springboot系列--web相关知识探索二
一、映射
指的是与请求处理方法关联的URL路径,通过在Spring MVC的控制器类(使用@RestController注解修饰的类)上使用注解(如
@RequestMapping、@GetMapping)来指定请求映射路径,可以将不同的HTTP请求映射到相应的处理方法上。说白了就是将具体的请求映射到具体的接口当中。
二、springboot对Rest风格的支持
springboot默认情况下是支持Rest风格,但是唯独对表单类型的请求例外。表单情况下提交请求,无论你的method是put还是delete都会变成get请求。如果想要在表单类型下使用rest风格请求方式,需要把表单method属性设置为post,隐藏域设置为_method=put,这个时候请求才会进入到put类型的接口当中。
隐藏域:<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete">
原理:
表单提交以后,会被springboot中的OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter组件拦截,当然前提是开启了这个组件,不然表单也无法使用rest风格请求。OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter是继承HiddenHttpMethodFilter,请求会打到这个类的doFilterInternal方法上。该方法原理如下:
spring:
mvc:
hiddenmethod:
filter:
enabled: true #开启页面表单的Rest功能
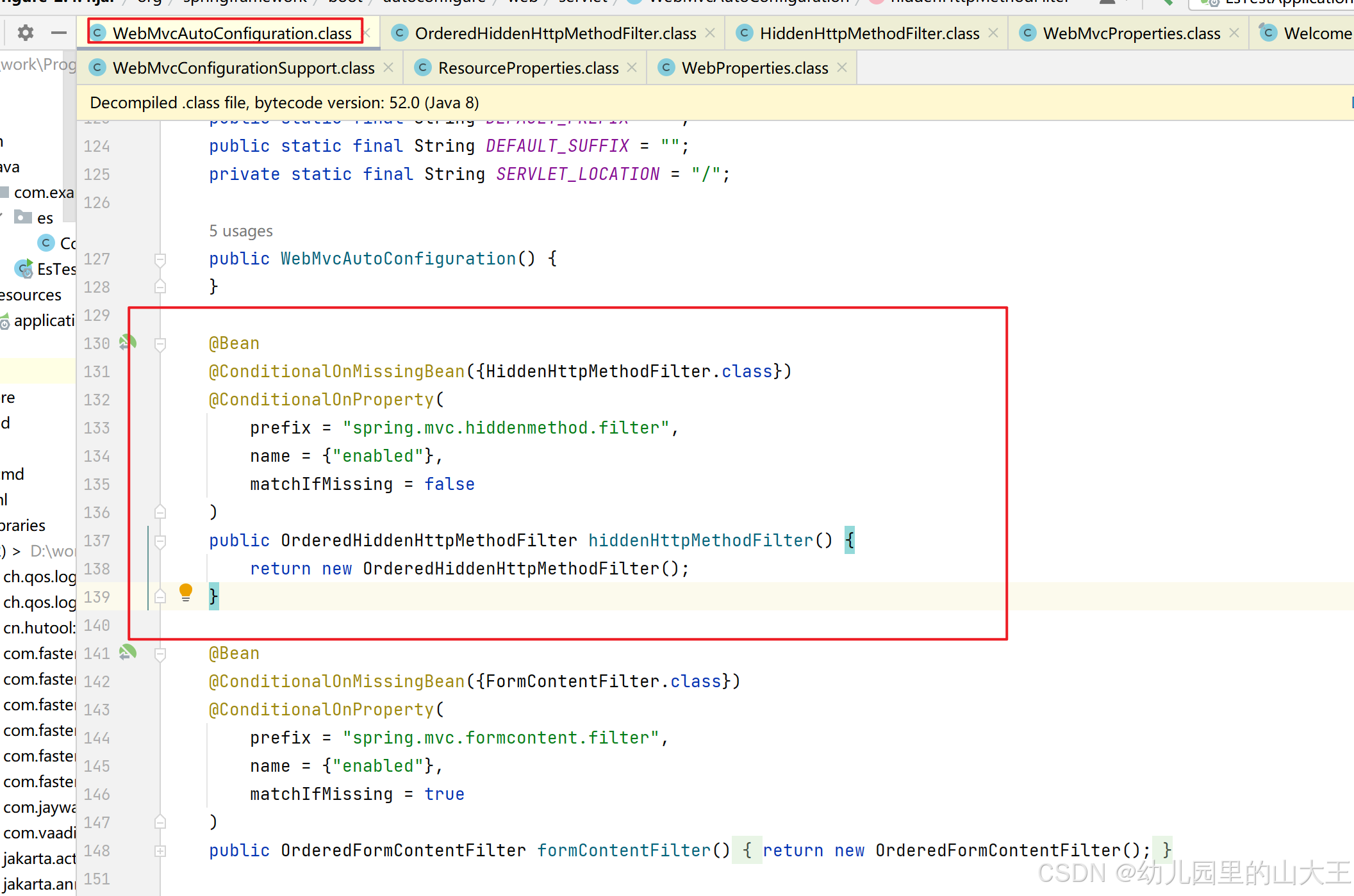
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request;
// 只有post请求才会打到这里,所以表单请求必须是post
if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.exception") == null) {
// 请求需要带this.methodParam对应的是_method,paramValue 对应的是具体的请求类型
String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);
// 不为空的时候才进去处理
if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) {
String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
