Linux操作系统小项目——实现《进程池》
文章目录
- 前言:
- 代码实现:
- 原理讲解:
- 细节处理:
前言:
在前面的学习中,我们简单的了解了下进程之间的通信方式,目前我们只能知道父子进程的通信是通过匿名管道的方式进行通信的,这是因为这点我们就可以简简单单的来写一个项目————进程池
代码实现:
Task.hpp文件
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
class Channel
{
public:
Channel(int wfd, int child_process_id, std::string child_process_name)
: _wfd(wfd)
, _child_process_id(child_process_id)
, _child_process_name(child_process_name)
{}
~Channel(){}
int Get_wfd() { return _wfd;}
int Get_child_process_id() { return _child_process_id;}
std::string Get_child_process_name() { return _child_process_name;}
void CloseChannel() { close(_wfd); }
void Wait()
{
pid_t rid = waitpid(_child_process_id, nullptr, 0);
if (rid < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Filed to wait" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
std::cout << "Wait success!" << std::endl;
}
private:
int _wfd;
int _child_process_id;
std::string _child_process_name;
};
void task_print()
{
std::cout << "Hey! This is task_print" << std::endl;
}
void task_load()
{
std::cout << "Yo! This is task_load" << std::endl;
}
void task_flush()
{
std::cout << "Dude! This is task_flush" << std::endl;
}
typedef void (*task_ptr)(void); // function pointer
task_ptr task_arr[3]; // function pointer's array
void TaskLoad()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
task_arr[0] = task_print;
task_arr[1] = task_load;
task_arr[2] = task_flush;
std::cout << "Task are all be loaded!" << std::endl;
std::cout << "------------------------" << std::endl;
}
int ChoseTask()
{
int n = rand() % 3;
return n;
}
int PipeNumber(int times)
{
static int _pipe = 0;
int next = _pipe;
_pipe++;
_pipe %= times;
return next;
}
void WriteToPipe(int p_number, int t_number, std::vector<Channel> Channels)
