Vue和axios零基础学习
Vue的配置与项目创建
在这之前要先安装nodejs
安装脚手架
官网
Home | Vue CLI (vuejs.org)
先运行,切换成淘宝镜像源,安装速度更快
npm config set registry http://registry.npm.taobao.org

创建项目
用编译器打开一个空文件,在终端输入创建代码

以下是步骤



选择N



运行结果

配置serve
配置完以下,就可以改动代码,效果实时更新到页面上,对于开发来说很方便。
但只有社区版idea在这里才有npm可以选


模板语法
绑值语法

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
<div>
<!-- {{num++}},不要这么写,别在这里运算,否则可能出错 -->
{{num}}
</div>
<div>{{bool}}</div>
<div>{{ arr.find(v => v.name === '张三')?.age }}</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.16/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',//element
//把vue的实例绑定到id是app的上面
//
data: {
message: 'Hello I\'m lmm',
num: 1,
bool: true,
arr: [{ name: '张三', age: 20 }]
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
渲染html(v-html)

<template>
<div>
<div>{{rowHtml}}</div>
<div v-html="rowHtml"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'test',
data(){
return{
rowHtml: '<a href="https://www.taobao.com/">淘宝</a>'
}
}
}
</script>
可以看到绑值语法是不能渲染出链接的

绑定属性(v-bind)


使用场景
1.绑定 HTML 属性
- 用于动态设置元素的属性,例如
href、src、class、id等。
<a v-bind:href="linkUrl">Click here</a>
<img v-bind:src="imageUrl" alt="Dynamic Image">
2.绑定多个属性
- 可以通过对象语法绑定多个属性。
<div v-bind="objectProps"></div>
export default {
data() {
return {
objectProps: {
id: 'my-div',
class: 'my-class',
title: 'This is a title'
}
}
}
}实例
<template>
<div>
<a :href="url">点击这里访问淘宝</a>
<br>
<img :src="img" alt="Demo Image">
<br>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import logo from '@/assets/logo.png';
export default {
name: 'test',
data() {
return {
url: 'https://www.taobao.com/',
// img: '@/asset/logo.png'
//注意要先导入才能用
img:logo
}
}
}
</script>

事件绑定(v-on)

快捷绑定
直接写在行内


绑定方法


<template>
<div>
<div :style="{ width: '100px', height: '100px', backgroundColor: color }" @click="changeColor" id="testColor">
点我
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'test',
data() {
return {
color: 'red' // 初始化颜色为红色
}
},
methods: {
changeColor() {
// 切换颜色
this.color = this.color === 'red' ? 'blue' : 'red';
}
}
}
</script>

判断(v-if)

如果为真,就渲染该内容
<template>
<div>
<div v-if="color === '红色'">红色</div>
<div v-else>黑色</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import logo from '@/assets/logo.png';
export default {
name: 'test',
data() {
return {
color:'黑色'
}
}
}
</script>


列表渲染(v-for)



每个元素都要有唯一索引,绑定key
在实际开发中,每个元素都有写好的索引,所以用不上index。
如果没有的话,就用index来记录
<template>
<div v-for="item in fruits">{{item}}</div>
<div v-for="item in user" :key="item.id">用已写好的索引:{{key}}{{item.name}}</div>
<div v-for="(item,index) in user" :key="index">用系统分配的索引:{{key}}{{item.name}}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'test',
data() {
return {
fruits:['苹果','香蕉','西瓜'],
user:[
{
id:'1001',
name:'alicia'
},
{
id:'1002',
name:'fafa'
},
{
id:'1003',
name:'cami'
}
]
}
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>

双向绑定(v-model)


<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="str">
<p>{{str}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'test',
data() {
return {
str:''
}
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>



