Java-数据结构-链表-LinkedList(二)|ू・ω・` )
文本目录:
☛一、LinkedList(无头双向非循环链表的结构):
☛ 二、LinkedList的模拟实现:
❄️1、操作方法:
▶(1)、display()方法:
▶(2)、size()方法:
▶(3)、contains(int key)方法:
▶(4)、addFirst(int data)方法:
▶(5)、addLast(int data)方法:
▶(6)、addIndex(int index,int data)方法:
▶(7)、remove(int data)方法:
▶(8)、removeAllKey(int data)方法:
❄️2、 总代码:
☛三、Java自带的LinkedList:
❄️1、LinkedList的使用:
♠(1)、LinkedList的构造方法:
♠(2)、LinkedList的常用操作:
▷1、indexOf(Object o)方法:
▷2、lastIndexOf(Object o)方法:
▷3、subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)方法:
♠(3)、LinkedList的遍历:
▷1、使用sout直接遍历:
▷ 2、使用for-each直接遍历:
▷ 4、使用迭代器逆序遍历:
☛ 四、ArrayList和LinkedList的区别:
☛ 总结:
 一、LinkedList(无头双向非循环链表的结构):
一、LinkedList(无头双向非循环链表的结构):
对于我们的无头双向链表的结构呢,因为是双向的所以呢,我们每个节点要有两个存储地址的地方,一个存储数据的地方,这样呢,每一个节点都可以访问它的前一个节点和后一个节点了。
我们来看看它的结构是什么样的并且看看其对于结构代码的实现:
这个呢,就是双向无头非循环链表的节点的结构,其是由这以一个节点构成的。
我们来看看是怎样构成的:
我们结构看完了,我们来看看我们怎样使用代码来实现这个节点,我们来看:
 二、LinkedList的模拟实现:
二、LinkedList的模拟实现:
❄️1、操作方法:
我们在双向无头非循环链表中要实现的方法,和我们在单向无头非循环链表中的我们自己实现的方法是差不多的方法,所以我们也可以去实现IList接口,来重写方法,以便于管理。
▶(1)、display()方法:
打印双向无头非循环链表。
我们的display() 方法,还是非常简单的,我们只需要遍历一遍链表就可以了,都用不到prev这个地址,和我们在单行无头非循环链表中的代码是差不多的。我们来看:
▶(2)、size()方法:
返回链表的长度。
这个也和我们之前写单向无头非循环链表的方法是差不多的,我们直接看代码:

▶(3)、contains(int key)方法:
查找链表中是否有key这个数据的节点。
那么这个嘛,你懂得~
▶(4)、addFirst(int data)方法:
头插方法。
对于这个链表的头插方法呢和我们之前的不同,对于我们头插呢,要先把newNode的next放head,之后再把head的prev放newNode,之后我们要把head往前移动,但是呢在执行之前呢,我们要先注意的是,当我们的链表为空的时候呢,我们要把 newNode=head=last,我们来看看我们的思路图:
我们来看看代码是如何实现的: 
▶(5)、addLast(int data)方法:
尾插方法。
这个尾插方法的操作呢和我们上面的头插是类似的操作,我们也是先判断链表是否为空,如果为空要执行 head=last=newNode 操作,当我们不为空的时候呢,要把 newNode 的地址存放到 last 的 next 里面,newNode 的 prev 里面要存放 last 的地址,最后再把 last 往后移。还是老样子,我们先来看看思路图:
OK,我们在理解这个尾插的操作之后呢,我们来看看代码是如何实现的:
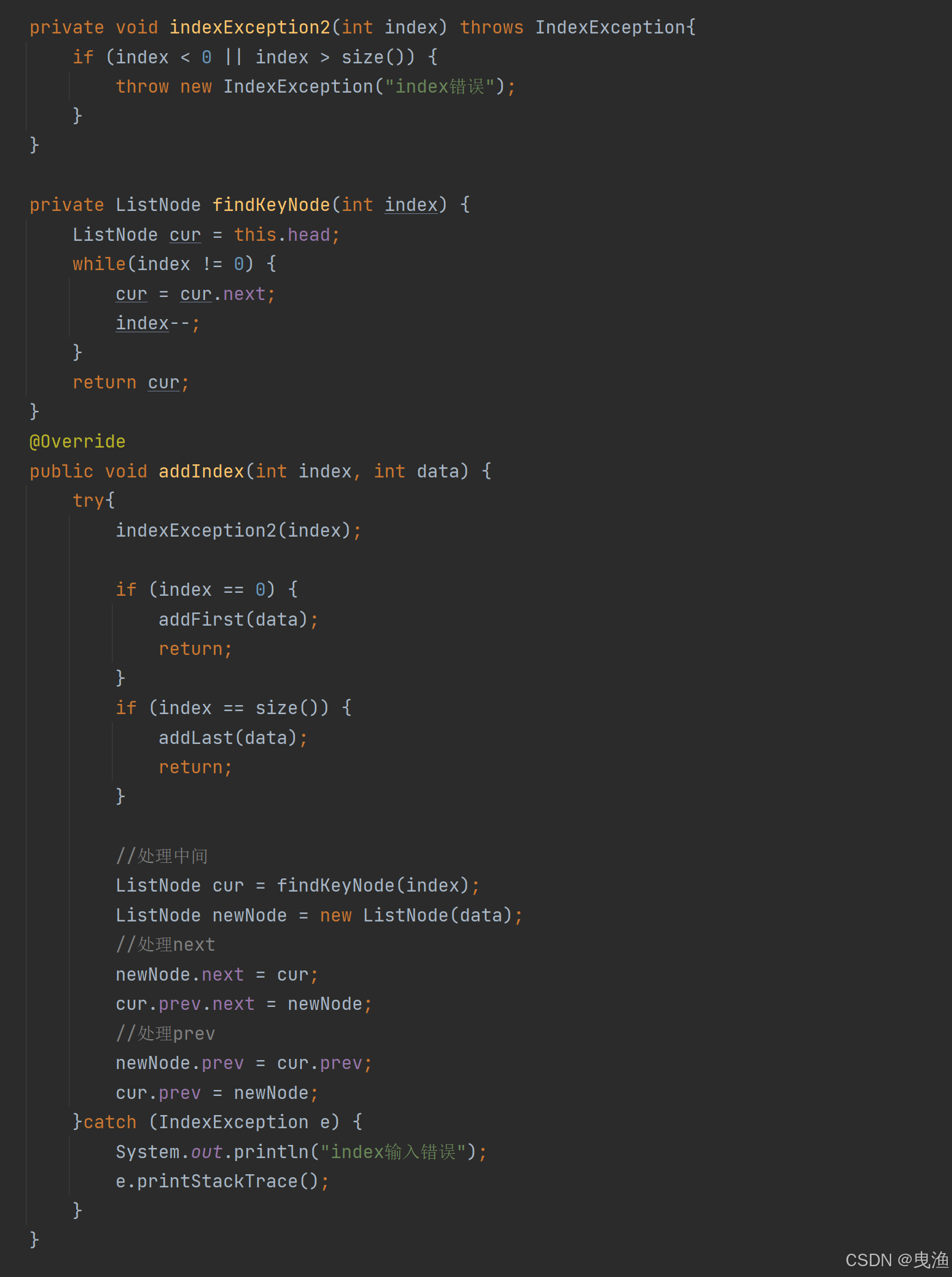
▶(6)、addIndex(int index,int data)方法:
在index这个位置插入data这个数据的节点。
对于这个方法呢,在双向链表中和在单向链表中是不一样的,我们在单向链表中我们要找到添加位置节点的前一个节点,但是呢对于双向链表我们可以直接找要添加的位置的节点就可以了。但是在执行这个操作之前呢,我们要先判断index是否是有效的,并且在index=0,index =链表的长度 的时候分别进行头插和尾插操作就可以了。
我们还是老样子,先来看思路图:
我们来看看代码是怎样实现的:
▶(7)、remove(int data)方法:
删除第一次出现data的这个数据的节点。
对于这个remove方法和上面那个方法是相似的,我们同样不需要找删除节点的前一个节点,我们同样只需要找要删除的那个节点就可以了。但是这个方法还是很麻烦的,我们在删除的过程中呢,要考虑很多的地方。
我们先来看看在中间的时候删除操作是怎样执行的:
接下来我们来![]() 我们需要 注意的地方:
我们需要 注意的地方:
1、删除的地方是 head 这个位置的时候:
2 、删除的地方是 last 这个位置的时候: 
OK,我们也分析了这么多了,我们来看看代码是如何实现这个操作的吧:
▶(8)、removeAllKey(int data)方法:
删除出现data的这个数据的所有节点。
