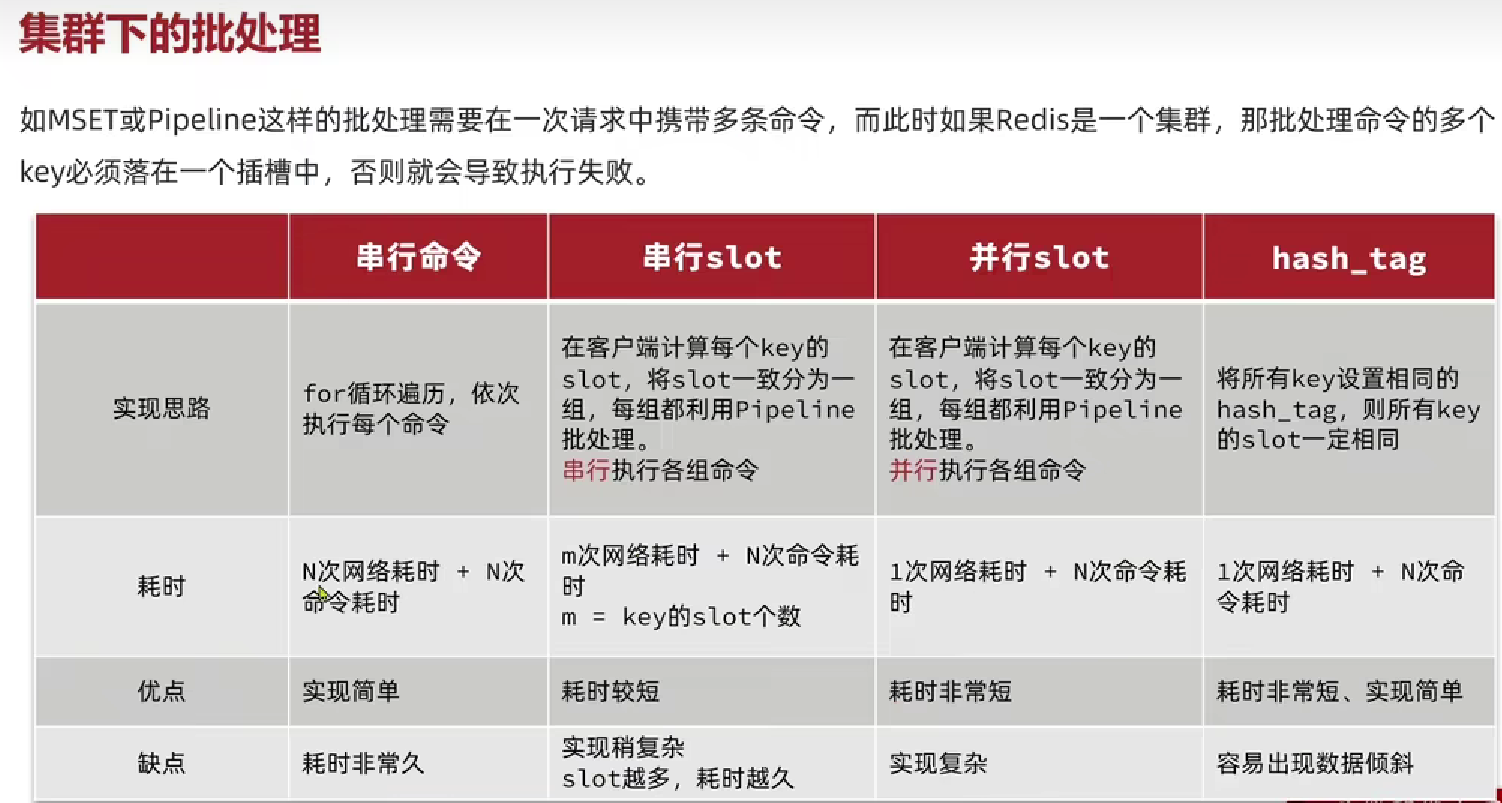
5.2 批处理优化
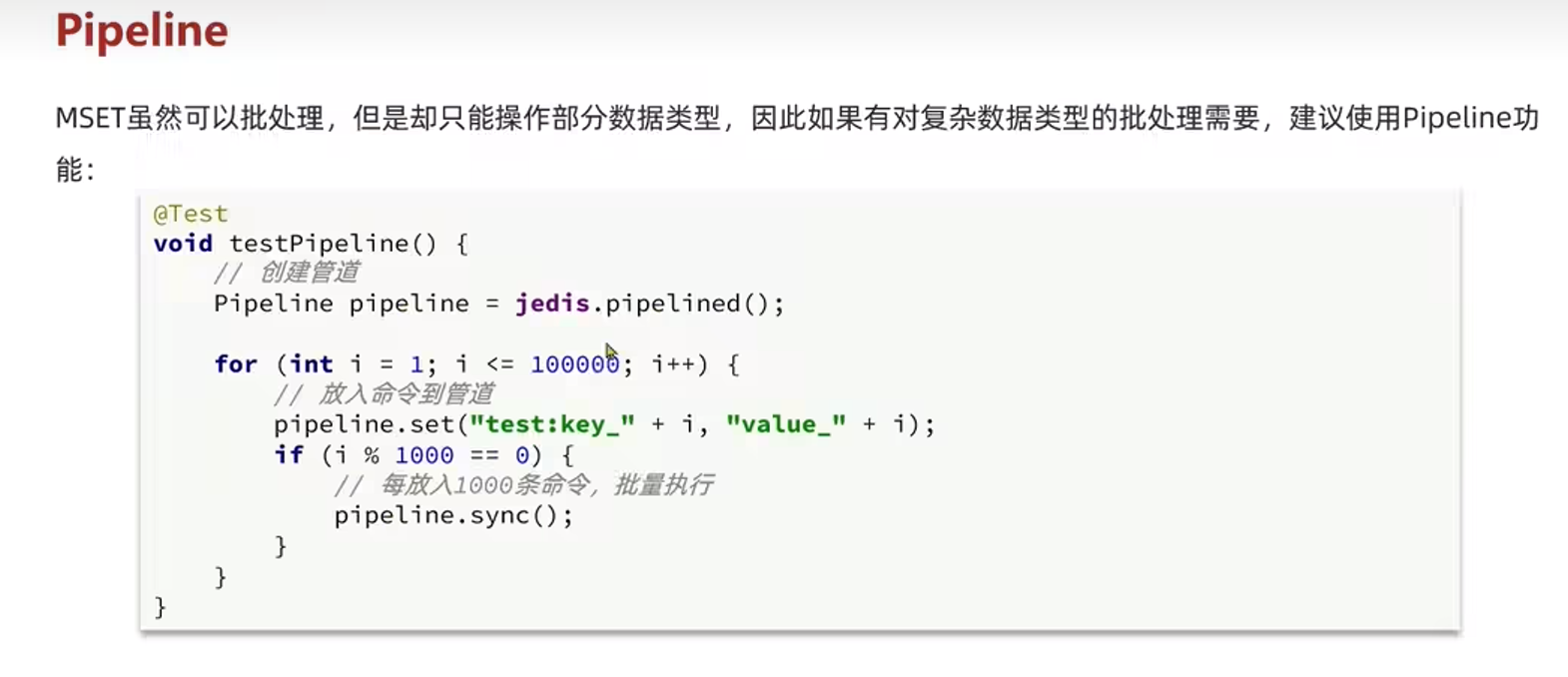
- 批处理一次性执行太多任务会阻塞网络
- 原生的M操作
- Pipeline
- pipeline的多个命令不具有原子性
5.2.1 集群模式下的批处理
5.3 服务端优化
5.3.1 持久化配置

5.3.2 慢查询
- 该配置重启会恢复,要用就配置可以修改配置文件
- 其他命令

5.3.3 服务器安全配置

- 安全配置
- Redis一定要设置密码
- 禁止线上使用下面命令: keys、flushall、flushdb、config set等命令。可以利用rename-command禁用。(在redis.conf文件下设置
rename-command keys xxx123xxxdfsda) - bind:限制网卡,禁止外网网卡访问禁止线上使用下面命令(在redis.conf文件下设置)
- 开启防火墙开启防火墙
- 不要使用Root账户启动Redis
- 尽量不要使用默认端口
5.3.4 内存配置

