深入FastAPI:表单和文件上传详解

引言
大家好,我是GISerLiu 😁,一名热爱AI技术的GIS开发者。本系列文章是我跟随DataWhale 2024年11月学习赛的FastAPI学习总结文档;在实际开发中,我们经常需要处理表单数据和文件上传。本文将深入探讨如何在 FastAPI 中处理表单和文件,并通过详细的代码示例和解释,帮助读者由浅入深地理解这些概念。 💕💕😊
一、表单数据的处理
1. 表单数据的基本概念
在 Web 开发中,表单数据通常是通过 HTML 表单提交的。与 JSON 数据不同,表单数据通常使用 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 或 multipart/form-data 编码格式。FastAPI 提供了 Form 类来处理这些表单数据。
① 安装依赖
要使用 FastAPI 处理表单数据,首先需要安装 python-multipart 库。这个库提供了对表单数据的解析支持。
pip install python-multipart

② 使用 Form 类
Form 类是 FastAPI 中用于声明表单字段的类。与 Body 类似,Form 类允许你定义表单字段的类型和验证规则。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Form
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/login/")
async def login(username: str = Form(), password: str = Form()):
"""
处理用户登录请求,接收表单字段 username 和 password
"""
return {"username": username}
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用 uvicorn 运行 FastAPI 应用
uvicorn.run(app, host='127.0.0.1', port=8009)
- Form继承自Body类
- 声明表单体要显式使用 Form ,否则,FastAPI 会把该参数当作查询参数或请求体(JSON)参数。
- 规范要求字段必须命名为 username 和 password,并通过表单字段发送,不能用 JSON。
在这个例子中,username 和 password 是通过表单提交的字段。FastAPI 会自动解析这些字段,并将其作为函数参数传递。下面是测试效果:
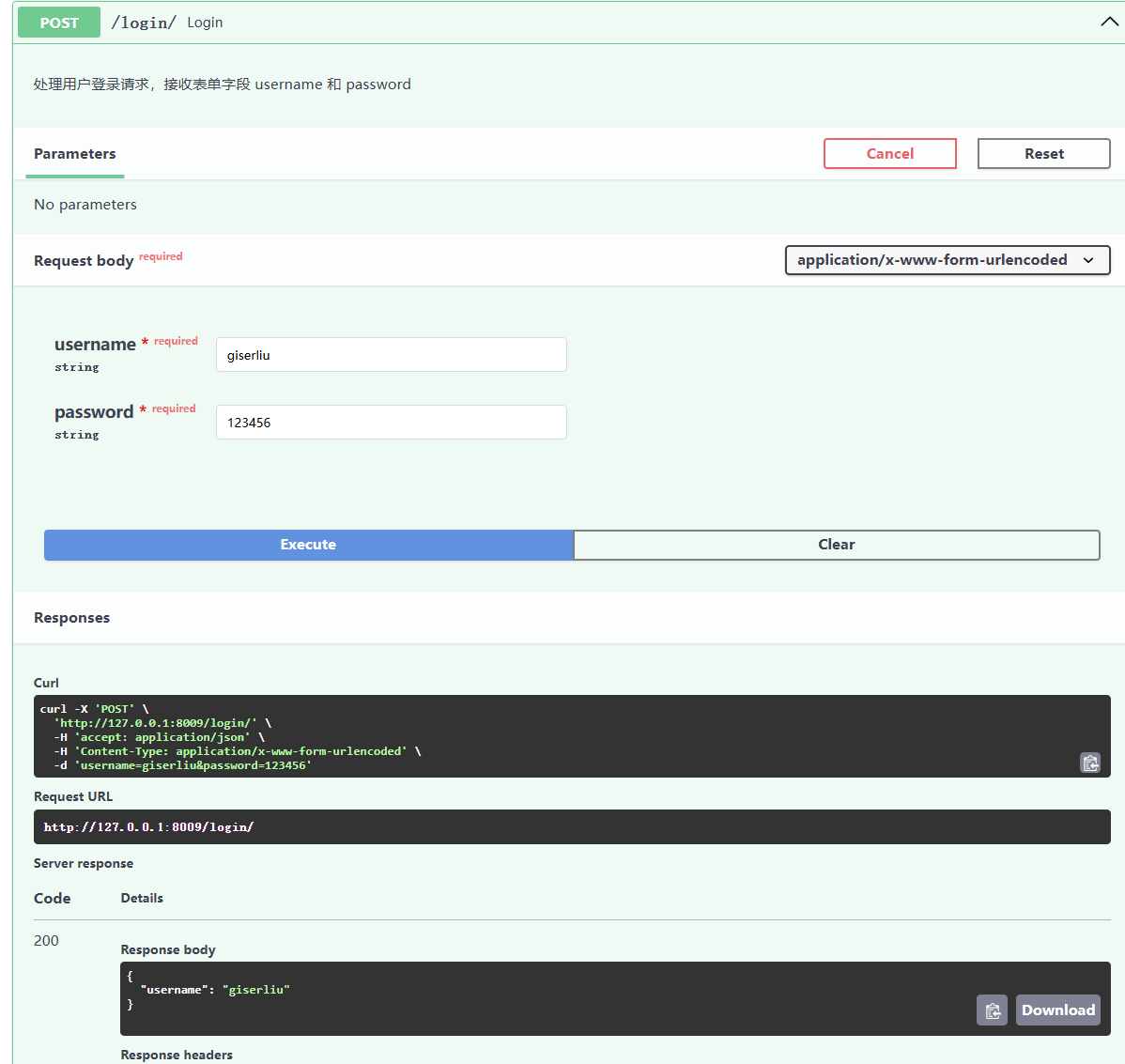
开发者可在一个路径操作中声明多个 Form 参数,但不能同时声明要接收 JSON 的 Body 字段。因为此时请求体的编码是 application/x-www-form-urlencoded,不是 application/json。这不是 FastAPI 的问题,而是 HTTP 协议的规定。****😊
2. 表单数据的验证
与 JSON 数据类似,表单数据也可以进行验证。FastAPI 提供了丰富的验证功能,可以通过 Form 类来实现。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Form, HTTPException
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/login/")
