Algo-Lab 2 Stack Queue ADT
Lab 2: Stack & Queue ADT
Part 1
这里只说一下最小栈的思路,我们可以在定义一个栈,来同步存储当前情况下的占的最小值。最小栈第一时间的想法可能是设定一个变量,每次push进来栈中的元素进行对比,保持最小值,但是这样做并没有考虑到如果POP时的各种情况。因此,我们设置一个最小值的栈,他和存储的栈同步Push和Pop,只是,它每次push 的是栈目前存储的元素中的最小的值,这样就解决了 Pop 后的最小值问题了。
public class StackMin<AnyType extends Comparable<AnyType>> implements StackInterface<AnyType> {
private static final int MAX_SIZE = 1024;
private AnyType[] xstack;
private AnyType[] minstack;
private int size;
public StackMin() {
this.xstack = (AnyType[]) new Object[MAX_SIZE];
this.minstack = (AnyType[]) new Object[MAX_SIZE];
this.size = 0;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return this.size;
}
@Override
public AnyType pop() throws EmptyStackException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
return this.xstack[--this.size];
}
@Override
public AnyType peek() throws EmptyStackException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
return this.xstack[this.size - 1];
}
@Override
public void push(AnyType item) {
if (this.size < MAX_SIZE) {
this.xstack[this.size++] = item;
if (size == 0 || item.compareTo(this.minstack[size - 1]) < 0) {
this.minstack[this.size] = item;
} else {
this.minstack[this.size] = this.minstack[size - 1];
}
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
this.size = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
public AnyType findMin() {
return this.minstack[this.size - 1];
}
}
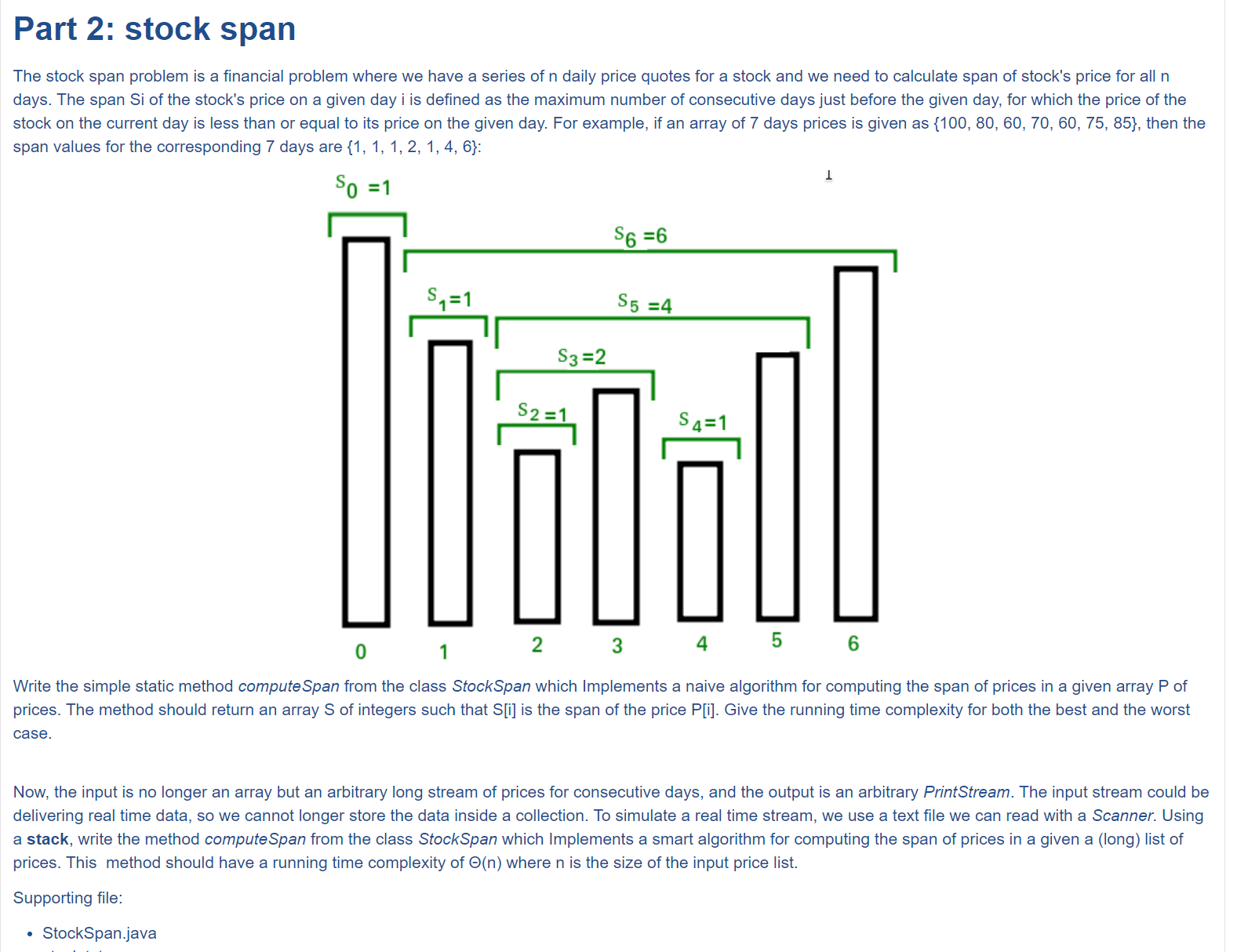
Part 2
这个题目的主要思想是,寻找第一个比自己小的数距离,从暴力的角度来想,我每次遍历一个数字,就从这个数向前遍历,直到遇到比自己大的数为止,这样的时间复杂度是n方;考虑优化的话,可以进一步想到,如果前面的数比自己小,那么它的结果的距离范围的数字都会比自己小,则可以剪枝一部分遍历的时间;我们可以进一步的优化,设置一个栈,如果当前元素小于栈顶元素,则索引的距离即为所求;如果当前元素比栈顶元素值大的时候,则一直Pop出站,直到栈顶元素更大的时候,这时,两者的索引距离就是范围。下面是两种情况下的代码,一种是直接给了完整的数组可以查询的,一种是等待输入流随时输入随时输出的。
/**
* Simple computeSpan static function
* working on arrays
*/
public static int[] computeSpan(int[] input) {
int len = input.length;
int[] spans = new int[len];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && input[stack.peek()] <= input[i]) {
stack.pop();
}
spans[i] = (stack.isEmpty()) ? (i + 1) : (i - stack.peek());
stack.push(i);
}
return spans;
}
/**
* Compute the span of the input values
* using a stack.
* Complexity: THETA(n) where is n is the
* number of values to compute the span of
*/
public void computeSpan() {