{
static int i = 1;
int n = write(Channels[p_number].Get_wfd(), &t_number, sizeof(t_number));
if(n < 0)
{
std::cerr << "failed to write" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
std::cout << i++ << "->the number of task '" << t_number << "' have writen in pipe ' " << p_number << "' already" << std::endl;
}
void work(int rfd)
{
while(true)
{
sleep(1);
int file_buffer = 0;
int n = read(rfd, &file_buffer, sizeof(file_buffer));
if(n < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Failed to read" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
else if(n == 0)
{
std::cout << "child process : " << getpid() << " quit" << std::endl;
break;
}
task_arr[file_buffer]();
}
}
processpool.cc文件
#include "Task.hpp"
void CreateChannels(int nums, std::vector<Channel> *Channels)
{
for (int i = 0; i < nums; ++i)
{
// create pipe
int pipefd[2] = {0};
int n = pipe(pipefd);
if (n < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Failed to create pipe" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
// create child process
int pid = fork();
if (pid == 0)
{
// child
if (!Channels->empty())
{
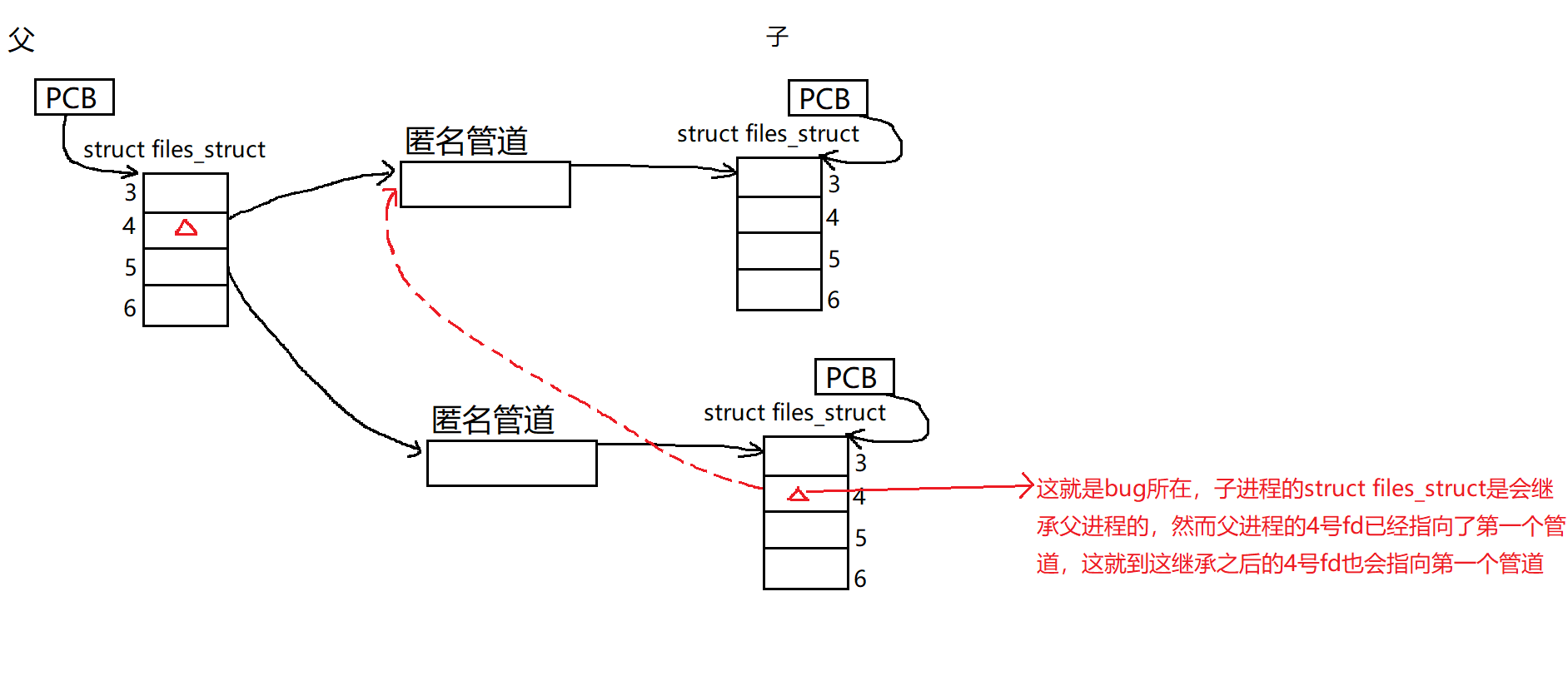
std::cout << "----Before I close my pipefd[1], I have to close the wfd which inherited by the father process's struct files_struct!" << std::endl;
for (auto &channel : *Channels)
channel.CloseChannel();
}
std::cout << "Here is child process!" << std::endl;
close(pipefd[1]); // as child process close unnecessary wfd
work(pipefd[0]);
close(pipefd[0]);
exit(0);
}
// father
std::string name = "Channel No.";
std::string Number = std::to_string(i);
name += i;
close(pipefd[0]); // as father process close unnecessary rfd
Channels->push_back({pipefd[1], pid, name});