- 查看内存使用情况的命令:
memory xxxinfo memory

- 两个查看客户端链接信息的命令
info clientclient list
5.3.5 集群相关问题
- 集群的完整性问题

- 集群的带宽问题

- 集群带来的其他问题

6 Redis底层原理
6.1 底层数据结构
6.1.1 SDS动态数组


6.1.2 Intset

- intset升级

- 优点
- Redis会确保Intset中的元素唯一、有序
- 具备类型升级机制,可以节省内存空间
- 底层采用二分查找方式来查询
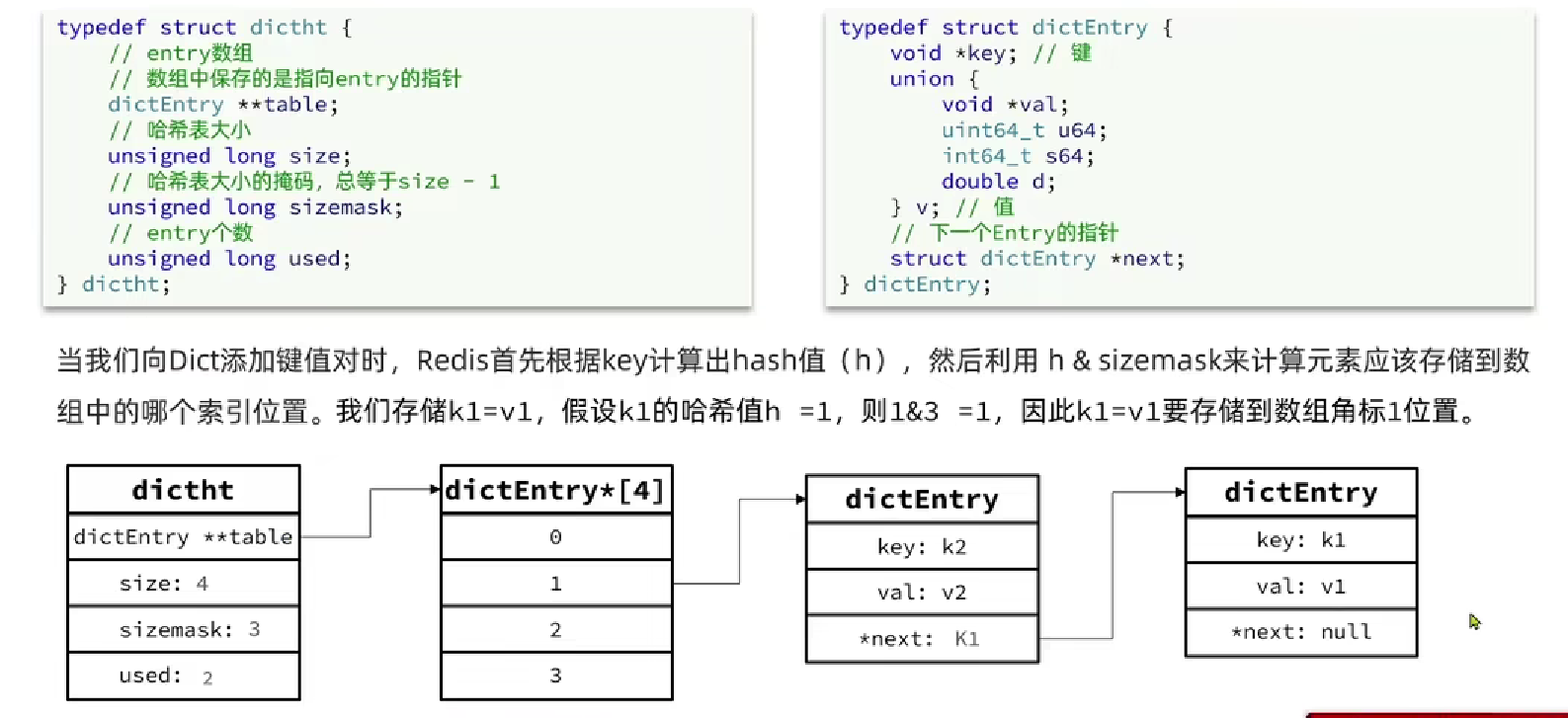
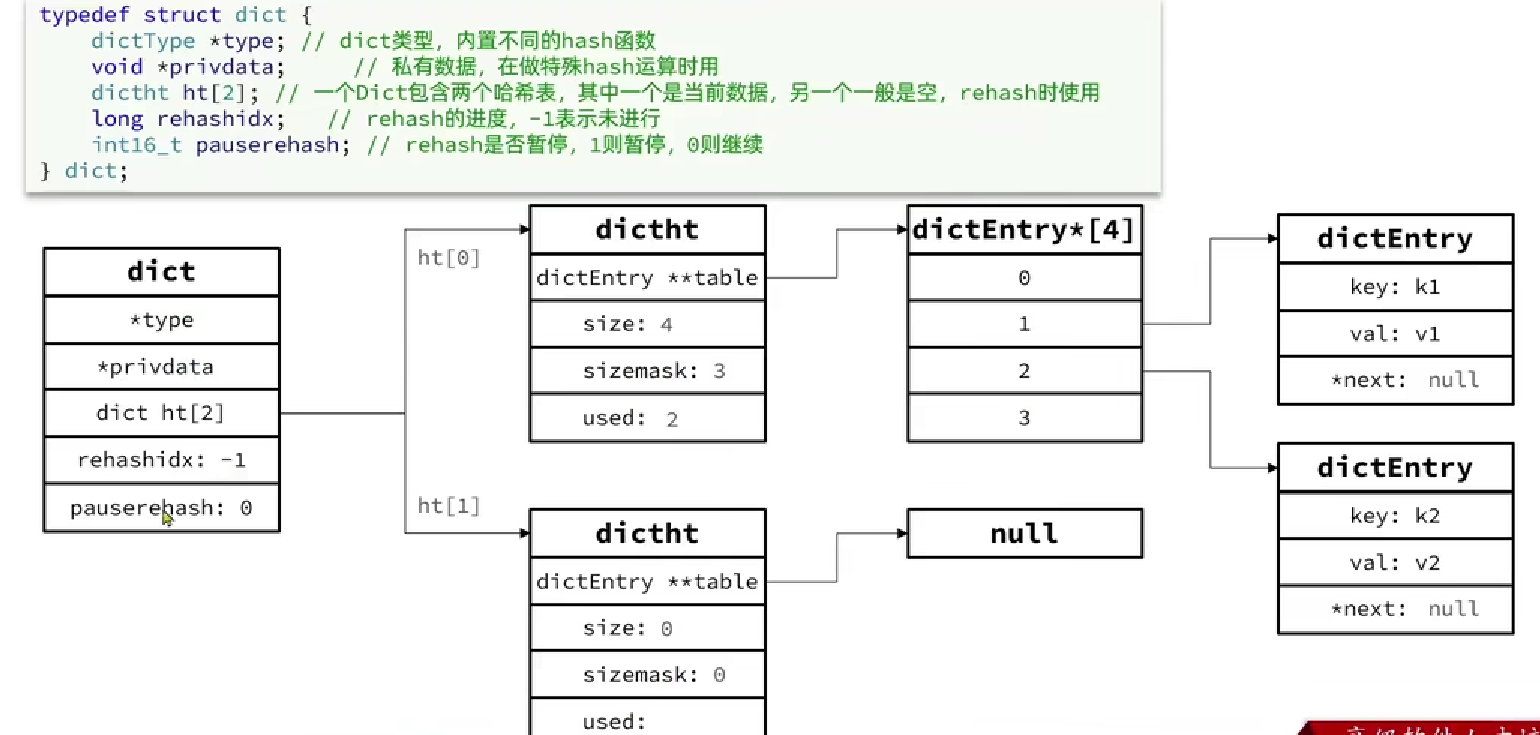
6.1.3 Dict
- Dict由三部分组成:
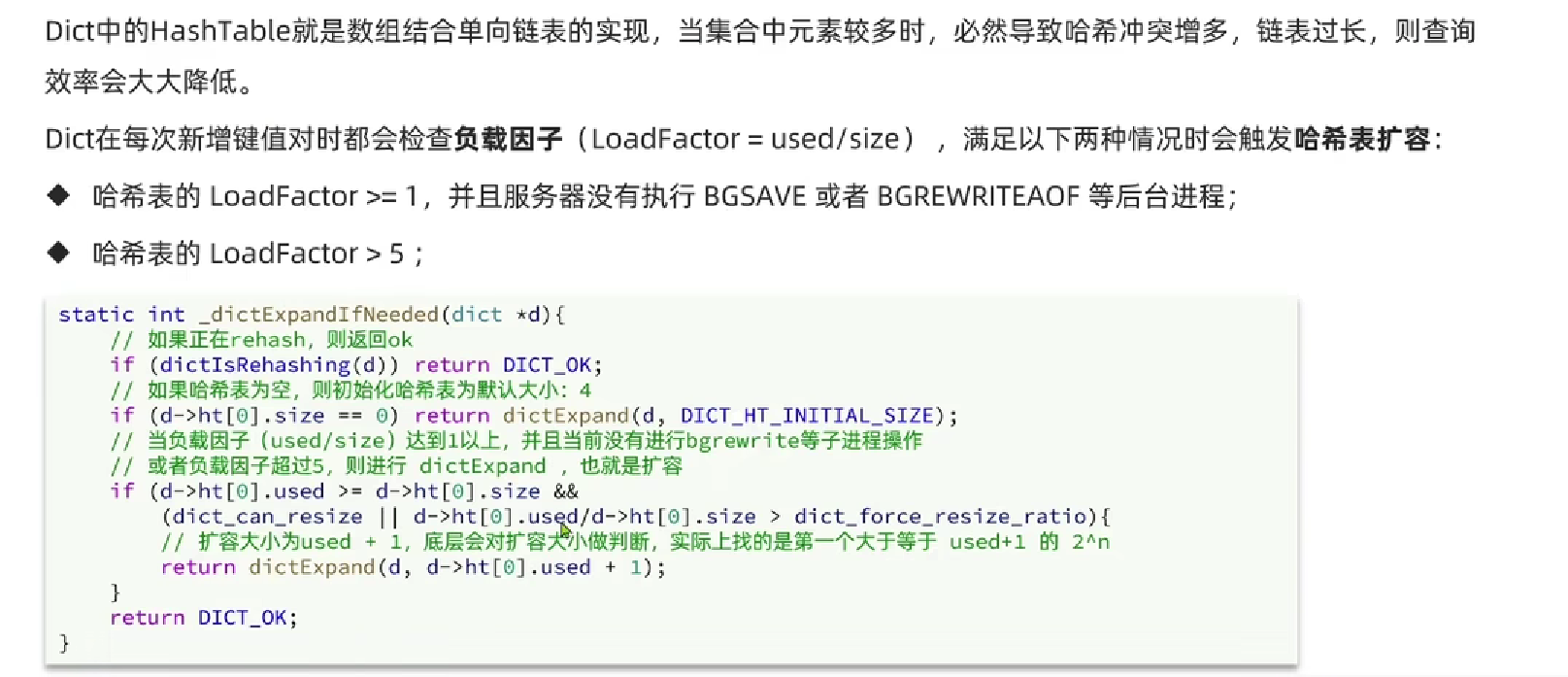
- Dict的扩容机制
- 渐进式rehash

