Java常见数据结构
数组
- 数组的特性
- 存储空间是连续的
- 长度是不可变的
- 只能存储 相同的类型(不严谨)
- 可以通过下标访问数组的内容 a[10] 复杂度是O1
- 每个元素的默认是为'零'值 0 null false -> 一个对象的基本的数据域的初始化也是这样的
- Student 类中的username属性 默认值
链表
-
查找麻烦
-
插入和删除简单
-
可以定点删除和插入
-
非连续的
-
无限定长度
-
节点 类 结构体
-
删除是用指针指向其他的节点
-
线程不安全
-
查询效率不好 On
栈
先进后出
队列
先进先出
两个队列实现栈
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
public MyStack() {
}
public void push(int x) {
queue2.add(x);
while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {
queue2.add(queue1.remove());
}
// 交换队列引用
Queue<Integer> temp = queue2;
queue2 = queue1;
queue1 = temp;
}
public int pop() {
return queue1.remove();
}
public int top() {
if (queue1.isEmpty()){
return 0;
}
return queue1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.push(3);
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
}
}
两个栈实现队列
import java.util.Stack;
public class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
public MyQueue() {
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()){
inOut();
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()){
inOut();
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();
}
public void inOut(){
while (!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(2);
myQueue.push(9);
myQueue.push(8);
int result = myQueue.pop();
int result2 = myQueue.peek();
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(result2);
}
}
