【MySQL】数据的增删查改
文章目录
- 1. 插入数据(Create)
- 1.1 全列插入
- 1.2 指定列插入
- 1.3 多行数据插入
- 1.4 插入否则更新
- 1.5 替换
- 2. 读取数据(Retrieve)
- 2.1 select列
- 2.2 where条件
- 2.3 结果排序
- 2.4 筛选分页结果
- 3. 修改数据(Update)
- 4. 删除数据(delete)
- 4.1 删除数据
- 4.2 截断表
- 5. 插入查询的结果
- 6. 分组与聚合统计
- 6.1 聚合统计
- 6.2 group by子句分组
对数据的操作本质上就是增删查改,在mysql中,他们有特别的名字,我们将其称为
CRUD(
Creat Retrieve Update Delete),接下来我们依次介绍这些内容
1. 插入数据(Create)
语法:
insert [into] table_name
[column [, column ...]]
values (value_list)[, (value_list)] ...
value_list: value [, value] ...
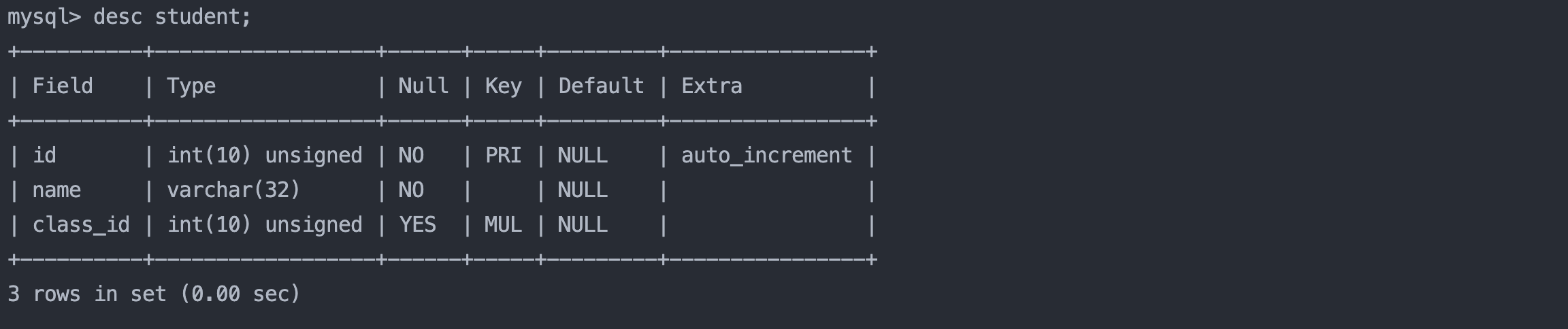
接下来的测试表结构:
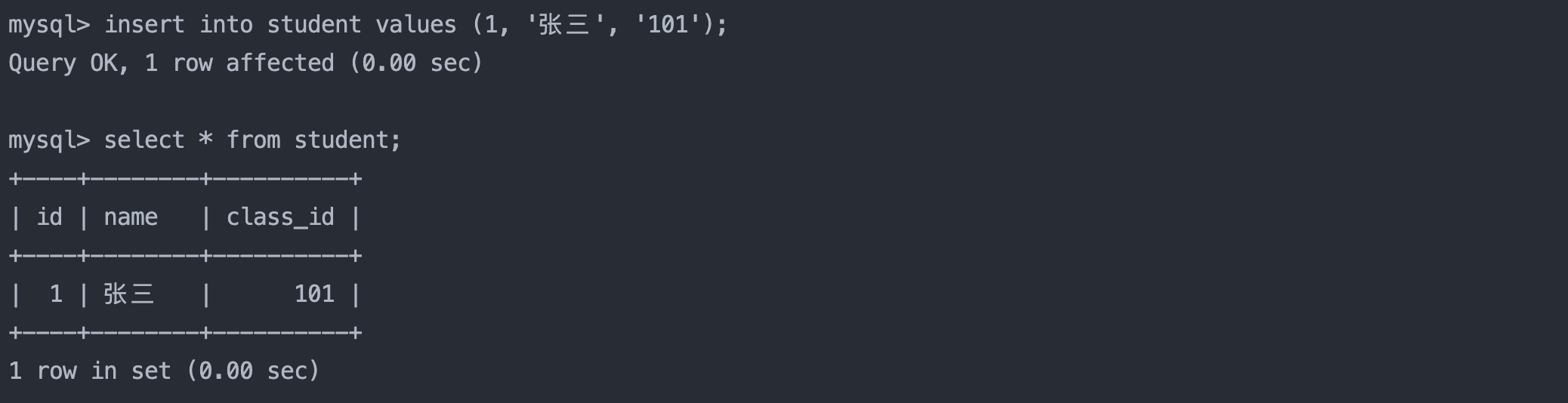
1.1 全列插入
insert into student values (1, '张三', '101');
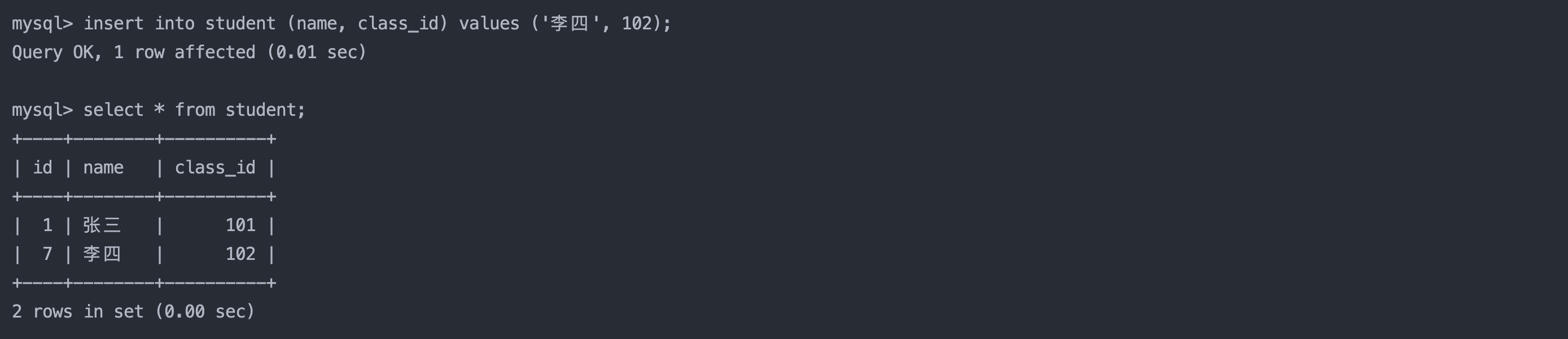
1.2 指定列插入
insert into student (name, class_id) values ('李四', 102);
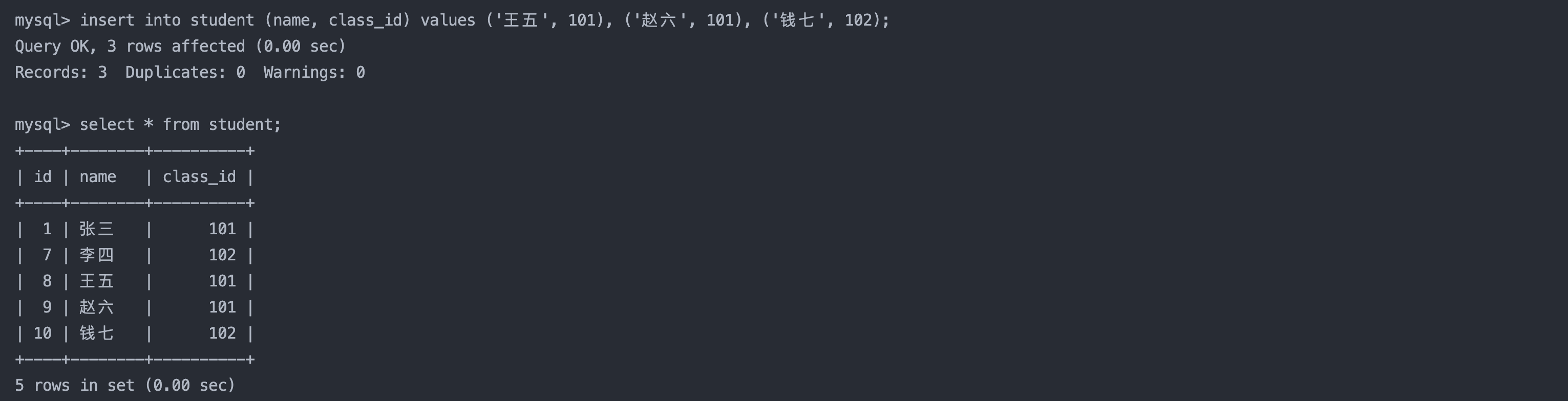
1.3 多行数据插入
insert into student (name, class_id) values ('王五', 101), ('赵六', 101), ('钱七', 102);
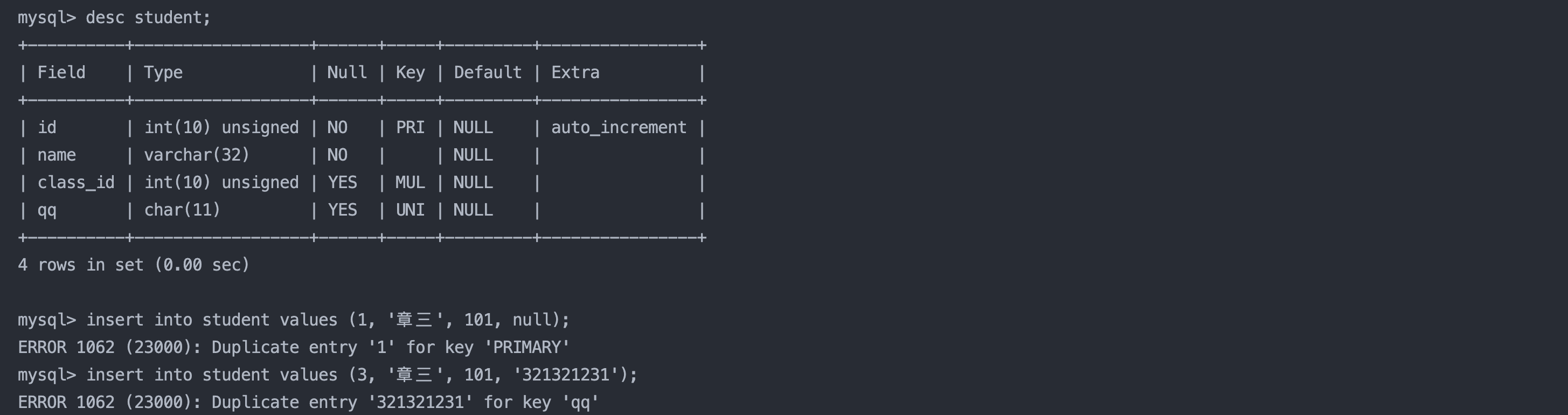
1.4 插入否则更新
数据插入时,可能会因为主键或者唯一键冲突而导致插入失败,此时可以选择性的进行同步更新操作。
语法:
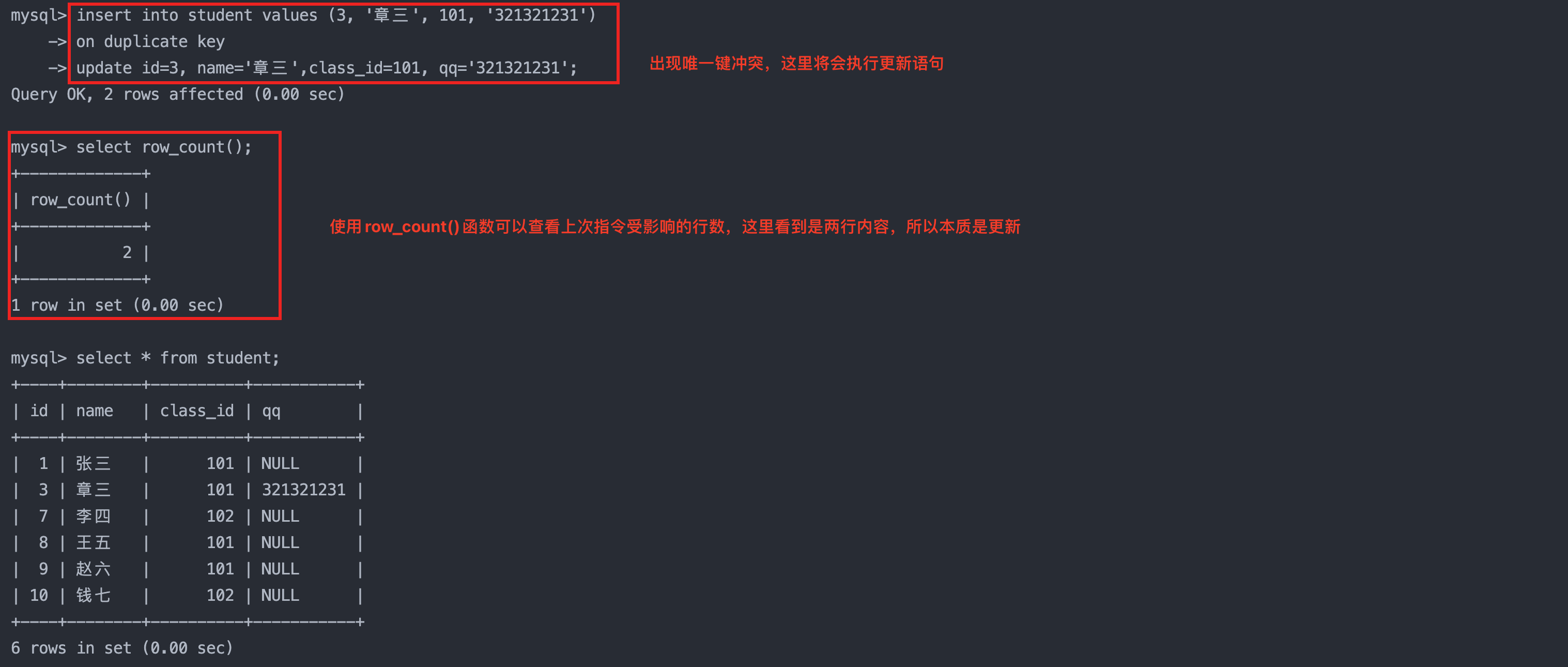
insert ... on duplicate key update
column = value [, column = value] ...
