mini-jquery
mini-jquery
无new构建思路
jQuery官方采用IIFE(立即执行函数)以及对原型链的操作完成了对于无new构建的实现,那么无new构建是怎么实现的呢?
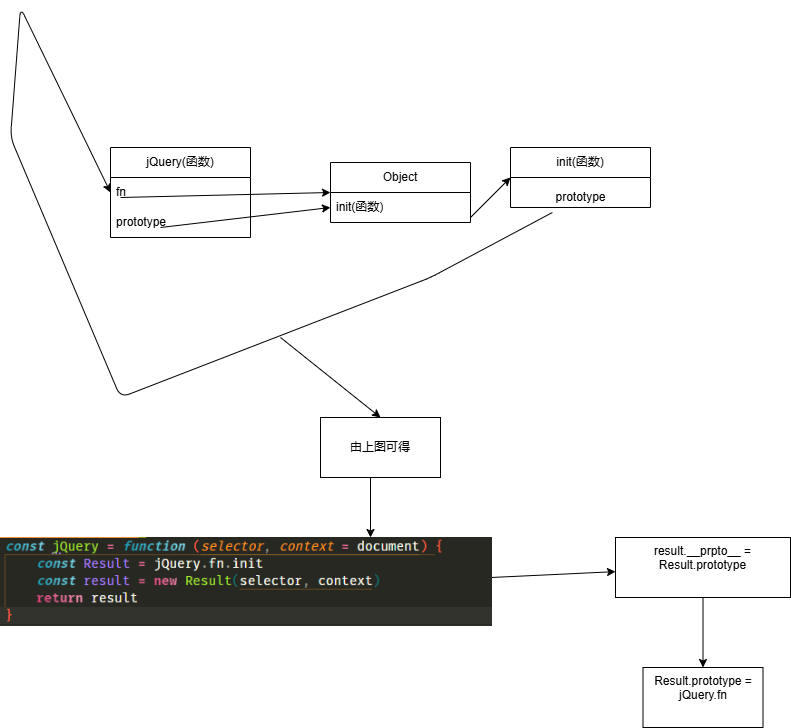
- 由上图可得,jQuery既是函数也是对象,因此我们可以在对象上面添加属性fn,同时函数上面都有一个属性prototype,prototype是一个对象,我们让我们自己添加的属性fn与prototype指向同一个内存空间,然后在这个内存空间添加一个函数命名为init,因为每一个函数都有一个属性prototype,因此我们可以改变prototype的指向,让其指向fn。
- 由图上代码,我们可以知道
new Result(selector, context)返回一个对象,每一个对象都有__proto__属性,__proto__属性指向其构造函数的prototype。 - 最终执行
jQuery函数会返回一个对象,this指向jQuery.fn.init这个函数,除此以外,我们在jQuery.fn上添加的属性最终也会因为原型链的关系可以拿到。
获取DOM元素的实现
实现了无new构建以后,获取DOM元素就很简单了。jQuery早期获取DOM元素采用的是getElementById等,而随着技术的发展,querySelectorAll方法已经可以取代获取元素的一系列方法了,一个方法就实现通过id、class、标签获取DOM元素,早期还要通过各种判断来执行不同的方法
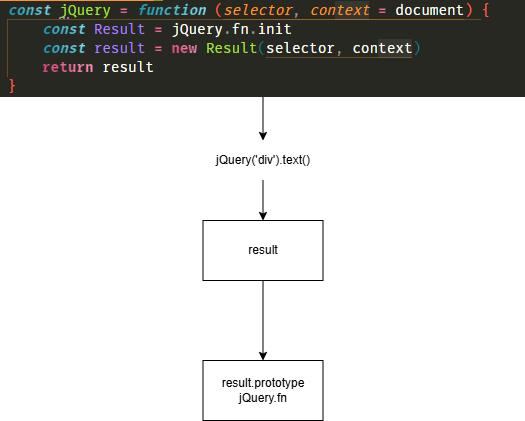
const jQuery = function (selector, context = document) {
const Result = jQuery.fn.init
const result = new Result(selector, context)
return result
}
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype
jQuery.fn.init = function (selector, context) {
if (!selector) return this
this.dom = context.querySelectorAll(selector)
return this
}
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn
jquery各类方法的实现
jQuery.fn.text = function (text) {
if (text === undefined) {
return Array.from(this.dom).map(node => node.textContent)
}
Array.from(this.dom).forEach(node => node.textContent = text)
return this
}
// css
jQuery.fn.css = function (key, value) {
this.dom.forEach(el => el.style[key] = value)
return this
}
// parent
jQuery.fn.parent = function () {
return this.dom[0].parentElement
}
// 相邻下一个的元素
jQuery.fn.next = function () {
return this.dom[0].nextElementSibling
}
// 相邻上一个的元素
jQuery.fn.prev = function () {
return this.dom[0].previousElementSibling
}
// 所有兄弟元素
jQuery.fn.siblings = function () {
const parent = this.parent()
const children = parent.children
return Array.from(children).filter(child => child !== this.dom[0])
}
jquery动画的实现
- 记录原始状态
- 记录要变化的状态
- 计算增量
- 计算帧率60fps的progress(进度)
/**
*
* @param {*} properties 要变化的状态
* @param {*} duration 总耗时
* @param {*} callback 额外执行的操作
*/
jQuery.fn.animate = function (properties, duration, easing = 'linear', callback) {
// 1. 记录原始状态
// 2. 记录要变化的状态
// 3. 计算增量
// 4. 计算帧率60fps progress进度
const startStyle = {}
// 获取dom元素
const currentDom = this.dom[0]
// 记录从页面加载到此刻所经历的时间(微秒)
const startTime = performance.now()
for (const key in properties) {
startStyle[key] = parseFloat(getComputedStyle(currentDom)[key])
}
const animateStep = (currentTime) => {
//currentTime 表示上一帧的渲染结束时间