list
hashmap
多叉树
二叉树
- 每个节点最多拥有两个子节点
- 每个节点最多有一个父节点
- 只有一个根节点
- 遍历
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 层次遍历
搜索二叉树
- 左边比根小
- 右边比根大
- 查找时间 最优 Ologn ~ On 不太稳定
class TreeQueue<F> {
private F[] arr = (F[]) new Object[10];
private int addindex = 0;
private int getindex = 0;
public void add(F x) {
if(addindex - getindex == arr.length) {//判断是否满了
F[] arr2 = (F[]) new Object[arr.length * 2];
for(int i = getindex; i < addindex; i++) {
arr2[ i % arr2.length ] = arr[i% arr.length ];
}
arr = arr2;
}
arr[addindex%arr.length] = x;
addindex++;
}
public F get() {
if(addindex == getindex) {//判断是否满了
return null;
}else {
F x = arr[getindex%arr.length];
getindex++;
return x;
}
}
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
public String toString() {
return " 树的节点是:"+val;
}
public static void add(TreeNode x,int val) {
if(val>x.val) {
if(x.right == null) {
TreeNode temp = new TreeNode(val);
x.right = temp;
}
else {
add(x.right,val);
}
}else {
if(x.left == null) {
TreeNode temp = new TreeNode(val);
x.left = temp;
}
else {
add(x.left,val);
}
}
}
public static void zhongxuprint(TreeNode x) {
if(x.left!=null) {
qianxuprint(x.left);
}
System.out.print(x.val+" ");
if(x.right!=null) {
qianxuprint(x.right);
}
}
public static void qianxuprint(TreeNode x) {
System.out.print(x.val+" ");
if(x.left!=null) {
qianxuprint(x.left);
}
if(x.right!=null) {