}
}
void ControlChannels(int times, std::vector<Channel> Channels)
{
for (int i = 0; i < times; ++i)
{
sleep(1);
// chose pipe number to be writen in pipe
int pipe_number = PipeNumber(times);
// chose task number to write in pipe
int task_number = ChoseTask();
// write task number to the pointed pipe
WriteToPipe(pipe_number, task_number, Channels);
}
}
void CleanChannels(std::vector<Channel> Channels)
{
for (auto &channel : Channels)
{
channel.CloseChannel();
// channel.Wait();
}
// for (auto &channel : Channels)
// {
// channel.Wait();
// }
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc == 1)
{
std::cerr << "Need more argc! need more option!" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
int nums = std::stoi(argv[1]);
std::vector<Channel> Channels;
// load all the function
TaskLoad();
// 1、create channels and child process
CreateChannels(nums, &Channels);
// 2、control channels
ControlChannels(nums, Channels);
// 3、free channels and wait child process exit
CleanChannels(Channels);
// sleep(100);
return 0;
}
原理讲解:
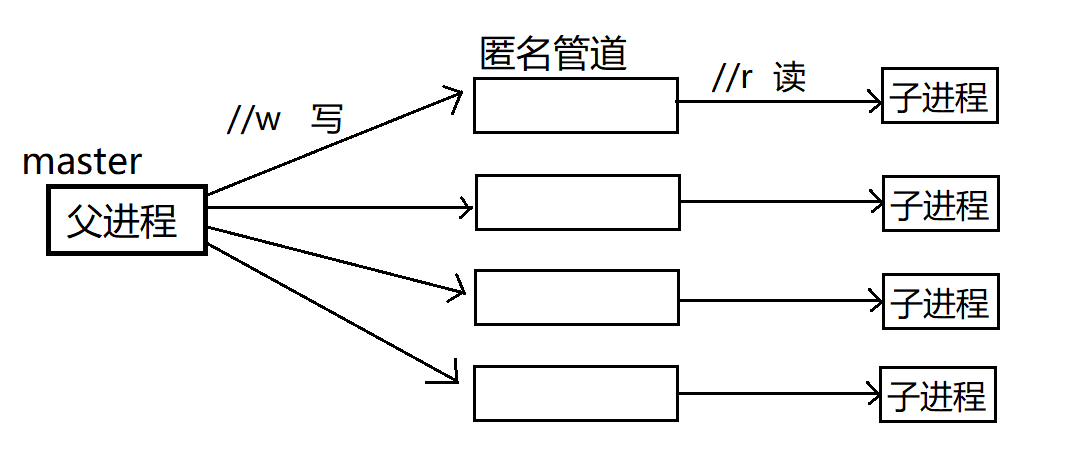
其实这个进程池项目通过画图就很好能做出来:
细节处理:
-
由图片可知,未来可能我们要实现很多个任务的时候完全可以采用进程池的方式来解决,与之前处理任务不同的是,以前我们是要执行一个任务就创建一个子进程,而这个不一样,现在是提前就已经开辟好了一堆子进程。
所以先提前创建好适量的子进程,有任务就交给子进程执行,这么做更适合多任务的并发操作,因为节省了创建子进程的操作。 -
未来master可以将任务发送至管道内部,以此来唤醒子进程来处理任务,但是要注意父进程不可针对的使用同一个管道,应当在多个管道直接轮询写入,这就保证了后端任务划分的负载均衡。
-
具体的实现将任务发送至管道内部,从代码的角度来看其实就是将函数发送到管道之中,所以我们可以先创建一个函数指针数组来进行管理各个函数,未来在将任务写入至管道也仅仅需要传递下标(数字)即可。
-
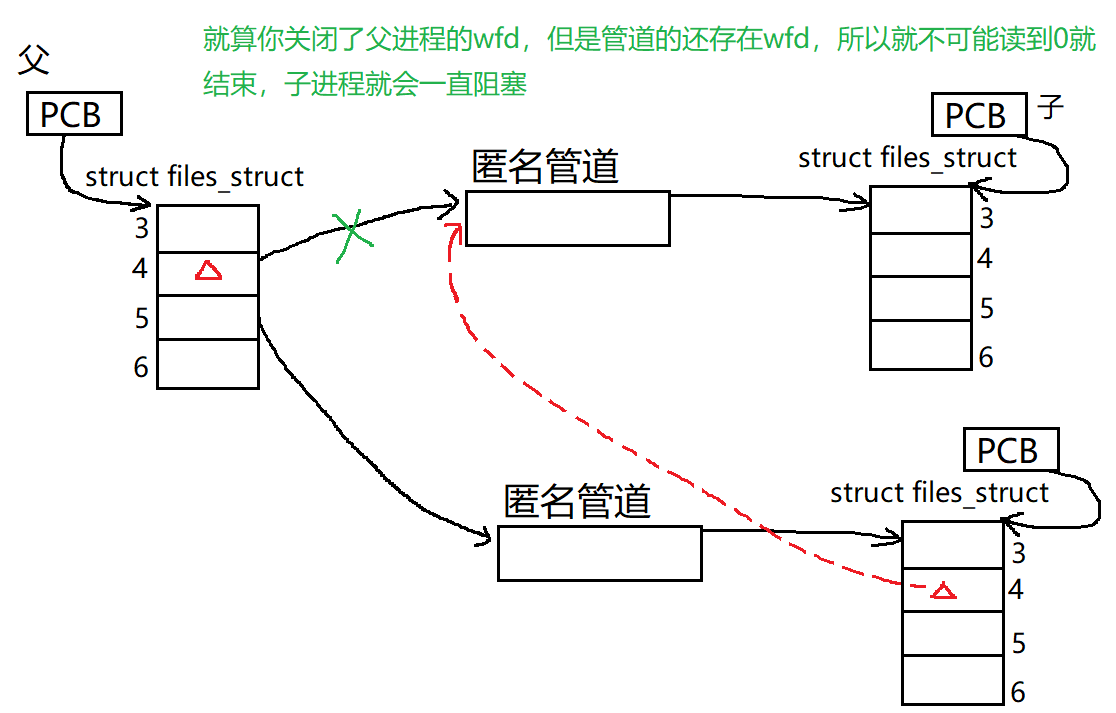
在回收的时候我们也要额外注意!我们可以先让父进程遍历所有管道并关闭所有管道的
wfd(这主要依据管道的5种特征——“若是管道的wfd关闭了,且rfd还没关闭,那么迟早会读到文件末尾,那么read系统调用就会返回0,就会结束读取”),再遍历一遍,等待每一个子进程退出。等待的原因其实是为了能够在子进程执行完后进行回收,从而避免出现“孤儿进程”。 -
(BUG!!!!!)切记!不可以一边关闭管道的
wfd再等待子进程退出,这会造成子进程阻塞!!!