react jsx基本语法,脚手架,父子传参,refs等详解
1,简介
1.1 概念
react是一个渲染html界面的一个js库,类似于vue,但是更加灵活,写法也比较像原生js,之前我们写出一个完成的是分为html,js,css,现在我们使用react库我们把html和js结合在一起,在js中写html
1.2 原生js痛点
- 用dom的API去操作dom,繁琐且效率低
- 用js直接操作dom,浏览器会进行大量的回流和重绘
- 原生js没有组件化的编程方案,代码复用性低,哪怕有模块话的概念,但模块化也只能拆解一个个js,对样式和结构也没办法拆解,组件化就相当于3剑客整体拆解,成为一个个的小功能
1.3 react特点
- 采用组件化模式,声明式编码,提高开发效率和组件复用性
- 在React Native中可以用react预发进行安卓、ios移动端开发
- 使用虚拟dom和有些的diffing算法,尽量减少与真实dom的交互,提高性能
2,react基本语法
2.1 初次体验react
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- 引入react核心库 -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入react-dom,用于支持react操作DOM -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入babel,用于将jsx转为js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
const demo = <span>Hello Word</span>
ReactDOM.render(demo, document.querySelector('#app'))
</script>
我们在这里写了一个div,id为app,其次我们引入了一些react的库,最后我们在js中创建了一个span标签,使用react库里面的ReactDOM里面的方法render,把span标签渲染到app元素去
2.2 JSx基本语法使用
1.渲染定义的元素,需要使用{},vue的话是{{}},在react中是{}
const name = "张三";
<div>
{name}
</div>
2.样式的类名不再使用class,而是className
const name = "张三";
<div className="active">
{name}
</div>
3.内联样式,要用style={{key:value}}的形式去写。
const name = "张三";
<div className="active" style="{{color:'red'}}">
{name}
</div>
4.只有一个根标签,可以使用<></>空标签当根标签
const name = "张三";
< >
<div className="active" style="{{color:'red'}}">
{name}
</div>
</ >
5.标签必须闭合
6.undefined/null/Boolean 类型
2.4 语句与表达式
-
表达式:每一个表达式都会返回一个值,可以放在任何需要使用的地方
列如:
- a
- a * b + a + b
- dome()
- arr.map()
-
语句
- if(){}
- for(){}
- switch(){}
-
混入map表达式
const data = ['dome1', 'dome2', 'dome3'] const VDOM = ( <div> <h1>HEllo WORD</h1> <h2>React遍历对象与数组</h2> <ul> { data.map((v, index) => { return <li key={index}>{v}</li> }) } </ul> </div> ) ReactDOM.render(VDOM, document.querySelector('#test'))
2.5 react面向组件编程
1.函数式组件(适用于简单组件)
- 函数式组件定义时首字母必须
大写 render渲染时必须使用标签
const MyDome = ()=>{
return <>
<div>
你好
</div>
</>
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyDome />, document.querySelector('#test'))
2.类组件(适用于复杂组件)
- 类组件必须继承React.Component
- 必须写render函数
- 必须有返回值
class MyDome extends React.Component {
render(){
return <>
<div>
你好
</div>
</>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyDome />, document.querySelector('#test'))
2.6 组件实例的三大特性
1.state数据储存状态
-
普通函数的形式直接在事件中调用
this的指向undefined可以在构造函数中利用bind,apply,call改变this的指向 -
setState 用于更新state中的数据,里面包含一个对象要改变的值 (
注意点,setState是异步的,可以传递对象或者函数,且每次调用render函数都会重新渲染)
// state使用
class Wether extends React.Component {
// 1. 继承React组件实例上添加的属性
// 2. 构造器的this指向构造函数的实例对象
// 3. render() 函数中的this也指向构造函数的实例对象
constructor(props) {
// super继承父组件属性
super(props)
this.state = { isHost: false, wind: '炎热' }
// 改变this的指向
this.demo = this.demo.bind(this)
}
render() {
const { isHost } = this.state
// this.function 是直接调用this指向window
return (
<div onClick={this.demo} >{isHost ? '雨天' : '晴天'}</div>
)
}
demo() {
// this.state.isHost = !this.state.isHost // 取反 状态不能直接更改(React响应捕捉不到)
let isHost = this.state.isHost
// 修改状态需要用setState
this.setState({ isHost: !isHost })
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Wether />, document.querySelector('#test'))
2.props的使用
2.1 基本使用:
props就是在调用组件的时候在组件中添加属性传到组件内部去使用- 基本使用
props直接在实例上的 key=value 会追加到React实例props上 - 对象解构的方式使用
类组件props
class Person extends React.Component{
render(){
const {name,age,sex} = this.props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>性别:{sex}</li>
<li>年龄:{age}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
//渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Person name="小李" age={20} sex="男"/>,document.getElementById('test1'))
const p = {name:'老刘',age:18,sex:'女'}
// 对象解构的方式使用
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p}/>,document.getElementById('test3'))
函数组件props
function Person (props){