1.5 替换
语法:
replace [into] table_name
[column [, column ...]]
values (value_list)[, (value_list)] ...
value_list: value [, value] ...

2. 读取数据(Retrieve)
案例构建:
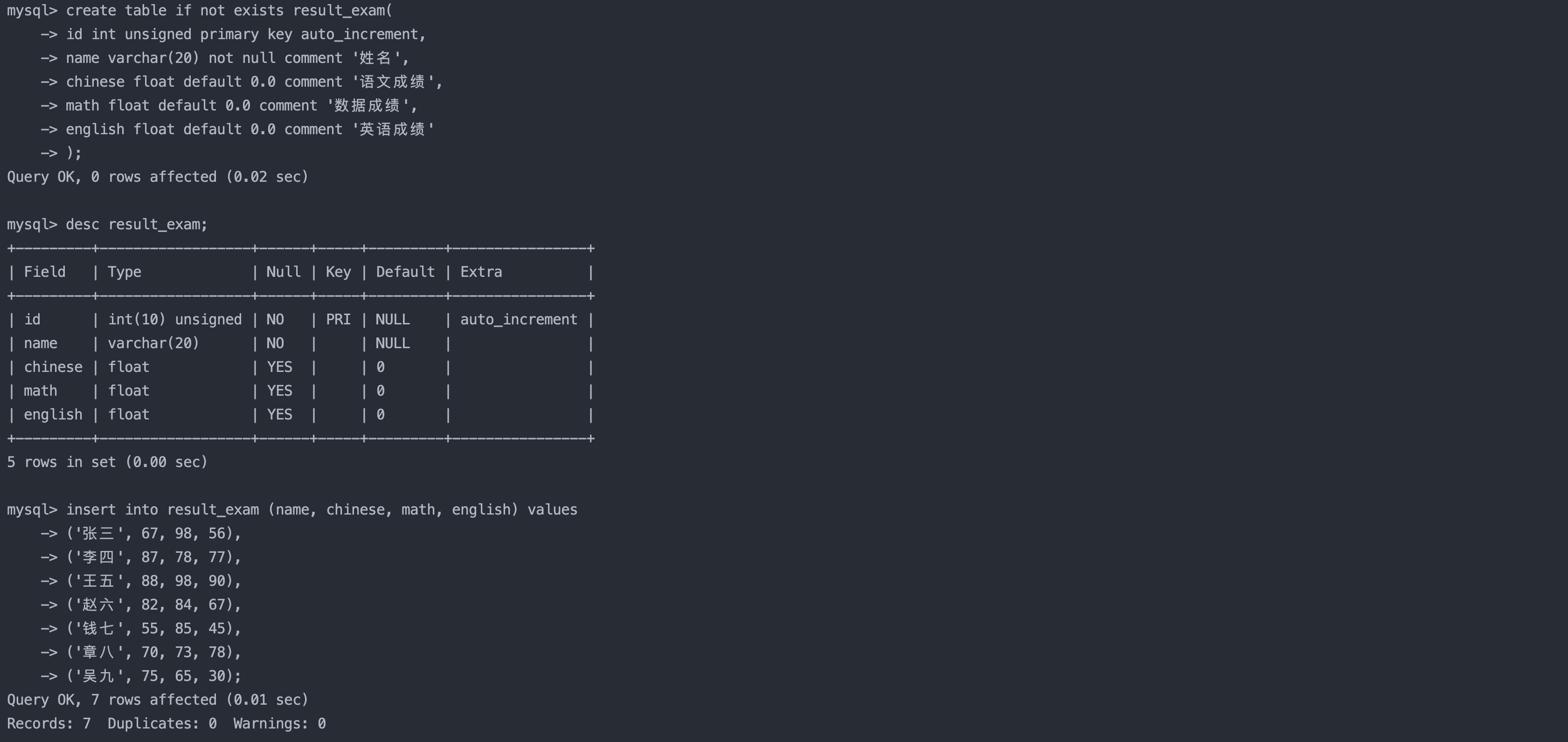
create table if not exists result_exam(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null comment '姓名',
chinese float default 0.0 comment '语文成绩',
math float default 0.0 comment '数据成绩',
english float default 0.0 comment '英语成绩'
);
insert into result_exam (name, chinese, math, english) values
('张三', 67, 98, 56),
('李四', 87, 78, 77),
('王五', 88, 98, 90),
('赵六', 82, 84, 67),
('钱七', 55, 85, 45),
('章八', 70, 73, 78),
('吴九', 75, 65, 30);
2.1 select列
基本语法:
SELECT
[DISTINCT] {* | {column [, column] ...} -- 这里可以是*或者任何列,列之间使用“,”隔开
[FROM table_name] -- 这里是从那个表中查询
[WHERE ...] -- 筛选表中符合条件的数据
[ORDER BY column [ASC | DESC], ...] -- 对筛选出来的数据进行排序
LIMIT ... -- 对排序出的数据进行分页显示
注意:通常情况下不建议使用 * 进行全列查询
- 查询的列越多,意味着需要传输的数据量越大;
- 可能会影响到索引的使用。(索引待后面课程讲解)
1. 全列查询

2. 指定列查询

3. 表达式查询与计算
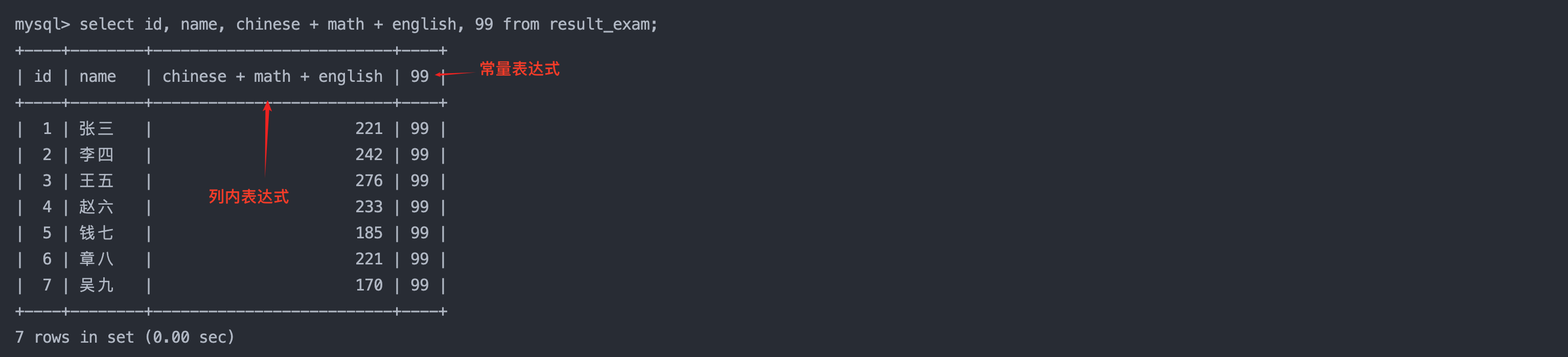
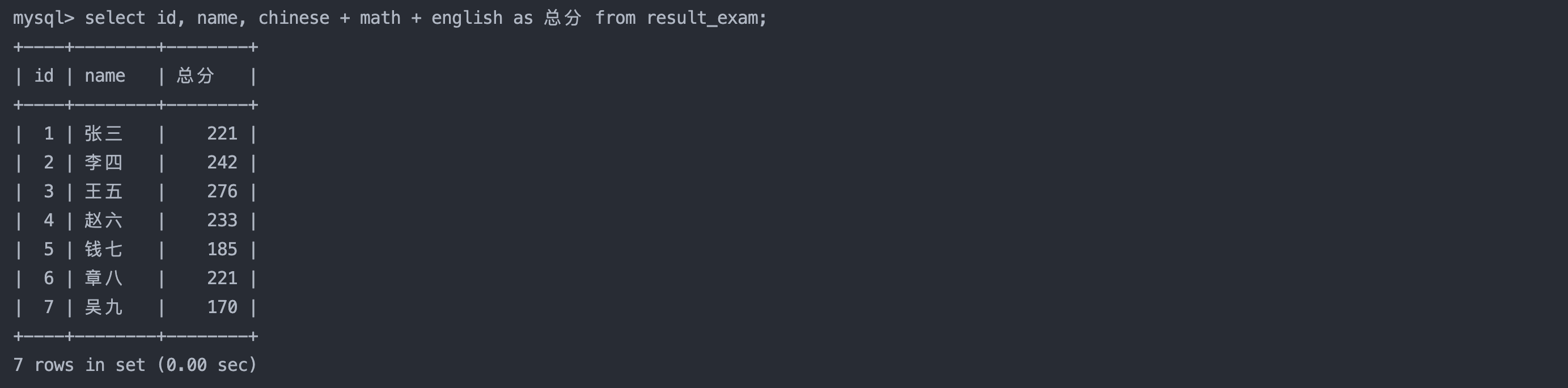
4. 为查询结果指定别名
语法:
select column [as] alias_name [...] from table_name;
5. 去重结果
语法:
select distinct ...

2.2 where条件
和C/C++的条件表达式类似,这里的条件也是选取表达式为真的结果,那么自然会有一些比较运算符和逻辑运算符
- 比较运算符
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| >,>=,<,<= | 大于,大于等于,小于,小于等于 |
| = | 等于,NULL不安全,例如NULL = NULL的结果是NULL |
| <=> | 等于,NULL安全,例如NULL = NULL的结果是true(1) |
| !=,<> | 不等于 |
| between a0 and a1 | 范围匹配,[a0,a1],如果a0 <= value <= a1,返回true |
| in(option, …) | 如果是option中的任意一个,返回true |
| is null | 是null |
| is not null | 不是null |
| Like | 模糊匹配。%表示任意多个(包括0个)任意字符;_表示任意一个字符 |
- 逻辑运算符
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| and | 多个条件都必须为true(1), 结果才是true(1) |
| or | 任意一个条件为true(1),结果为true(1) |
