POSIX信号量以及利用POSIX信号量实现基于循环队列的高效生产者消费者模型



目录
- `🍁POSIX信号量 `
- `🍁信号量的相关接口介绍`
- *初始化信号量*
- *销毁信号量*
- *等待信号量*
- *发布信号量*
- `🍁(POSIX信号量):基于环形队列的生产消费模型`
- `🍁基于环形队列的生产消费模型代码实现`
🍁POSIX信号量
POSIX信号量和SystemV信号量作用相同,都是用于同步操作,达到无冲突的访问共享资源目的。 但POSIX可以用于线程间同步。
🍁信号量的相关接口介绍
初始化信号量
#include <semaphore.h>
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
- 参数:
- pshared:0表示线程间共享,非零表示进程间共享
- value:信号量初始值
销毁信号量
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
等待信号量
- 功能:等待信号量,会将信号量的值减1
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem); //P()
发布信号量
- 功能:发布信号量,表示资源使用完毕,可以归还资源了。将信号量值加1。
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);//V()
注意:申请成功后,不需要判断资源是否具备条件,因为申请成功后,就一定有对应的资源提供给你,从而可以有效减少内部判断(与条件变量相比,代码上少很多的判断)。
🍁(POSIX信号量):基于环形队列的生产消费模型
上一节生产者-消费者的例子是基于阻塞队列实现的,其空间可以动态分配,现在基于固定大小的环形队列重写这个程序
环形队列采用数组模拟,用模运算来模拟环状特性
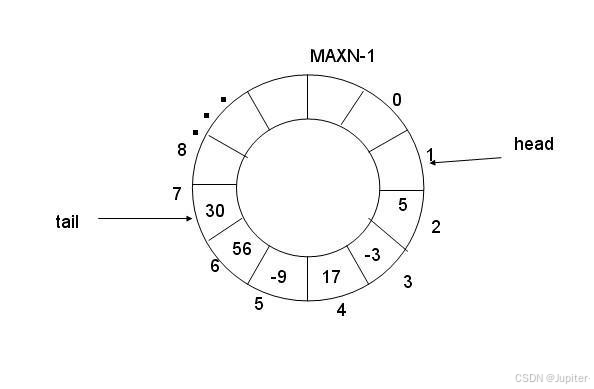
环形结构起始状态和结束状态都是一样的,不好判断为空或者为满,所以可以通过加计数器或者标记位来判断满或者空。另外也可以预留一个空的位置,作为满的状态。
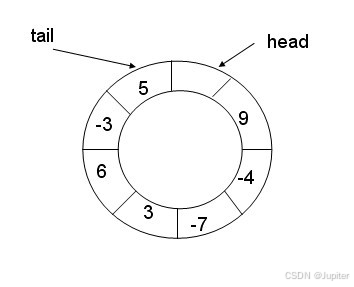
但是我们现在有信号量这个计数器,就很简单的进行多线程间的同步过程。
🍁基于环形队列的生产消费模型代码实现
实现思想:定义两个下标,记录生产者和消费者的位置,便于在指定下标下生产和执行任务,定义两个信号量,生产者和消费者各一个,记录自己的资源,定义两个锁,生产者消费者各一个,为了让生产者之间与消费者之间实现互斥。
伪代码:

main.cc
#include <iostream>
#include "thread.hpp"
#include "ringqueue.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
using namespace ThreadModule;
void consumer(Ring_Queue<int> &rq)
{
sleep(1);
while (true)
{
sleep(2);
int data = 0;
rq.pop(&data);
cout << "consumer consume data is:" << data << endl;
}
}
void product(Ring_Queue<int> &rq)
{
sleep(1);
int cnt = 10;
while (true)
{
rq.Enqueue(cnt); //让数字模拟任务
cout << "productor product data is:" << cnt++ << endl;
}
}
void InitConsumer(vector<Thread<Ring_Queue<int>>> *threads, int n, Ring_Queue<int> &rq)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
string name = "comsumer -" + to_string(i + 1);
threads->emplace_back(consumer, rq, name);
}
}
void Initproductor(vector<Thread<Ring_Queue<int>>> *threads, int n, Ring_Queue<int> &rq)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
string name = "product -" + to_string(i + 1);
threads->emplace_back(product, rq, name);
}
}
void StartAll(vector<Thread<Ring_Queue<int>>> &threads)
{
for (auto &thread : threads)
{
thread.start();
}
}
void waitAllthread(vector<Thread<Ring_Queue<int>>> &threads)
{
for (auto &thread : threads)
{
thread.join();
}
}
int main()
{
Ring_Queue<int> *rq = new Ring_Queue<int>(5);
vector<Thread<Ring_Queue<int>>> threads;
InitConsumer(&threads, 3, *rq); //初始化消费者线程(创建)