// ALLOWED_METHODS 包含delete、put、patch等类型,也就是说隐藏域所带的值必须是这几个
if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) {
// 这里就是对原始请求进行包装,将隐藏域的值作为新的请求类型。包装了原生请求的HttpMethodRequestWrapper类重写了getMethod方法,返回的是传入的method
requestToUse = new HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method);
}
}
}
filterChain.doFilter((ServletRequest)requestToUse, response);
}
static {
ALLOWED_METHODS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(HttpMethod.PUT.name(), HttpMethod.DELETE.name(), HttpMethod.PATCH.name()));
}// 包装了原生请求的类
private static class HttpMethodRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private final String method;
// 将外部的method重新赋值进来
public HttpMethodRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request, String method) {
super(request);
this.method = method;
}
// 重写了getMethod,返回的是外部赋予的值
public String getMethod() {
return this.method;
}
}表单提交指定了隐藏域需要带_method为key,值为put、patch、delete等参数,才能修改成符合rest风格请求。这是由于key="_method",是在底层源码写死了的。
public class HiddenHttpMethodFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private static final List<String> ALLOWED_METHODS;
public static final String DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM = "_method";
// 此处写死了隐藏域key必须为_method
private String methodParam = "_method";
public HiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
}
public void setMethodParam(String methodParam) {
Assert.hasText(methodParam, "'methodParam' must not be empty");
this.methodParam = methodParam;
}
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request;
if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.exception") == null) {
String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) {
String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) {
requestToUse = new HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method);
}
}
}
filterChain.doFilter((ServletRequest)requestToUse, response);
}
static {
ALLOWED_METHODS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(HttpMethod.PUT.name(), HttpMethod.DELETE.name(), HttpMethod.PATCH.name()));
}
private static class HttpMethodRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private final String method;
public HttpMethodRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request, String method) {
super(request);
this.method = method;
}
public String getMethod() {
return this.method;
}
}
}
如果想要修改,可以重写这个组件。
//自定义filter
@Bean
public HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter(){