组件基础

scoped:如果在style中添加此属性,就代表着,当前样式,只在当前组件中生效
使用组件步骤


组件的组织

上图想表达的是,组件间的使用是可以嵌套的
Props组件交互
prop可以使组件之间有数据传递

使用案例
父组件向子组件传递数据。被导入的组件是父组件。
App.vue 组件(父组件):
<template>
<div id="app">
<Test :age="age" :name="name" :arr="arr"></Test>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Test from "@/components/test";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Test
},
data() {
return {
age: 18,
name: 'chen',
arr: [1, 2, 3]
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
test.vue 组件(子组件):
<template>
<p>props传递数据</p>
<div>{{ age }}</div>
<div>{{ name }}</div>
<div v-for="i in arr" :key="i">{{ i }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Test',
props: {
age: {
type: Number,
default: 0
},
name: {
type: String,
default: ''
},
arr: {
type: Array,
default: function () {
return [];
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
/* 添加样式 */
</style>
Prop类型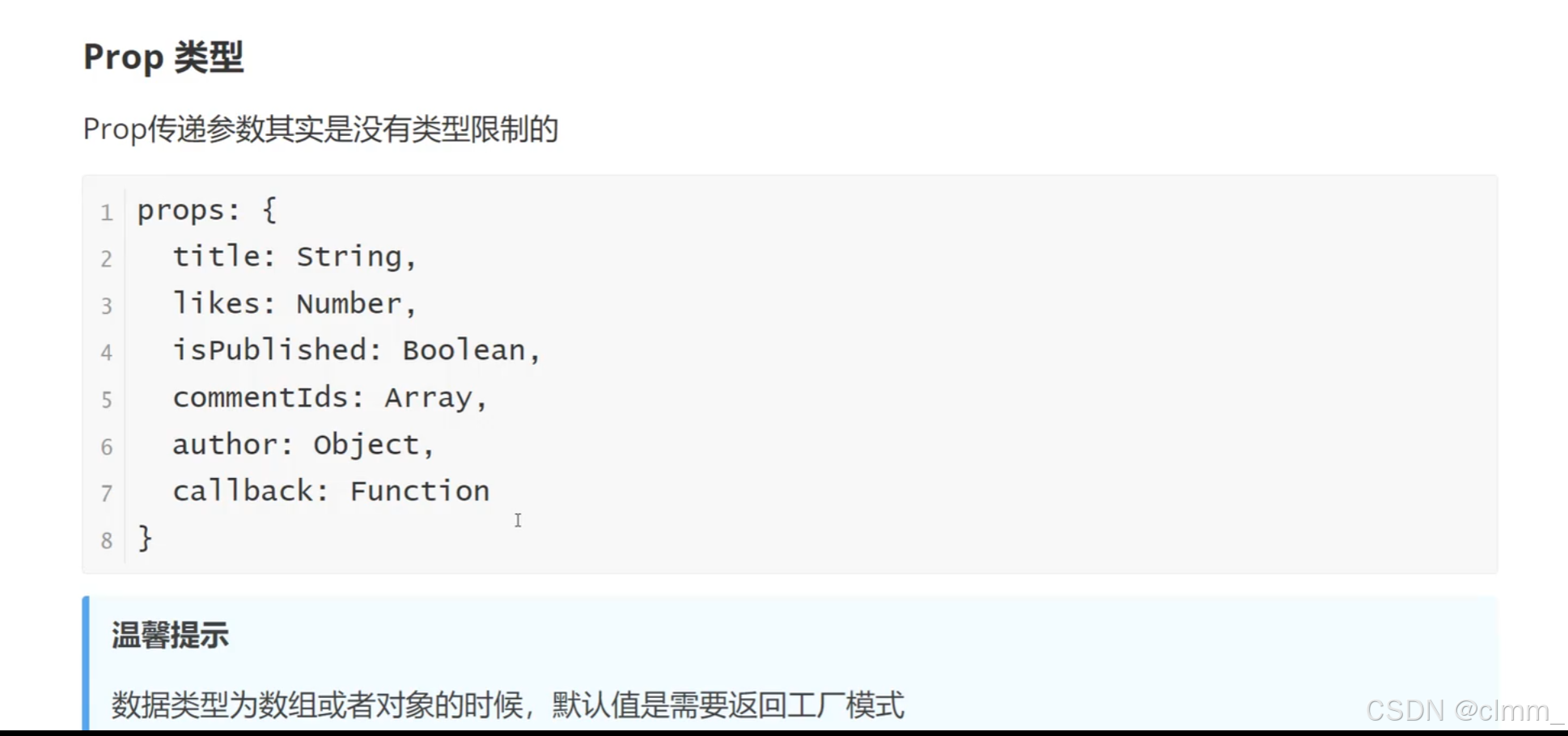
需要注意的是,传递数组和对象必须使用函数进行返回

