数据结构和算法-01背包问题02-背包问题常见解决方案
0-1背包
0-1背包的算法回顾
算法核心两种情况[动态规划]
-
当前物品不放入物品
dp[n][c] = dp[n-1][c]; //n表示当前的物品索引,c是当前的背包容量 -
当前物品放入背包
dp[n][c] = dp[n-1][c - weight[n-1]] + vals[n-1];
0-背包的一般描述
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][capacity+1];
for(int n = 1; n<=length; n++){
for(int c = 1; c <= capacity; c++){
dp[n][c] = Math.max(
dp[n-1][c],
dp[n-1][c-weight[n-1]] + vals[n-1];
);
}
}
一般解决方案
public class KnapackDp {
public int knapack(int[] weight, int[] vals, int capacity) {
final int LENGTH = weight.length;
int[][] dp = new int[W+1][capacity+1];
for(int n = 1; n <= LENGTH ;n++){
for(int c = 1; c <= capacity; c++){
if(weight[n-1] <= c){
dp[n][c]= Math.max(dp[n-1][c],
dp[n-1][c-weight[n-1]]+vals[n-1]);
}else {
dp[n][c] = dp[n-1][c];
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<dp.length;i++){
for(int j = 0; j<dp[i].length;j++){
System.out.print(dp[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
return dp[W-1][capacity];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] weight = {2, 1, 3};
int[] val = {4, 2, 3};
int capacity = 4;
System.out.println(new KnapackDp().knapack(weight, val, 4));
}
}
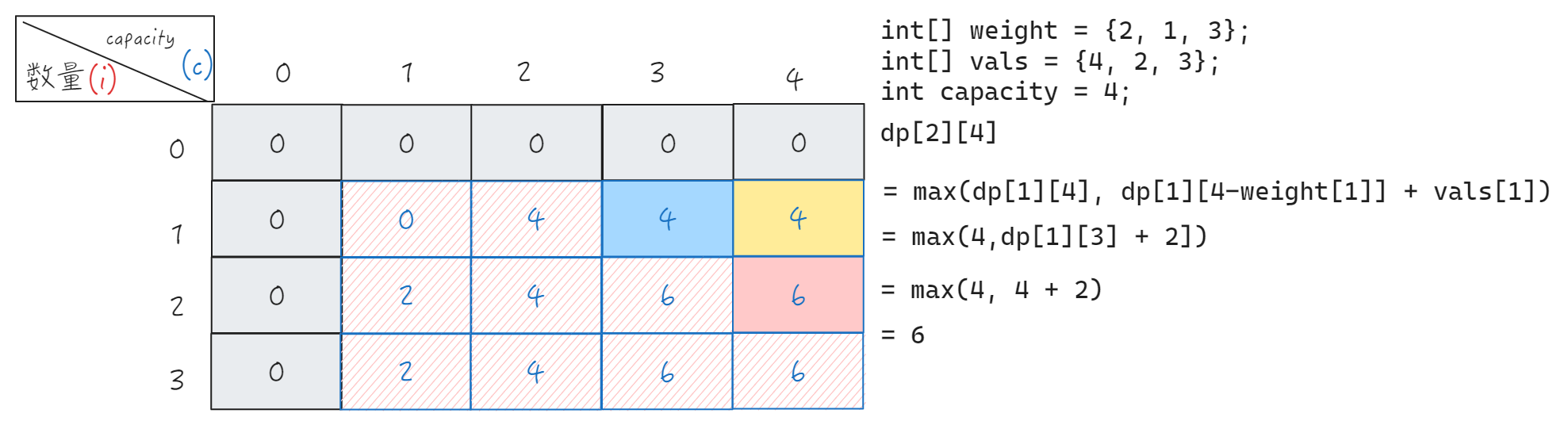
经典题目
分割等和子集
题目
[力扣416]416. 分割等和子集 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
给你一个 只包含正整数 的 非空数组 nums 。请你判断是否可以将这个数组分割成两个子集,使得两个子集的元素和相等。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,5,11,5]
输出:true
解释:数组可以分割成 [1, 5, 5] 和 [11] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,5]
输出:false
解释:数组不能分割成两个元素和相等的子集。
解题思路
-
如果两个子集的和相等,那么这个数组和一定是偶数
int capacity = 0; for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ capacity+=nums[i]; } -
对任意一个子集定义状态转移方程(0-1背包问题)
dp[i][c] = dp[i - 1][c] || dp[i - 1][c - nums[i - 1]];
参考实现
class Solution {
public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int capacity = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
capacity+=nums[i];
}
if(capacity %2 != 0) return false;
capacity /=2;
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[n + 1][capacity + 1];
dp[0][0] = true;
// i表示第几个数
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int c = 1; c <= capacity; c++) {
if (nums[i - 1] <= c) {
dp[i][c] = dp[i - 1][c] || dp[i - 1][c - nums[i - 1]];
}else{
dp[i][c] = dp[i-1][c];
}
}
}
return dp[n][capacity];
}
}
目标和
题目
[力扣494] 494. 目标和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
给你一个非负整数数组 nums 和一个整数 target 。
向数组中的每个整数前添加 '+' 或 '-' ,然后串联起所有整数,可以构造一个 表达式 :
- 例如,
nums = [2, 1],可以在2之前添加'+',在1之前添加'-',然后串联起来得到表达式"+2-1"。
返回可以通过上述方法构造的、运算结果等于 target 的不同 表达式 的数目。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,1,1,1], target = 3
输出:5
解释:一共有 5 种方法让最终目标和为 3 。
-1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
+1 - 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