| not | 条件为true(1),结果为false(0) |
案例:
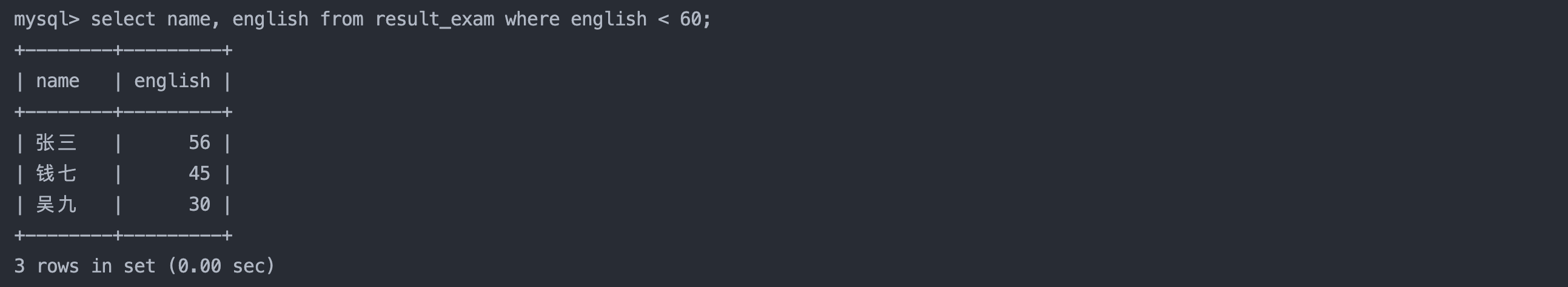
1. 英语不及格的同学及英语成绩 ( < 60 )
select name, english from result_exam where english < 60;
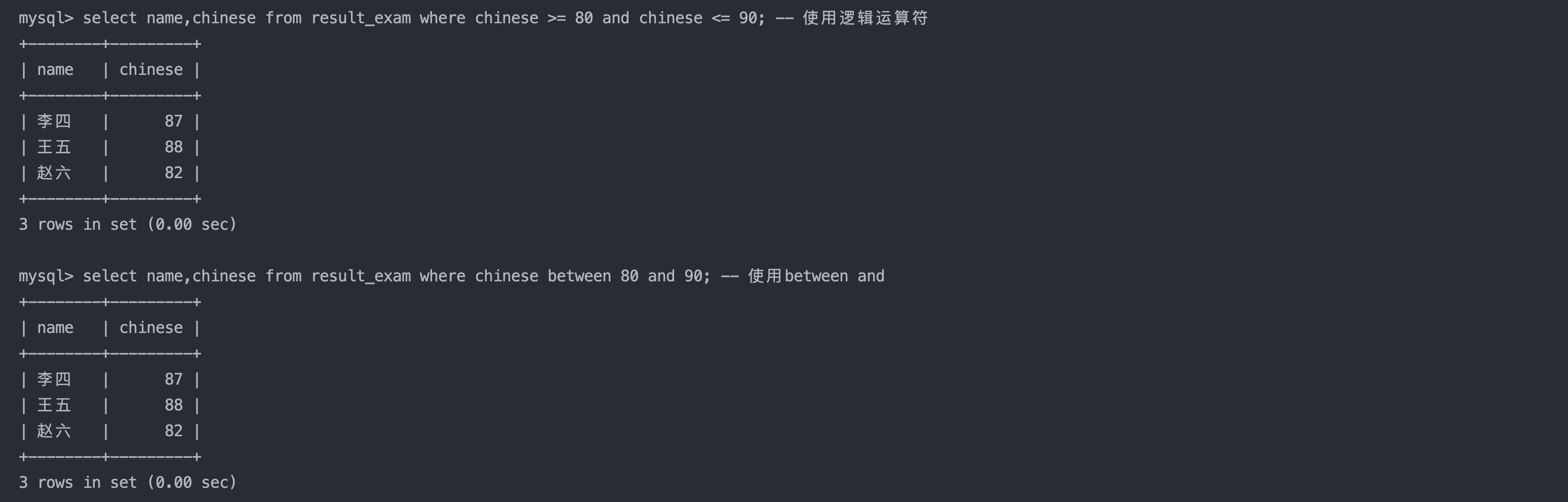
2. 语文成绩在 [80, 90] 分的同学及语文成绩
select name,chinese from result_exam where chinese >= 80 and chinese <= 90; -- 使用逻辑运算符 select name,chinese from result_exam where chinese between 80 and 90; -- 使用between and
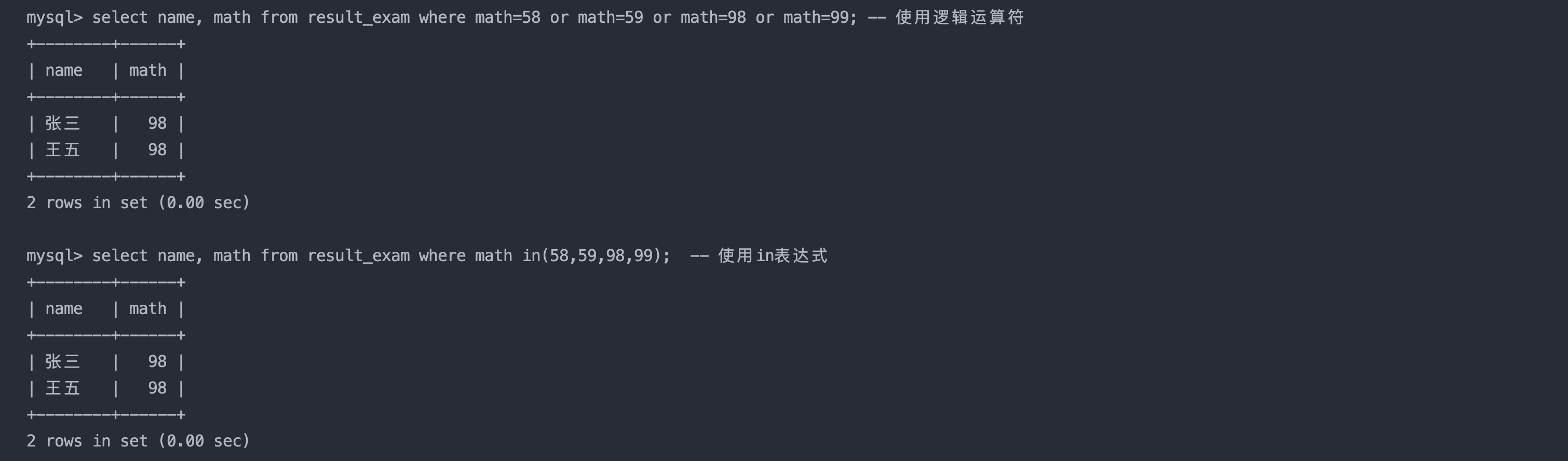
3. 数学成绩是 58 或者 59 或者 98 或者 99 分的同学及数学成绩
select name, math from result_exam where math=58 or math=59 or math=98 or math=99; -- 使用逻辑运算符 select name, math from result_exam where math in(58,59,98,99); -- 使用in表达式
4. 姓张的同学 及 张某同学
select * from result_exam where name like '张%'; -- % 匹配任意多个(包括 0 个)任意字符 select * from result_exam where name like '张_'; -- _ 匹配1个任意字符
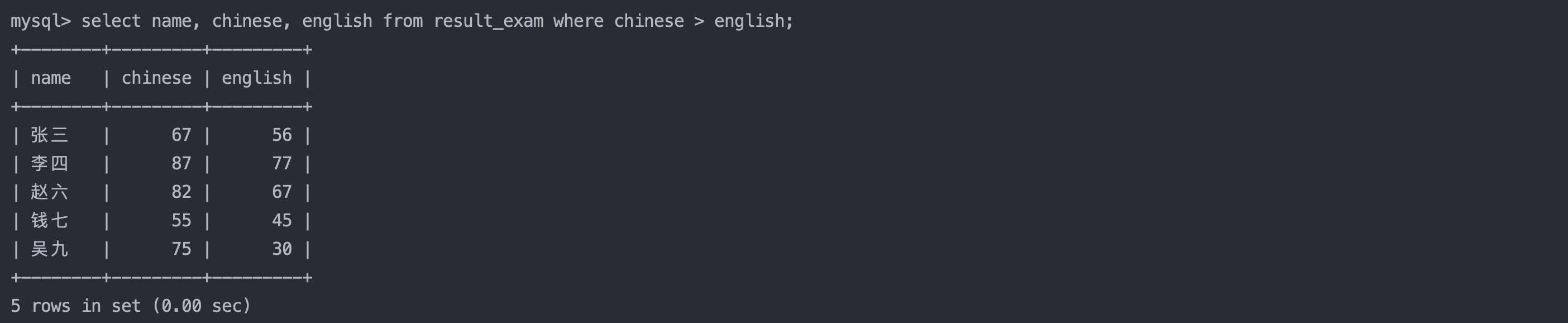
5. 语文成绩好于英语成绩的同学
select name, chinese, english from result_exam where chinese > english;
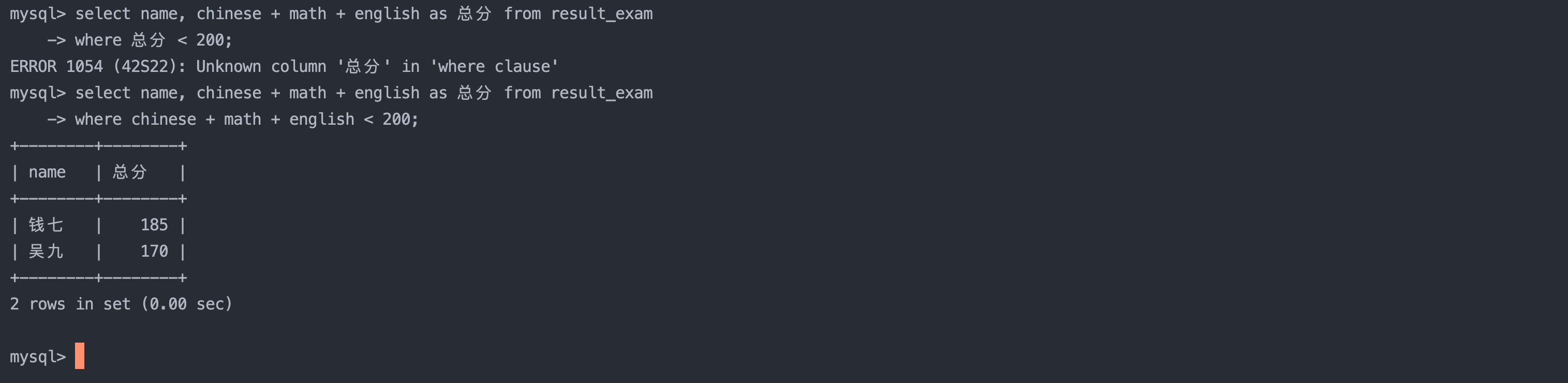
6. 总分在 200 分以下的同学
select name, chinese + math + english as 总分 from result_exam where chinese + math + english < 200; -- 注意,这里不能在where子句中使用select的重命名,因为查询语句中是先执行where子句,此时还没有重命名
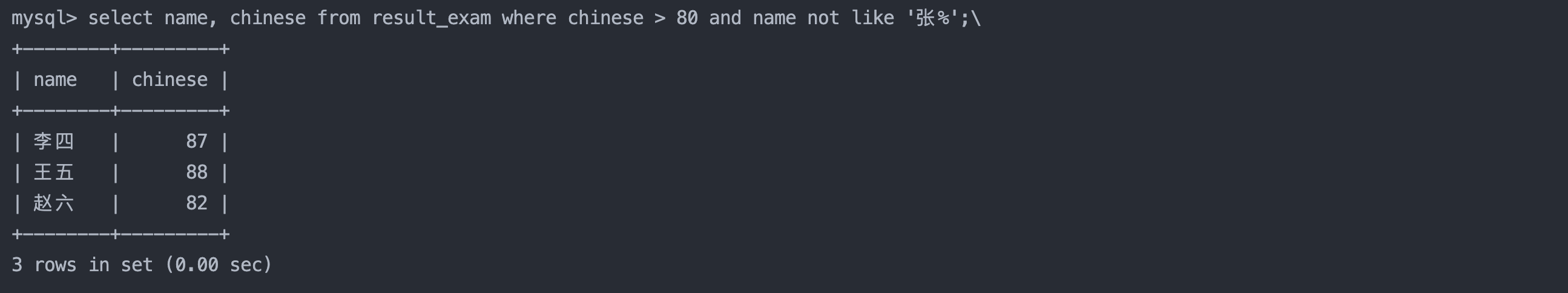
7. 语文成绩 > 80 并且不姓张的同学
select name, chinese from result_exam where chinese > 80 and name not like '张%';
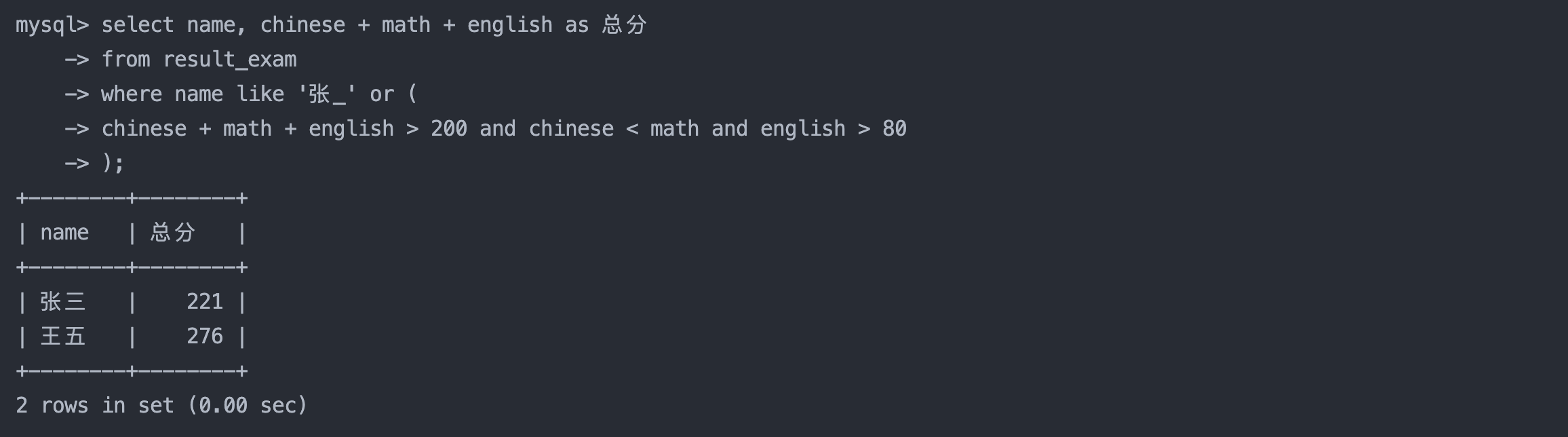
8. 张某同学,否则要求总成绩 > 200 并且 语文成绩 < 数学成绩 并且 英语成绩 > 80
select name, chinese + math + english as 总分 from result_exam where name like '张_' or ( chinese + math + english > 200 and chinese < math and english > 80 );
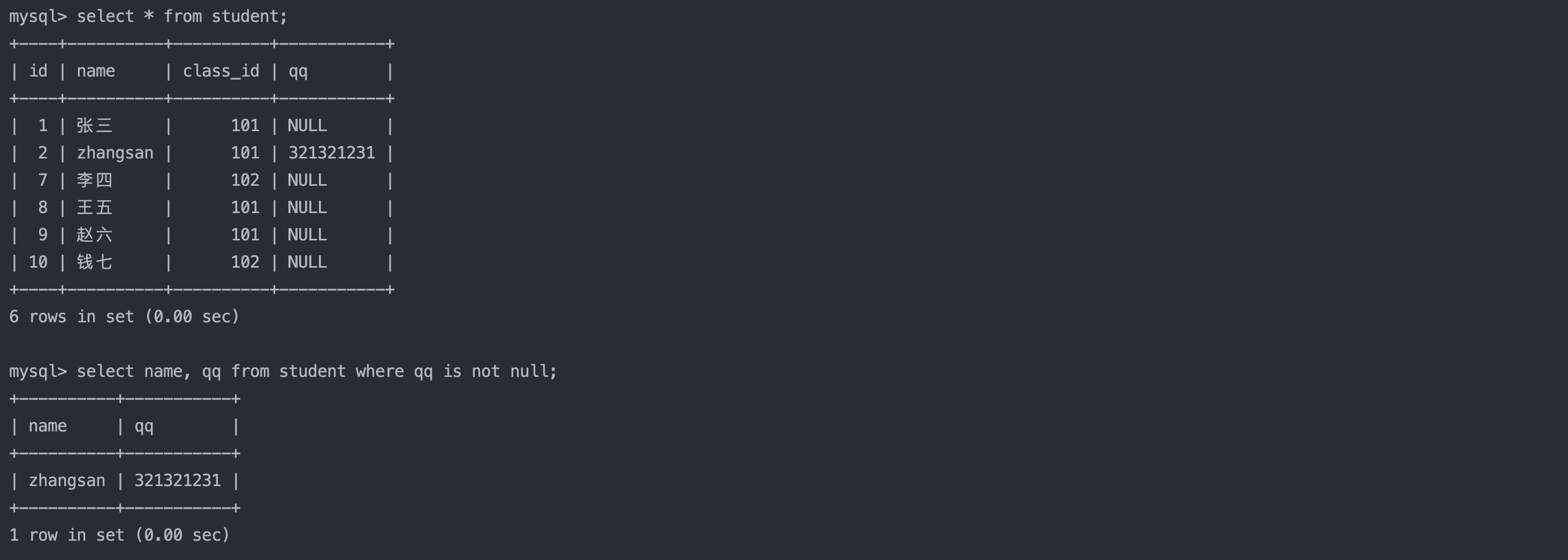
9. NULL查询
select name, qq from student where qq is not null;
在最开始我们说到where的比较运算符中有NULL安全和NULL不安全之分,这里我们演示一下
2.3 结果排序
select ... from table_name [where ...]