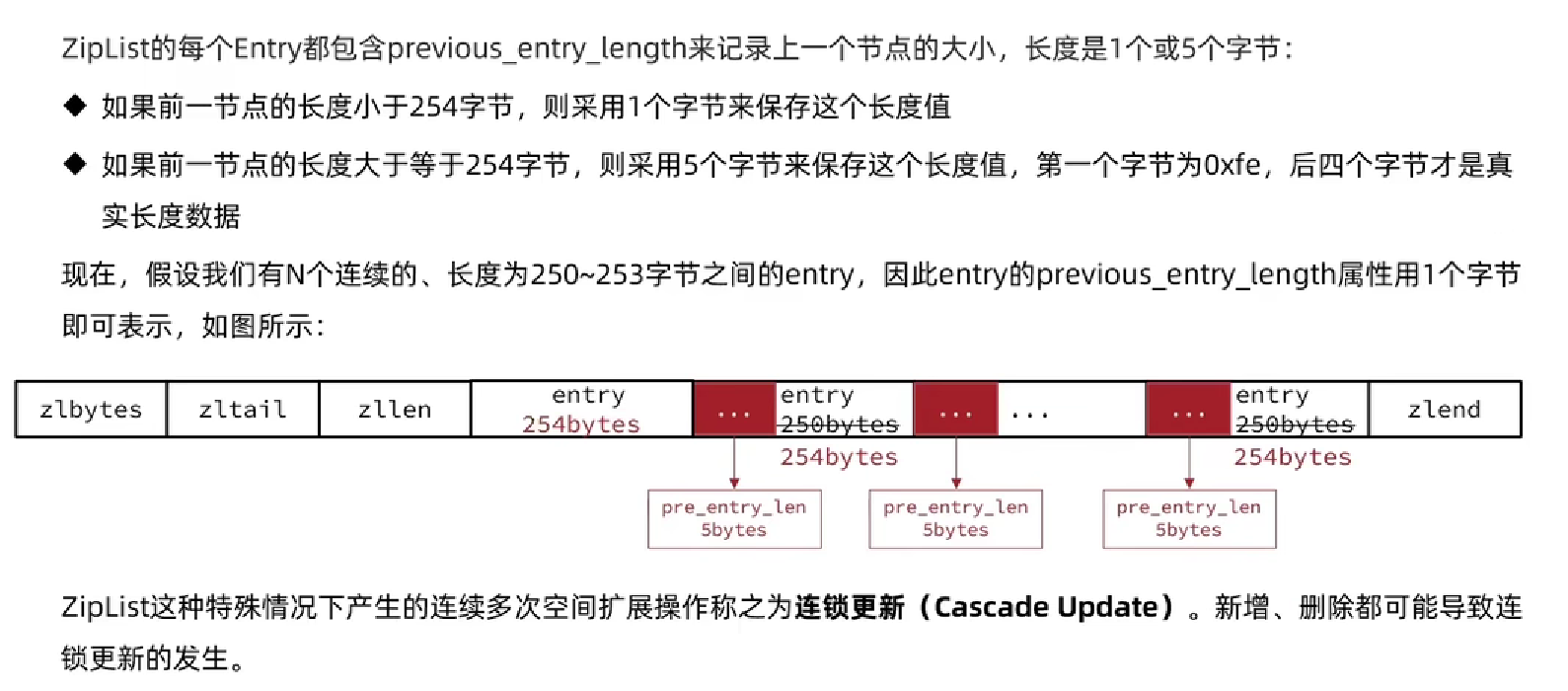
6.1.4 ZipList


-
encoding编码(小端)
-
字符串类型编码(00、01、10开头)
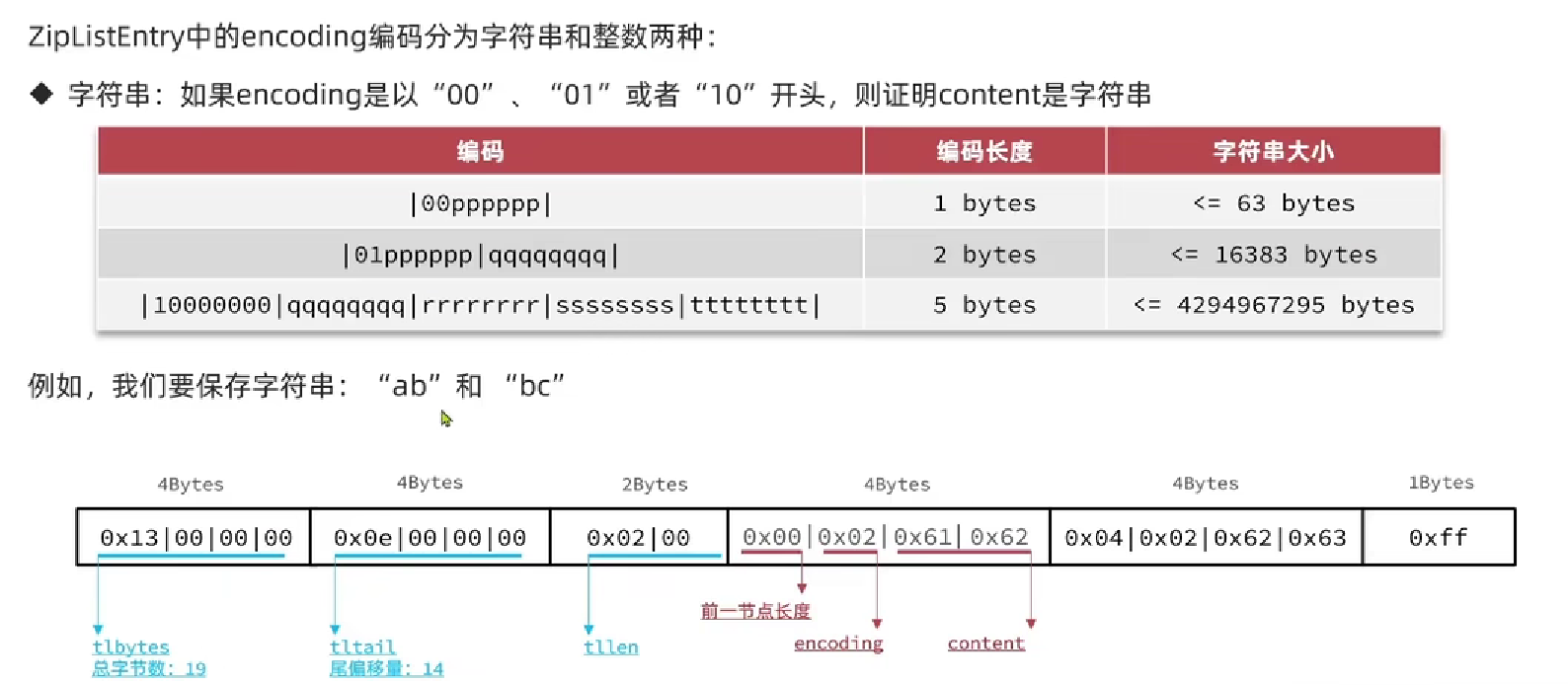
-
整数类型编码