HiddenHttpMethodFilter methodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter();
// 这个时候,key就必须等于_test了
methodFilter.setMethodParam("_test");
return methodFilter;
}三、请求映射原理
springmvc中所有的请求都是会先经过DispatcherServlet(前端控制器)这个类,这个类的其中一个父类HttpServlet,这个类有几个方法,doGet、doPost、doPut、doDelete,就是最原始处理get、put等请求的方法,HttpServlet是一个抽象类,这些方法是在FrameworkServlet中实现的。
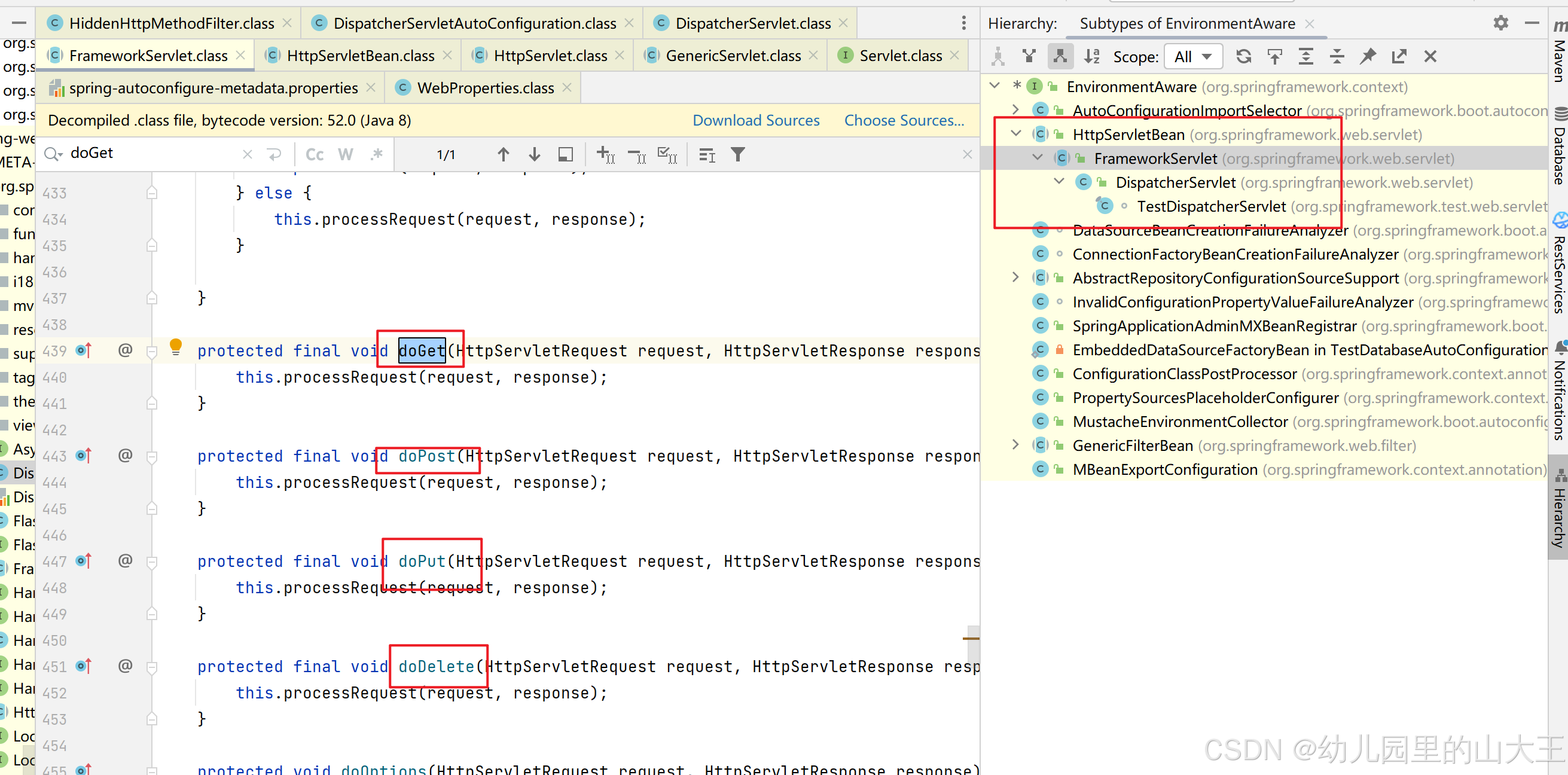
里面每一个doGet、doPost等方法都调用了processRequest这个方法。
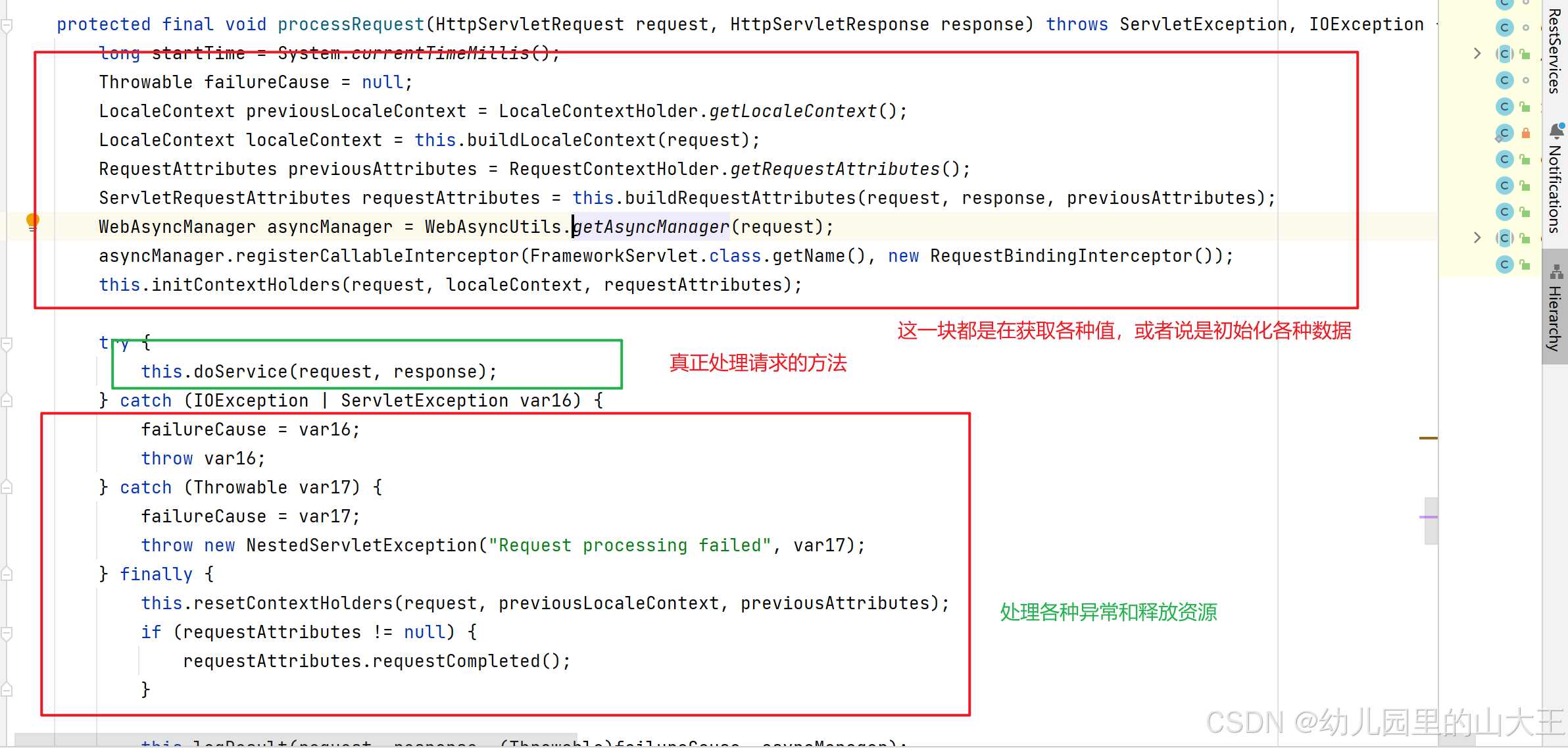
FrameworkServlet类中的这个方法是一个抽象方法,
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest var1, HttpServletResponse var2) throws Exception;所以需要看它的子类DispatcherServlet里面的doService方法。这个方法调用了doDispatch这个方法,每个请求进来都是调用到它。
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
this.logRequest(request);
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
label104:
while(true) {
String attrName;
do {
if (!attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
break label104;
}
attrName = (String)attrNames.nextElement();
} while(!this.cleanupAfterInclude && !attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet"));
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, this.getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath)request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