const {name,age,sex} = props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名:{name}</li>
<li>性别:{sex}</li>
<li>年龄:{age}</li>
</ul>
)
}
ReactDOM.render(<Person name="小李" age={20} sex="男"/>,document.getElementById('test1'))
const p = {name:'老刘',age:18,sex:'女'}
// 对象解构的方式使用
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p}/>,document.getElementById('test3'))
总结:
- 每个组件都会有props属性
- 组件标签的所有属性都保存在props
- 组件内部不能改变外部传进来的props属性值
做限制类型,默认值使用
实例.propTypes={ }对象里面包含要限制的数据类型实例.defaultProps={ }对象里面包含的是默认的属性值
class DataLimit extends React.Component {
speck=()=>{
console.log(this.props)
}
render() {
const { name, age, sex } = this.props
// 注意点为props为只读属性不能修改
return (
<div>
<h2>{name}</h2>
<h2>{age+1}</h2>
<h2>{sex}</h2>
<h2 onClick={this.speck}> 点击事件</h2>
</div>
)
}
}
// propType 限制类型 (是否必传等)
// 1.PropTypes.string 限制为字符串
// 2.PropTypes.string.isRequired 限制为必传
// 3. 限制方法为func
DataLimit.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
sex: PropTypes.string,
speak: PropTypes.func
}
// prop传值 默认值
DataLimit.defaultProps = {
sex: "女"
}
const data = { name: '张珊珊', age: 18, sex: "男" }
ReactDOM.render(<DataLimit {...data} />, document.querySelector('#test1'))
简写方式
static关键字给类添加属性
//类中可以直接写赋值语句,如下代码的含义是:给Car的实例对象添加一个属性,名为a,值为1
class Car {
constructor(name,price){
this.name = name
this.price = price
// this.wheel = 4
}
a = 1
wheel = 4
static demo = 100
}
const c1 = new Car('奔驰c63',199)
console.log(c1);
console.log(Car.demo); // 100
3.refs使用
refs是组件实例对象中的属性,它专门用来收集那些使用ref标签的dom元素,比方说,组件中的input添加了一个ref=“input1”,那么组件实例中的refs就=
{input1:input(真实dom)},这样就可以通过this.refs.input1拿到input标签dom了,就不需要想原生js那样通过添加属性id,然后通过document.getElementById(“id”)的方式拿
- 用ref绑定的dom会被收集到 refs这个对象中
class PersonRefs extends React.Component {
clickRef = () => {
console.log(this); // {Input:dom节点 }
console.log(this.refs.Input);
}
render() {
// 字符串形式的ref
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref="Input"/>
<button ref="button" onClick={this.clickRef}>点击Refs </button>
<input ref="input02" type="text" />
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<PersonRefs />, document.querySelector('#test'))
回调函数的形式
class RefsFunc extends React.Component {
addInput = () => {
alert(this.input.value)
// const { input1 } = this
// alert(input1.value)
}
state = {
isShow: true
}
isShowEvent = () => {
const { isShow } = this.state
console.log(isShow);
this.setState({ isShow: !isShow })
}
// ref 中写成这个只会回调一次
CurrentEvent = (vnode) => {
this.input02 = vnode
console.log('xxxxxx');
}
render() {
//🌎 默认回调一次
//🌎更新时,调用两次
// Vnode => this.input1 = Vnode 回调函数 ref 回调形式
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref={CurrentNode => { this.input = CurrentNode; console.log('更新调用两次'); }} defaultValue="默认值" />
<input type="text" ref={this.CurrentEvent} />
<input type="text" ref={Vnode => this.input = Vnode} defaultValue="默认值" />
<button onClick={this.addInput}> 函数形式的Input使用 </button>
<p>{this.state.isShow ? "更新false" : "更新true"}</p>
<button onClick={this.isShowEvent}>切换内联函数调用</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(< RefsFunc />, document.querySelector('#test'))
createRef的方式
React.createRef调用后可以返回一个容器,该容器可以存储被ref所标识的节点,返回一个要ref绑定的dom节点, 且key唯一
class RefsFunc extends React.Component {
// 实例上添加一个myInput
myInput = React.createRef()
componentDidMount = () => {
console.log(this);
console.log(this.myInput.current.value);
// this.currentRefs.current.focusTextInput();
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref={this.myInput} />
<button onClick={this.componentDidMount}>createRef生成容器标识refDOM节点</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(< RefsFunc />, document.querySelector('#test'))
2.7 React事件处理与委托
- 操作的事件与要操作的组件数据在同一个dom节点时,利用事件委托的方式
class Demo extends React.Component{
//展示左侧输入框的数据 refs