async def login(username: str = Form(min_length=4), password: str = Form(min_length=6)):
"""
处理用户登录请求,验证 username 和 password 的长度
"""
return {"username": username}
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用 uvicorn 运行 FastAPI 应用
uvicorn.run(app, host='127.0.0.1', port=8009)
在这个例子中,我们通过 Form 类的参数 min_length 来验证 username 和 password 的最小长度。如果验证失败,FastAPI 会自动返回 400 错误。验证失败案例如下:

二、文件上传的处理
1. 文件上传的基本概念
在 Web 开发中,文件上传是一个常见的需求。FastAPI 提供了 UploadFile 类来处理文件上传。UploadFile 类提供了对上传文件的访问和操作方法。
① 安装依赖
与表单数据处理类似,文件上传也需要 python-multipart 库的支持。
pip install python-multipart
② 使用 UploadFile 类
UploadFile 类是 FastAPI 中用于处理文件上传的类。它提供了对上传文件的访问和操作方法。
from fastapi import FastAPI, UploadFile, HTTPException
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/uploadfile/")
async def create_upload_file(file: UploadFile):
"""
处理文件上传请求,返回上传文件的详细信息
"""
# 读取文件内容
contents = await file.read()
# 统计文件内容的字节数
content_bytes = len(contents)
# 尝试解码文件内容为字符串,并统计字符数
try:
content_chars = len(contents.decode('utf-8'))
except UnicodeDecodeError:
content_chars = None
# 检查文件类型
if file.content_type.startswith("image/"):
file_content_info = "Binary image content"
elif content_chars is not None:
file_content_info = contents.decode('utf-8')
else:
file_content_info = "Binary content"
# 返回文件的详细信息
return {
"filename": file.filename,
"content_type": file.content_type,
"size_in_bytes": content_bytes,
"size_in_chars": content_chars,
"file_content_info": file_content_info
}
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用 uvicorn 运行 FastAPI 应用
uvicorn.run(app, host='127.0.0.1', port=8009)
这个代码会读取文件,检查文件类型并且输出一些统计信息!