Initproductor(&threads, 1, *rq); //初始化生产者线程(创建)
StartAll(threads); //启动所有的线程
waitAllthread(threads);
return 0;
}
ringqueue.hpp
#pragma
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <pthread.h>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class Ring_Queue
{
public:
//封装PV操作
void P(sem_t *p)
{
sem_wait(p);
}
void V(sem_t *v)
{
sem_post(v);
}
public:
Ring_Queue(int cap) : _ring_queue(cap), _cap(cap), _consumer_dex(0), _product_dex(0)
{
sem_init(&_room, 0, _cap);
sem_init(&_data, 0, 0);
pthread_mutex_init(&_consumer_mutex, nullptr);
pthread_mutex_init(&_product_mutex, nullptr);
}
void Enqueue(const T &in)
{
//申请信号量,如果申请成功,则说明有对应的资源,内部不用判断
P(&_room);
//加锁,目的:让生产者之间互斥
pthread_mutex_lock(&_product_mutex);
// 生产
_ring_queue[_product_dex++] = in;
_product_dex %= _cap;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_product_mutex);
V(&_data);
}
void pop(T *out)
{
P(&_data);
//目的:让消费者之间互斥
pthread_mutex_lock(&_consumer_mutex);
// 消费
*out = _ring_queue[_consumer_dex++];
_consumer_dex %= _cap;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_consumer_mutex);
V(&_room);
}
~Ring_Queue()
{
sem_destroy(&_room);
sem_destroy(&_data);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_consumer_mutex);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_product_mutex);
}
private:
// 1.环形队列
vector<T> _ring_queue; //循环队列
int _cap; //队列总容量
int _consumer_dex; //消费者的下标
int _product_dex; //生产者的下标
sem_t _room; //生产者的信号量
sem_t _data; //消费者的信号量
pthread_mutex_t _consumer_mutex; //消费者间的锁
pthread_mutex_t _product_mutex; //生产者间的锁
};
thread.hpp
#ifndef __THREAD_HPP__
#define __THREAD_HPP__
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
namespace ThreadModule
{
template <class T>
using func_t = std::function<void(T &)>;
template <class T>
class Thread
{
public:
Thread(func_t<T> func, T &data, std::string &name)
: _func(func), _data(data), _name(name), _stop(true)
{
}
void execute()
{
_func(_data);
}
static void *threadrun(void *args)
{
Thread<T> *self = static_cast<Thread<T> *>(args);
self->execute();
return nullptr;
}
bool start()
{
int n = pthread_create(&_tid, nullptr, threadrun, this);
if (!n)
{
_stop = false;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void stop()
{
_stop = true;
}
void detach()
{
if (!_stop)
pthread_detach(_tid);
}
std::string name()
{
return _name;
}
void join()
{
if (!_stop)
pthread_join(_tid, nullptr);
}
~Thread() {}
private:
pthread_t _tid;
func_t<T> _func;
T &_data;
std::string _name;
bool _stop;
};
}
#endif