showData = ()=>{
console.log(this.myrefs.value);
}
// 操作的事件与要操作的组件数据在同一个dom节点时,利用事件委托的方式
//展示右侧输入框的数据(target 处理数据)
showData2 = (event)=>{
alert(event.target.value);
}
render(){
return(
<div>
<input ref={e=>this.myrefs=e} type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据"/>
<button onClick={this.showData}>点我提示左侧的数据</button>
<input onBlur={this.showData2} type="text" placeholder="失去焦点提示数据"/>
</div>
)
}
}
//渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Demo a="1" b="2"/>,document.getElementById('test'))
2.8 受控组件与非受控组件
非受控组件
- 获取要提交的值为现用现取
class Login extends React.Component{
handleSubmit = (event)=>{
event.preventDefault() //阻止表单提交
const {username,password} = this
alert(`你输入的用户名是:${username.value},你输入的密码是:${password.value}`)
}
render(){
return(
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
用户名:<input ref={c => this.username = c} type="text" name="username"/>
密码:<input ref={c => this.password = c} type="password" name="password"/>
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
//渲染组件
ReactDOM.render(<Login/>,document.getElementById('test'))
受控组件
//受控组件 , 事件触发Input中 传在数据的值
class Login extends React.Component{
//初始化状态
state = {
username:'', //用户名
password:'' //密码
}
//保存用户名到状态中
saveUsername = (event)=>{
this.setState({username:event.target.value})
}
//保存密码到状态中
savePassword = (event)=>{
this.setState({password:event.target.value})
}
//表单提交的回调
handleSubmit = (event)=>{
event.preventDefault() //阻止表单提交
const {username,password} = this.state
alert(`你输入的用户名是:${username},你输入的密码是:${password}`)
}
render(){
return(
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
用户名:<input onChange={this.saveUsername} type="text" name="username"/>
密码:<input onChange={this.savePassword} type="password" name="password"/>
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
//渲染组件
ReactDOM.render(<Login/>,document.getElementById('test'))
2.9 高阶函数与函数柯里化
1.高阶函数
- 如果一个函数符合下面2个规范中的任何一个,那该函数就是高阶函数。
- 若A函数,接收的参数还是一个函数,那么A就可以称之为高阶函数。
- 若A函数,调用的返回值依然是一个函数,那么A就可以称之为高阶函数。
- 常见的高阶函数有:
Promise、setTimeout、arr.map()等等
2.函数柯里化 参考链描] 让函数的职责不再单一
柯里化回调
onChange={this.InputName('username')('xxxx')}共调用三次,react调用,默认返回的值为target
/创建组件
class Login extends React.Component {
// 初始化状态
state = {
username: "默认值",
password: ""
}
// 实时更新状态, 数据维护在state中为受控组件(相当于vue里面的v-model)
InputName = (dataType) => {
// onChange默认的返回一个函数
//回调的是一个函数 (既函数的柯里化)
return (Type) => {
console.log([Type]);
return (e) => {
this.setState({ [dataType]: e.target.value })
}
}
}
InputPassWord = (e) => {
this.setState({ password: e.target.value })
}
handlySubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
alert(`userName: ${this.state.username} passwrod : ${this.state.password}`,)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<form onSubmit={this.handlySubmit} >
{ /* <div>value 绑定默认值</div>*/}
<input type="text" value={this.state.username} onChange={this.InputName('username')('xxxx')} name="username" />
<input type="text" onChange={this.InputPassWord} name="password" />
<button>提交</button>
</form>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Login />, document.querySelector('#test'))
高阶回调
class Login extends React.Component {
// 初始化状态
state = {
username: "默认值",
password: ""
}
// 实时更新状态, 数据维护在state中为受控组件(相当于vue里面的v-model)
InputName = (dataType, event) => {
// onChange默认的返回一个函数
// [datatype]使用变量作为属性名
this.setState({ [dataType]: event.target.value })
}
InputPassWord = (e) => {
this.setState({ password: e.target.value })
}
handlySubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
alert(`userName: ${this.state.username} passwrod : ${this.state.password}`,)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<form onSubmit={this.handlySubmit} >
{ /* <div>不用柯里化的方式实现
1. onChange 先调用一个event函数在event 函数中又调用了this.InputName这个函数