// 这行代码之前,其实大部分逻辑都是初始化设置各种值,doDispatch就是做各种转发
this.doDispatch(request, response);
} finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted() && attributesSnapshot != null) {
this.restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
下面是doDispatch源码以及一些与原理
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 找到当前请求使用哪个Handler(Controller的方法)处理
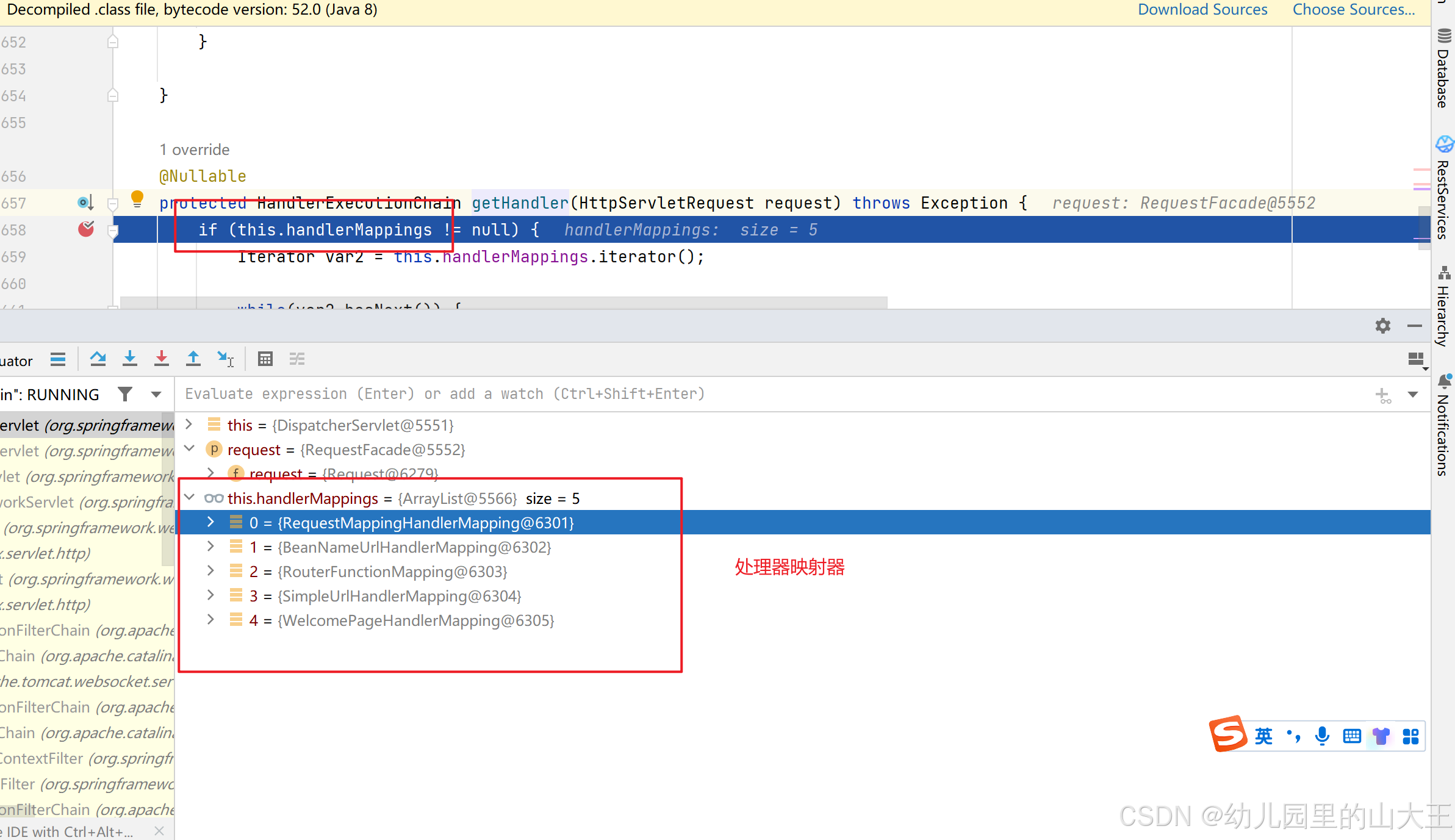
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
//HandlerMapping:处理器映射。 @Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 循环遍历每个处理器映射器
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
Iterator var2 = this.handlerMappings.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
// 处理请求的处理器映射器RequestMappingHandlerMapping
HandlerMapping mapping = (HandlerMapping)var2.next();
// 通过url获取到具体的处理器映射器
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
1、this.handlerMappings != null中handlerMappings就是springboot所有的处理器映射器。2、其中RequestMappingHandlerMapping:保存了所有@RequestMapping 和handler的映射规则。其实就是保存了@RequestMapping中配置的各种url和对应的controller
3、 所有的请求映射都在HandlerMapping中。然后通过HandlerMapping找到请求url对应的具体的controller。
4、SpringBoot自动配置欢迎页的 WelcomePageHandlerMapping 。访问 /能访问到index.html;