order by column [asc|desc], [...];
-- asc 为升序(从小到大) -- desc 为降序(从大到小) -- 默认为 ASC
注意:没有 ORDER BY 子句的查询,返回的顺序是未定义的,永远不要依赖这个顺序
案例:
1. 同学及数学成绩,按数学成绩升序显示
select name, math from result_exam order by math;
2. 同学及 qq 号,按 qq 号排序显示
select name, qq from student order by qq;
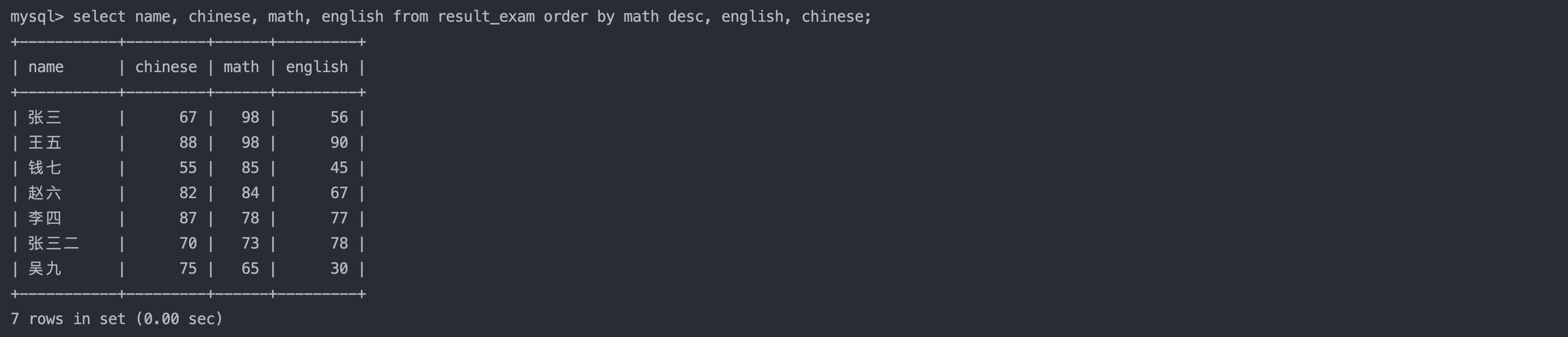
3. 查询同学各门成绩,依次按 数学降序,英语升序,语文升序的方式显示
select name, chinese, math, english from result_exam order by math desc, english, chinese; -- order by的排序顺序可以有多个排序规则,按照先后顺序排序,执行排序
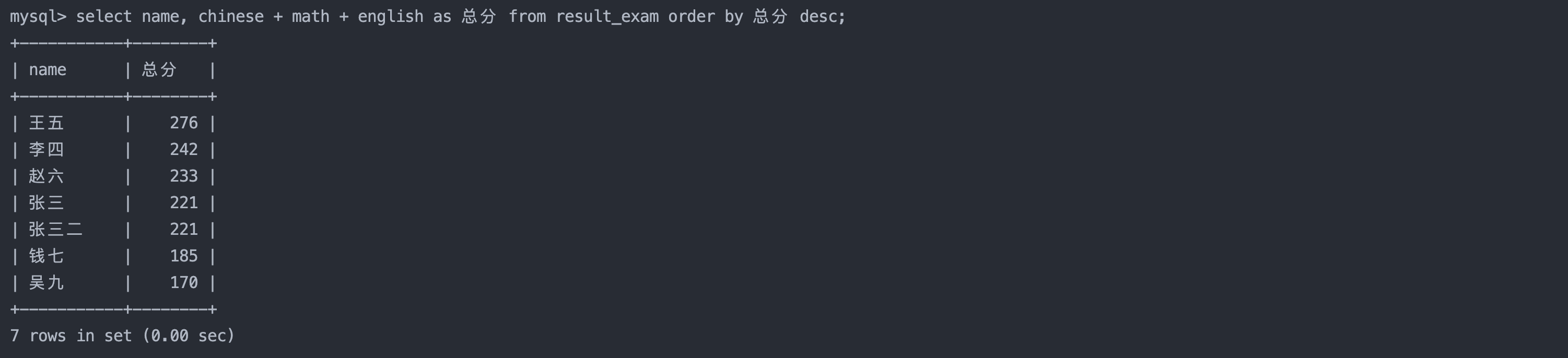
4. 查询同学及总分,由高到低
select name, chinese + math + english as 总分 from result_exam order by 总分 desc; -- 在order by的时候可以使用 select 语句的地方重命名的表达式,因为order by的执行本质上是将select查询到的内容进行排序,所以是先执行select再执行order by
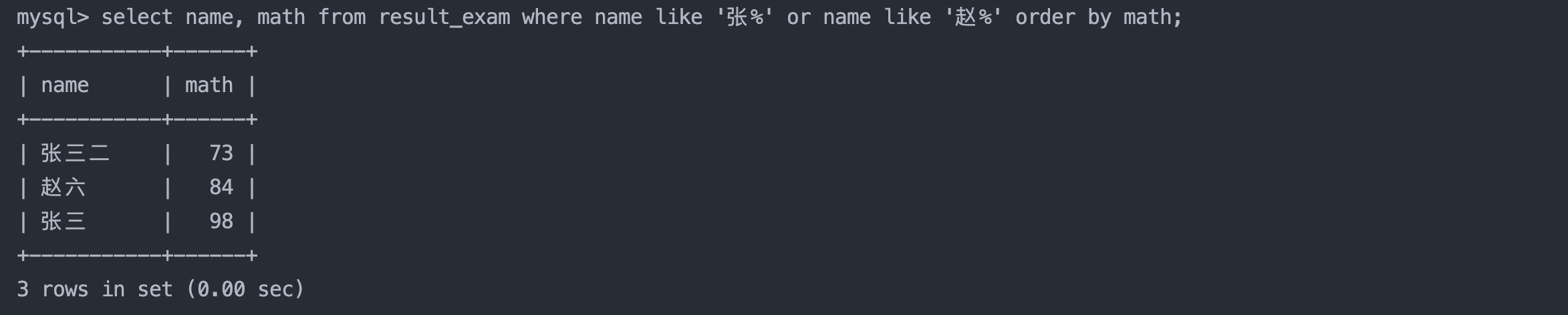
5. 查询姓张的同学或者姓赵的同学数学成绩,结果按数学成绩由高到低显示
select name, math from result_exam where name like '张%' or name like '赵%' order by math;
2.4 筛选分页结果
语法:
-- 起始下标为 0
-- 从 0 开始,筛选 n 条结果
select ... from table_name [where ...] [order by ...] limit n;
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果
select ... from table_name [where ...] [order by ...] limit s, n;
-- 从 s 开始,筛选 n 条结果,比第二种用法更明确,建议使用
select ... from table_name [WHERE ...] [order by ...] limit n offset s;
建议:对未知表进行查询时,最好加一条 LIMIT 1,避免因为表中数据过大,查询全表数据导致数据库卡死
案例:
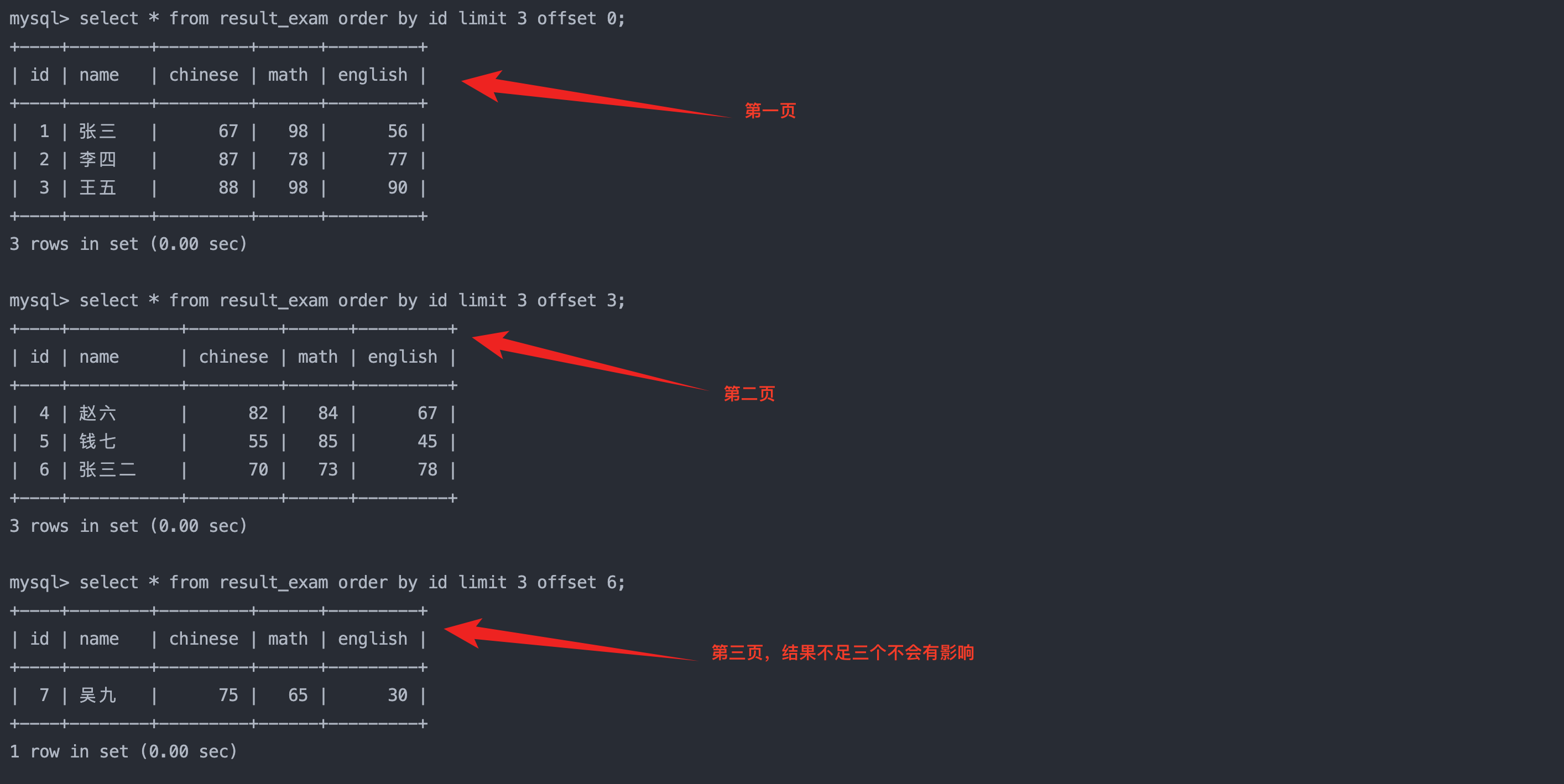
1按 id 进行分页,每页 3 条记录,分别显示 第 1、2、3 页
select * from result_exam order by id limit 3 offset 0; select * from result_exam order by id limit 3 offset 3; select * from result_exam order by id limit 3 offset 6;
3. 修改数据(Update)
语法:
update table_name set column = expr [, column = expr ...]
[where ...] [order by ...] [limit ...]
