go切片的深入学习以及context库的使用
Go切片专项学习
go切片扩容机制
go1.18 之前:
1.如果期望容量大于当前容量的两倍就会使用期望容量;
2.如果当前切片的长度小于 1024 就会将容量翻倍;
3.如果当前切片的长度大于 1024 就会每次增加 25% 的容量,直到新容量大于期望容量;
go1.18 之后:
1.如果期望容量大于当前容量的两倍就会使用期望容量;
2.如果当前切片的长度小于阈值(默认 256)就会将容量翻倍;
3.如果当前切片的长度大于等于阈值(默认 256),就会每次增加 25% 的容量,基准是 newcap + 3*threshold,直到新容量大于期望容量;
第一条相同,新扩容机制在长度小于256以下时,扩容机制仍然和旧的一样,不同的是,当大于256的时候扩容会按照指定的公式进行扩容。
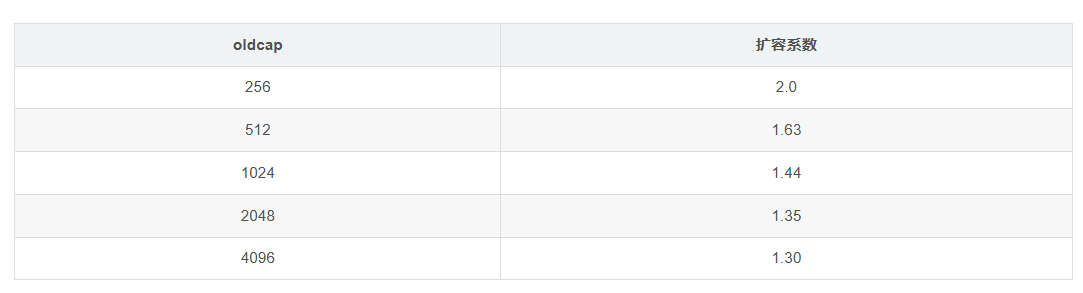
最后求极限扩容系数会趋近于1.25。
这样做的目的是为了控制让小的切片容量增长速度快一点,减少内存分配次数,而让大切片容量增长率小一点,更好地节省内存。
前几天朋友让我看了一道题:挺有意思的,短短几行代码就把切片的性质说的一清二楚。
package main
import "fmt"
func SliceRise(s []int) {
s = append(s, 0)
fmt.Printf("s = %v\n", s)
for i := range s {
s[i]++
}
}
func main() {
s1 := []int{1, 2}
s2 := s1
s2 = append(s2, 3)
SliceRise(s1)
SliceRise(s2)
fmt.Printf("s1 = %v\n", s1)
fmt.Printf("s2 = %v\n", s2)
}
这个代码输出结果是:
s = [1 2 0]
s = [1 2 3 0]
s1 = [1 2]
s2 = [2 3 4]
我们看看为什么?
首先,第一个s由于扩容,导致了底层数组改变,所以方法内和方法外是两个不同的结构,
第二个s在方法外就已经扩容了,进入方法内后底层数组指针仍然没有改变,这就是关键点了,既然没有改变,为什么内部是长度为4,外侧就为3了呢?
肯定会有很多人认为最后结果是2341 。
原因就在于切片是值传递的,传递进去的是原始切牌的拷贝,进入后新切片长度为4,容量为4,而在外侧的切片长度为3,容量为4,这就导致了只能输出前三位。
Context
Context 是 golang 中十分重要的接口,用于定义 goroutine 中的上下文信息,context 常用于以下几种情况:
- 数据传递: 在多个 goroutine中传递数据
- 超时管理: 通过配置超时时间,可以方便地配置协程的终止时间
- 终止协程: 通过使用
cancel()方法,协程可以很方便地终止,可以批量管理多个协程的终止
type Context interface {
Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) // 返回上下文的截止时间
Done() <-chan struct{} // 返回一个只读的channel,用于通知上下文完成或取消
Err() error // 返回上下文的错误原因
Value(key interface{}) interface{} // 返回与key相关的值
}
(context接口定义了以上方法)context.Background():返回一个空的Context,通常作为根上下文使用,不带任何取消、超时或元数据。
ctx := context.Background()
context.TODO():返回一个空的Context,用于暂时没有上下文的地方,通常在开发中使用,需要在后续补充具体的上下文。
context.TODO():返回一个空的Context,用于暂时没有上下文的地方,通常在开发中使用,需要在后续补充具体的上下文。
context.WithTimeout(parent Context, timeout time.Duration):返回一个新的Context,带有一个超时。超时后,Done()通道会关闭,并且Err()方法返回context.DeadlineExceeded。
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)
defer cancel()
context.WithCancel(parent Context):返回一个新的Context和一个取消函数。调用取消函数会取消这个上下文及其所有派生上下文。
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
defer cancel() // 确保在完成时调用取消函数
context.WithDeadline(parent Context, deadline time.Time):返回一个新的Context,带有一个截止时间。超过截止时间后,Done()通道会关闭,并且Err()方法返回context.DeadlineExceeded。
deadline := time.Now().Add(5 * time.Second)
ctx, cancel := context.WithDeadline(context.Background(), deadline)
defer cancel()
context.WithValue(parent Context, key, value interface{}):返回一个新的Context,带有值。值可以用于传递元数据或请求范围的数据。
ctx := context.WithValue(context.Background(), "key", "value")
value := ctx.Value("key")
在gin框架中我们经常会用到gin.Context这个方法,他和context.Context的主要区别是什么呢?