</div>*/}
<input type="text" value={this.state.username} onChange={(event) => {this.InputName('username', event)}
} name="username" />
<input type="text" onChange={this.InputPassWord} name="password" />
<button>提交</button>
</form>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Login />, document.querySelector('#test'))
2.10 组件的生命周期
老版的生命周期过程
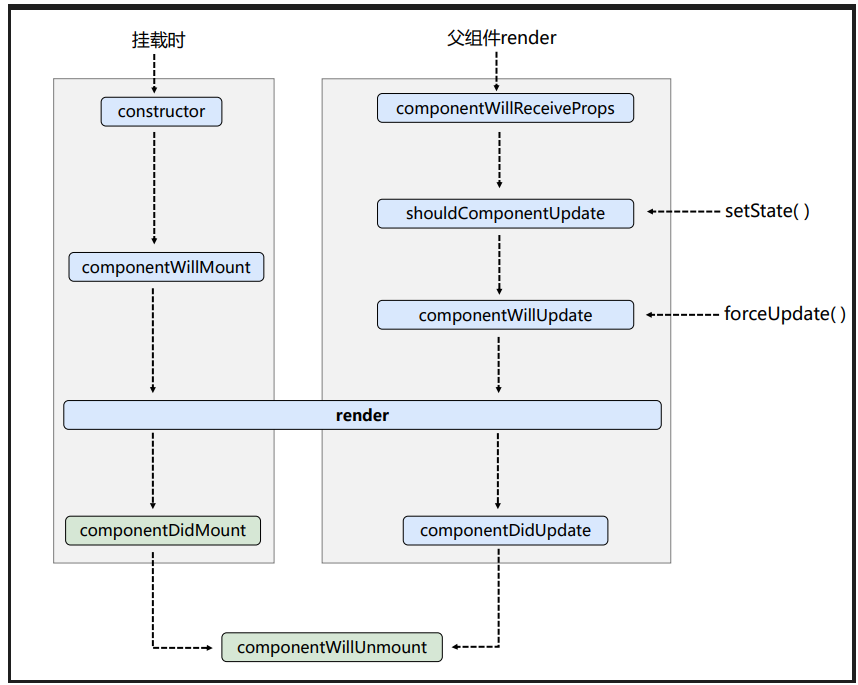
**挂载时:**先执行构造器(constructor)=》组件将要挂载(componentWillMount)=》组件挂载渲染(render)=》组件挂载完成(componentDidMount)=》组件销毁(componentWillUnmount)
**组件内部状态更新:**组件是否应该更新(shouldComponentUpdate)=》组件将要更新(componentWillUpdate)=》组件更新渲染(render)=》组件更新完成(componentDidUpdate)
**强制更新:**调用this.forceUpdate(),这个api和setState一样都是react自带的,一般这个强制更新很少用,它的执行流程就是比上述的正常更新流程少一步询问是否更新(shouldComponentUpdate)
**父组件重新render:**调用组件将要接收新props(componentWillReceiveProps)=》组件是否应该更新(shouldComponentUpdate)=》组件将要更新(componentWillUpdate)=》组件更新渲染(render)=》组件更新完成(componentDidUpdate)
新版的声明周期
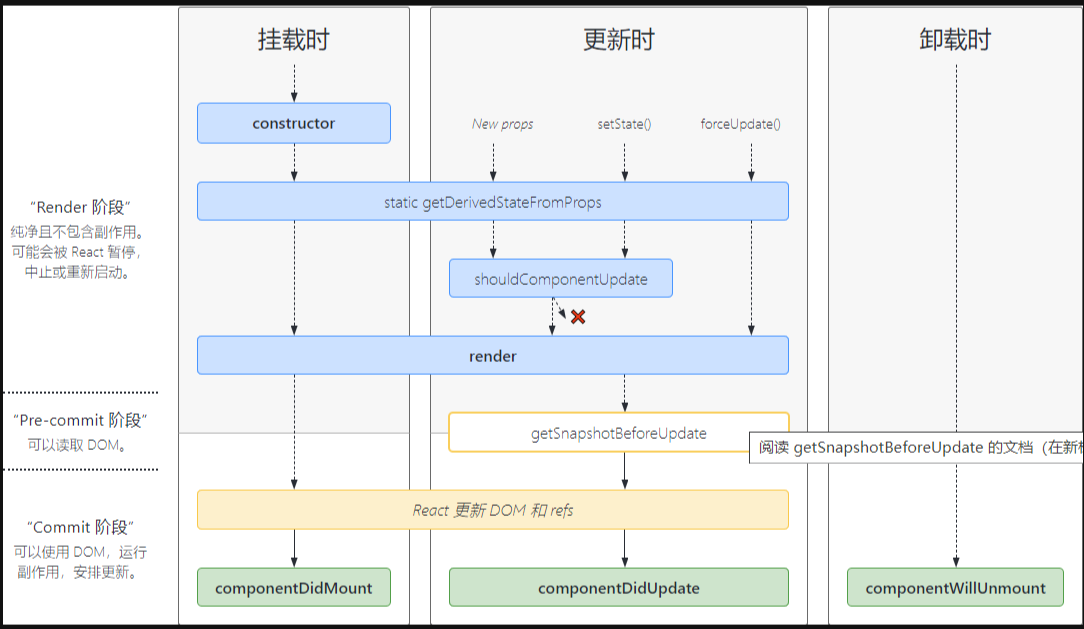
**新版生命周期函数和旧版的差别:**新版即将废弃老的3个钩子(componentWillMount、componentWillReceiveProps、componentWillUpdate),新增了2个钩子(getDerivedStateFromProps、getSnapshotBeforeUpdate)
生命周期代码参考
class Count extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
console.log('构造器,constructor');
}
state = {
count: 1
}
handlyAdd = () => {
let { count } = this.state
count++;
this.setState({ count })
}
// 2. 挂载中
render() {
console.log('挂载中 render');
const { count } = this.state
return (
<div>
<p>当前的数字 {count}</p>
<button onClick={this.handlyAdd}>点我加一</button>
<button onClick={this.UnMountEvent}> 卸载组件</button>
<button onClick={this.mandatoryUpdate}> 强制更新,不改状态</button>
</div>
)
}
// 新增加的钩子(相当于将要挂载 或将要更新的钩子)
// 用处: state值完全取决于props
// 注意点 写入必须返回值
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
console.log("新增加的钩子 getDerivedStateFormProps");
console.log('state', state);
// 返回一个对象
return props
}
// 新增加的钩子 (在更新之前获取快照)
// 注意点 必须返回一个快照 或null
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() {
return '更新之前的值'
}
//3 挂载完毕
componentDidMount() {
console.log('挂载完毕 componentDidMount');
}
// 更新的组件
// 1. 组件是否可以更新 返回值ture 或false
shouldComponentUpdate() {
console.log('组件是否可以更新 shouldComponentUpdate');
// 🚗 注意点1. 这个方法不写默认可以更新 为true
// 2. 方法写入了 ,没有return 默认为false
return true
}
// 4. 组件更新完成(拿到之前的值,可以获取getSnapshotBeforeUpdate这个钩子return的值)
componentDidUpdate(preProps, preState, preValue) {
console.log('组件更新完毕 componentWillUpdate');
console.log('组件更新完成', preProps, preState, preValue);
}
//999 卸载组件
UnMountEvent = () => {
console.log('卸载DOM节点 unmountComponentAtNode');
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.querySelector('#test'))
}
// 强制更新 不走shouldComponentUpdate()函数
mandatoryUpdate = () => {
this.forceUpdate()
}
}
// 父子组件生命周期
class Myfalter extends React.Component {
state = {
name: "父组件信息"
}
fatherEmitSon = () => {
const { name } = this.state
this.setState({ name: '修改父组件的信息' })
}
render() {
const { name } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2>我是父组件</h2>
<h3>-----------------------------------</h3>
<button onClick={this.fatherEmitSon}>修改父组件值传递给子组件 </button>
< Myson name={name} />
</div>
)
}
}
class Myson extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>我是子组件</h2>
<p>我将要展示父组件的内容: <span style={{ color: 'red' }}>{this.props.name}</span></p>
</div>
)
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('子组件挂载时调用 componentDidMount');
}
componentWillReceiveProps(props) {
// 1. (第一次接受值默认没有调用)子组件更新触发的生命周期 可以传递值
console.log('xxxxxxxxx', props);
}
shouldComponentUpdate() {
console.log('组件是否可以更新 shouldComponentUpdate');
// 🚗 注意点1. 这个方法不写默认可以更新 为true
// 2. 方法写入了 ,没有return 默认为false
return true
}
// 2. 组件将要更新
// 3. render(){}
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log('组件将要更新 componentWillUpdate');
}
// 4. 组件更新