const elapsed = currentTime - startTime // 持续时间
const progress = Math.min(elapsed / duration, 1) // 进度
const cssNumberProperties = ['opacity', 'zIndex', 'fontWeight', 'lineHeight', 'zoom']
for (const key in properties) {
const startValue = startStyle[key] // 原始值
const endValue = parseFloat(properties[key]) // 目标值
const currentValue = startValue + (endValue - startValue) * progress
currentDom.style[key] = cssNumberProperties.includes(key) ? currentValue : currentValue + 'px'
}
if (progress < 1) {
requestAnimationFrame(animateStep)
} else {
callback && callback()
}
}
// 返回当前60fps所需要的时间(微秒)
requestAnimationFrame(animateStep)
}
requestAnimationFrame的回调函数会在每一次浏览器重绘前执行,这个回调函数的参数表示表示上一帧的渲染结束时间
我们使用performance.now()来记录从页面加载到此刻所经历的时间(微秒),因为其返回的值与requestAnimationFrame回调函数参数的值都是微秒级别的
动画曲线的实现
const animateStep = (currentTime) => {
const easingFunctions = {
linear: t => t,
easeIn: t => t * t,
easeOut: t => t * (2 - t),
easeInOut: t => t < 0.5 ? 2 * t * t : -1 + (4 - 2 * t) * t
}
const easingFunction = easingFunctions[easing] || easingFunctions.linear
//currentTime 表示上一帧的渲染结束时间
const elapsed = currentTime - startTime // 持续时间
const progress = Math.min(elapsed / duration, 1) // 进度
const easedProgress = easingFunction(progress)
const cssNumberProperties = ['opacity', 'zIndex', 'fontWeight', 'lineHeight', 'zoom']
for (const key in properties) {
const startValue = startStyle[key] // 原始值
const endValue = parseFloat(properties[key]) // 目标值
const currentValue = startValue + (endValue - startValue) * easedProgress
currentDom.style[key] = cssNumberProperties.includes(key) ? currentValue : currentValue + 'px'
}
if (progress < 1) {
requestAnimationFrame(animateStep)
} else {
callback && callback()
}
}
jquery支持插件
// 支持插件
jQuery.fn.$extend = function (obj) {
for (const key in obj) {
this[key] = obj[key]
}
return this
}
这里的this指向jQuery.fn
jquery支持ajax
jQuery.ajax = function (url, options) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open(options.method || 'GET', url, true)
xhr.send(options.data || null)
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status === 200) {
resolve(xhr.responseText)
} else {
reject(xhr.statusText)
}
}
}
})
}
jquery当DOM渲染完毕执行的函数
jQuery.ready = function (callback) {
if (document.readyState === 'complete') {
callback()
} else {
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', callback)
}
}
DOMContentLoaded事件会在DOM渲染完毕之后立即执行callback函数
不监听load事件的原因?
load事件在DOM渲染完毕之后,还会等css、图片等资源加载完成才执行回调,单纯只是操作DOM的话没有必要等待css、图片等资源加载完毕