Stack<Integer> priceStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> indexStack = new Stack<>();
int day = 0;
while (input.hasNextInt()) {
int price = input.nextInt();
int span = 1;
while (!priceStack.isEmpty() && priceStack.peek() <= price) {
priceStack.pop();
indexStack.pop();
}
if (indexStack.isEmpty()) {
span = day + 1;
} else {
span = day - indexStack.peek();
}
priceStack.push(price);
indexStack.push(day);
output.printf("value: %d span: %d\n", price, span);
day++;
}
}
Part 3
用链表写一个队列就不说了,寻找pair,浅谈一下,暴力的话,n方的复杂度依次遍历;优化的话,放在哈希表中,减去O(n)的查询的复杂度
public static void showPairs(int n, String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException, EmptyQueueException {
ListQueue<Integer> queue = new ListQueue<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(new File(fileName));
while (scanner.hasNextInt()) {
queue.offer(scanner.nextInt());
}
scanner.close();
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int index = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer num = queue.poll();
if (map.containsKey(num - n)) {
System.out.println("(" + (num - n) + "," + num + ")");
}
map.put(num, index++);
}
}
Part 4
用栈来写一个队列,思路也很简单,使用两个栈,一个输入,一个输出,当输出栈为空时,将输入栈的值全部压到输出栈中
package tiei.aads.adt;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* A class for queues implemented with stacks
*/
public class StackQueue<AnyType> implements QueueInterface<AnyType> {
private Stack<AnyType> instack = new Stack<>();
private Stack<AnyType> outstack = new Stack<>();
@Override
public int size() {
return this.instack.size() + this.outstack.size();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.instack.isEmpty() && this.outstack.isEmpty();
// return QueueInterface.super.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public void offer(AnyType item) {
this.instack.push(item);
}
@Override
public AnyType poll() throws EmptyQueueException {
if(this.outstack.isEmpty()){
while (this.instack.isEmpty()){
this.outstack.push(this.instack.pop());
}
}
return outstack.pop();
}
@Override
public AnyType peek() throws EmptyQueueException {
if(this.outstack.isEmpty()){
while (this.instack.isEmpty()){
this.outstack.push(this.instack.pop());
}
}
return outstack.peek();
}
}
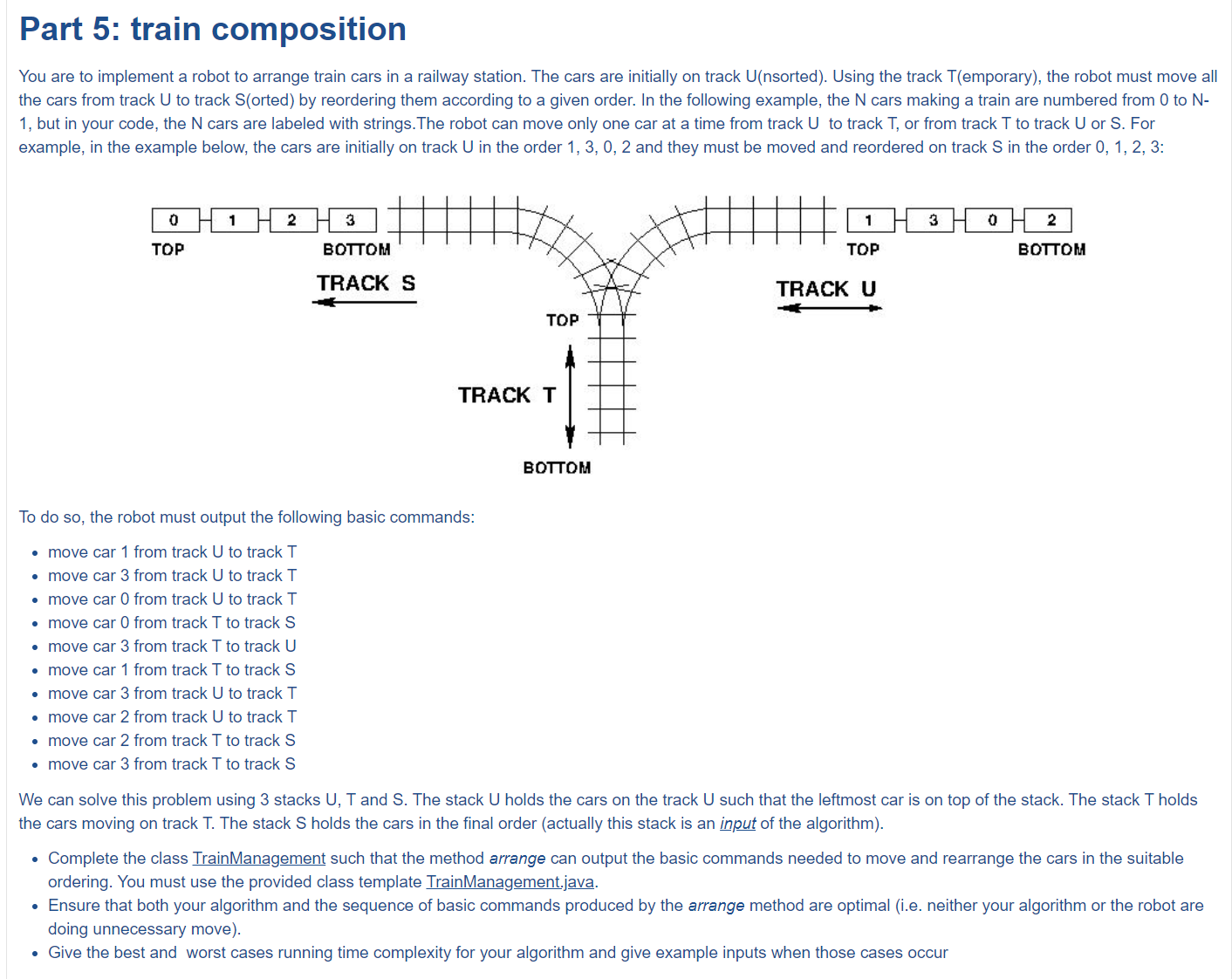
Part 5