自定义事件组件交互
自定义事件是 Vue 中子组件与父组件进行交互的一种灵活方式。子组件可以通过
this.$emit触发事件,父组件则通过事件监听器来处理这些事件。这样可以让组件之间的通信更加模块化和清晰。自定义事件可以在组件中反向传递数据,prp可以将数据从父组件传递到子组件,那么反向如何操作呢,就可以利用自定义事件实现
$emit
子组件向父组件传递数据。被导入的组件是父组件。
子组件
<template>
<button @click="sendMsg">点击传递数据</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Test',
data(){
return{
msg:'子组件向父组件传递数据'
}
},
methods:{
sendMsg(){
this.$emit('onEvent',this.msg)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
/* 添加样式 */
</style>
父组件
<template>
<div id="app">
<Test @onEvent="getMsg"></Test>
<div>{{msg}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Test from "@/components/test";
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
msg:''
}
},
components: {
Test
},
methods:{
getMsg(data){
this.msg = data
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>

组件生命周期

生命周期概述
Vue 组件的生命周期可以分为以下几个阶段:
- 创建阶段
- 挂载阶段
- 更新阶段
- 销毁阶段
每个阶段都有特定的生命周期钩子函数,你可以在这些钩子函数中执行相应的逻辑。
1. 创建阶段
-
beforeCreate: 在实例被初始化之后,数据观测和事件配置之前调用。这时data和methods还不可用。 -
created: 实例已创建,数据观测和事件配置完成。这时可以访问data、methods和computed,但 DOM 还未生成。
2. 挂载阶段
-
beforeMount: 在挂载开始之前被调用,render函数首次被调用。这时模板已经编译,但尚未被渲染到 DOM 中。 -
mounted: 挂载完成后调用,此时组件已经被渲染到 DOM 上。可以访问 DOM 元素和进行 DOM 操作。网络请求是放在这块。因为元素被渲染出来之后,还需要向后台请求数据。
3. 更新阶段
-
beforeUpdate: 数据更新之前调用,render函数将被重新调用。这时你可以在 DOM 更新之前做一些处理。 -
updated: 数据更新之后调用,此时 DOM 也已经更新。可以执行一些依赖于 DOM 更新的操作。
4. 销毁阶段
-
beforeUnmount: 卸载之前调用,此时组件仍然可以访问其数据和 DOM。 -
unmounted: 卸载完成后调用,此时组件及其所有的子组件都已经被销毁。可以在这里进行清理工作,比如清除定时器、取消网络请求等。

axios
安装与引入

常用请求方法

如果不写的话,默认是get
查询参数(get)

<template>
<div>
{{data}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Test',
data(){
return{
data:{}
}
},
mounted(){
this.$axios({
url: 'http://hmajax.itheima.net/api/city',
//查询参数
params: {
pname: '福建省'
}
}).then(result => {
this.data = result
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
/* 添加样式 */
</style>

数据提交(post)


<template>
<div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Test',
mounted(){
this.$axios({
url: 'http://hmajax.itheima.net/api/register',
method: 'post',
data: {
username: 'clmm1234567',
password: '123123'
}
}).then(result => {
console.log(result)
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
/* 添加样式 */
</style>
总结

网络请求封装
vue路由
了解



学到了路由,那么记得创建vue项目的时候把router选上,会自动配置路由文件

App.vue
<template>
<div>
<router-link to="/">首页</router-link>|
<router-link to="/about">关于</router-link>
<div>123</div>
<router-view></router-view>
<div>321</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import Test from "@/components/Test.vue";
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
// Test
},
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
index.js
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router';
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView';
import AboutView from '../views/AboutView';
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: AboutView
}
];
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes
});
export default router;
main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
import router from './router';
import axios from 'axios';
// 创建 Vue 应用实例
const app = createApp(App);
// 配置 axios 实例
app.config.globalProperties.$axios = axios;
// 使用路由
app.use(router);
// 挂载应用
app.mount('#app');
路由传递参数