-
-
连锁更新问题
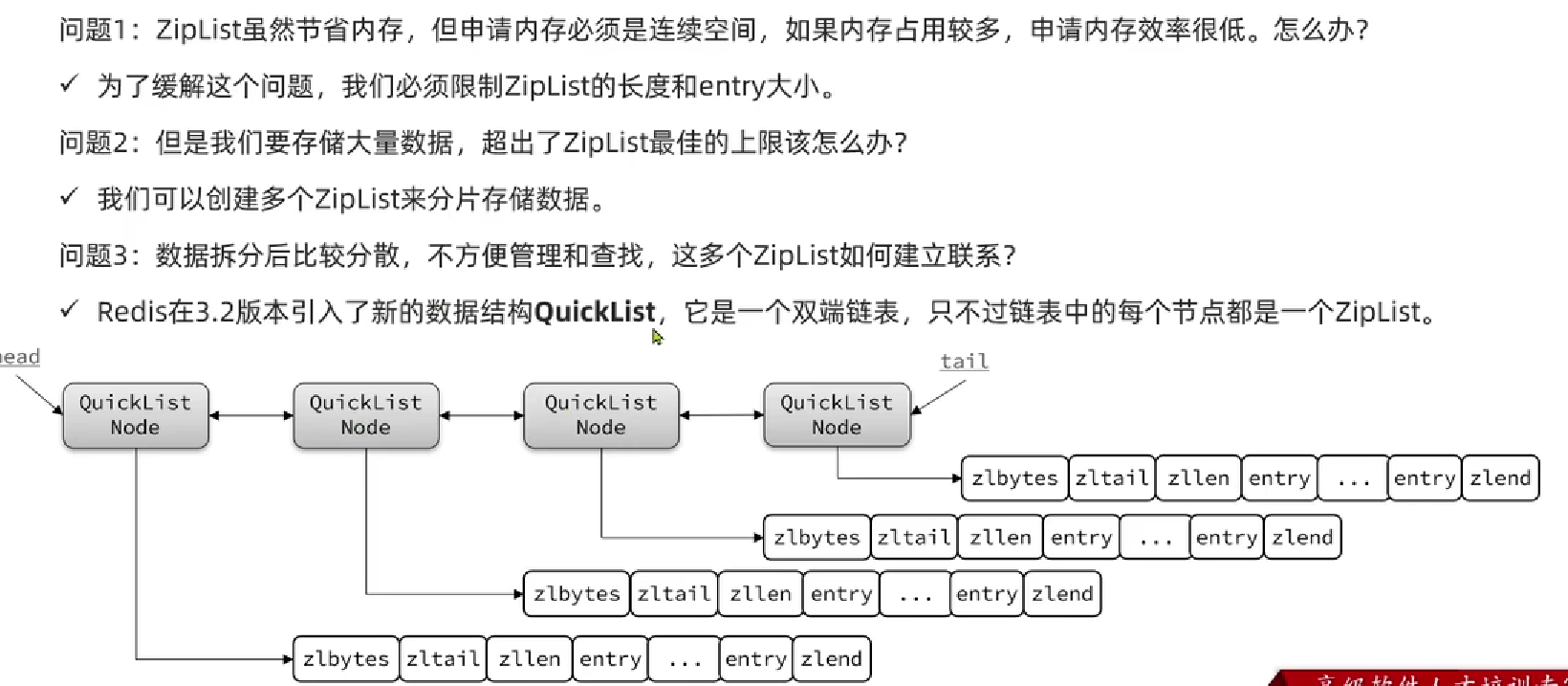
6.1.5 QuickList
-
QuickList = LinkList + ZipList
-
QuickList:限制ZipList的大小,解决内存分配的效率问题
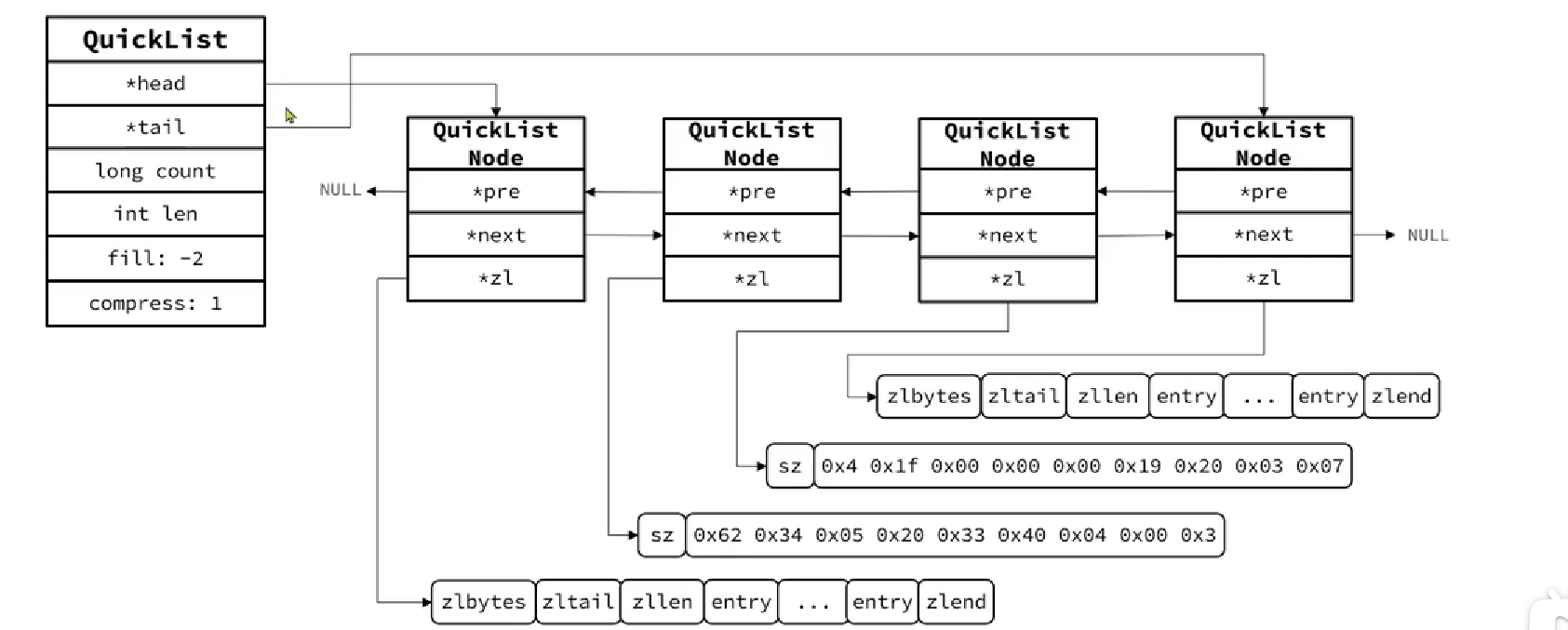
- 如何限制ZipList大小