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('组件更新完毕 componentWillUpdate');
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Count />, document.querySelector('#test'))
// ReactDOM.render(<Myfalter />, document.querySelector('#test'))
3. react脚手架基本配置
react脚手架,在昨天我已经发布了教程包括路由,状态管理都有,在我的上一篇文章,地址为:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74079648/article/details/143485923?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
4. 在脚手架中基本语法
4.1父子通信,props ,事件
父组件在展示子组件时,会传递一些数据给子组件:采用如下方法
父组件通过
属性=值的形式来传递给子组件数据,或采用解构的形式传参
子组件通过this.props获取父组件传递过来的数据
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
books: [
{name: "算法导论", price: 79},
{name: "数据结构", price: 69},
{name: "漫画算法", price: 59},
]
}
}
render() {
const { books } = this.state
return (
<div>
{/* 将数据传递给子组件 */}
<Header books={books}/>
</div>
)
}
}
- 子组件接受父组件传递的数据
export class Header extends Component {
render() {
// 接受父组件传递过来的参数
const { books } = this.props
return (
<div>
<ul>
{
books.map(item => {
return (
<li key={item.name}>
名称: {item.name} 价格: {item.price}
</li>
)
})
}
</ul>
</div>
)
}
}
回调函数,子组件向父组件传递消息:
在React中同样是通过props传递消息,只是让父组件给子组件传递一个回调函数,在子组件中调用这个函数即可;
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import ConterButton from './c-cpn/ConterButton'
export class App extends Component {
state = {conter: 100}
changeConter() {
let {conter}= this.state
conter++
this.setState({ conter })
}
render() {
const { conter } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2>{conter}</h2>
{/* 向子组件中传入一个事件 */}
<ConterButton getConter={this.changeConter()}/>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
- 子组件在按钮发生点击时, 对父组件的传递的函数进行回调,
import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class ConterButton extends Component {
btnClick() {
// 当按钮发生点击事件时, 对父组件传递过来的函数进行回调
this.props.getConter()
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.btnClick}>+1</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default ConterButton
4.2 refs 与 事件冒泡
- 父组件通过
React.createRef()创建Ref,保存在实例属性myRef上。父组件中,渲染子组件时,定义一个Ref属性,值为刚创建的myRef。 - 父组件调用子组件的myFunc函数,传递一个参数,子组件接收到参数,打印出参数。
- 参数从父组件传递给子组件,完成了父组件向子组件通信。
import React, { Component, Fragment } from 'react';
class Son extends Component {
myFunc(name) {
console.log(name);
}
render() {
return <div></div>;
}
}
// 父组件
export default class Father extends Component {
this.myRef = React.createRef();
componentDidMount() {
// 调用子组件的函数,传递一个参数
this.myRef.current.myFunc('Jack');
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Son ref={this.myRef} />
</div>
);
}
}
4.3 消息订阅-发布机制
原先react传递数据基本用的是props,而且只能父组件传给子组件,如果子组件要传数据给父组件,只能先父组件传一个函数给子组件,子组件再调用该方法,把数据作为形参传给父组件,那考虑一个事情,兄弟间组件要如何传递数据呢?这就要引出下面这个消息订阅-发布机制
工具库:PubSubJs
下载:npm install pubsub-js --save
使用:
- 先引入:import PubSub from “pubsub-js”
- 要接收数据方订阅:
PubSub.subscribe('消息名',(data)=>{ console.log(data) }) - 传递数据方发布:
PubSub.publish('消息名',data)
- 组件A订阅信息
// A组件内的状态
state = {
users:[],
isFirst:true,
isLoading:false,
err:''
}
// 订阅了消息名为updateState的消息事件
componentDidMount(){
// 方法返回两个值(第一个值是订阅与发布共有的属性,第二个是接受发布的信息)
this.token = PubSub.subscribe('updateState',(_,data)=>{
this.setState(data) // 将收到的状态data更新
})
}
// 页面销毁前删除消息订阅 以防消息泄露
componentWillUnmount(){
PubSub.unsubscribe(this.token)
}
- 组件B发布信息
// 发布消息名为updateState的消息事件
PubSub.publish('updateState',{isFirst:false,isLoading:true})
axios.get(`https://api.github.com/search/users?q=${keyWord}`).then(res=>{
PubSub.publish('updateState',{users:res.data.items,isLoading:false})
}).catch(err=>{
PubSub.publish('updateState',{err:err.message,isLoading:false})
})
React18 eventBus使用
安装 npm i hy-event-store
创建实例
import { HYEventBus } from "hy-event-store"
const eventBus = new HYEventBus()
export default eventBus
- emit传递事件
nextClick() {
eventBus.emit("bannerNext", {nickname: "kobe", level: 99})
