清理Go/Rust编译时产生的缓存
Go
Mac 1T的磁盘频频空间高级,发现是/Users/yourname/Library/Caches/go-build 目录占用了大量空间。
此目录保存来自 Go 构建系统的缓存构建工件。
如果目录太大,请运行go clean -cache。
运行go clean -fuzzcache以删除模糊缓存。
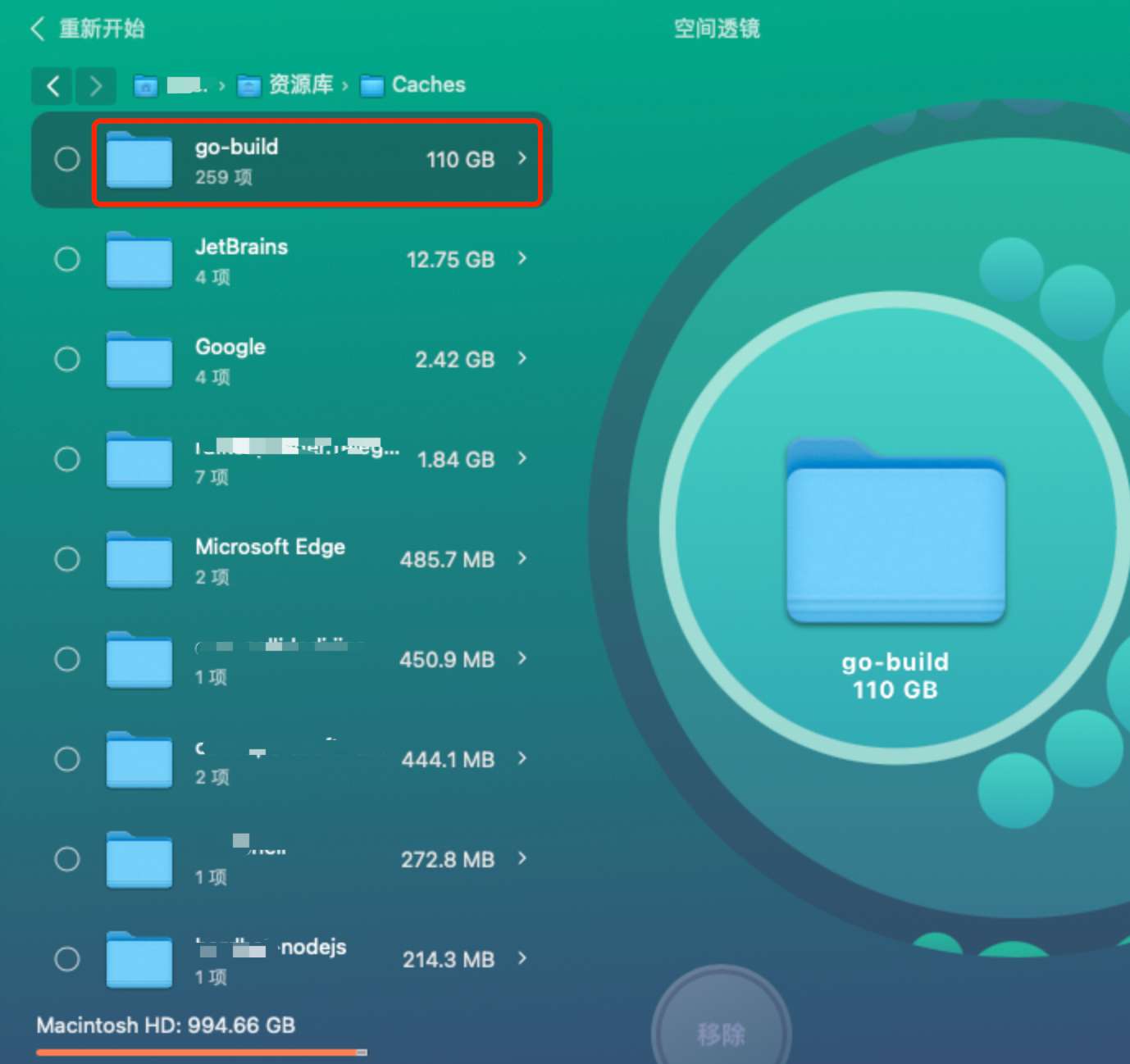

当时直接手工清理了。
之后不多久,该目录又占据了50多G的空间
du -sh */ | sort -h
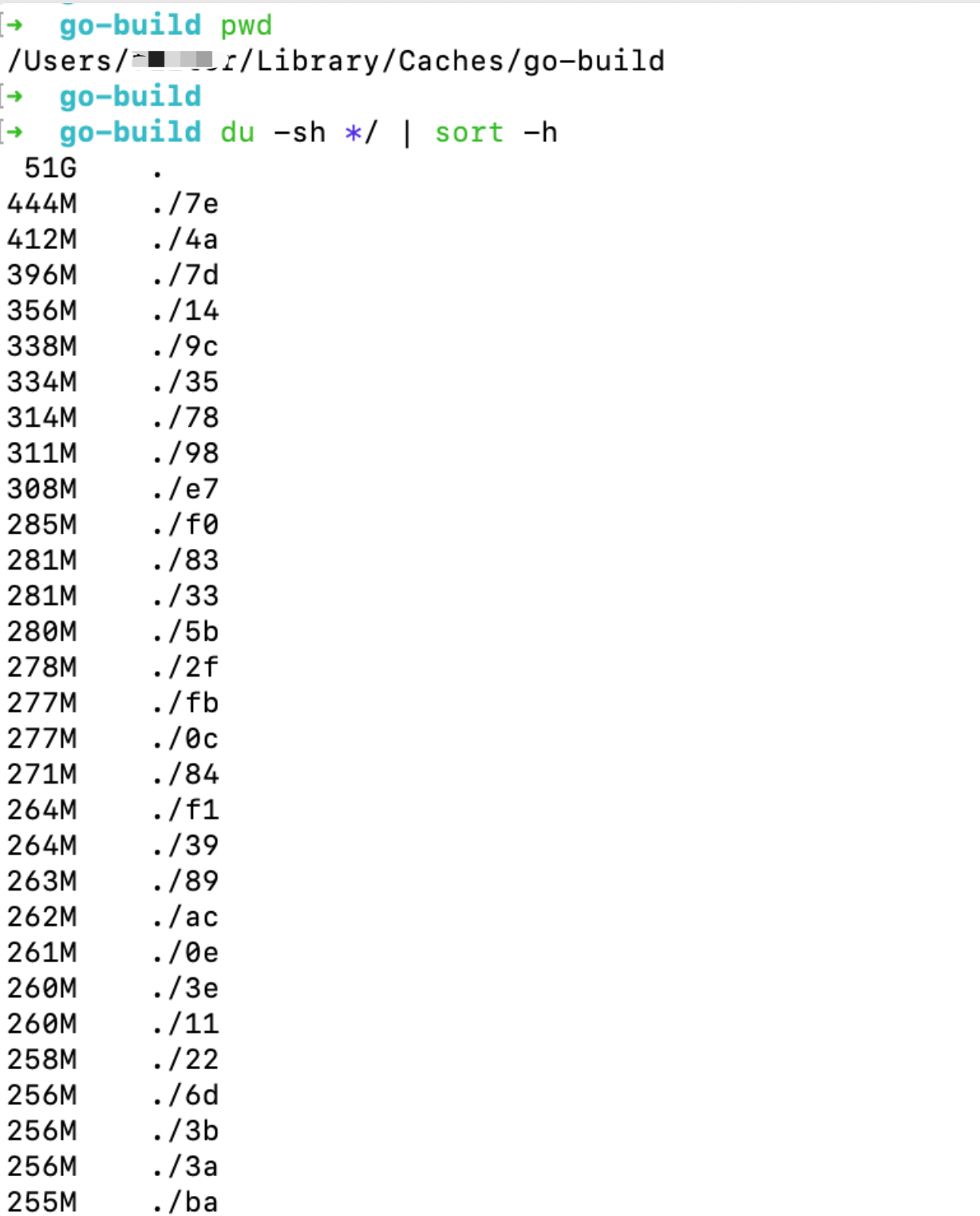
执行 go clean -cache

除了
go clean -cache
还有
-
go clean -fuzzcache删除模糊缓存 -
go clean -modcache删除mod的缓存
Rust
另外Rust也占用了大量空间(而且Rust不仅编译速度慢,编译出来的产物,debug模式下也相当大)
在构建 Rust 项目时,Rust 的包管理器 cargo 会在多个目录中生成缓存和构建产物。
1. cargo 会将下载的依赖项缓存到这个目录下,通常位于用户的主目录中:
~/.cargo
其中包括:
registry:下载的 crate 的源代码和元数据。git:从 Git 仓库中获取的依赖项。
查看这个目录的大小:
du -sh ~/.cargo
清理:
使用 cargo 自带的清理命令来清理缓存:
cargo clean
该命令需要到具体的项目目录下执行
这个命令会删除当前项目的 target 目录中的所有构建产物。
如果你想要清理全局缓存和编译产物,可以直接删除 ~/.cargo 目录下的缓存:
rm -rf ~/.cargo/registry
rm -rf ~/.cargo/git
2. target 目录
每个 Rust 项目在构建时会在项目根目录下生成一个 target/ 目录,用于存储构建产物,包括编译后的二进制文件、依赖项的编译结果等。这个目录可能会占用大量空间,尤其是当有多个构建配置(如 debug 和 release)时。
要查看某个项目的 target/ 目录的大小,运行:
du -sh /path/to/your/project/target
清理:
target/ 目录是 Rust 项目构建后的产物,通常可以安全地删除,特别是如果只是在本地开发时使用。
要删除项目中的 target 目录,进入项目根目录并运行:
rm -rf target
或者,如果你想批量清理多个项目中的 target 目录,可以在终端中使用 find 命令递归查找并删除 target 目录:
find /path/to/your/projects -type d -name target -exec rm -rf {} +
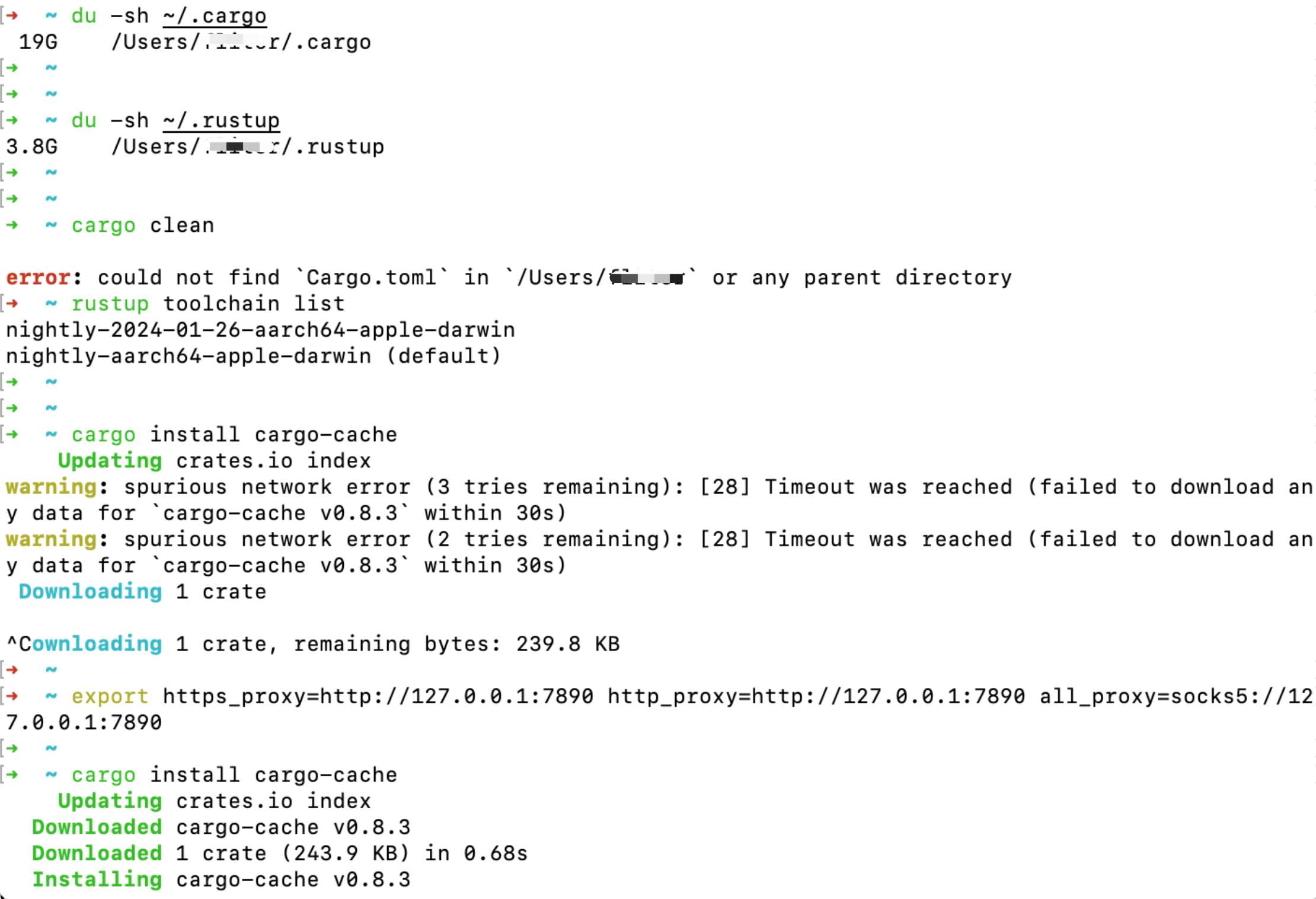
3. ~/.rustup 目录
Rust 工具链 (rustup) 也会占用一些空间,通常位于 ~/.rustup 目录下。这个目录存储了 Rust 工具链的版本、标准库和其他工具。