案例:
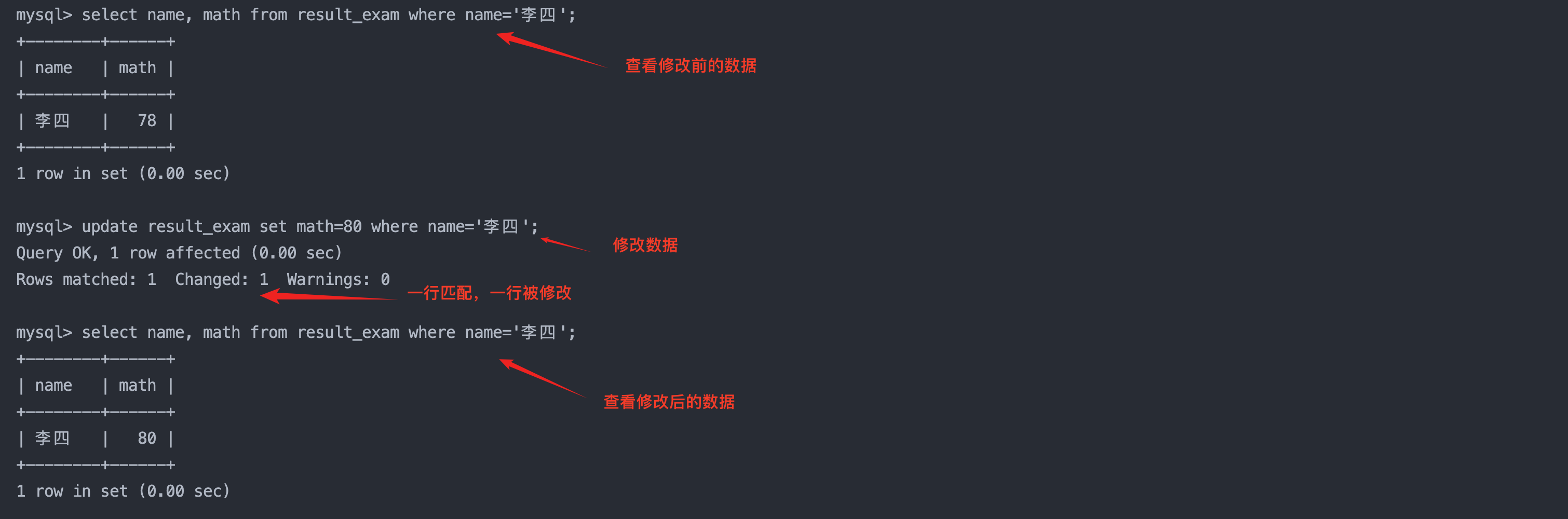
1. 将李四的数学成绩变更为80分
update result_exam set math = 80 where name = '李四';
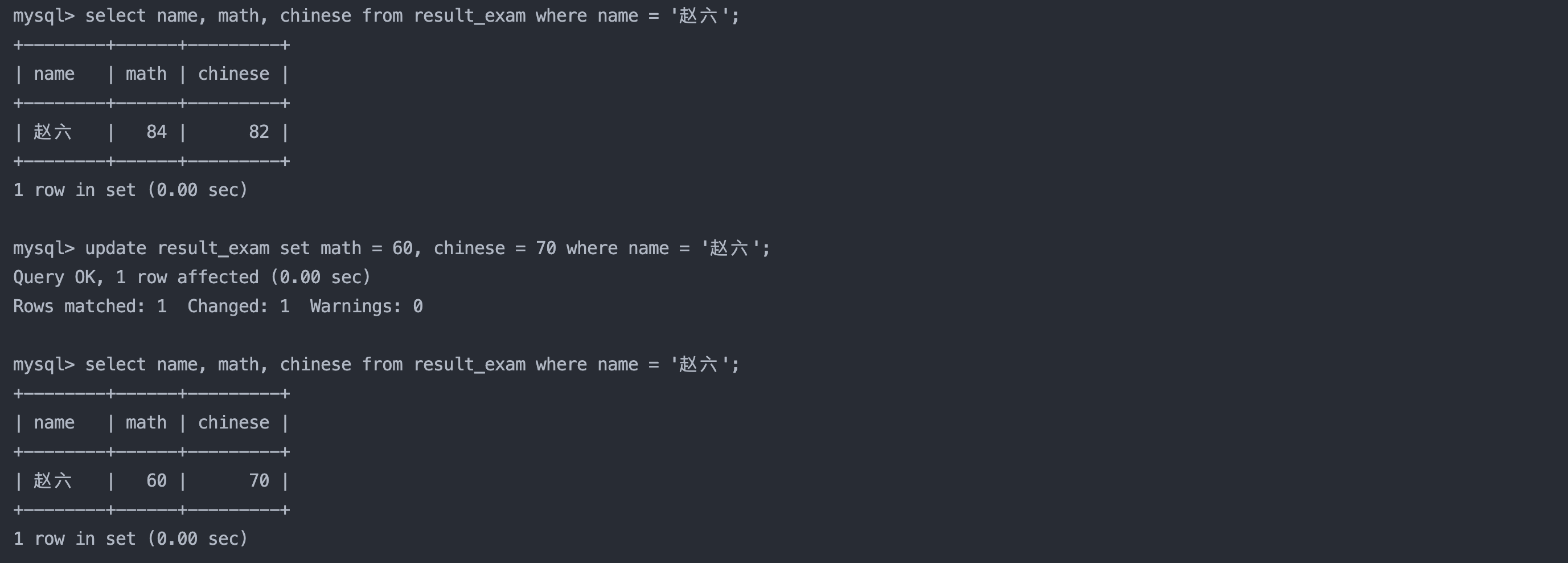
2. 将赵六同学的数学成绩变更为 60 分,语文成绩变更为 70 分
update result_exam set math = 60, chinese = 70 where name = '赵六';
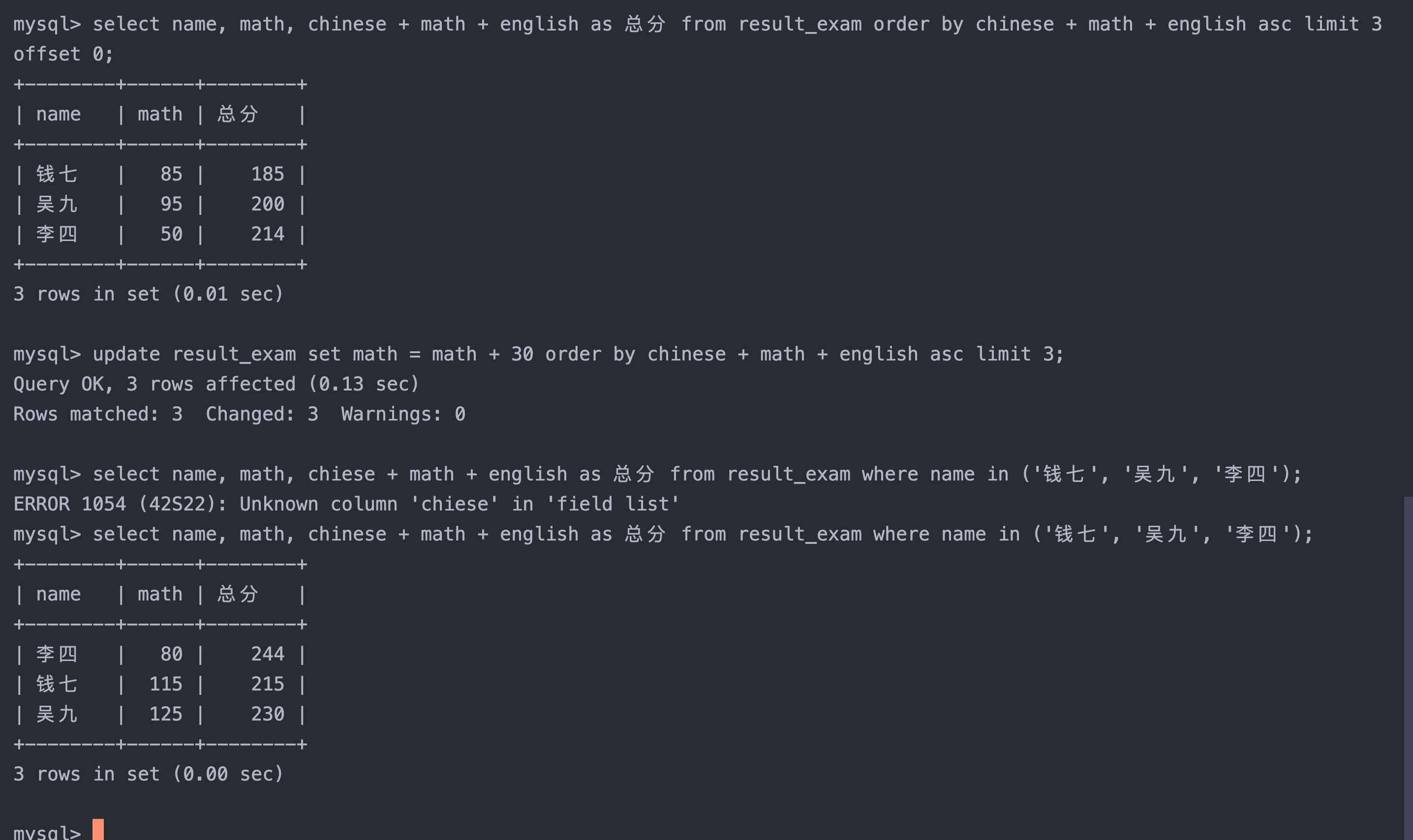
3. 将总成绩倒数前三的 3 位同学的数学成绩加上 30 分
select name, math, chinese + math + english as 总分 from result_exam order by chinese + math + english asc limit 3 offset 0; -- 查看数据 update result_exam set math = math + 30 order by chinese + math + english asc limit 3; -- 修改指定数据 select name, math, chinese + math + english as 总分 from result_exam where name in ('钱七', '吴九', '李四'); -- 查看之前修改的数据
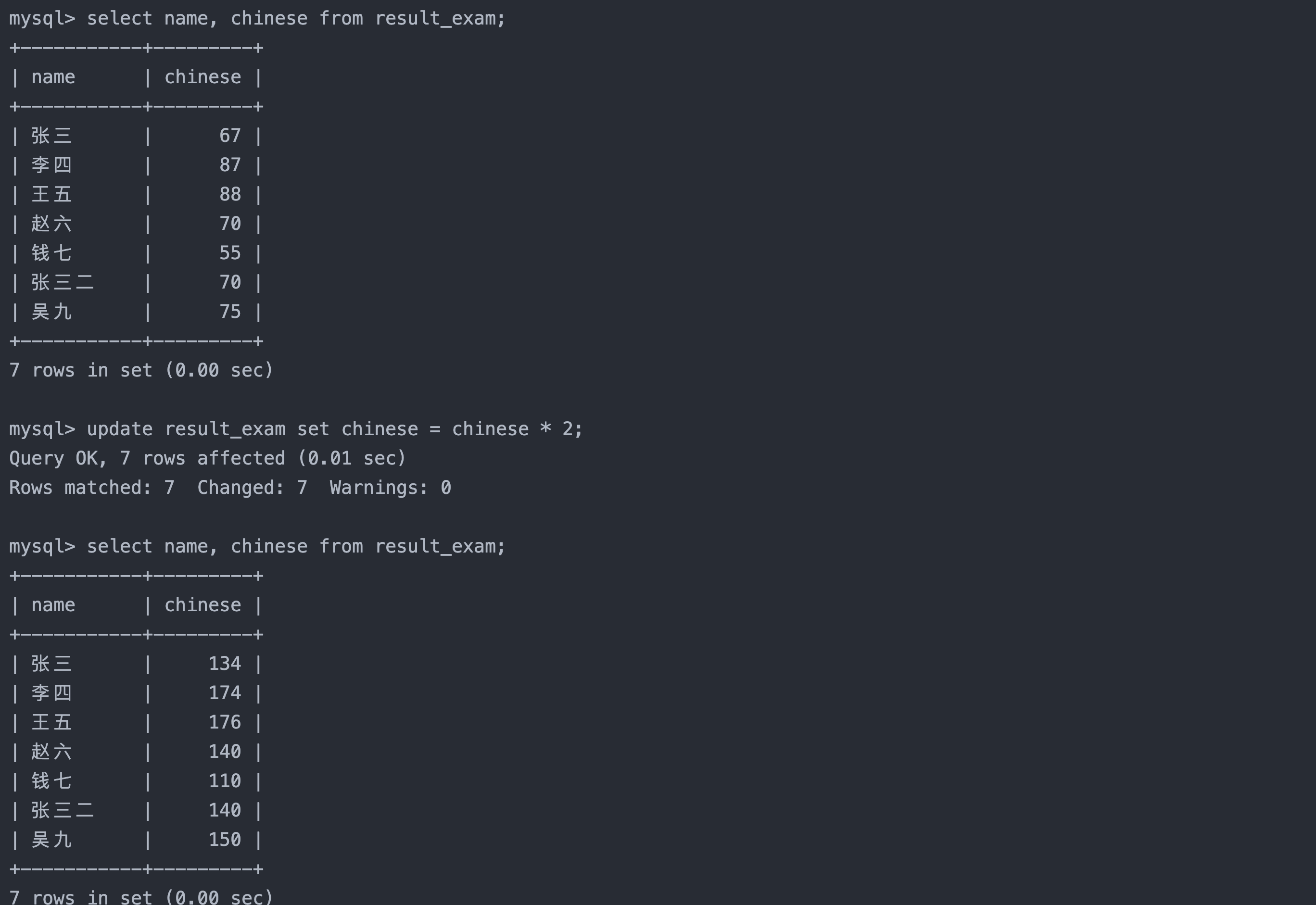
4. 将所有同学的语文成绩更新为原来的2倍
select name, chinese from result_exam; -- 查看全表 update result_exam set chinese = chinese * 2; -- 没有限制则更新全表 select name, chinese from result_exam; -- 查看更新后的数据
4. 删除数据(delete)
4.1 删除数据
语法:
delete from table_name [where ...] [order by ...] [limit ...]
案例:
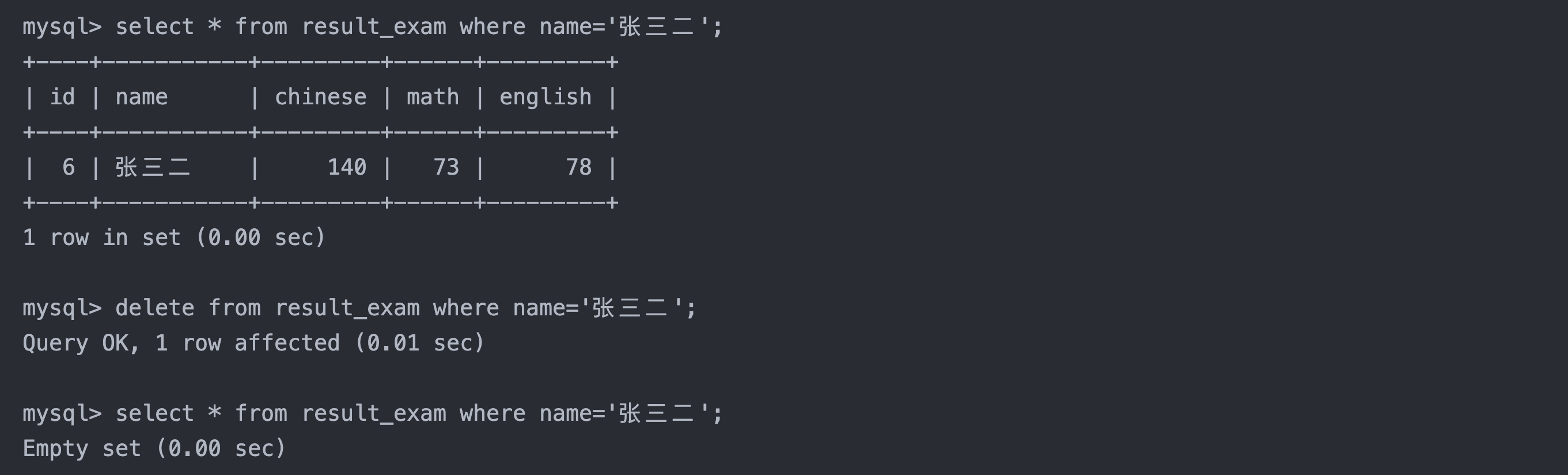
1. 删除张三二的成绩
select * from result_exam where name='张三二'; delete from result_exam where name='张三二'; select * from result_exam where name='张三二';