}
- on监听事件
componentDidMount() {
eventBus.on("bannerNext", this.bannerNextClick, this)
}
- 销毁,防止内存泄漏
componentWillUnmount() {
eventBus.off("bannerNext", this.bannerNextClick)
}
5. React Hooks 及其扩展
- 在函数式组件中并没有this,因此React提供的Hooks,这就让你在函数式组件中可以使用state或其他特性
- 常使用的Hooks有
React.useState(),React.useEffect(),React.useRef()
5.1 setState的两种用法
注意点 : setState更新是异步的
5.1.1 对象更新
setState(stateChange, [callback])------对象式的setState- stateChange为状态改变对象(该对象可以体现出状态的更改)
- callback是可选的回调函数, 它在状态更新完毕、界面也更新后(render调用后)才被调用
this.setState({count},()=>{
console.log(this.state.count);
})
// 或者
this.setState({count:count+1})
5.1.2 函数回调式更新
setState(updater, [callback])------函数式的setState
- updater为返回stateChange对象的函数。
- updater可以接收到state和props。
- callback是可选的回调函数, 它在状态更新、界面也更新后(render调用后)才被调用。
- 函数回调直接接受 state
this.setState((state)=>( { count: state.count+1 }))
5.2 Hooks 之 useState
- State Hook让函数组件也可以有state状态, 并进行状态数据的读写操作
语法: const [xxx, setXxx] = React.useState(initValue)
-
useState()说明:
- 参数: 第一次初始化指定的值在内部作缓存
- 返回值: 包含2个元素的数组, 第1个为内部当前状态值, 第2个为更新状态值的函数
-
setXxx()2种写法:
- setXxx(newValue): 参数为非函数值, 直接指定新的状态值, 内部用其覆盖原来的状态值
- setXxx(value => newValue): 参数为函数, 接收原本的状态值, 返回新的状态值, 内部用其覆盖原来的状态值
import React from "react";
// 1. 注意点 函数式组件命名 首字母大写
// 2. useState 初始调用后会把值缓存起来,不会因为函数的再次调用把count重新赋值为0
// 3.hooks 必须在最顶层使用 不能在if for 等使用
// 4.useState 如果没有传递参数,那么初始化值为undefined
// 5. 箭头函数写法 const DemoCount= React.memo(()=>{ })
export default function DemoCount(params) {
// 第一个是返回的值, 第二个参数返回一个函数设置第一个返回的值
let [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
function add() {
// count++;
// setCount(count); //第一种写法
setCount(count=>count+1)
}
return (
<div>
<h1>{count}</h1>
<button onClick={add}>点击+1</button>
<button onClick={()=>setCount(count-1)}>点击-1</button>
</div>
);
}
5.3 Hooks之useEffect
- Effect Hook 可以让你在函数组件中执行副作用操作(用于模拟类似组件中的生命周期钩子)
- React中的副作用操作:
- 发ajax请求数据获取
- 设置订阅 / 启动定时器
- 手动更改真实DOM
语法: useEffect(() => {
// 在此可以执行任何带副作用操作
return () => { // 在组件卸载前执行
// 在此做一些收尾工作, 比如清除定时器/取消订阅等
}
}, [stateValue]) // 如果指定的是[], 回调函数只会在第一次render()后执行
- 可以把 useEffect Hook 看做如下三个函数的组合
componentDidMount()
componentDidUpdate()
componentWillUnmount()
// 卸载组件
import React from "react";
function App() {
const [showChild, setShowChild] = React.useState(true);
function unmound() {
setShowChild(false);
}
return (
<>
{showChild && <DemoCount />}
<button onClick={unmound}>卸载组件</button>
</>
);
}
// useEffect 相当于componentDidMount,或者 componentDidUpdate (主要看第二个值传不传)
function DemoCount() {
let [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
React.useEffect(() => {
let timer = setInterval(() => {
setCount((count) => count + 1);
}, 1000);
return () => {
// 返回值为清除定时器
clearInterval(timer);
};
}, []); // 传一个数组,表示检测谁,(默认不传,检测所有,传空数组谁也不检测)
function add() {
setCount((count) => count + 1);
}
return (
<div className="id">
<h1>{count}</h1>
<button onClick={add}>点击+1</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
5.4 Hooks之useRef
- Ref Hook可以在函数组件中存储/查找组件内的标签或任意其它数据
语法: const refContainer = useRef()
function App() {
const myrefs = React.useRef();
function getRefsValue() {
console.log(myrefs.current.value);
}
return (
<div>
<input ref={myrefs} type='text' />
<button onClick={getRefsValue}>ref</button>
</div>
);
}
5.5 Fragment代替根标签
- render 函数中都都需一个根标签,这样会都渲染一个不需要的dom节点,利用
Fragment代替就不会渲染
import React, { Fragment } from "react";
// Fragment 忽略标签,|| <></> 区别在于是否需要key
function App() {
const myrefs = React.useRef();
function getRefsValue() {
console.log(myrefs.current.value);
}
return (
<Fragment>
<input ref={myrefs} type="text" />
<button onClick={getRefsValue}>ref</button>
</Fragment>
);
}
5.6 Context的使用
- Context 提供了一种在组件之间共享此类值的方式,而不必显式地通过
组件树的逐层传递 props- Context 主要应用场景在于很多不同层级的组件需要访问同样一些的数据。