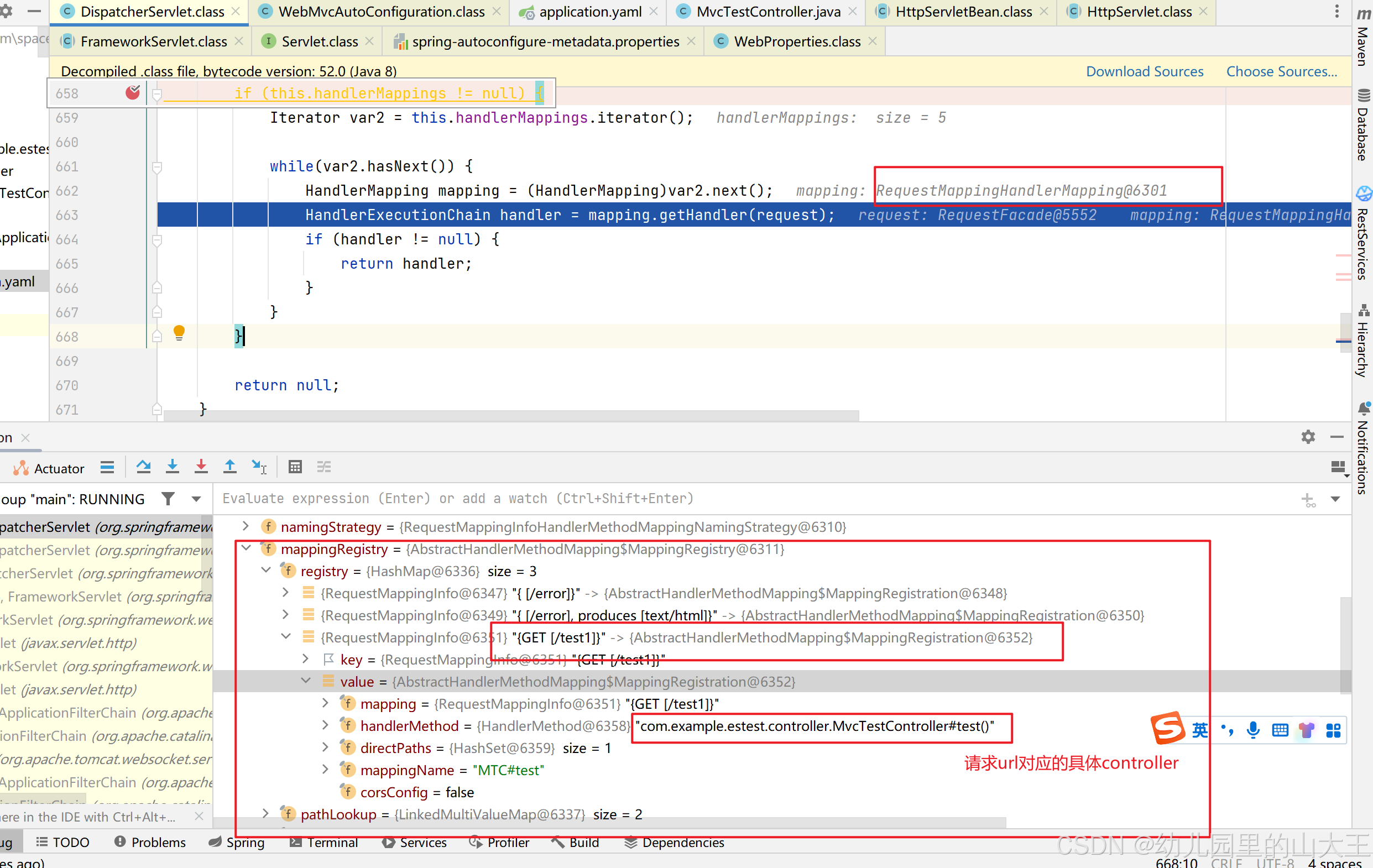
springboot底层通过url获取到具体的controller原理,需要从
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
这个方法进入


protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 获取@GetMapping("/test1")上的请求路径/test1
String lookupPath = this.initLookupPath(request);
//mappingRegistry保存了所有的请求路径对应的controller信息,加锁是防止并发获取
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
HandlerMethod var4;
try {
// 根据url和请求信息,找到controller中对应能够处理的方法,其实就是具体的那个接口的信息
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = this.lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
var4 = handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null;
} finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
return var4;
}
// 这个方法主要是获取url请求路径
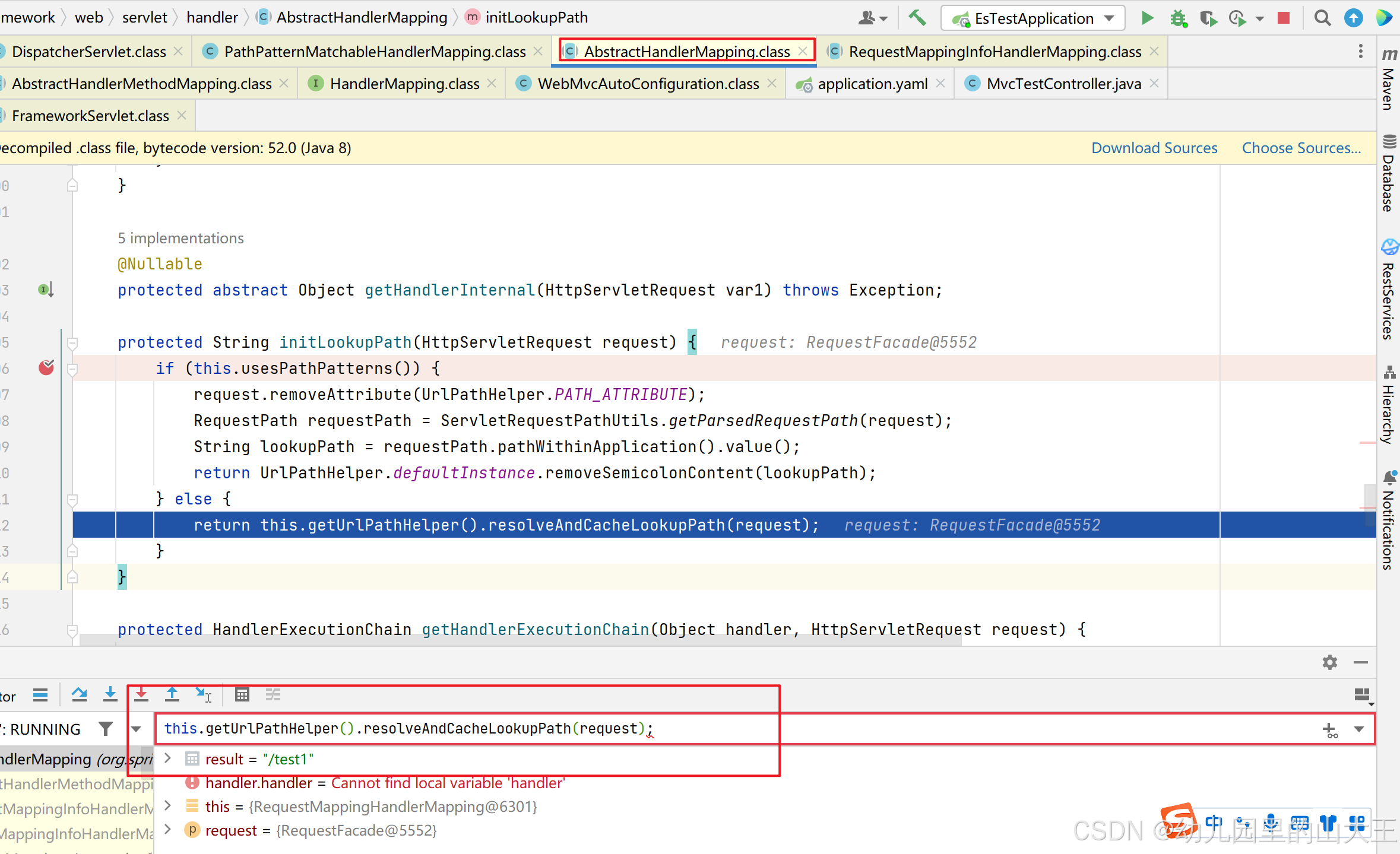
protected String initLookupPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (this.usesPathPatterns()) {
request.removeAttribute(UrlPathHelper.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
RequestPath requestPath = ServletRequestPathUtils.getParsedRequestPath(request);
String lookupPath = requestPath.pathWithinApplication().value();
return UrlPathHelper.defaultInstance.removeSemicolonContent(lookupPath);
} else {