+1 + 1 - 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
+1 + 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 3
+1 + 1 + 1 + 1 - 1 = 3
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1], target = 1
输出:1
解决方案
对于一个数组,假设正数部分和(X)和负数部分和(Y)。
sum = X + Y;
target = X - Y;
2X = sum + target;
X = (sum +target) / 2;
sum + target 不能为负数,如果为负数结果为负数
sum + target 必然为偶数,否则X的结果为小数。
设置背包容量 capacity = (target +sum )/2;
动态转换方程
-
不选的情况(默认)
dp[i][c] = dp[i - 1][c]; -
选中的情况
if (nums[i - 1] <= c) { // 1 dp[i][c] += dp[i - 1][c - nums[i - 1]]; }
参考实现
class Solution {
// y为负数部分
// x - y = target, x+ y = sum
// 2x = target +sum ; x = (target + sum)/2
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
int sum = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
sum += num;
}
if (target + sum < 0 || (target + sum) % 2 != 0)
return 0;
int capacity = (target + sum) / 2;
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][capacity + 1];
dp[0][0] =1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int c = 0; c <= capacity; c++) {
dp[i][c] = dp[i - 1][c]; // 0
if (nums[i - 1] <= c) { // 1
dp[i][c] += dp[i - 1][c - nums[i - 1]];
}
}
}
return dp[n][capacity];
}
}
最后一块石头重量II
题目
[力扣1049] 1049. 最后一块石头的重量 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
有一堆石头,用整数数组 stones 表示。其中 stones[i] 表示第 i 块石头的重量。
每一回合,从中选出任意两块石头,然后将它们一起粉碎。假设石头的重量分别为 x 和 y,且 x <= y。那么粉碎的可能结果如下:
- 如果
x == y,那么两块石头都会被完全粉碎; - 如果
x != y,那么重量为x的石头将会完全粉碎,而重量为y的石头新重量为y-x。
最后,最多只会剩下一块 石头。返回此石头 最小的可能重量 。如果没有石头剩下,就返回 0。
示例 1:
输入:stones = [2,7,4,1,8,1]
输出:1
解释:
组合 2 和 4,得到 2,所以数组转化为 [2,7,1,8,1],
组合 7 和 8,得到 1,所以数组转化为 [2,1,1,1],
组合 2 和 1,得到 1,所以数组转化为 [1,1,1],
组合 1 和 1,得到 0,所以数组转化为 [1],这就是最优值。
示例 2:
输入:stones = [31,26,33,21,40]
输出:5
解决方案
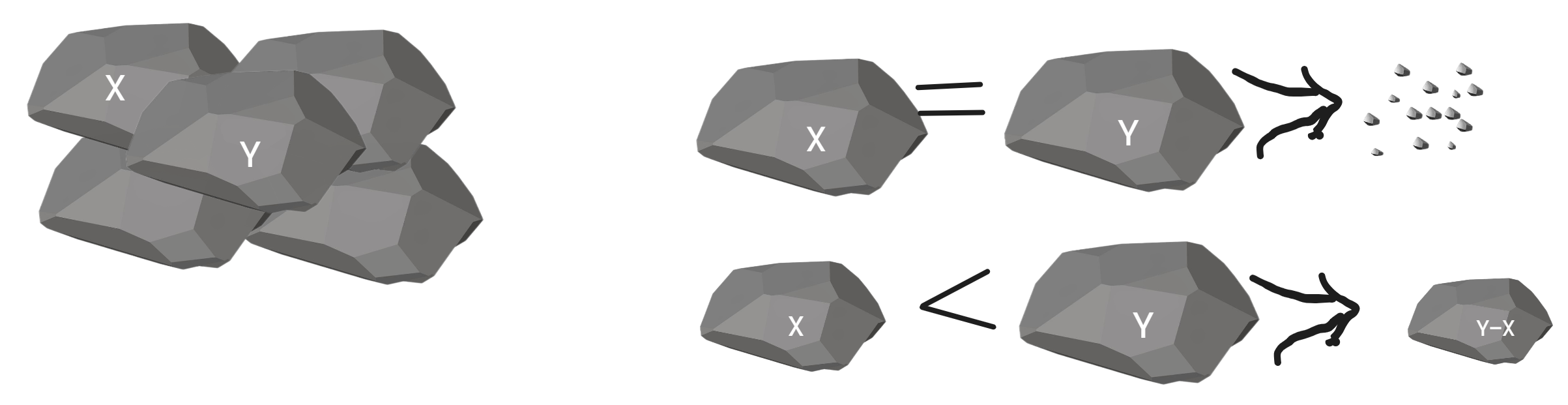
两块石头可能会都变为碎石,或者重量为Y-X,所以石块的重量不会超过: 总重/2;
int sum = 0;
for(int s : stones){
sum+=s;
}
int capacity = sum/2;
定义数组存储动态转移数据:
int n = stones.length;
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][capacity+1];
状态转移方程
if (stones[i-1] <= c) {
dp[i][c] = Math.max(
dp[i - 1][c],
dp[i - 1][c - stones[i - 1]] + stones[i - 1]
);
}else{
dp[i][c] = dp[i-1][c];
}
参考实现
class Solution {
public int lastStoneWeightII(int[] stones) {
int n = stones.length;
int sum = 0;
for (int s : stones) {
sum += s;
}
int capacity = sum / 2;
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][capacity + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int c = 1; c <= capacity; c++) {
if (stones[i - 1] <= c) {
dp[i][c] = Math.max(
dp[i - 1][c],
dp[i - 1][c - stones[i - 1]] + stones[i - 1]);
} else {
dp[i][c] = dp[i - 1][c];
}
}
}
// System.out.println("sum:" + sum);
// System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(dp));
return sum - 2 * dp[n][capacity];
}
}