qianxuprint(x.right);
}
}
public static void houxuprint(TreeNode x) {
if(x.left!=null) {
qianxuprint(x.left);
}
if(x.right!=null) {
qianxuprint(x.right);
}
System.out.print(x.val+" ");
}
public static void cengxuprint(TreeNode root) {
TreeQueue<TreeNode> que = new TreeQueue<>();
que.add(root);
while(true) {
TreeNode x = que.get();
if(x!=null) {
System.out.print(x.val+" ");
if(x.left!=null) {
que.add(x.left);
}
if(x.right!=null) {
que.add(x.right);
}
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
public static void search(TreeNode root,int x) {
if(x == root.val) {
System.out.println("找到了"+root.val);
return;
}
if(x > root.val) {
if(root.right==null) {
System.out.println("木有这个值");
}else {
search(root.right,x);
}
}else {
if(root.left==null) {
System.out.println("木有这个值");
}else {
search(root.left,x);
}
}
}
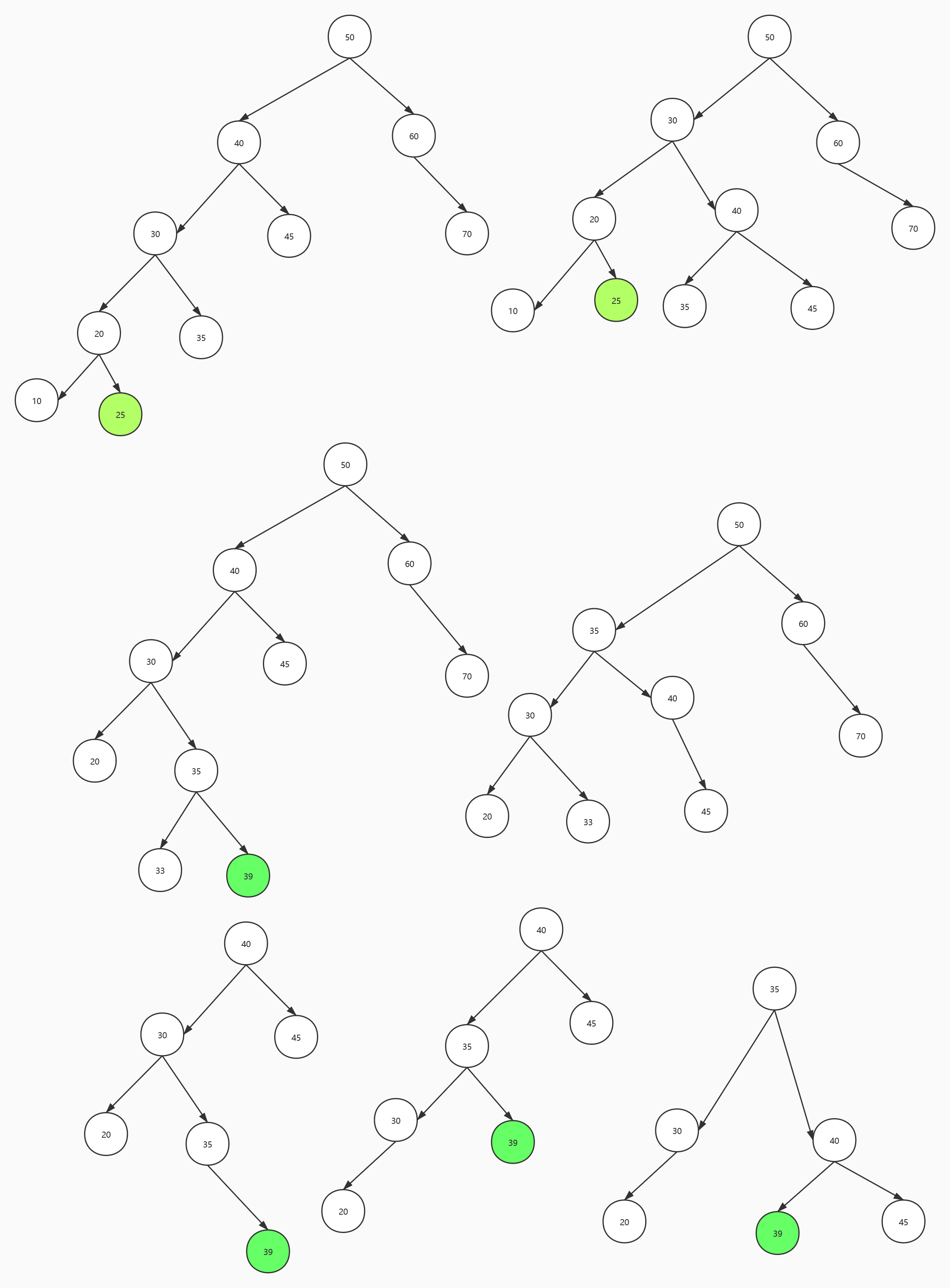
}平衡二叉树
- 旋转 如何旋转 如何平衡
- 最小不平衡子树
- LL型
- LR型
- 任何一个节点 左右子树高度差不超过1
- RR型
- RL型自己画一下
红黑树
- 近似的平衡二叉查找树
- 要么是红的要么是黑的
- 叶子节点nil节点是黑的
- 根节点是黑的 心是一个黑心呀
- 节点会变色
- 红色节点的子节点一定是黑的 不能两个连续的红色节点
- 任意一个节点 到任何一个叶子的路径 是具有相同数目的黑色节点的
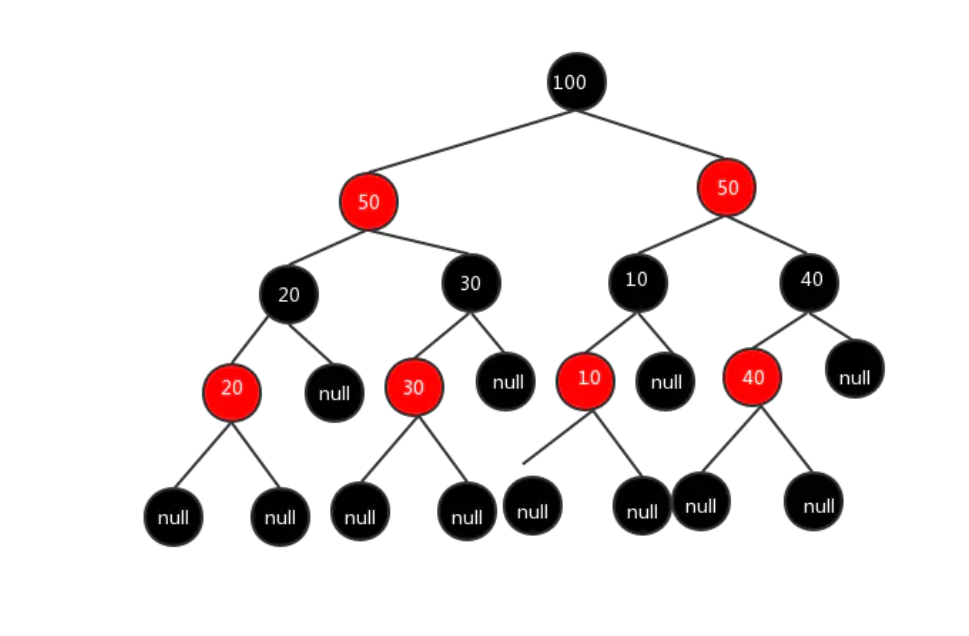
关于红黑树(R-B tree)原理,看这篇如何 - 工匠初心 - 博客园
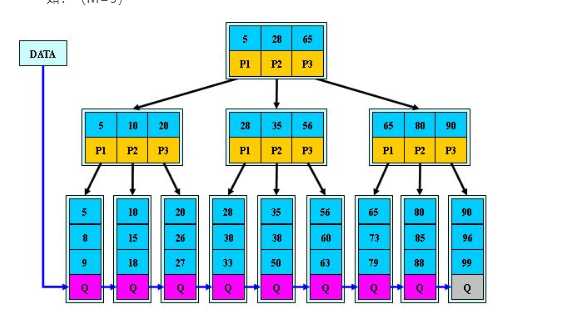
b-树
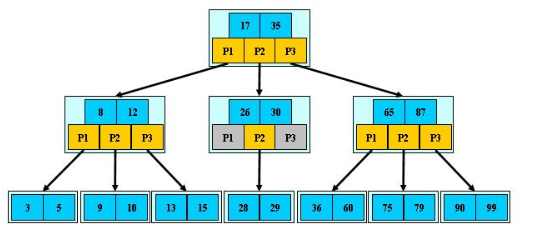
image-20200727175514447
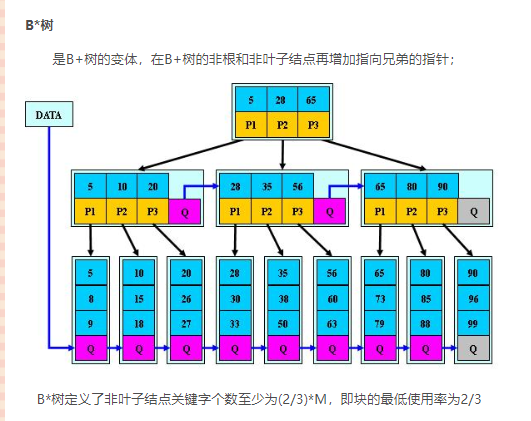
b+树
image-20200727175531655
- mysql的底层实现 存储结构
- 索引
-