2. 删除整张表
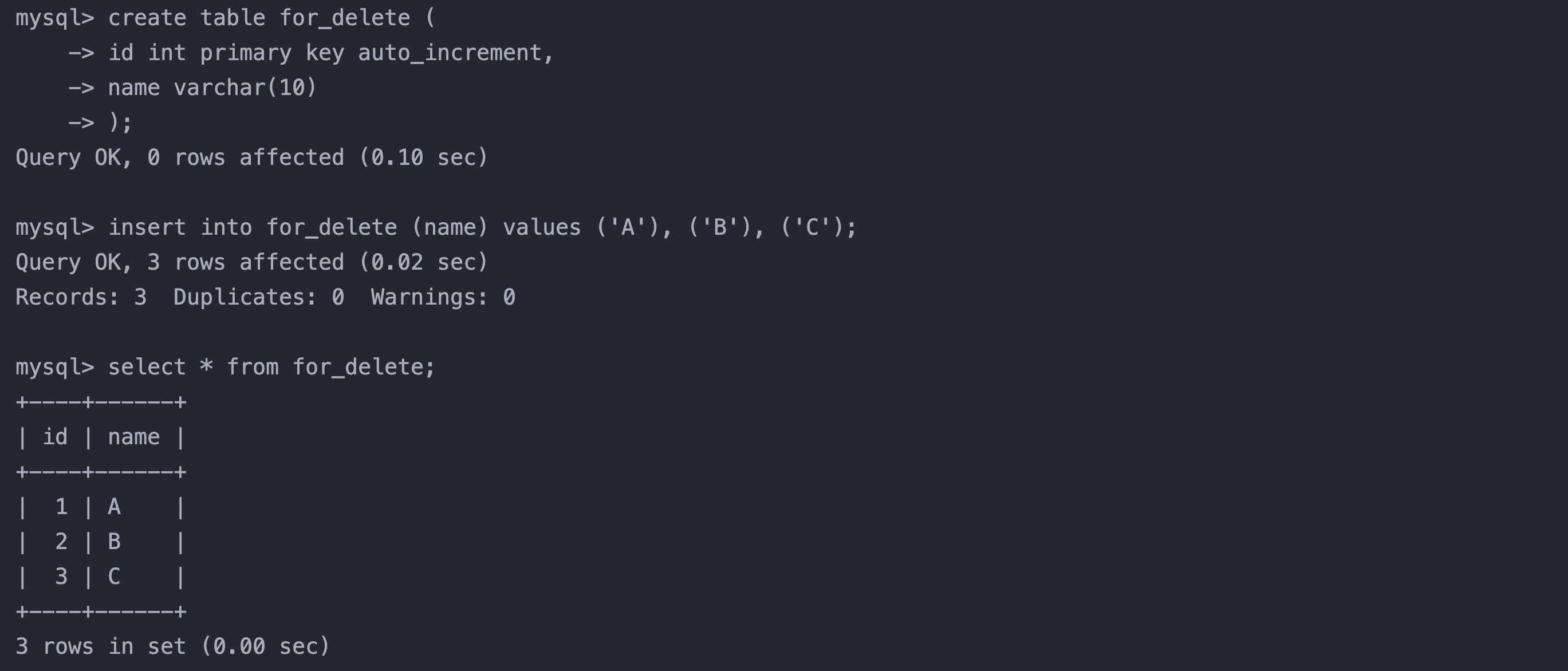
-- 准备测试表 create table for_delete ( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(10) ); -- 插入表数据 insert into for_delete (name) values ('A'), ('B'), ('C'); -- 查看插入的数据 select * from for_delete; -- 删除表 delete from for_delete; -- 查看删除之后的结果 select * from for_delete;
4.2 截断表
语法:
truncate [table] table_name
注意:这个操作慎用,原因如下
- 只能对整表操作,不能像
delete一样针对部分数据操作;- 实际上 MySQL 不对数据操作,所以比
delete更快,但是truncate在删除数据的时候,并不经过真正的事物,所以无法回滚- 会重置
auto_increment项
案例:
create table for_truncate (id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20)); -- 准备测试表
insert into for_truncate (name) values ('A'), ('B'), ('C'); -- 插入测试数据
select * from for_truncate; -- 查看测试数据
truncate for_truncate; -- 截断整表数据,注意影响行数是 0,所以实际上没有对数据真正操作
select * from for_truncate; -- 查看删除结果
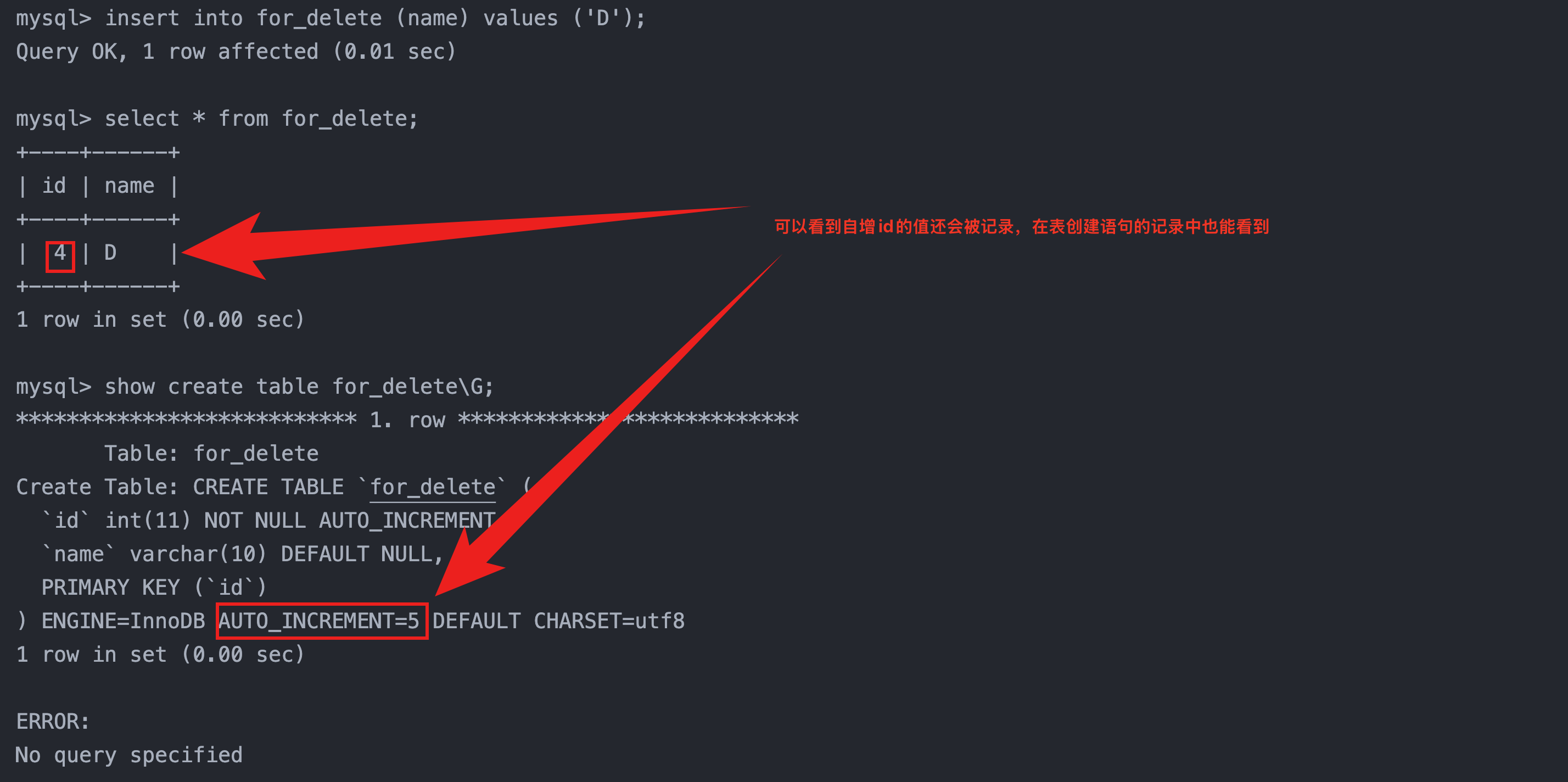
insert into for_truncate (name) values ('D'); -- 再插入一条数据,自增 id 在重新增长
select * from for_truncate; -- 查看数据
show create table for_truncate\G; -- 查看表结构,会有 AUTO_INCREMENT=2 项
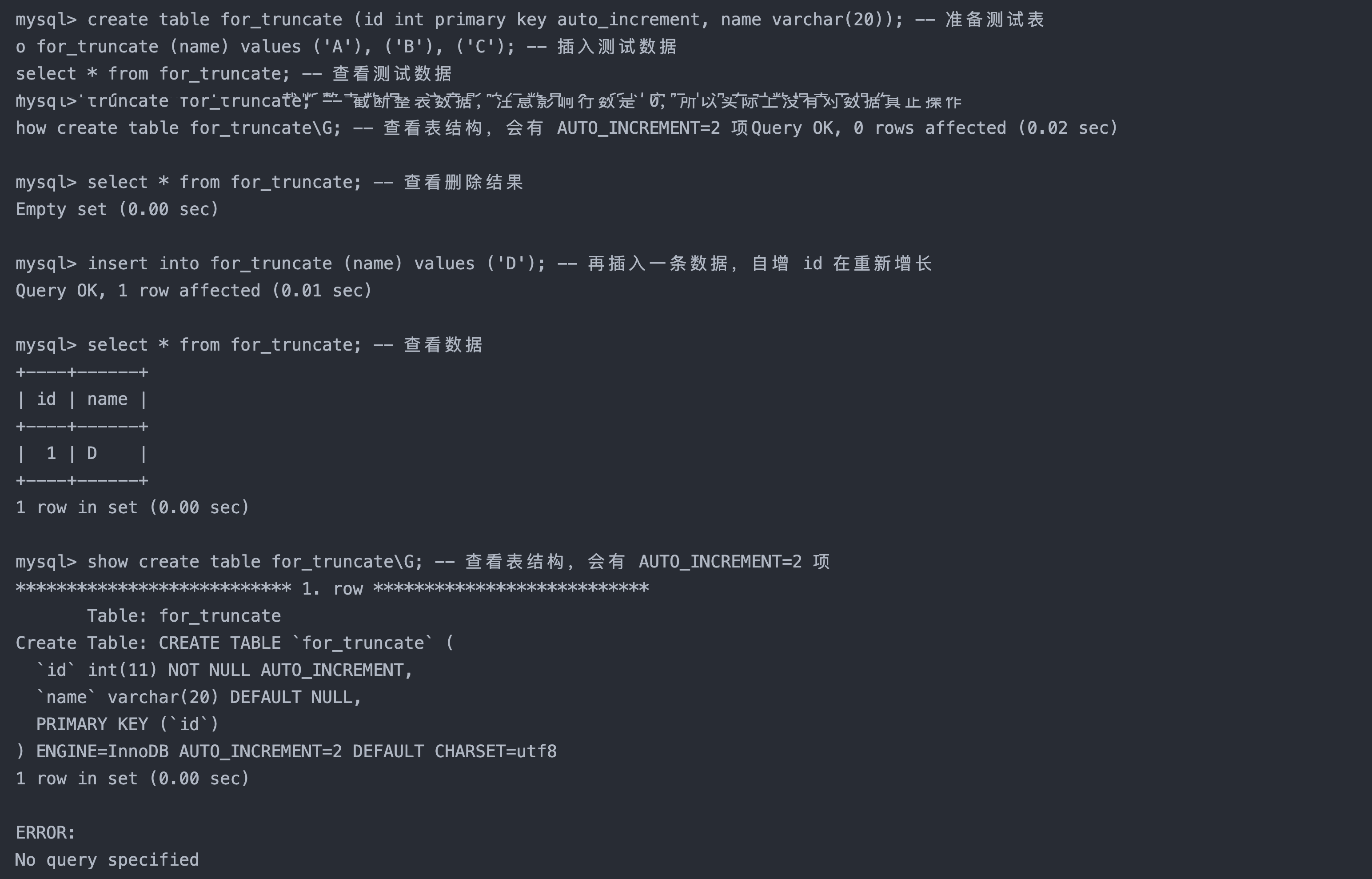
5. 插入查询的结果
案例:
insert into table_name [(column [, column ...])]
select ...
