【设计模式】结构型模式(三):桥接模式、外观模式
结构型模式(三):桥接模式
- 4.桥接模式(Bridge)
- 4.1 结构
- 4.2 示例
- 4.2.1 抽象类
- 4.2.2 细化抽象类
- 4.2.3 实现类接口
- 4.2.4 具体实现类
- 4.2.5 客户端
- 5.外观模式(Facade)

4.桥接模式(Bridge)
桥接模式(Bridge Pattern)是设计模式中的一种结构型模式,主要用于 将抽象部分与实现部分分离,使它们可以独立变化。这种模式在多种场景下非常有用,尤其是在需要将抽象和实现解耦的情况下。以下是桥接模式的主要特点和应用场景:
- 分离抽象和实现:将抽象部分和实现部分分离,使它们可以独立变化。
- 减少类的爆炸性增长:通过将抽象和实现解耦,可以减少类的数量,提高系统的可维护性。
- 动态切换实现:可以在运行时动态切换实现部分,而不需要修改客户端代码。
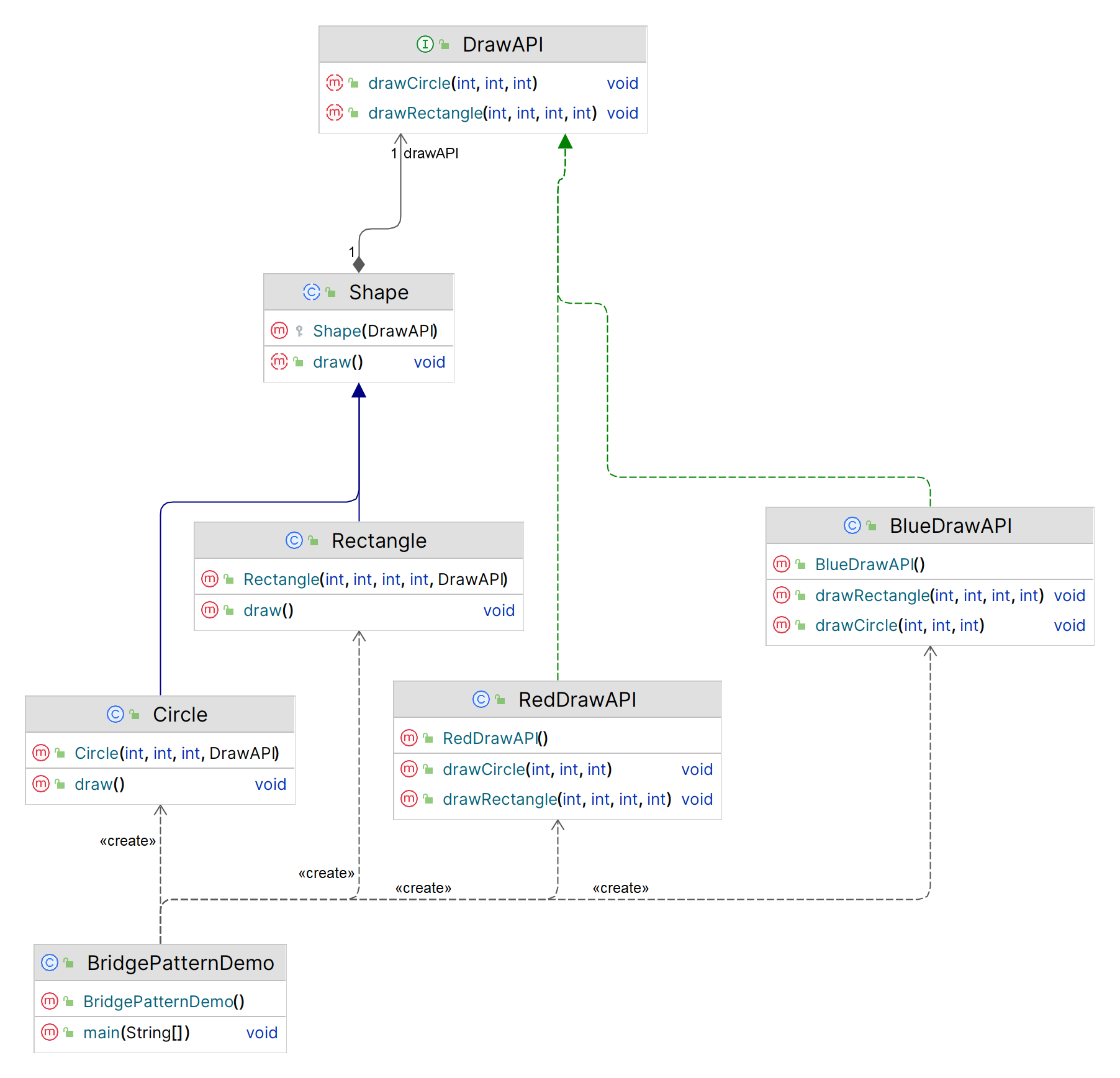
4.1 结构
Abstraction(抽象类):定义抽象类的接口,包含一个对实现部分的引用。RefinedAbstraction(细化抽象类):扩展抽象类,提供更具体的实现。Implementor(实现类接口):定义实现类的接口,具体实现类需要实现这个接口。ConcreteImplementor(具体实现类):实现实现类接口,提供具体的实现。
4.2 示例
假设我们有一个图形绘制系统,需要支持不同的图形(圆形、方形等)和不同的绘制方式(如使用不同的颜色或填充方式)。我们可以使用桥接模式来实现这个系统。
4.2.1 抽象类
// 抽象类
public abstract class Shape {
protected DrawAPI drawAPI;
protected Shape(DrawAPI drawAPI) {
this.drawAPI = drawAPI;
}
public abstract void draw();
}
4.2.2 细化抽象类
// 细化抽象类
public class Circle extends Shape {
private int x, y, radius;
public Circle(int x, int y, int radius, DrawAPI drawAPI) {
super(drawAPI);
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
drawAPI.drawCircle(x, y, radius);
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
private int x, y, width, height;
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height, DrawAPI drawAPI) {
super(drawAPI);
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
drawAPI.drawRectangle(x, y, width, height);
}
}
4.2.3 实现类接口
// 实现类接口
public interface DrawAPI {
void drawCircle(int x, int y, int radius);
void drawRectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height);
}
4.2.4 具体实现类
// 具体实现类
public class RedDrawAPI implements DrawAPI {
@Override
public void drawCircle(int x, int y, int radius) {
System.out.println("Drawing Circle [Color: Red, x: " + x + ", y: " + y + ", radius: " + radius);
}
@Override
public void drawRectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height) {
System.out.println("Drawing Rectangle [Color: Red, x: " + x + ", y: " + y + ", width: " + width + ", height: " + height);
}
}
public class BlueDrawAPI implements DrawAPI {
@Override
public void drawCircle(int x, int y, int radius) {
System.out.println("Drawing Circle [Color: Blue, x: " + x + ", y: " + y + ", radius: " + radius);