context.Context:
- 用于跨 goroutine 传递上下文信息。
- 适用于处理超时、取消、传递请求范围的数据等。
gin.Context:
- 用于 Gin 框架中处理 HTTP 请求和响应。
- 提供了处理请求参数、设置响应、存储数据等功能。
超时示例:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
// 创建一个带有超时的 context,超时时间为 3 秒
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 3*time.Second)
defer cancel() // 在 main 函数结束时取消 context
// 启动一个 Goroutine 进行某些工作
go doWork(ctx)
// 等待工作完成
select {
case <-ctx.Done(): // 如果 context 超时或被取消
fmt.Println("Main: work canceled or timed out")
}
}
func doWork(ctx context.Context) {
fmt.Println("Worker: started work")
// 模拟工作过程,工作时间为 5 秒
workDuration := 5 * time.Second
select {
case <-time.After(workDuration): // 工作完成
fmt.Println("Worker: work completed")
case <-ctx.Done(): // 如果收到 context 的取消信号
fmt.Println("Worker: work canceled due to:", ctx.Err())
}
}
## Context
`Context` 是 golang 中十分重要的接口,用于定义 `goroutine` 中的上下文信息,`context` 常用于以下几种情况:
- 数据传递: ==在多个 goroutine中传递数据==
- 超时管理: 通过配置超时时间,可以方便地配置协程的终止时间
- 终止协程: 通过使用 `cancel()` 方法,协程可以很方便地终止,可以批量管理多个协程的终止
```go
type Context interface {
Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) // 返回上下文的截止时间
Done() <-chan struct{} // 返回一个只读的channel,用于通知上下文完成或取消
Err() error // 返回上下文的错误原因
Value(key interface{}) interface{} // 返回与key相关的值
}
(context接口定义了以上方法)context.Background():返回一个空的Context,通常作为根上下文使用,不带任何取消、超时或元数据。
ctx := context.Background()
context.TODO():返回一个空的Context,用于暂时没有上下文的地方,通常在开发中使用,需要在后续补充具体的上下文。
context.TODO():返回一个空的Context,用于暂时没有上下文的地方,通常在开发中使用,需要在后续补充具体的上下文。
context.WithTimeout(parent Context, timeout time.Duration):返回一个新的Context,带有一个超时。超时后,Done()通道会关闭,并且Err()方法返回context.DeadlineExceeded。
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)
defer cancel()
context.WithCancel(parent Context):返回一个新的Context和一个取消函数。调用取消函数会取消这个上下文及其所有派生上下文。
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
defer cancel() // 确保在完成时调用取消函数
context.WithDeadline(parent Context, deadline time.Time):返回一个新的Context,带有一个截止时间。超过截止时间后,Done()通道会关闭,并且Err()方法返回context.DeadlineExceeded。
deadline := time.Now().Add(5 * time.Second)
ctx, cancel := context.WithDeadline(context.Background(), deadline)
defer cancel()
context.WithValue(parent Context, key, value interface{}):返回一个新的Context,带有值。值可以用于传递元数据或请求范围的数据。
ctx := context.WithValue(context.Background(), "key", "value")
value := ctx.Value("key")
在gin框架中我们经常会用到gin.Context这个方法,他和context.Context的主要区别是什么呢?
context.Context:
- 用于跨 goroutine 传递上下文信息。
- 适用于处理超时、取消、传递请求范围的数据等。
gin.Context:
- 用于 Gin 框架中处理 HTTP 请求和响应。
- 提供了处理请求参数、设置响应、存储数据等功能。
超时示例:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
// 创建一个带有超时的 context,超时时间为 3 秒
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 3*time.Second)
defer cancel() // 在 main 函数结束时取消 context
// 启动一个 Goroutine 进行某些工作
go doWork(ctx)
// 等待工作完成
select {
case <-ctx.Done(): // 如果 context 超时或被取消
fmt.Println("Main: work canceled or timed out")
}
}
func doWork(ctx context.Context) {
fmt.Println("Worker: started work")
// 模拟工作过程,工作时间为 5 秒
workDuration := 5 * time.Second
select {
case <-time.After(workDuration): // 工作完成
fmt.Println("Worker: work completed")
case <-ctx.Done(): // 如果收到 context 的取消信号
fmt.Println("Worker: work canceled due to:", ctx.Err())
}
}