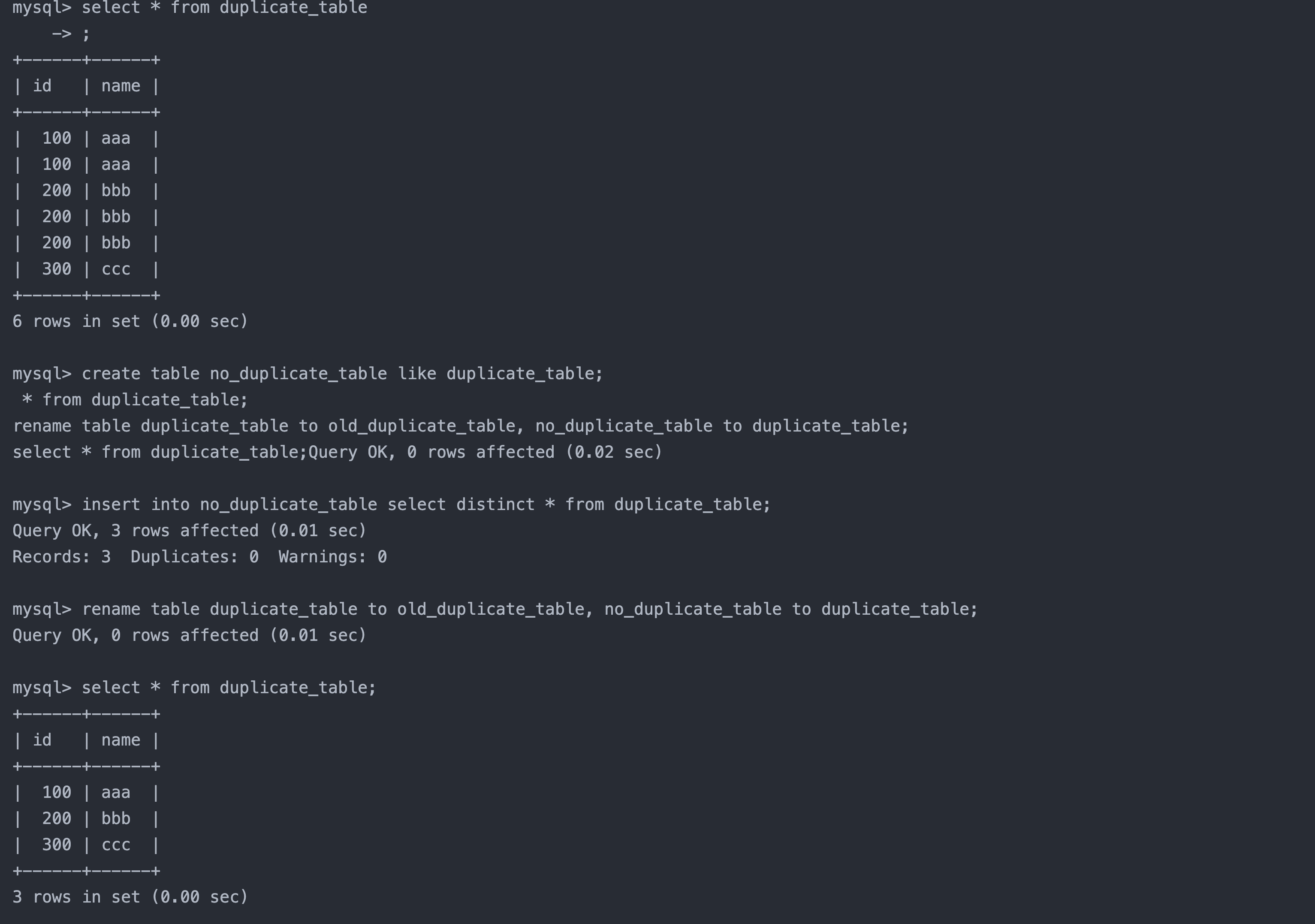
案例:删除表中的的重复复记录,重复的数据只能有一份
create table duplicate_table (id int, name varchar(20)); -- 创建原数据表
-- 插入测试数据
insert into duplicate_table values (100,'aaa'), (100, 'aaa'), (200,'bbb'), (200,'bbb'), (200,'bbb'), (300,'ccc');
处理思路:
- 创建一张空表 no_duplicate_table,结构和 duplicate_table 一样
- 将 duplicate_table 的去重数据插入到 no_duplicate_table
- 通过重命名表,实现原子的去重操作
- 查看最终结果
代码:
create table no_duplicate_table like duplicate_table; insert into no_duplicate_table select distinct * from duplicate_table; rename table duplicate_table to old_duplicate_table, no_duplicate_table to duplicate_table; select * from duplicate_table;
6. 分组与聚合统计
6.1 聚合统计
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| count([distinct] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 数量 |
| sum([distinct] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 总和,不是数字没有意义 |
| avg([distinct] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 平均值,不是数字没有意义 |
| max([distinct] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 最大值,不是数字没有意义 |
| min([distinct] expr) | 返回查询到的数据的 最小值,不是数字没有意义 |
案例:
1. 统计班级共有多少同学
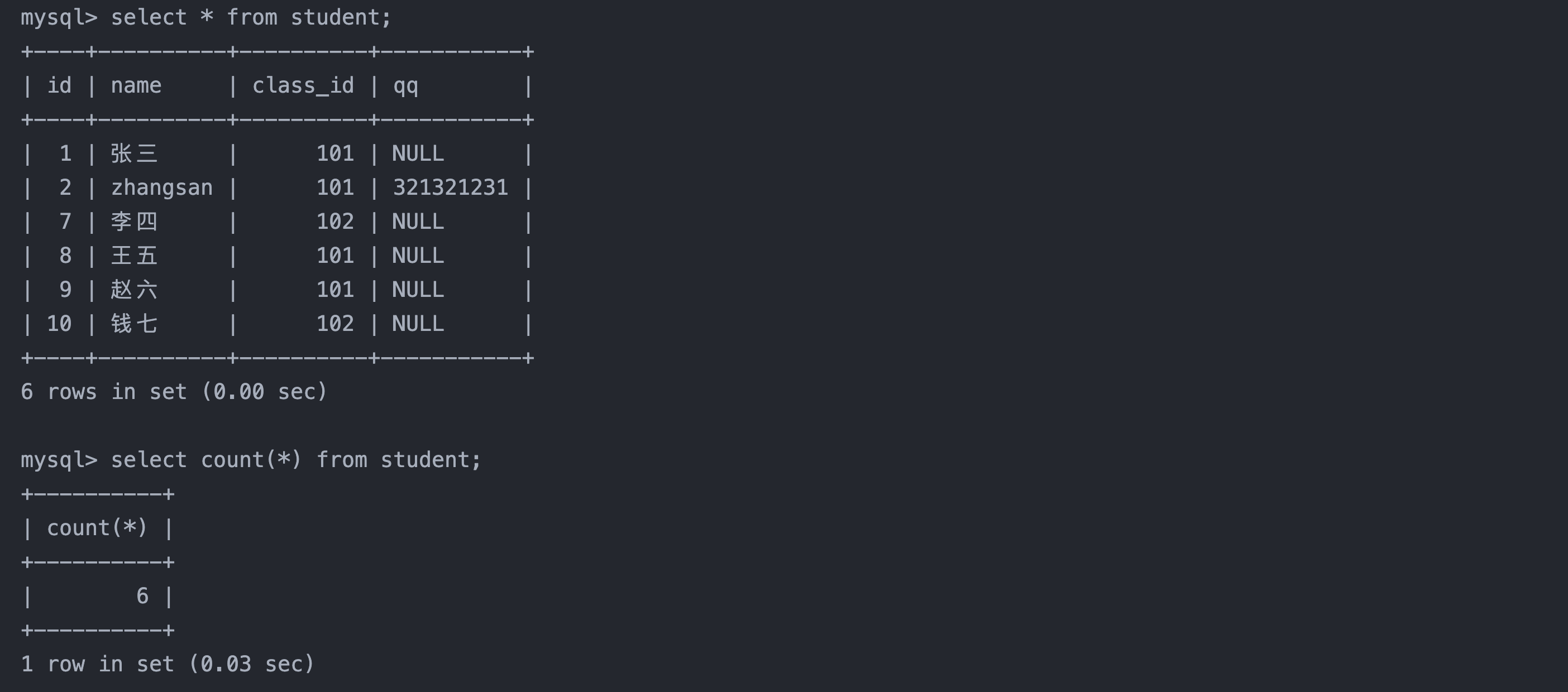
select count(*) from student;
2. 统计班级收集的 qq 号有多少
select count(qq) from student; -- NULL不计入结果
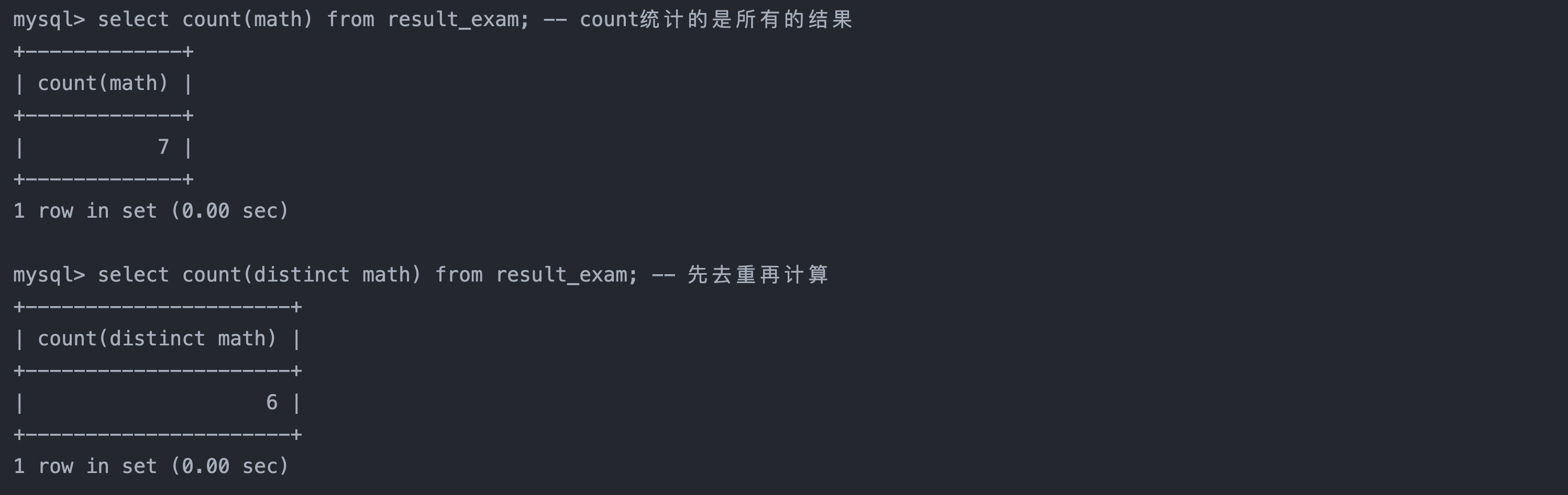
3. 统计本次考试的数学成绩分数个数
select count(math) from result_exam; -- count统计的是所有的结果 select count(distinct math) from result_exam; -- 先去重再计算
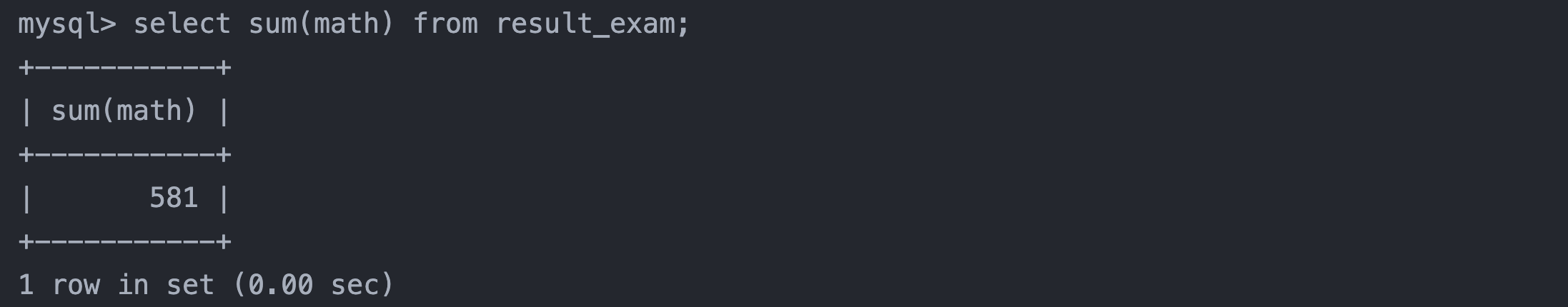
4. 统计数学成绩总分
select sum(math) from result_exam;
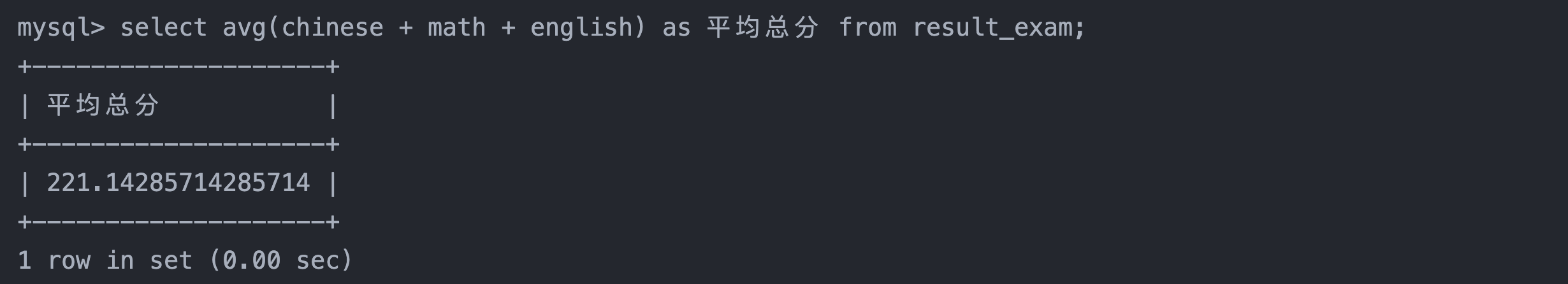
5. 统计平均总分
select avg(chinese + math + english) as 平均总分 from result_exam;
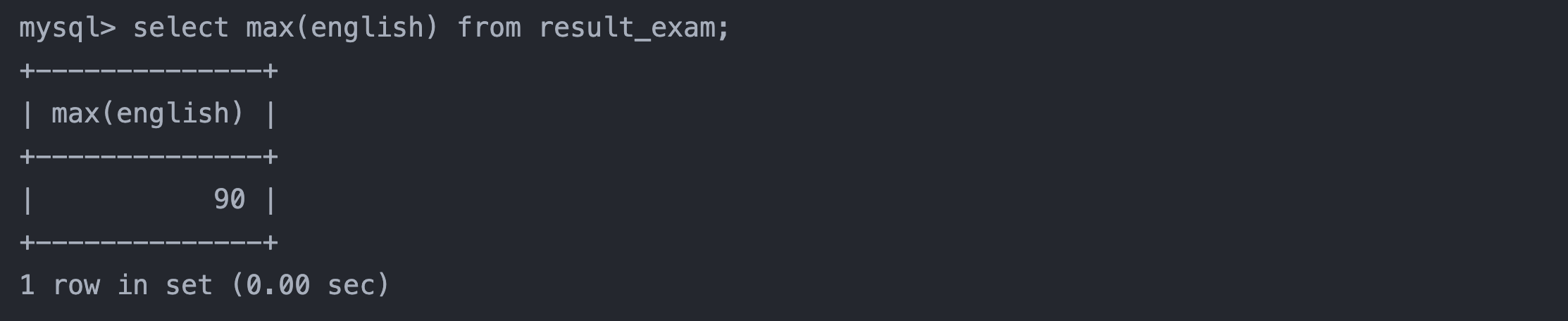
6. 返回英语最高分
select max(english) from result_exam;
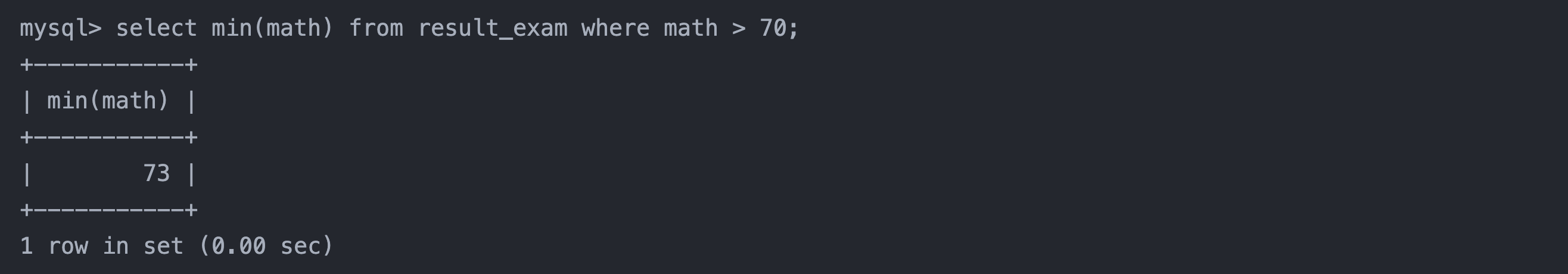
7. 返回 > 70 分以上的数学最低分
select min(math) from result_exam where math > 70;
6.2 group by子句分组
在select中使用group by 子句可以对指定列进行分组查询
select column1, column2, .. from table group by column;
案例:这是来自oracle 9i的经典测试表
DROP database IF EXISTS `scott`;
CREATE database IF NOT EXISTS `scott` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
USE `scott`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `dept`;
CREATE TABLE `dept` (
`deptno` int(2) unsigned zerofill NOT NULL COMMENT '部门编号',
`dname` varchar(14) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门名称',
`loc` varchar(13) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门所在地点'
);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `emp`;
CREATE TABLE `emp` (
`empno` int(6) unsigned zerofill NOT NULL COMMENT '雇员编号',
`ename` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇员姓名',
`job` varchar(9) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇员职位',
`mgr` int(4) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇员领导编号',
`hiredate` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '雇佣时间',
`sal` decimal(7,2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '工资月薪',
`comm` decimal(7,2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '奖金',
`deptno` int(2) unsigned zerofill DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门编号'
);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `salgrade`;
CREATE TABLE `salgrade` (
`grade` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '等级',