这个操作呢,当我们理解了上面的删除操作之后呢,对于这个操作就非常的简单了,这个是删除所有出现data这个数据的节点,所以我们要遍历一遍链表才能结束,所以和上面的代码十分的相似,就是你没有 return 这行代码而已,这里我们直接看代码:
▶(9)、clear()方法:
清除链表。
这个清除链表的代码呢和我们在写单向链表的时候是十分相似的。我们只需要在其基础上把prev也同样置为null就可以了,我们还是直接来看代码的实现:
❄️2、 总代码:
我们所有的代码都分析完事了,当然这些操作方法不是我们 Java 里 LinkedList 的所有方法,只是经常使用的操作,下面我们把这些代码结合起来看看:
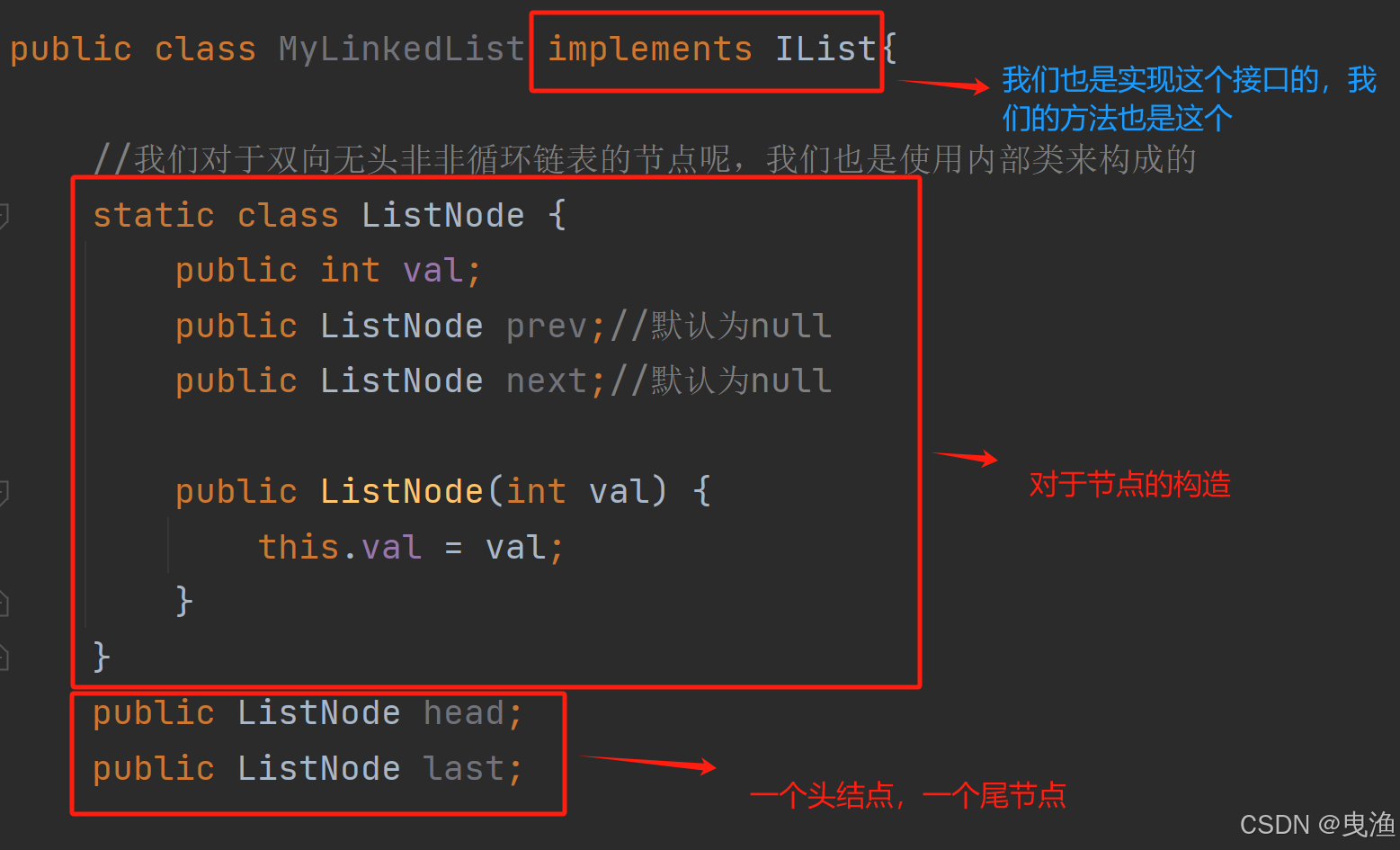
public class MyLinkedList implements IList{
//我们对于双向无头非非循环链表的节点呢,我们也是使用内部类来构成的
static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode prev;//默认为null
public ListNode next;//默认为null
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode last;
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = this.last = newNode;
}else {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
}
@Override
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = this.last = newNode;