}
@Override
public void drawRectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height) {
System.out.println("Drawing Rectangle [Color: Blue, x: " + x + ", y: " + y + ", width: " + width + ", height: " + height);
}
}
4.2.5 客户端
public class BridgePatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape redCircle = new Circle(100, 100, 50, new RedDrawAPI());
Shape blueRectangle = new Rectangle(10, 10, 100, 100, new BlueDrawAPI());
redCircle.draw();
blueRectangle.draw();
}
}
输出结果:
Drawing BridgePatternDemo.Circle [Color: Red, x: 100, y: 100, radius: 50
Drawing BridgePatternDemo.Rectangle [Color: Blue, x: 10, y: 10, width: 100, height: 100
5.外观模式(Facade)
外观模式(Facade Pattern)是一种设计模式,用于 为复杂的子系统提供一个简化的接口。它的主要目的是减少客户端与子系统之间的依赖关系,使客户端代码更容易理解和使用。以下是外观模式的几个关键点:
- 简化接口:外观模式通过提供一个统一的高层接口,使客户端代码可以更简单地访问子系统的功能,而不需要了解子系统的内部复杂性。
- 降低耦合度:客户端代码只需与外观类交互,而不必与子系统的多个类直接交互,从而降低了系统的耦合度。
- 提高灵活性:外观类可以灵活地控制对子系统的访问,可以在不改变客户端代码的情况下,修改子系统的实现。
假设你有一个 家庭影院系统,包括 DVD 播放器、投影仪、屏幕、音响等设备。每个设备都有自己的控制接口,如果直接操作这些设备,客户端代码会非常复杂。通过外观模式,可以创建一个家庭影院外观类,提供一个简单的接口来控制整个系统。
public class HomeTheaterFacade {
private DvdPlayer dvdPlayer;
private Projector projector;
private Screen screen;
private Amplifier amplifier;
public HomeTheaterFacade(DvdPlayer dvdPlayer, Projector projector, Screen screen, Amplifier amplifier) {
this.dvdPlayer = dvdPlayer;
this.projector = projector;
this.screen = screen;
this.amplifier = amplifier;
}
public void watchMovie(String movie) {
System.out.println("Get ready to watch a movie...");
screen.down();
projector.on();
dvdPlayer.play(movie);
amplifier.on();
}
public void endMovie() {
System.out.println("Shutting movie theater down...");
screen.up();
projector.off();
dvdPlayer.stop();
amplifier.off();
}
}
通过这个外观类,客户端代码可以非常简单地控制整个家庭影院系统:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DvdPlayer dvdPlayer = new DvdPlayer();
Projector projector = new Projector();
Screen screen = new Screen();
Amplifier amplifier = new Amplifier();
HomeTheaterFacade facade = new HomeTheaterFacade(dvdPlayer, projector, screen, amplifier);
facade.watchMovie("The Matrix");
facade.endMovie();
}
}
这样,客户端代码只需要调用外观类的 watchMovie 和 endMovie 方法,而不需要关心每个设备的具体操作。