测试结果如下:


如上图所示,测试通过@!👌🎉
2. 文件上传的验证
与表单数据类似,文件上传也可以进行验证。FastAPI 提供了丰富的验证功能,可以通过 UploadFile 类来实现。
from fastapi import FastAPI, UploadFile, HTTPException
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/uploadfile/")
async def create_upload_file(file: UploadFile):
"""
处理文件上传请求,验证文件类型并返回上传文件的详细信息
"""
# 验证文件类型
if not file.content_type.startswith("image/"):
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="File must be an image")
# 读取文件内容
contents = await file.read()
# 统计文件内容的字节数
content_bytes = len(contents)
# 尝试解码文件内容为字符串,并统计字符数
try:
content_chars = len(contents.decode('utf-8'))
except UnicodeDecodeError:
content_chars = None
# 检查文件类型
if file.content_type.startswith("image/"):
file_content_info = "Binary image content"
elif content_chars is not None:
file_content_info = contents.decode('utf-8')
else:
file_content_info = "Binary content"
# 返回文件的详细信息
return {
"filename": file.filename,
"content_type": file.content_type,
"size_in_bytes": content_bytes,
"size_in_chars": content_chars,
"file_content_info": file_content_info
}
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用 uvicorn 运行 FastAPI 应用
uvicorn.run(app, host='127.0.0.1', port=8009)
在这个例子中,我们通过 UploadFile 的 content_type 属性来验证上传文件的类型。如果文件不是图片类型,FastAPI 会自动返回 400 错误。
下面是测试案例:
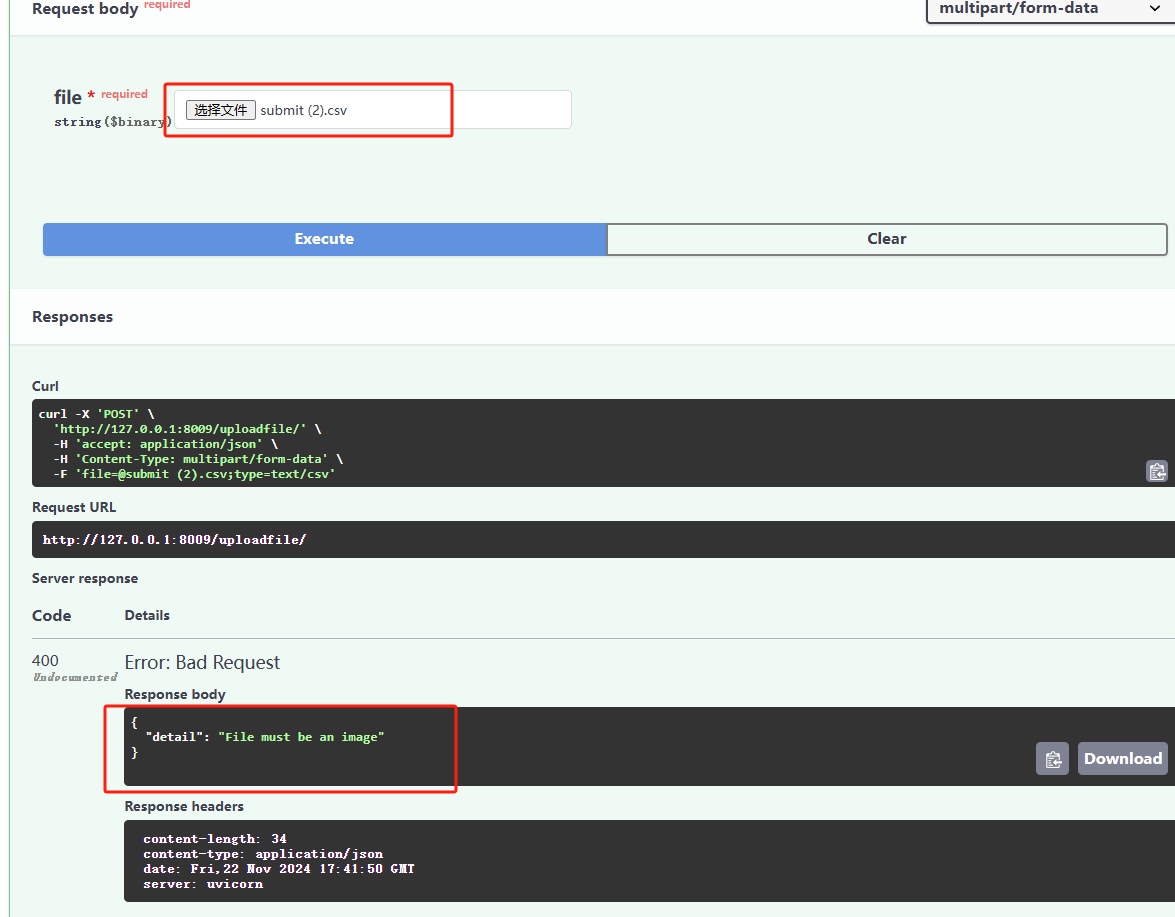