是一个经典的T形火车问题,主要思路就是,使用一个Map,存储下一个目标火车所在的栈,然后依次将不是目标的元素存储到另一个栈中(因为你需要考虑最简洁的移动方式,所以需要精准找到目标火车的位置;如果不需要最简洁的要求,完全可以在两个栈中依次寻找就跟我下面还没有优化完全的代码一样)(过段时间我一定改)
package tiei.aads.adt;
import java.util.*;
/**
* A class to arrange train configuration
*/
public class TrainManagement {
private String[] from; // the initial ordering
private String[] to; // the final ordering
private StackInterface<String> U; // to hold the cars on track U(nsorted)
private StackInterface<String> T; // to hold the cars on track T(emporary)
private StackInterface<String> S; // to hold the cars on track S(orted)
private Map<String, StackInterface<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
/**
* Build a TrainManagement object
* Preconditions:
* 'from' and 'to' have the same size N and are
* both permutations of each other
*/
public TrainManagement(String[] from, String[] to) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
U = new ArrayStack<>();
T = new ArrayStack<>();
S = new ArrayStack<>();
for (int i = from.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
U.push(from[i]);
map.put(from[i], U);
}
}
/**
* Output the basic move commands to transfer
* the cars from the 'from' order on track U
* to the 'to' order on track S
*/
public void arrange() throws EmptyStackException {
int toIndex = 0;
while (toIndex < to.length) {
String targetCar = to[toIndex];
boolean found = false;
while (!U.isEmpty()) {
String car = U.pop();
System.out.println("move car " + car + " from U to T");
T.push(car);
if (car.equals(targetCar)) {
found = true;
System.out.println("move car " + car + " from T to S");
T.pop();
toIndex++;
break;
}
}
while (!T.isEmpty() && !found) {
String car = T.pop();
System.out.println("move car " + car + " from T to U");
U.push(car);
}
}
}
/**
* A short main for quick testing
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws EmptyStackException {
String[] from = {"33", "11", "44", "22"};
String[] to = {"11", "22", "33", "44"};
TrainManagement tm = new TrainManagement(from, to);
tm.arrange();
}
// expected output
//
// move car 33 from U to T
// move car 11 from U to T
// move car 11 from T to S
// move car 44 from U to T
// move car 22 from U to T
// move car 22 from T to S
// move car 44 from T to U
// move car 33 from T to S
// move car 44 from U to T
// move car 44 from T to S
}