// 请求进来是在这里处理的
return this.getUrlPathHelper().resolveAndCacheLookupPath(request);
}
}
/**
String lookupPath:注解上的请求路径
HttpServletRequest request:具体请求
**/
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match> matches = new ArrayList();
// 通过url找到多个个能够处理的接口或者说方法。比如说/test1可能会有put请求,也有get请求。post请求等等
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 找到了多个接口,就是添加到这个方法里,这个方法会根据你请求进来的方式(post、get或put等等)匹配到最优的处理方法,也就是精确找到你这个进来的请求方式所对应的处理接口。并且把匹配到的放到第一位且一般只有一个,具体不展开叙述
this.addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
this.addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
return this.handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
} else {
// 这里就是从上面保存符合条件的集合中获取第一个,一般只有一个,如果有两个,例如/test1 get请求,写了两个方法且请求方式,路径都一样,就matches.size() > 1就为true,然后会进入里面的处理逻辑并报错
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match bestMatch = (Match)matches.get(0);
// 就是这里
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(this.getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = (Match)matches.get(0);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
Iterator var7 = matches.iterator();
while(var7.hasNext()) {
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match match = (Match)var7.next();
if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
}
} else {
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T>.Match secondBestMatch = (Match)matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
// 有两个相同的url且请求方式一致的处理方法
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
this.handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
// 这里就是获取到具体的处理方法,也就是接口对应的方法,例如/test1 对应的是com.example.estest.controller.MvcTestController#test()这个接口,会返回com.example.estest.controller.MvcTestController#test()这个东西的具体信息
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
}
} 


1、另外SpringBoot自动配置了默认配置了一个处理器映射器就是 RequestMappingHandlerMapping用于处理@GetMapping、@PusMapping、@RequestMapping等注解的映射
2、如果需要一些自定义的映射处理,我们也可以自己给容器中放HandlerMapping。自定义 HandlerMapping。可以参考WebMvcAutoConfiguration类下的requestMappingHandlerMapping组件定义。
@Bean
@Primary
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping(@Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager, @Qualifier("mvcConversionService") FormattingConversionService conversionService, @Qualifier("mvcResourceUrlProvider") ResourceUrlProvider resourceUrlProvider) {
return super.requestMappingHandlerMapping(contentNegotiationManager, conversionService, resourceUrlProvider);
}