- QuickList节点压缩


6.1.5 SkipList

- 底层结构


6.1.6 RedisObject

- 11种编码格式
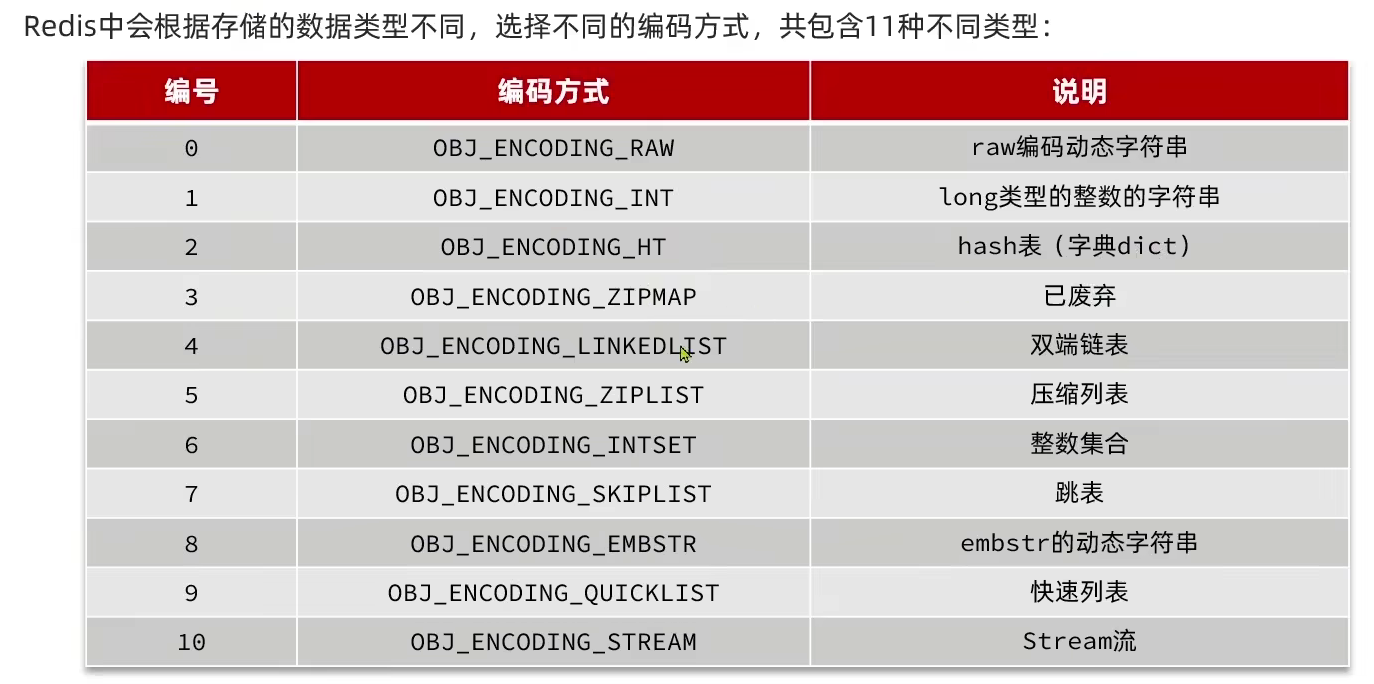
- 数据类型对应的编码格式

6.2 五种数据结构
6.2.1 String
raw:其基本编码方式是RAW,基于简单动态字符串(SDS)实现,存储上限为512mb。embstr:如果存储的SDS长度小于44字节,则会采用EMBSTR编码,此时object head与SDS是一段连续空间。申请内存时只需要调用一次内存分配函数,效率更高。int:如果存储的字符串是整数值,并且大小在LONG_MAX范围内,则会采用INT编码:直接将数据保存在RedisObject的ptr指针位置(刚好8字节),不再需要SDS了。
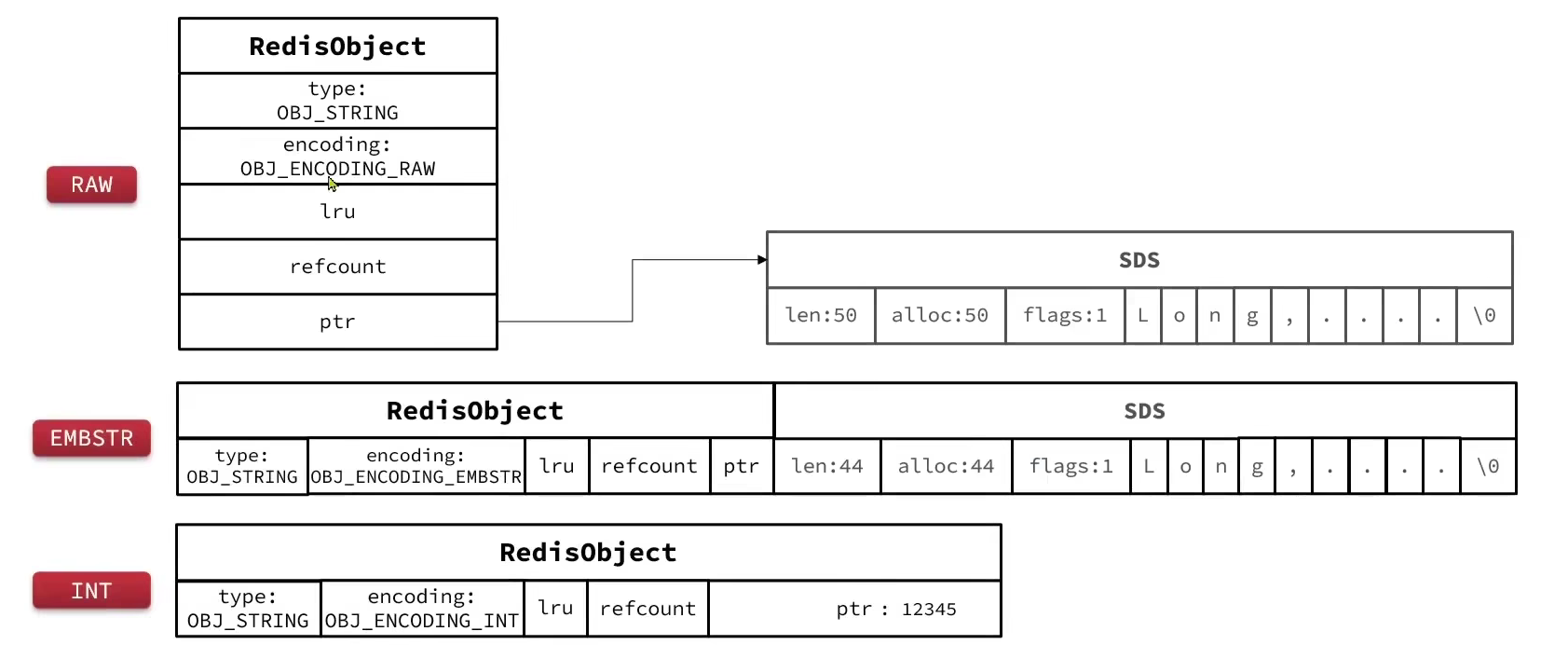
6.2.2 List