查看这个目录的大小:
du -sh ~/.rustup
清理:
rustup 也可能占用一些磁盘空间,尤其是当你安装了多个工具链或组件时。你可以查看当前安装的工具链:
rustup toolchain list
如果你发现了不再使用的工具链,可以卸载它们:
rustup toolchain uninstall <toolchain>
例如,卸载 nightly 版本:
rustup toolchain uninstall nightly
之前我已经手工把该目录下多达20G的文件都删了
cargo-cache 工具
推荐 使用 cargo-cache 工具查看和管理缓存
cargo-cache 是一个第三方工具,可以用来查看和清理 cargo 的缓存。可通过 cargo 安装这个工具:
cargo install cargo-cache
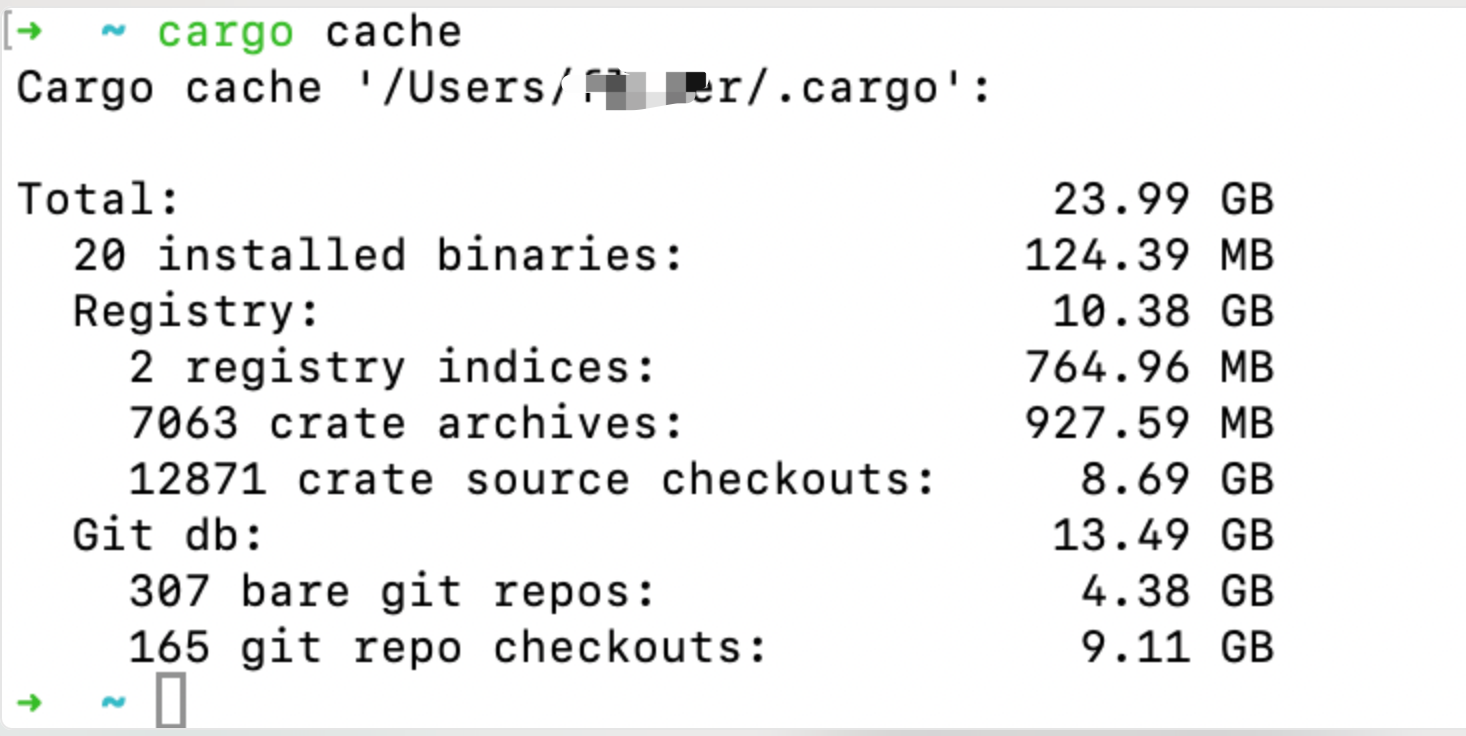
安装完成后,运行以下命令查看 cargo 缓存的详细信息:
cargo cache
输出显示的是 cargo 的缓存信息,包括 registry、git 和 target 目录的大小。
如果你想要清理缓存,也可以使用 cargo-cache:
cargo cache --remove-dir all
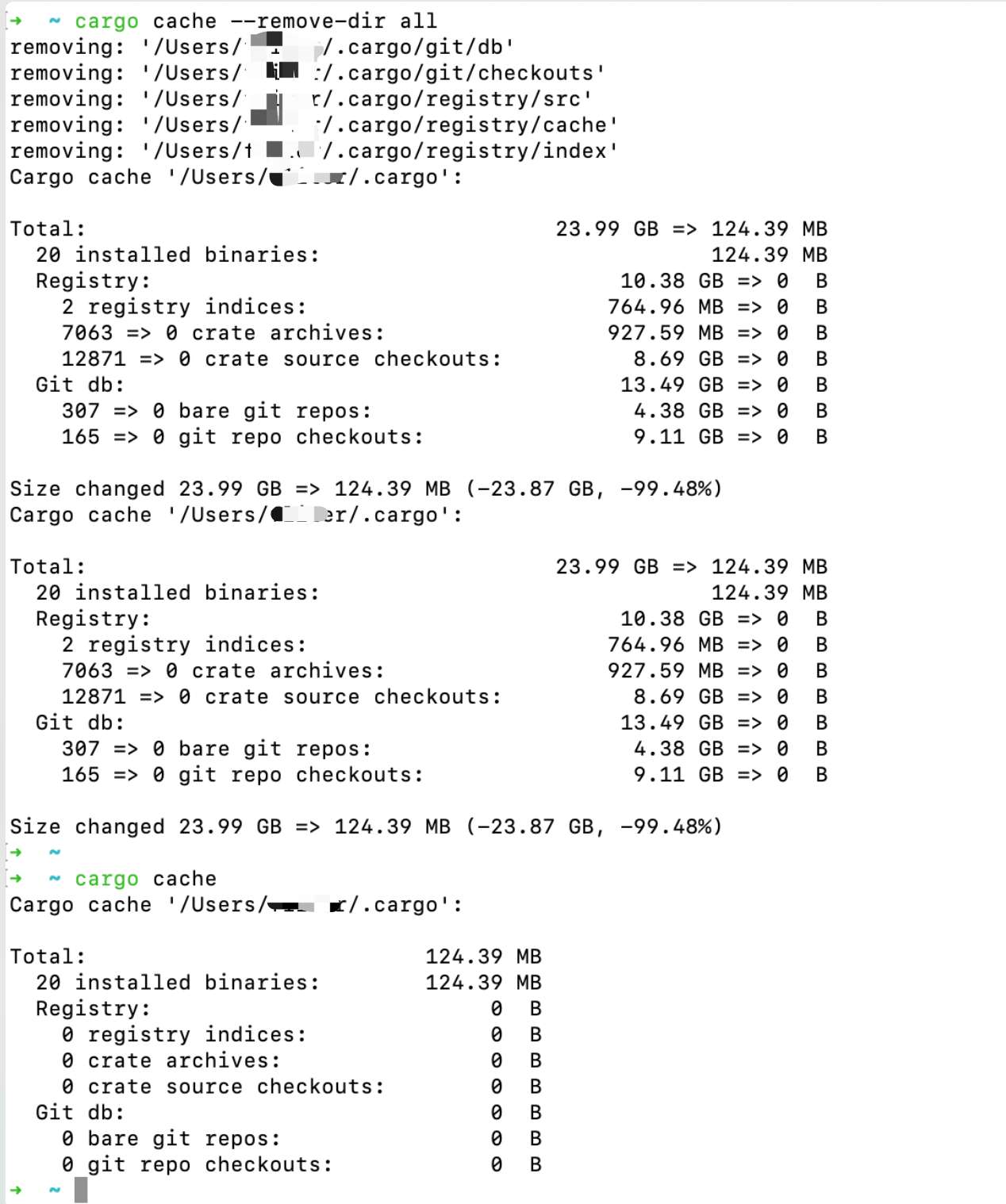
这是一把梭哈,还可以通过子命令,清理特定类型的缓存,清理超过x天没有使用的缓存等。