`losal` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '此等级最低工资',
`hisal` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '此等级最高工资'
);
insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc)
values (10, 'ACCOUNTING', 'NEW YORK');
insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc)
values (20, 'RESEARCH', 'DALLAS');
insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc)
values (30, 'SALES', 'CHICAGO');
insert into dept (deptno, dname, loc)
values (40, 'OPERATIONS', 'BOSTON');
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7369, 'SMITH', 'CLERK', 7902, '1980-12-17', 800, null, 20);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7499, 'ALLEN', 'SALESMAN', 7698, '1981-02-20', 1600, 300, 30);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7521, 'WARD', 'SALESMAN', 7698, '1981-02-22', 1250, 500, 30);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7566, 'JONES', 'MANAGER', 7839, '1981-04-02', 2975, null, 20);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7654, 'MARTIN', 'SALESMAN', 7698, '1981-09-28', 1250, 1400, 30);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7698, 'BLAKE', 'MANAGER', 7839, '1981-05-01', 2850, null, 30);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7782, 'CLARK', 'MANAGER', 7839, '1981-06-09', 2450, null, 10);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7788, 'SCOTT', 'ANALYST', 7566, '1987-04-19', 3000, null, 20);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7839, 'KING', 'PRESIDENT', null, '1981-11-17', 5000, null, 10);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7844, 'TURNER', 'SALESMAN', 7698,'1981-09-08', 1500, 0, 30);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7876, 'ADAMS', 'CLERK', 7788, '1987-05-23', 1100, null, 20);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7900, 'JAMES', 'CLERK', 7698, '1981-12-03', 950, null, 30);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7902, 'FORD', 'ANALYST', 7566, '1981-12-03', 3000, null, 20);
insert into emp (empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno)
values (7934, 'MILLER', 'CLERK', 7782, '1982-01-23', 1300, null, 10);
insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (1, 700, 1200);
insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (2, 1201, 1400);
insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (3, 1401, 2000);
insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (4, 2001, 3000);
insert into salgrade (grade, losal, hisal) values (5, 3001, 9999);
表结构如下:
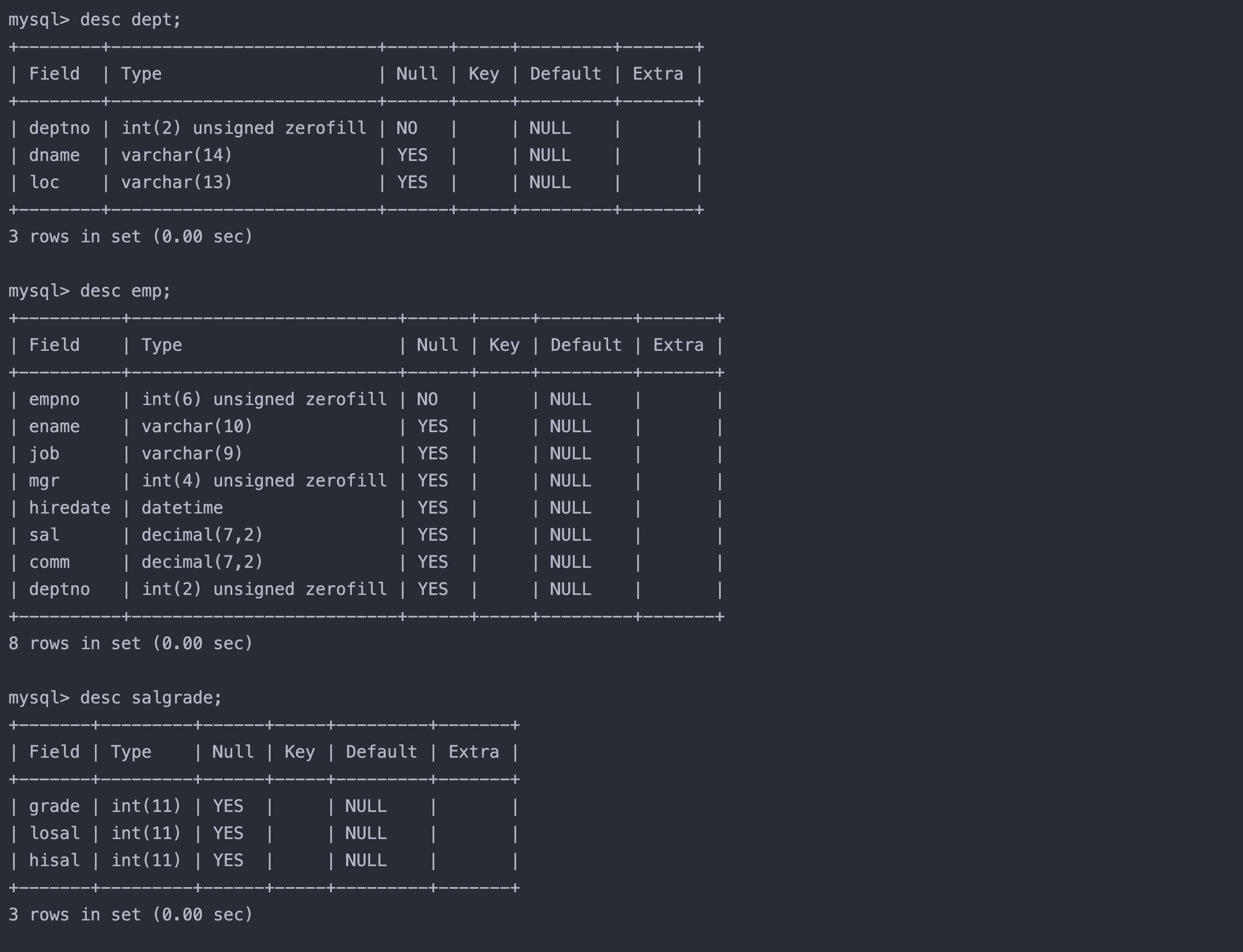
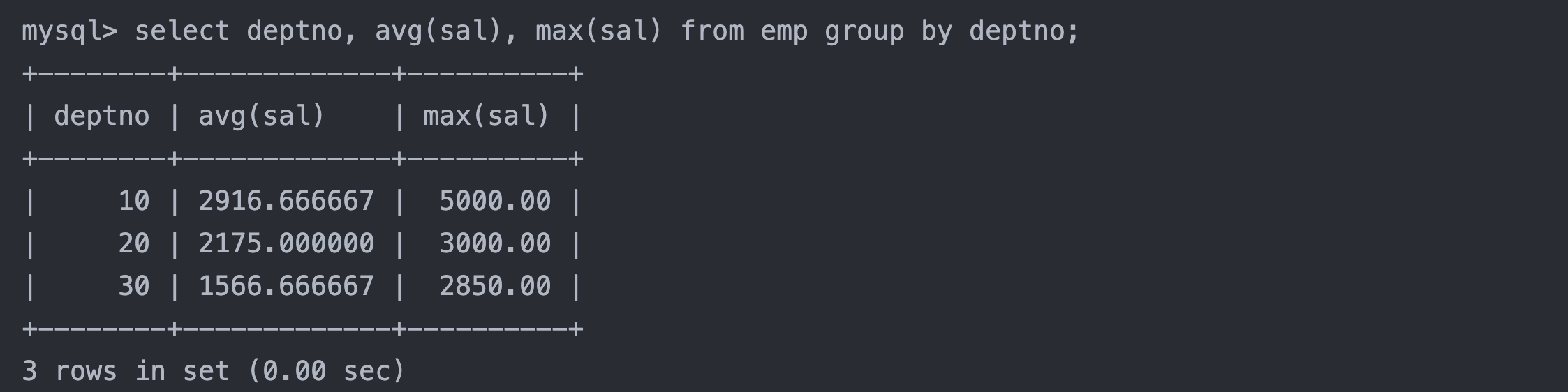
1. 如何显示每个部门的平均工资和最高工资
select deptno, avg(sal), max(sal) from emp group by deptno;
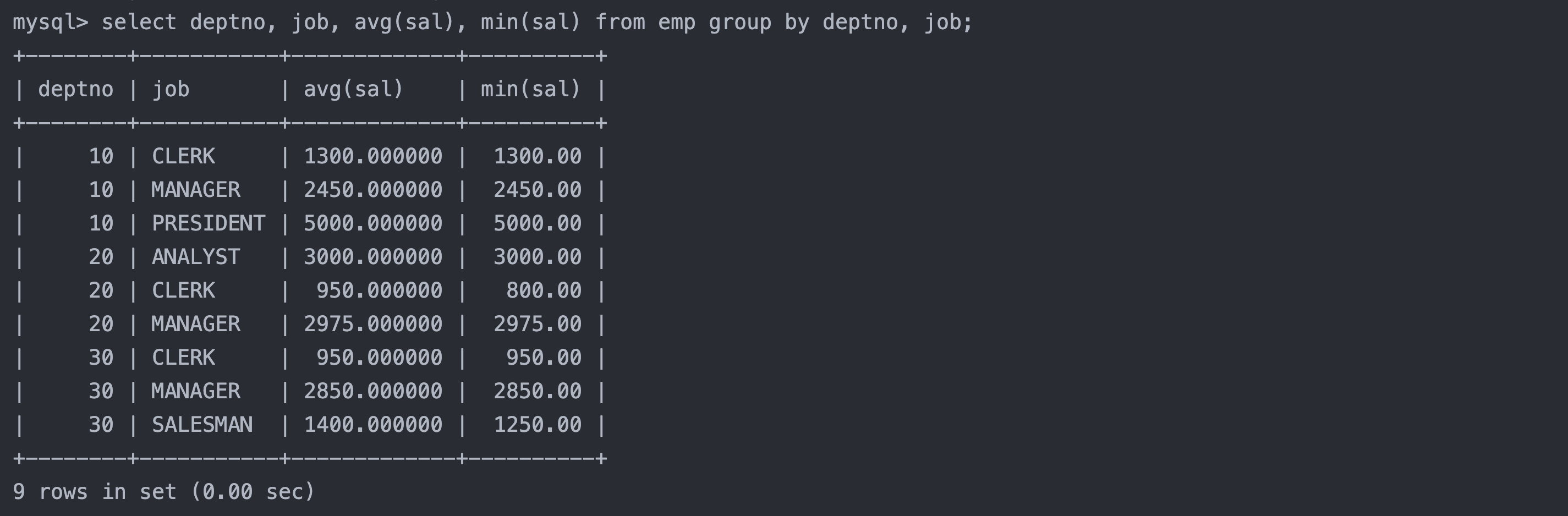
2. 显示每个部门的每种岗位的平均工资和最低工资
select deptno, job, avg(sal), min(sal) from emp group by deptno, job;
3. 显示平均工资低于2000的部门和它的平均工资
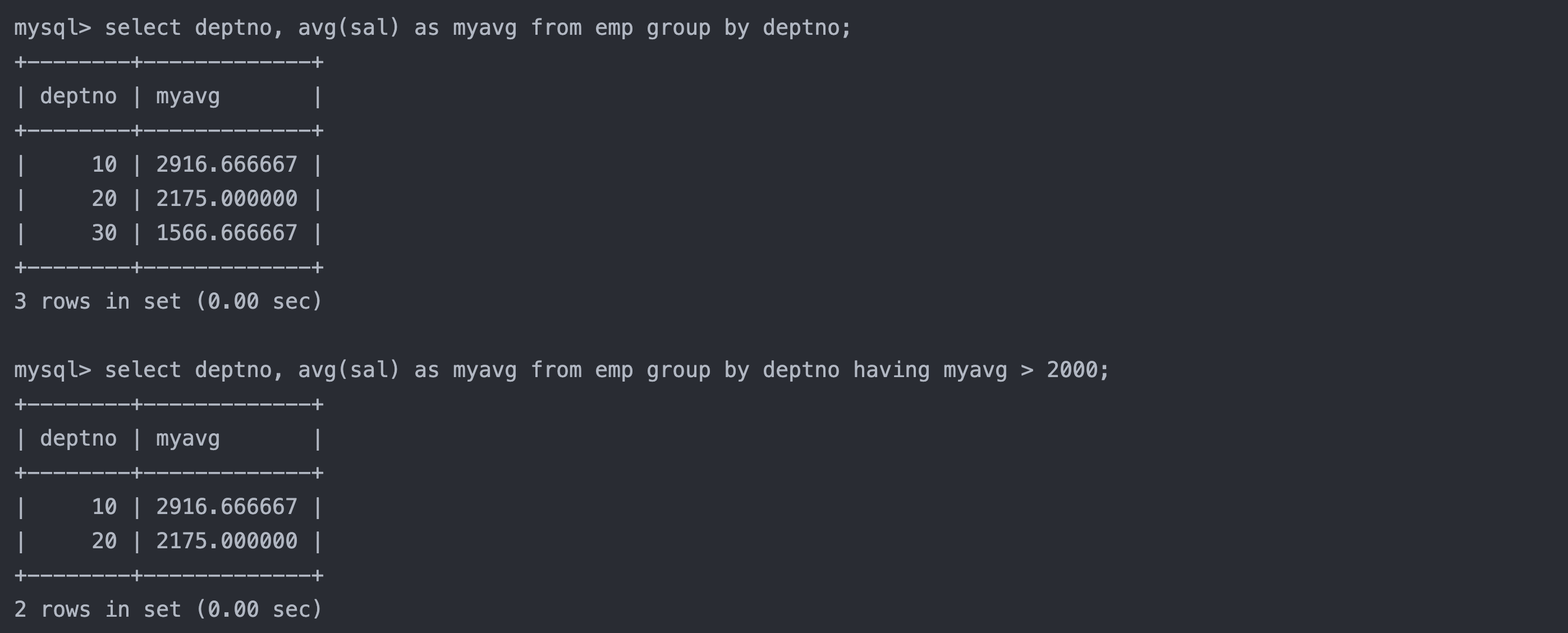
统计各个部门的平均工资
select deptno, avg(sal) as myavg from emp group by deptno;3.2 having和group by配合使用,对group by结果进行过滤
select deptno, avg(sal) as myavg from emp group by deptno having myavg > 2000;
注:having经常和group by搭配使用,作用是对分组进行筛选,作用有些像where
SQL查询中各个关键字的执行先后顺序 from > on> join > where > group by > with > having > select > distinct > order by > limit
本节完……