6.2.3 Set
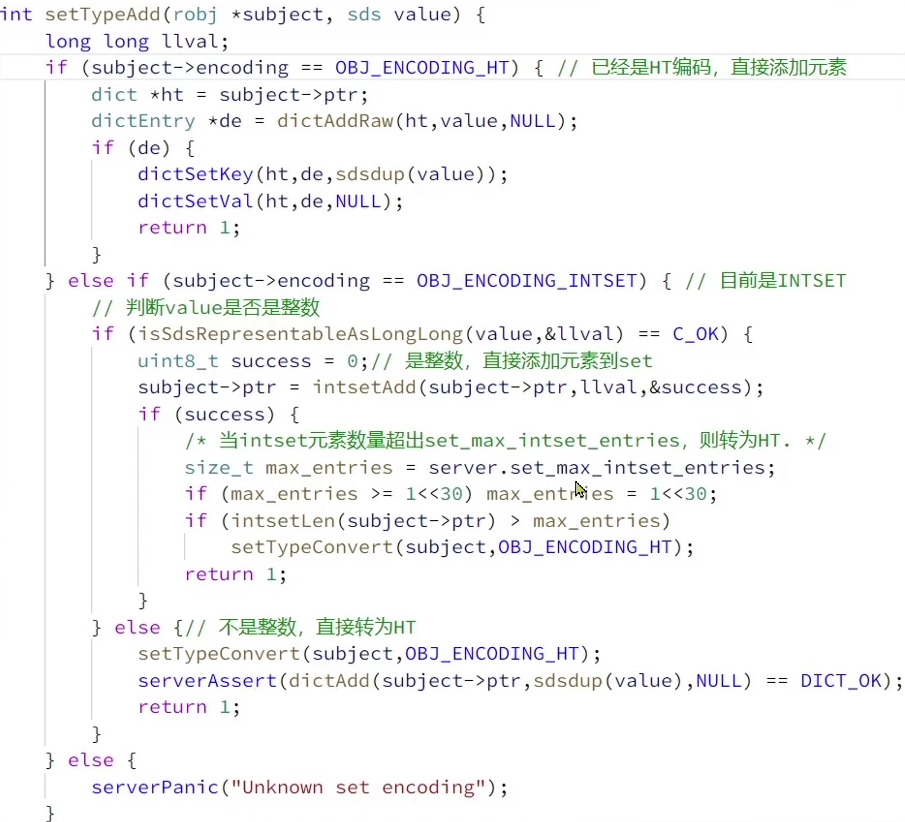
Set是Redis中的集合,不一定确保元素有序,可以满足元素唯一、查询效率要求极高。
-
Dict:为了查询效率和唯一性,set采用HT编码(Dict)。Dict中的key用来存储元素, value统一为null。 -
IIntSet:当存储的所有数据都是整数,并且元素数量不超过set-max-intset-entries时,Set会采用IntSet编码,以节省内存。
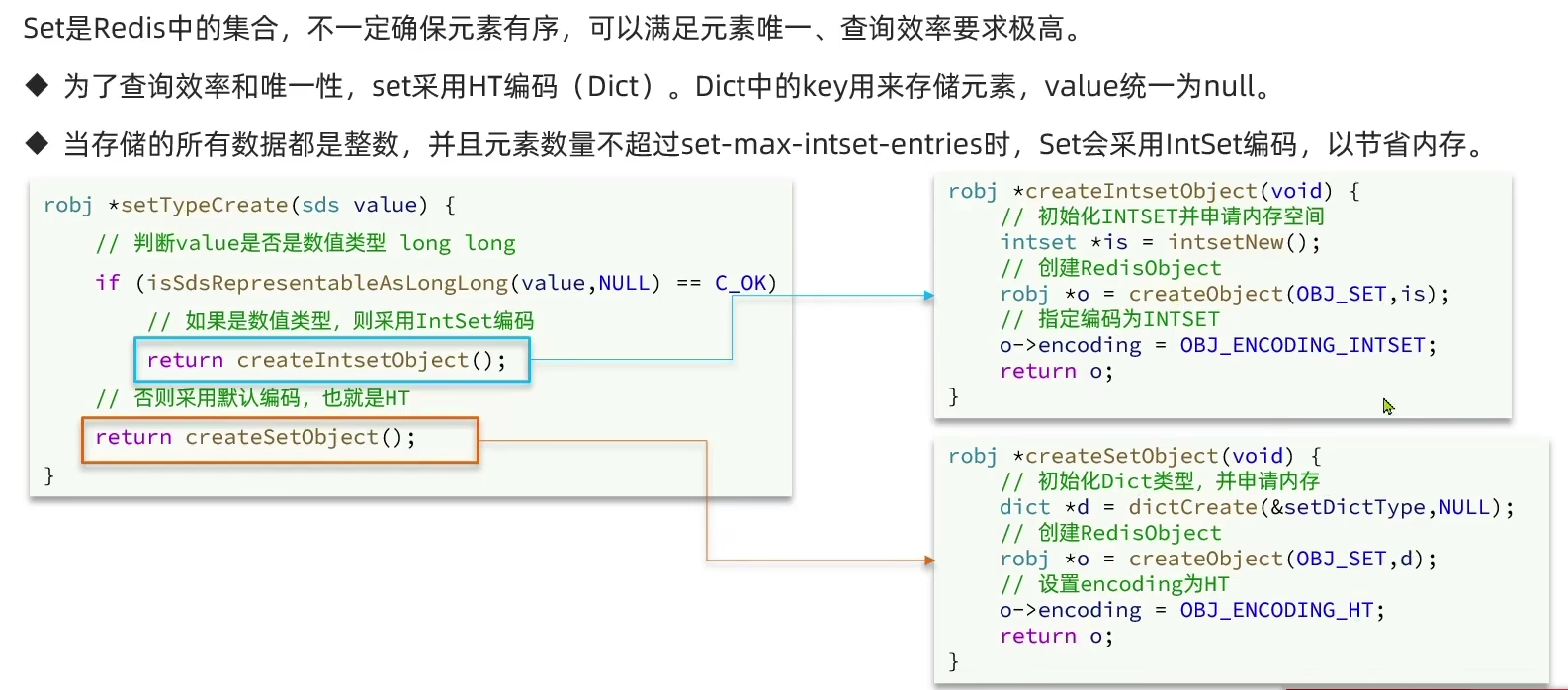
- 插入时类型转换
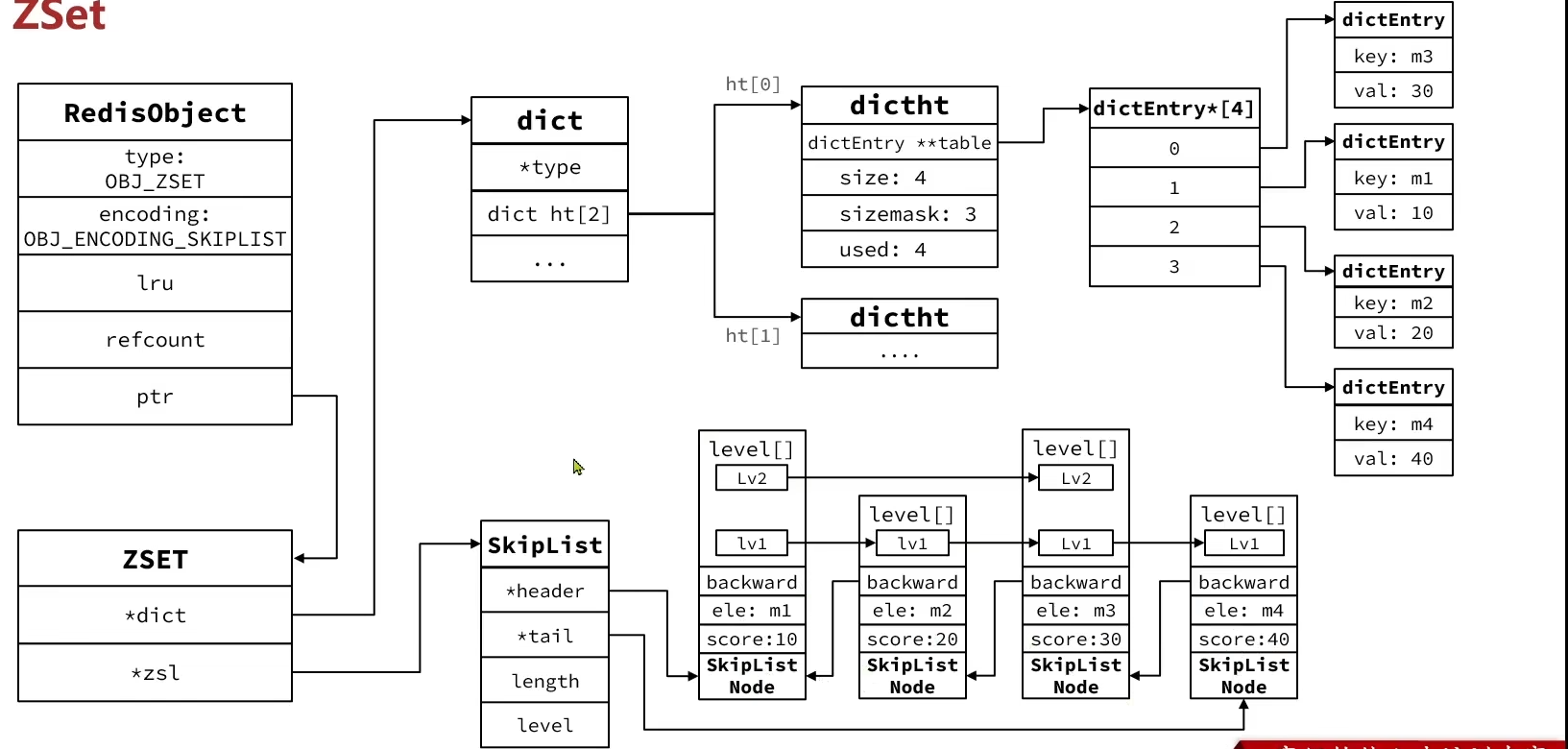
6.2.4 ZSet
zset底层数据结构必须满足键值存储、键必须唯一、可排序这几个需求
- SkipList:可以排序,并且可以同时存储score和ele值( member)
- HT ( Dict):可以键值存储,并且可以根据key找value
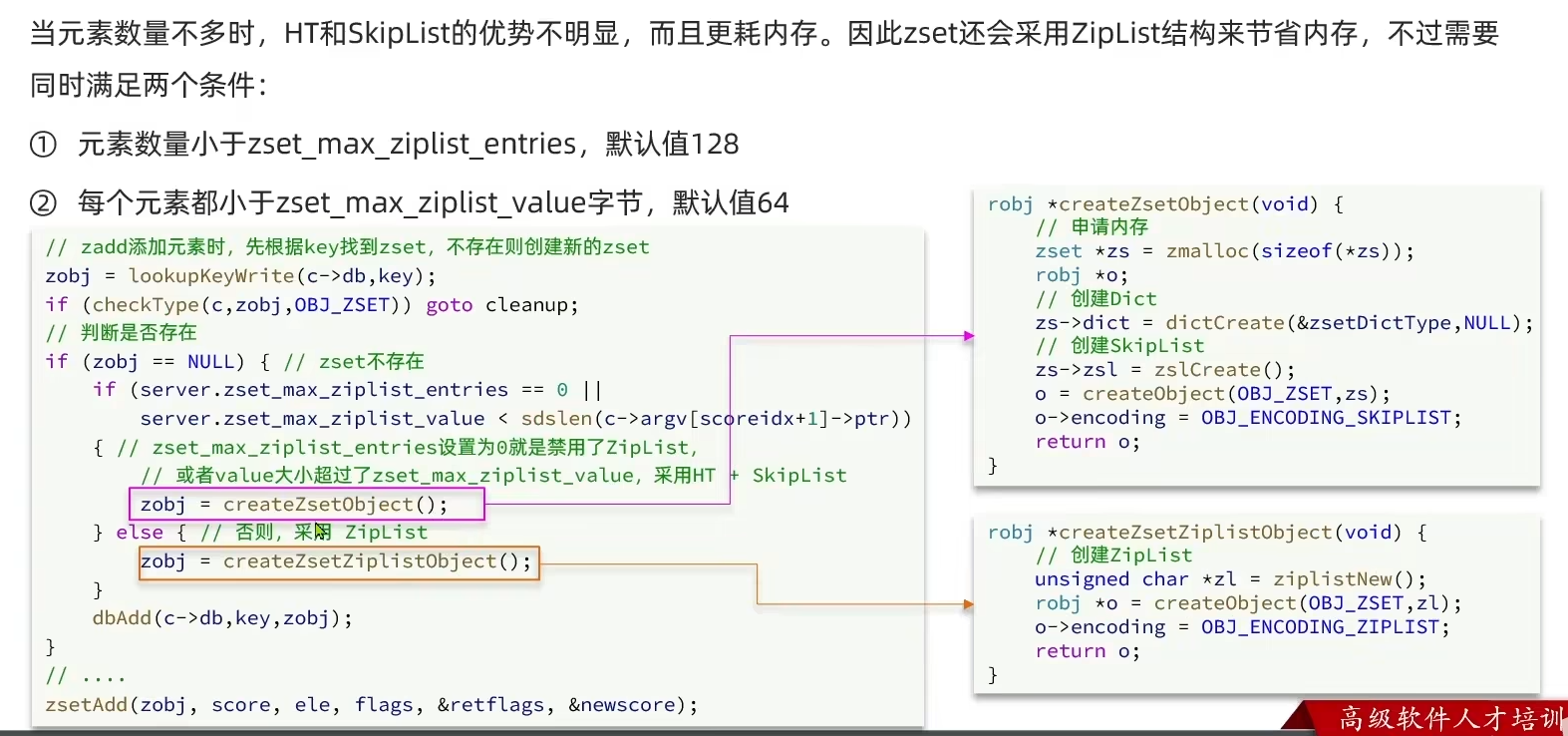
- 当元素不多时,使用ZipList编码