这里作者尝试上传一个csv文件,结果报错!如此一来,测试通过!👌
3. 多文件上传
FastAPI 支持同时上传多个文件。开发者可以通过声明一个包含 UploadFile 对象的列表来实现多文件上传。这里我们创建一个支持多种格式文件列表上传的Demo!
from fastapi import FastAPI, UploadFile, HTTPException
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/uploadfiles/")
async def create_upload_files(files: list[UploadFile]):
"""
处理多文件上传请求,返回上传文件的详细信息列表
"""
uploaded_files_info = []
for file in files:
# 读取文件内容
contents = await file.read()
# 统计文件内容的字节数
content_bytes = len(contents)
# 尝试解码文件内容为字符串,并统计字符数
try:
content_chars = len(contents.decode('utf-8'))
except UnicodeDecodeError:
content_chars = None
# 检查文件类型
if file.content_type.startswith("image/"):
file_content_info = "Binary image content"
elif content_chars is not None:
file_content_info = contents.decode('utf-8')
else:
file_content_info = "Binary content"
# 添加文件的详细信息到列表中
uploaded_files_info.append({
"filename": file.filename,
"content_type": file.content_type,
"size_in_bytes": content_bytes,
"size_in_chars": content_chars,
"file_content_info": file_content_info
})
# 返回所有上传文件的详细信息
return {"uploaded_files_info": uploaded_files_info}
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用 uvicorn 运行 FastAPI 应用
uvicorn.run(app, host='127.0.0.1', port=8009)
在这个例子中,files 是一个包含多个 UploadFile 对象的列表。FastAPI 会自动解析这些文件,并将其作为列表传递给函数。