router配置
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router'
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView'
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/AboutView.vue')
},
{
path:'/news',
name:'news',
component: ()=>import("../views/NewsView")
},
{
path:'/newsDetail/:name',
name:'newsDetail',
component: ()=>import("../views/NewsDetailView")
},
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes
})
export default router
NewView
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<li><router-link to="/newsDetail/网易">网易新闻</router-link></li>
<li><router-link to="/newsDetail/百度">百度新闻</router-link></li>
<li><router-link to="/newsDetail/猾伪">猾伪新闻</router-link></li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "NewsView"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>NewsDetailView
<template>
<div>
<h3>新闻</h3>
{{$route.params.name}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "NewsDetailView"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>嵌套路由配置

index.js
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router'
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView.vue'
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/AboutView.vue'),
redirect:'/about/b',
children: [
{
path: 'a',
component: () => import('../views/AboutSub/About_a')
},
{
path: 'b',
component: () => import('../views/AboutSub/About_b')
}
]
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes
})
export default router
AboutView.vue
<template>
<div class="about">
<router-link to="/about/a">a | </router-link>
<router-link to="/about/b">b</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
<h1>This is an about page</h1>
</div>
</template>
点进about页面默认是about_b,因为重定向了

Vue状态管理

可以集中管理所有组件,不像props只能在父子间传递数据
引入状态管理
创建项目的时候勾选vuex

如果在创建项目的时候已勾选vuex,下面的前三步就不用了



vue状态管理核心





案例--面经基础

配置路由
先做一个底部导航切换效果。
配置路由
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
const routes = [
{
path:'/',
component:()=>import('@/views/LayOut'),
children:[
{
path:'/collect',
component:()=>import('@/views/Collect')
},
{
path:'/like',
component:()=>import('@/views/Like')
},
{
path:'/user',
component:()=>import('@/views/User')
},
{
path:'/articleList',
component:()=>import('@/views/ArticleList')
},
]
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(process.env.BASE_URL),
routes
})
export default router
<template>
<div>
<div style="background-color: pink; width: 500px; height: 500px;">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<nav>
<router-link to="/articleList">面经 |</router-link>
<router-link to="/collect">收藏 |</router-link>
<router-link to="/like">喜欢 |</router-link>
<router-link to="/user">我的</router-link>
</nav>
</div>
</template>
<style>
a.router-link-active{
color: red;
}
</style>
需要注意的是,Layout中需要用router-view
Layout组件作为一个包裹组件使用,这意味着它可能需要呈现其子路由内容。Layout中的<router-view>组件用于展示其子路由(如/article、/like等)。这使得每个子路由在Layout组件内部渲染,同时Layout组件可以包含共同的布局或导航条。简而言之,
Layout中的<router-view>用于渲染Layout的子路由组件内容。这样,你可以在Layout组件中管理应用的布局和结构,同时动态展示不同的子视图。
<template>
<div>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Layout"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>首页请求渲染



<template>
<div>
<div v-for="item in articles"
:key="item.id"
>
<p>{{item.stem}}</p>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
export default {
name: "ArticleList",
data(){
return{
articles:[]
}
},
async created(){
const { data } = await axios.get(
'https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles',
);
this.articles = data.result.rows;
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
跳转详情页传参
查询参数
动态路由
路由配置
{
path:'/detail/:id',
component:() => import('@/views/ArticleDetail')
}路由使用
@click="$router.push(`/detail/${item.id}`)"
<template>
<div>
<div v-for="item in articles"
:key="item.id"
@click="$router.push(`/detail/${item.id}`)"
>
<p>{{item.stem}}</p>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
export default {
name: "ArticleList",
data(){
return{
articles:[]
}
},
async created(){
const { data } = await axios.get(
'https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles',
);
this.articles = data.result.rows;
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>面经详情页的路由接收
this.$route.params.id
<template>
<div>
面经详情
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ArticleDetail",
created() {
console.log(this.$route.params.id)
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>详情页渲染

<template>
<div>
{{article.content}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
export default {
name: "ArticleDetails",
data(){
return{
article:{}
}
},
async created() {
const id = this.$route.params.id
console.log(this.$route.params.id)
const {data} = await axios.get(`https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles/${id}`)
this.article = data.result
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
组件缓存