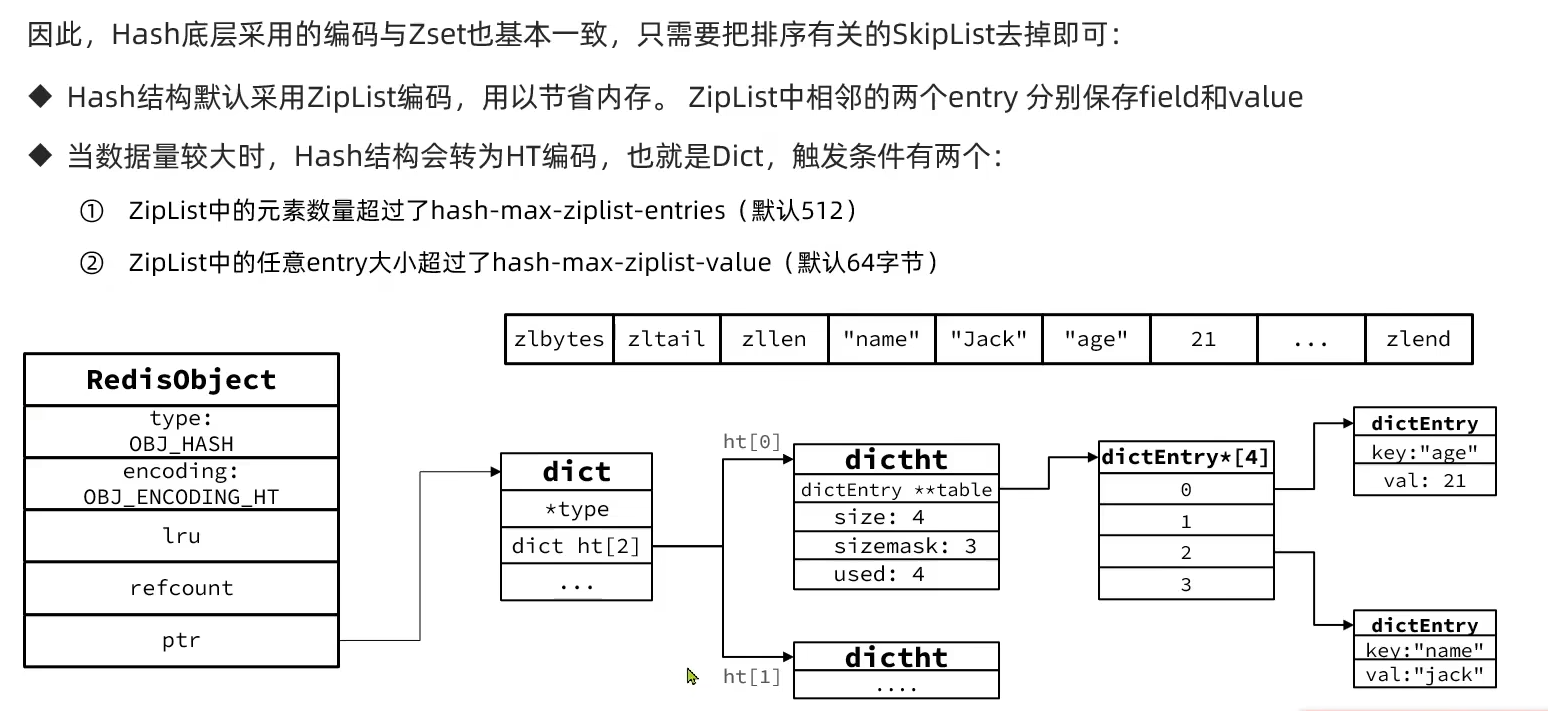
6.2.5 Hash
6.3 Redis网络模型
6.3.1 selecct

6.3.2 poll

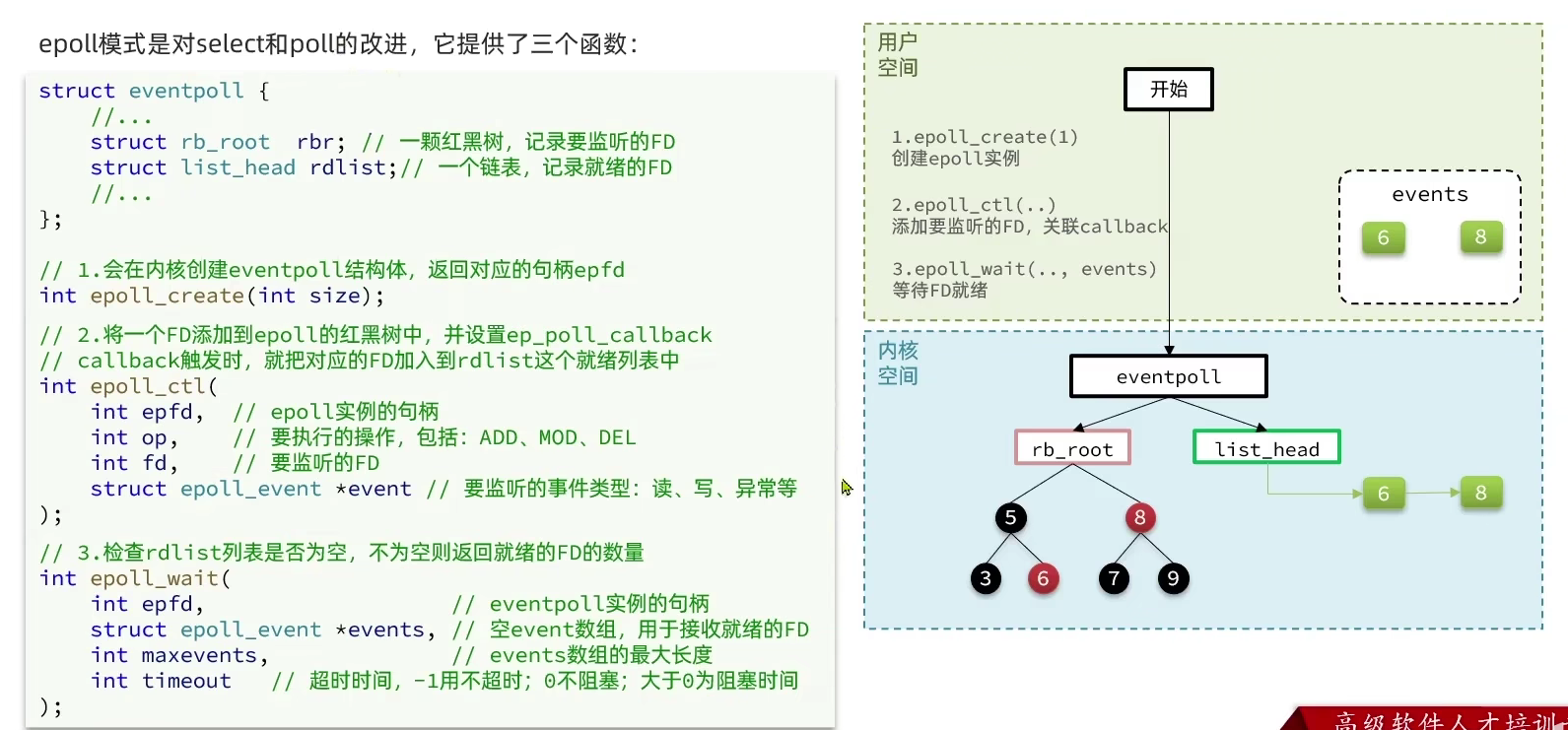
6.3.3 epoll
6.3.4 Redis网络模型
单线程?多线程?