详细命令:
cargo cache -help
cargo-cache 0.8.3
matthiaskrgr
Manage cargo cache
USAGE:
cargo cache [OPTIONS] [SUBCOMMAND]
OPTIONS:
-a, --autoclean
Removes crate source checkouts and git repo checkouts
-e, --autoclean-expensive
As --autoclean, but also recompresses git repositories
-f, --fsck
Fsck git repositories
-g, --gc
Recompress git repositories (may take some time)
-h, --help
Print help information
-i, --info
Print information cache directories, what they are for and what can be safely deleted
-k, --keep-duplicate-crates <N>
Remove all but N versions of crate in the source archives directory
-l, --list-dirs
List all found directory paths
-n, --dry-run
Don't remove anything, just pretend
-o, --remove-if-older-than <date>
Removes items older than specified date: YYYY.MM.DD or HH:MM:SS
-r, --remove-dir <dir1,dir2,dir3>
Remove directories, accepted values: all,git-db,git-repos,
registry-sources,registry-crate-cache,registry-index,registry
-t, --top-cache-items <N>
List the top N items taking most space in the cache
-V, --version
Print version information
-y, --remove-if-younger-than <date>
Removes items younger than the specified date: YYYY.MM.DD or HH:MM:SS
SUBCOMMANDS:
clean-unref remove crates that are not referenced in a Cargo.toml from the cache
help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
l check local build cache (target) of a rust project
local check local build cache (target) of a rust project
q run a query
query run a query
r query each package registry separately
registry query each package registry separately
sc gather stats on a local sccache cache
sccache gather stats on a local sccache cache
toolchain print stats on installed toolchains
trim trim old items from the cache until maximum cache size limit is reached
verify verify crate sources
另:
cargo-cache 是一个第三方工具,关于如何自己写一个cargo xxx命令可参考 Cargo的自定义命令扩展功能
好处是方便快捷,坏处是很难区分该命令是官方提供还是来自第三方,是否有安全隐患。
另外当Mac磁盘不够用时,重点”关照“以下目录的一些文件:
- ~/Library/Caches
- ~/Library/Logs
- ~/Library/Containers
- ~/Library/Cookies