}else {
this.last.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.last;
this.last = this.last.next;
}
}
private void indexException2(int index) throws IndexException{
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexException("index错误");
}
}
private ListNode findKeyNode(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(index != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
@Override
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
try{
indexException2(index);
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
//处理中间
ListNode cur = findKeyNode(index);
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(data);
//处理next
newNode.next = cur;
cur.prev.next = newNode;
//处理prev
newNode.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = newNode;
}catch (IndexException e) {
System.out.println("index输入错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
//开始删除
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.head != null) {
this.head.prev = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur == this.last) {
this.last = this.last.prev;
}else {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
//开始删除
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.head != null) {
this.head.prev = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur == this.last) {
this.last = this.last.prev;
}else {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
int log = 0;
while(cur != null) {
log++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return log;
}
@Override
public void display() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("");
}
@Override
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.prev = null;
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
this.head = this.last = null;
}
}
 三、Java自带的LinkedList:
三、Java自带的LinkedList:
对于这个 LinkedList 方面的知识我们也可以去到Java官网去查看:
在Java的LinkedList的官方文档
我们在 Java 每次使用双向链表的时候,不需要每次都去把我们这个自实现的代码重写一遍。在 Java 中呢,Java官方已经在底层里面添加了链表,而且这个链表的底层使用的就是双向无头非循环的链表来实现的。
对于Java自带的链表这里呢有一些注意:
▷1、LinkedList实现了List这个接口
▷2、LinkedList的底层使用双向链表
▷3、LinkedList不支持随机访问,因为没有实现RandoimAccess接口
▷4、LinkedList的任意位置的插入和删除的效率比较高,时间复杂度是O(1)
▷5、LinkedList适合用于任意位置的插入和删除
❄️1、LinkedList的使用:
♠(1)、LinkedList的构造方法:
我们的 LinkedList 的构造方法有两种构造方法:
1、无参构造:
2、 LinkedList(Collection <? extends E> c) 构造方法:
这个里面放的是实现Collection这个接口的对象,并且呢是 E 或者是 E 的子类。
我们来看看怎么使用:
这个就是在传入的参数之上进行操作的。
♠(2)、LinkedList的常用操作:
我们在自实现 LinkedList 的时候呢,我们大多数的操作都实现了,在Java自带的LinkedList 里面都有这个对应的操作,但是呢没有display() 这个方法。
但是呢,在Java 自带得LinkedList 里面呢,我们也有没有自实现的,我们来看看常用的操作是怎样进行的:
▷1、indexOf(Object o)方法:
返回第一个出现o的的位置下标。
▷2、lastIndexOf(Object o)方法:
返回最后一个o出现的位置下标。
我们来看看它们的使用案例:
▷3、subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)方法:
返回fromIndex下标到 toIndex下标的链表。
我们来看看使用例子:
♠(3)、LinkedList的遍历:
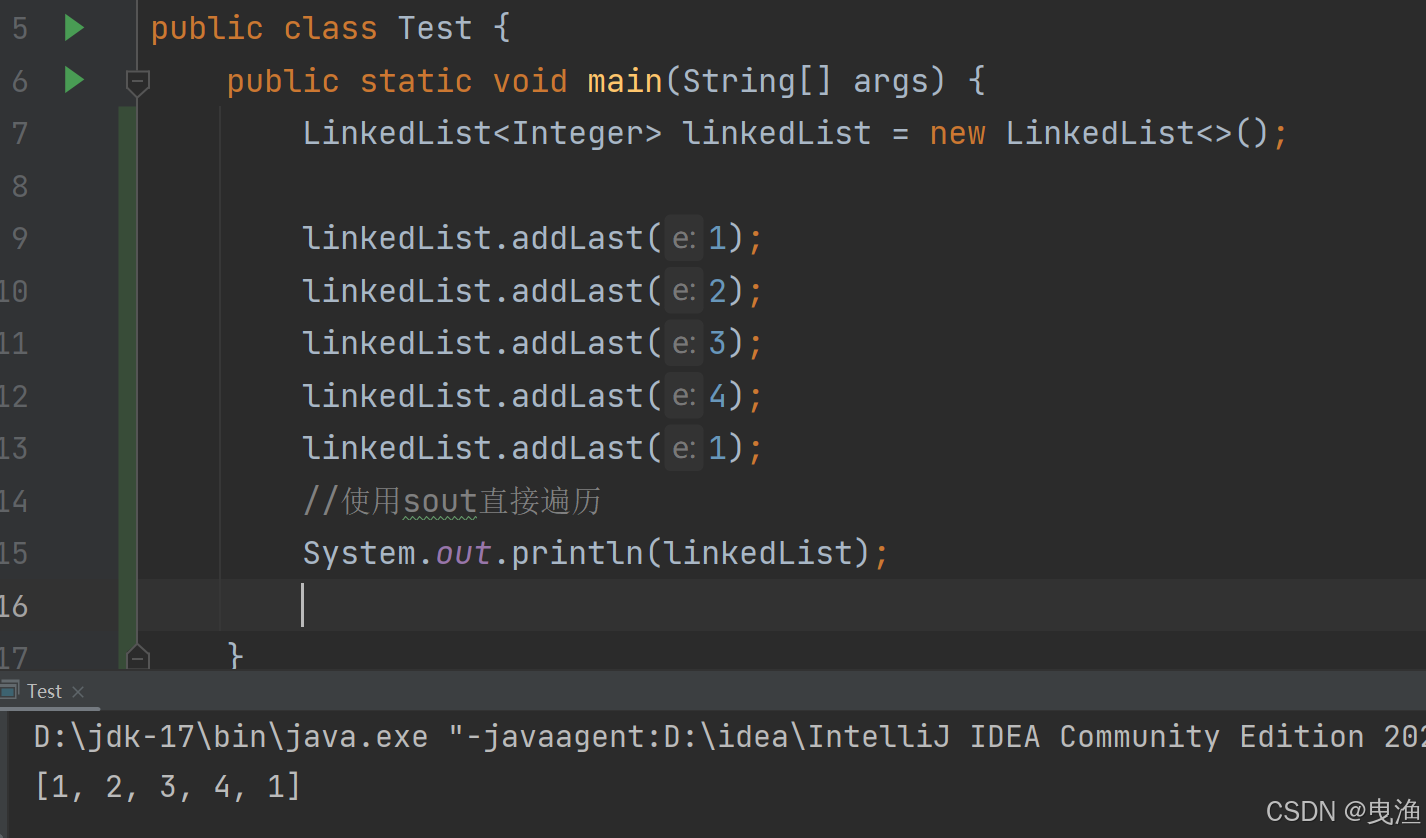
▷1、使用sout直接遍历:
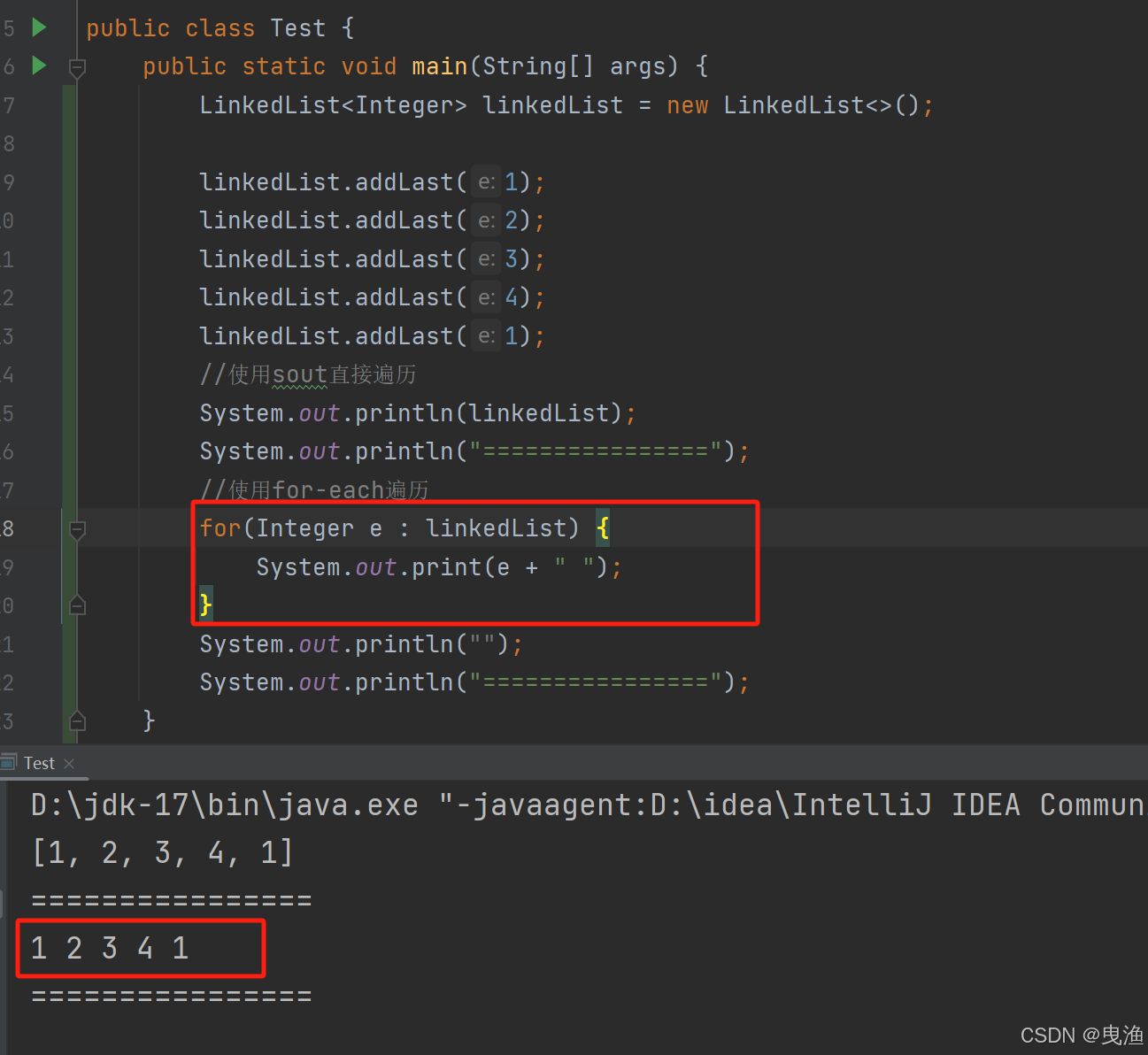
▷ 2、使用for-each直接遍历:
▷ 3、使用迭代器正序遍历:
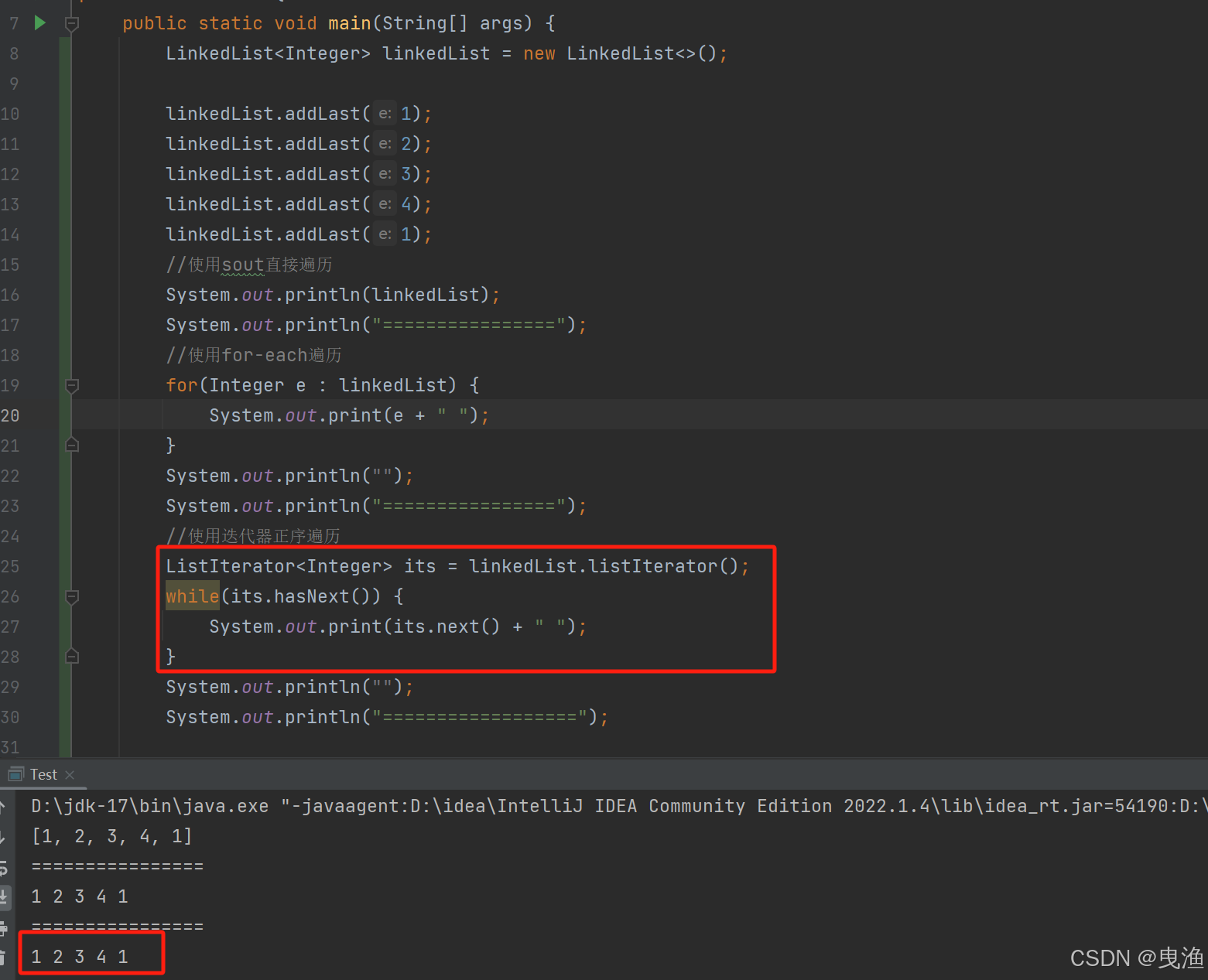
▷ 4、使用迭代器逆序遍历:
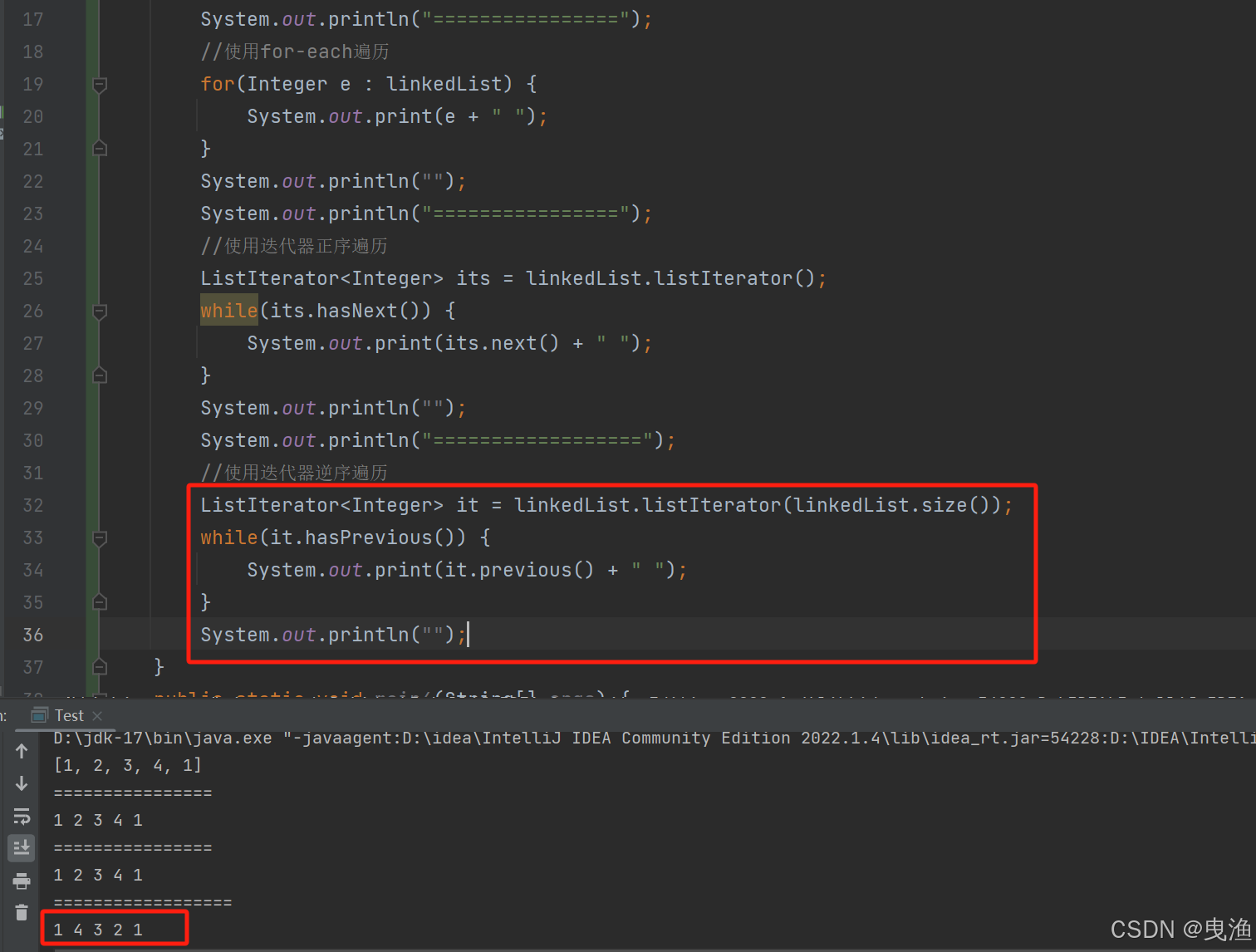
 四、ArrayList和LinkedList的区别:
四、ArrayList和LinkedList的区别:
这个呢我们直接看表格,比较直观,我们来看:
 总结:
总结:
OK了,关于我们的链表的相关知识就到这里就结束了,我们下次来看看有关于链表方面的练习题,让我们期待下次的见面吧,拜拜喽~~~