请谨慎使用,因为这会使得组件的复用性变差
5.6.1 提供的API
React.createContext
使用此API可以创建一个Context对象,组件会从最近的
Provider中读取对应的值。只有当组件所处的树种不存在Provider时,defaultValue参数才会生效
const MyContext = React.createContext(defaultValue);
Context.Provider
- Context对象会返回一个Provider组件
Provider接受一个value属性,传递给消费组件 当Provider的value属性值更变时,内部的所有消费组件都会重新渲染
context会根据引用标识进行重新渲染,所以当向value传递一个对象时,需要注意:当Provider重新渲染时,可能会触发Consumer意外渲染。为了防止这种情况,将value状态提升到父节点的state中
<MyContext.Provider value={某个值}/>
Context.Consumer
- Context对象会返回一个Consumer组件
需要一个函数作为子元素,函数接收context值,返回一个React节点
传递给函数的value值等价于组件树上方离这个context最近的Provider提供的value值。如果没有对应的Provider,value参数等同传递给createContext()的defaultValue
<MyContext.Consumer>
{value => /* 基于 context 值进行渲染*/}
</MyContext.Consumer>
Class.contextType
- 此属性可以让你使用
this.context来获取最近Context上的值。你可以在任何生命周期中访问到它,包括render函数中
const MyContext = React.createContext()
class MyClass extends React.Component {
render() {
let value = this.context;
/* 基于这个值进行渲染工作 */
}
}
MyClass.contextType = MyContext
- 同时,你也可以使用实验性的
public class fields语法中的static类属性初始化contextType,此外一般都是使用第二种用法
const MyContext = React.createContext()
class MyClass extends React.Component {
static contextType = MyContext
render() {
let value = this.context;
/* 基于这个值进行渲染工作 */
}
}
5.6.2 注意点
- 在使用时,类组件使用
Provider,Consumer可以用于类组件和函数式组件
// A->B->C , context 组件通信
import React, { Component } from "react";
// 需求C组件展示A组件的Name
// 创建上下文context
const MyContext = React.createContext();
export default class App extends Component {
state = {
name: "我是A组件,需要在C组件中展示",
nameInfo: "A组件的详细信息",
};
render() {
const { name, nameInfo } = this.state;
return (
<div>
<h2>A</h2>
<h5>----------------------</h5>
<MyContext.Provider value={{ name, nameInfo }}>
<B />
</MyContext.Provider>
</div>
);
}
}
class B extends Component {
render() {
return (
<>
<h2> B</h2>
<h5>----------------------</h5>
<C />
</>
);
}
}
// class C extends Component {
// // 声明接受context
// static contextType = MyContext;
// render() {
// console.log(this.context); //
// return (
// <div>
// <h2>C</h2>
// {/* <a href="1">{this.context}</a> */}
// <h5>----------------------</h5>
// </div>
// );
// }
// }
// 函数式组件使用context,Provider只使用于类组件, Consumer 可以用于类组件和函数式组件
function C() {
return (
<div>
<h2>C</h2>
<MyContext.Consumer>
{
value=> {
return `${value.name}`
}
}
</MyContext.Consumer>
<h5>----------------------</h5>
</div>
);
}
5.3 useContext
- Context Hook允许我们通过Hook来直接获取某个Context的值
import React, { memo, useEffect, useState } from 'react';
// import { ThemeContext } from './context/themContext';
// import { MyUserInfoContext } from './context/userInfo';
import Hooks from './hooks';
// 自定义hooks 需要以use开头
function useSumApp(Name) {
useEffect(() => {
console.log(Name)
return () => {
console.log(Name)
}
}, [Name])
}
const App01 = memo(() => {
// const themeStyleContext = useContext(ThemeContext)
// const userInfoContext = useContext(MyUserInfoContext)
const [themeStyleContext, userInfoContext] = Hooks()
console.log(themeStyleContext);
useSumApp('App01')
return (
<div>App01</div>
)
})
const App02 = memo(() => {
// const themeStyleContext = useContext(ThemeContext)
// const userInfoContext = useContext(MyUserInfoContext)
useSumApp('App02')
return (
<div>App02</div>
)
})
const App = memo(() => {
const [isShow, setIsShow] = useState(true)
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => setIsShow(!isShow)}>updata Component</button>
{isShow && <App01 />}
{isShow && <App02 />}
</div>
)
})
export default App
hooks的封装
import { ThemeContext } from './context/themContext';
import { MyUserInfoContext } from './context/userInfo';
import { useContext } from 'react';
export default function Hooks() {
const themeStyleContext = useContext(ThemeContext)
const userInfoContext = useContext(MyUserInfoContext)
return [themeStyleContext, userInfoContext]