6.4 Redis通信协议
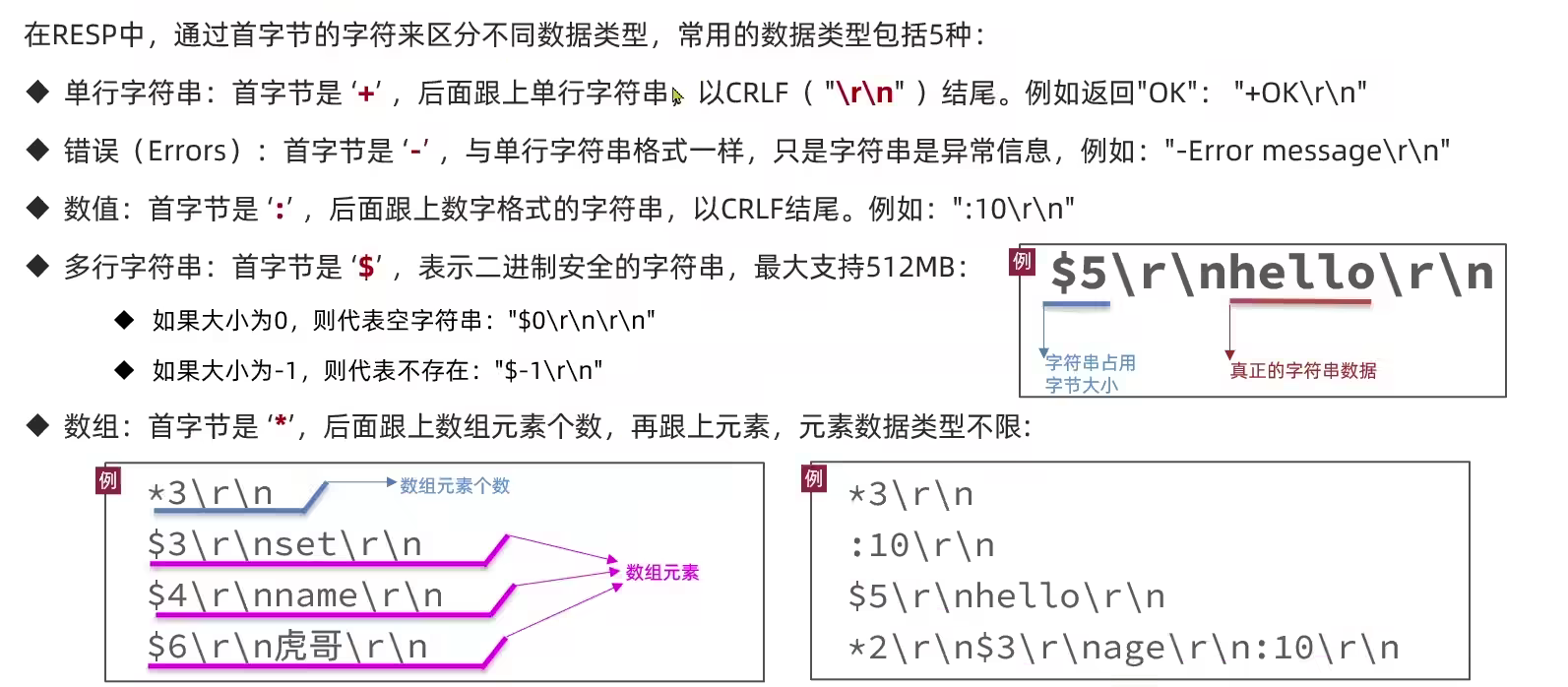
7 Redis实战
7.1 短信登录

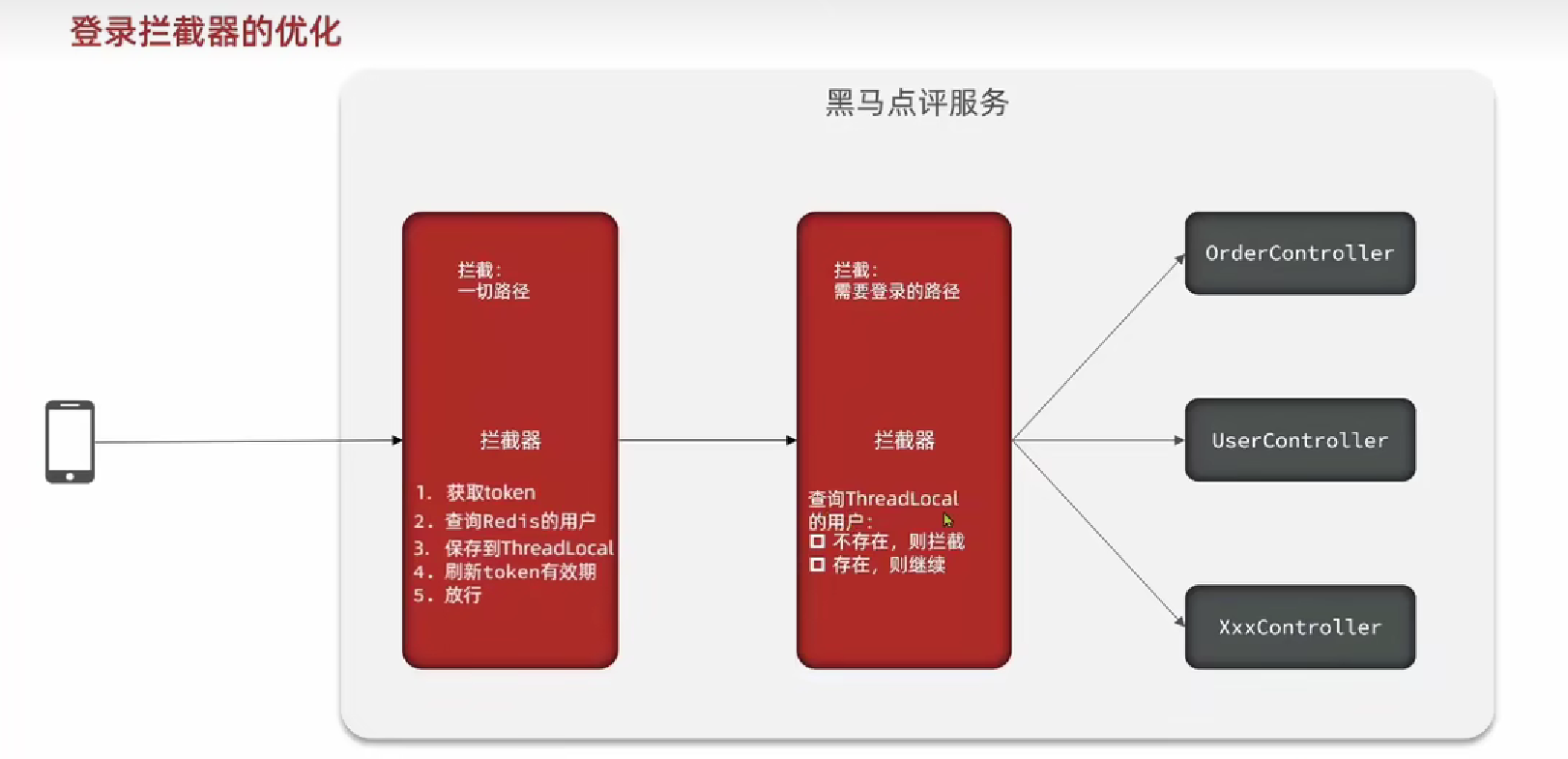
7.2 商户查询缓存
tXZN6w-1725528160173)]
6.2.4 ZSet
zset底层数据结构必须满足键值存储、键必须唯一、可排序这几个需求
- SkipList:可以排序,并且可以同时存储score和ele值( member)
- HT ( Dict):可以键值存储,并且可以根据key找value
[外链图片转存中…(img-zQwHt0dx-1725528160173)]
- 当元素不多时,使用ZipList编码
[外链图片转存中…(img-SCoUVdDn-1725528160173)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-KIqmlnJz-1725528160173)]
6.2.5 Hash
[外链图片转存中…(img-YExQQbXg-1725528160174)]
6.3 Redis网络模型
6.3.1 selecct
[外链图片转存中…(img-fFzuys3R-1725528160174)]
6.3.2 poll
[外链图片转存中…(img-OxEyBeGi-1725528160174)]
6.3.3 epoll
[外链图片转存中…(img-0SEZ3rgN-1725528160174)]
6.3.4 Redis网络模型
单线程?多线程?
[外链图片转存中…(img-fRIrVeDR-1725528160175)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-YhYlOECO-1725528160175)]
6.4 Redis通信协议
[外链图片转存中…(img-nUoZADFd-1725528160175)]
7 Redis实战
7.1 短信登录
[外链图片转存中…(img-auMEyc95-1725528160175)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-cedX1Yyj-1725528160176)]