}
5.7 PureComponent 拒接子组件render重新渲染
注意点 , 只要调用setState 父子组件中的render函数都会调用
- 避免上述情况,可以采用的方案为:
- 重写shouldComponentUpdate()方法 比较新旧state或props数据, 如果有变化才返回true,
- 如果没有返回false
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
// 这里可以判断是否更新子组件的render 当nextState与this.state的值相同时,返回false不同返回ture ,简单点说就是阀门是否打开
if (nextState.name === this.state.name) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
使用
PureComponent ``PureComponent重写了shouldComponentUpdate(),
只有state或props数据有变化才返回true 注意: 只是进行state和props数据的浅比较,
如果只是数据对象内部数据变了, 返回false 不要直接修改state数据, 而是要产生新数据
import React, { PureComponent } from "react";
// PureComponent 判断 子组件是否使用父组件的内容,数据更新时是否调用子组件的render
export default class App extends PureComponent {}
5.8 render props 插槽
- Vue中: 使用slot技术, 也就是通过组件标签体传入结构
- React中:使用children props: 通过组件标签体传入结构,使用render props: 通过组件标签属性传入结构, 一般用render函数属性
5.8.1 this.props.children 渲染
1. A组件使用
<B>
<C>xxxx</C>
</B>
2. 在B要使用C组件中调用 {this.props.children}渲染
- 但是上面也存在一个问题: 如果B组件需要A组件内的数据, ==> 做不到
5.8.2 this.props 渲染
// 父组件传递
const btn = <button>按钮2</button>;
<NavBarTwo
leftSlot={btn}
centerSlot={<h2>呵呵呵</h2>}
rightSlot={<i>斜体2</i>}
/>
// 子组件
const { leftSlot, centerSlot, rightSlot } = this.props
return (
<div className='nav-bar'>
<div className="left">{leftSlot}</div>
<div className="center">{centerSlot}</div>
<div className="right">{rightSlot}</div>
</div>
5.8.3 render props 渲染
<B render={(data) => <C data={data}></C>}></B>
B组件: {this.props.render(内部state数据)}
C组件: 读取A组件传入的数据显示 {this.props.data}
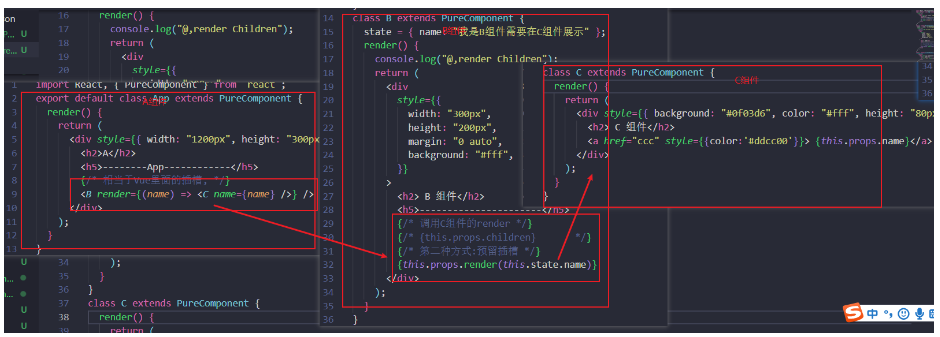
- 代码参考
import React, { PureComponent } from "react";
export default class App extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div style={{ width: "1200px", height: "300px", background: "red" }}>
<h2>A</h2>
<h5>--------App------------</h5>
{/* 相当于Vue里面的插槽, */}
<B render={(name) => <C name={name} />} />
</div>
);
}
}
class B extends PureComponent {
state = { name: "我是B组件需要在C组件展示" };
render() {
console.log("@,render Children");
return (
<div
style={{
width: "300px",
height: "200px",
margin: "0 auto",
background: "#fff",
}}
>
<h2> B 组件</h2>
<h5>----------------------</h5>
{/* 调用C组件的render */}
{/* {this.props.children} */}
{/* 第二种方式:预留插槽 */}
{this.props.render(this.state.name)}
</div>
);
}
}
class C extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div style={{ background: "#0f03d6", color: "#fff", height: "80px" }}>
<h2> C 组件</h2>
<a href="ccc" style={{color:'#ddcc00'}}> {this.props.name}</a>
</div>
);
}
}
ame='nav-bar'>
<div className="left">{leftSlot}</div>
<div className="center">{centerSlot}</div>
<div className="right">{rightSlot}</div>
</div>
5.8.3 render props 渲染
<B render={(data) => <C data={data}></C>}></B>
B组件: {this.props.render(内部state数据)}
C组件: 读取A组件传入的数据显示 {this.props.data}
[外链图片转存中…(img-QQS2JAWa-1730792486041)]
- 代码参考
import React, { PureComponent } from "react";
export default class App extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div style={{ width: "1200px", height: "300px", background: "red" }}>
<h2>A</h2>
<h5>--------App------------</h5>
{/* 相当于Vue里面的插槽, */}
<B render={(name) => <C name={name} />} />
</div>
);
}
}
class B extends PureComponent {
state = { name: "我是B组件需要在C组件展示" };
render() {
console.log("@,render Children");
return (
<div
style={{
width: "300px",
height: "200px",
margin: "0 auto",
background: "#fff",
}}
>
<h2> B 组件</h2>
<h5>----------------------</h5>
{/* 调用C组件的render */}
{/* {this.props.children} */}
{/* 第二种方式:预留插槽 */}
{this.props.render(this.state.name)}
</div>
);
}
}
class C extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div style={{ background: "#0f03d6", color: "#fff", height: "80px" }}>
<h2> C 组件</h2>
<a href="ccc" style={{color:'#ddcc00'}}> {this.props.name}</a>
</div>
);
}
}