下面测试案例中,我们选择上传机器学习模型文件(.pt),csv文件和markdown格式的文件;
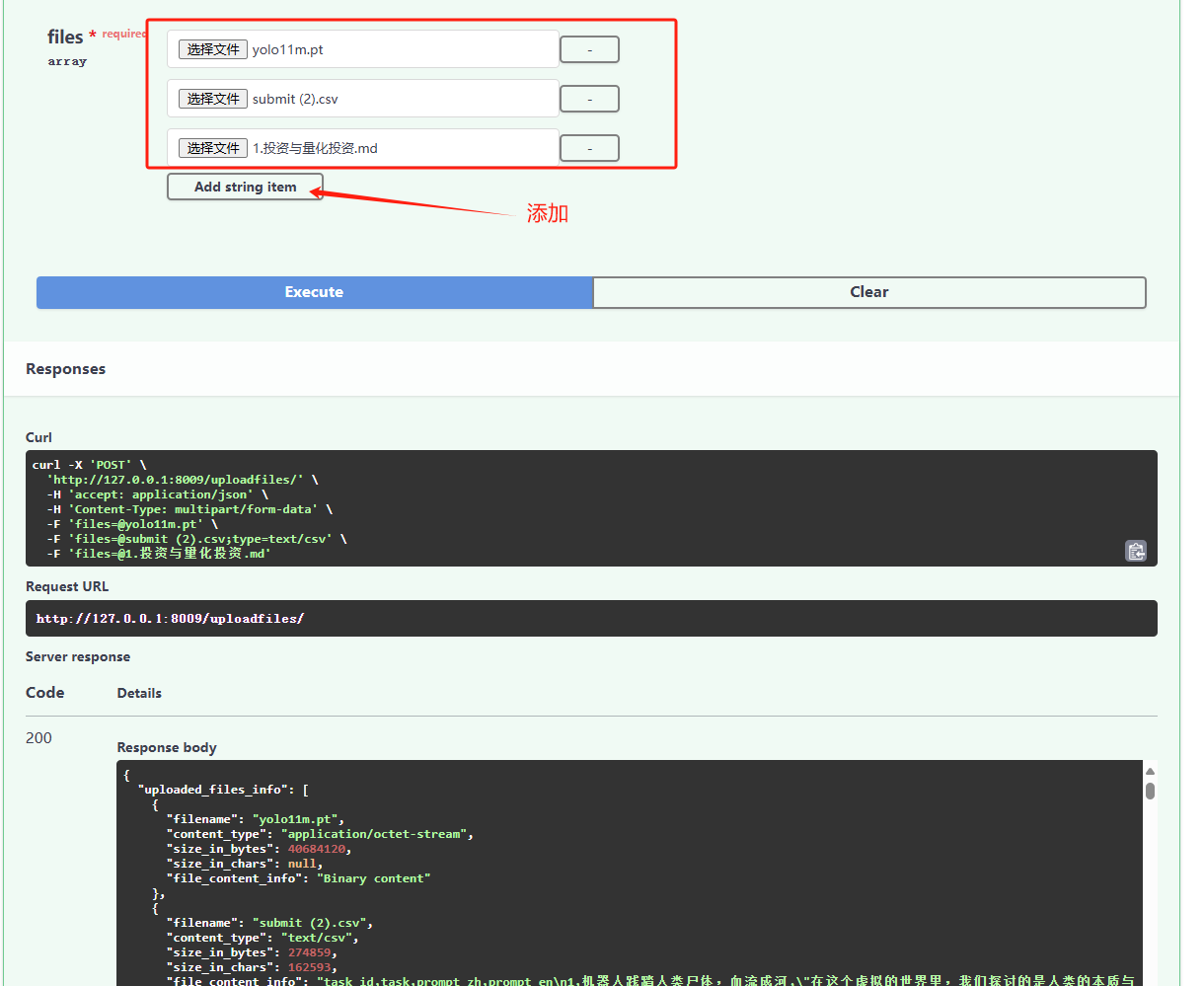
4. 可选文件上传
在某些情况下,你可能希望文件上传是可选的。FastAPI 允许你通过设置默认值为 None 来实现可选文件上传。
from fastapi import FastAPI, UploadFile, HTTPException, File, Form
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/uploadfile/")
async def create_upload_file(
file: UploadFile | None = File(None), # 可选文件上传
description: str = Form(...) # 必填的表单字段
):
"""
处理可选文件上传请求,如果未上传文件,返回提示信息;否则返回上传文件的详细信息
"""
if not file:
return {"message": "No upload file sent"}
# 读取文件内容
contents = await file.read()
# 统计文件内容的字节数
content_bytes = len(contents)
# 尝试解码文件内容为字符串,并统计字符数
try:
content_chars = len(contents.decode('utf-8'))
except UnicodeDecodeError:
content_chars = None
# 检查文件类型
if file.content_type.startswith("image/"):
file_content_info = "Binary image content"
elif content_chars is not None:
file_content_info = contents.decode('utf-8')
else:
file_content_info = "Binary content"
# 返回文件的详细信息
return {
"filename": file.filename,
"content_type": file.content_type,
"size_in_bytes": content_bytes,
"size_in_chars": content_chars,
"file_content_info": file_content_info,
"description": description # 返回表单字段
}
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用 uvicorn 运行 FastAPI 应用
uvicorn.run(app, host='127.0.0.1', port=8009)
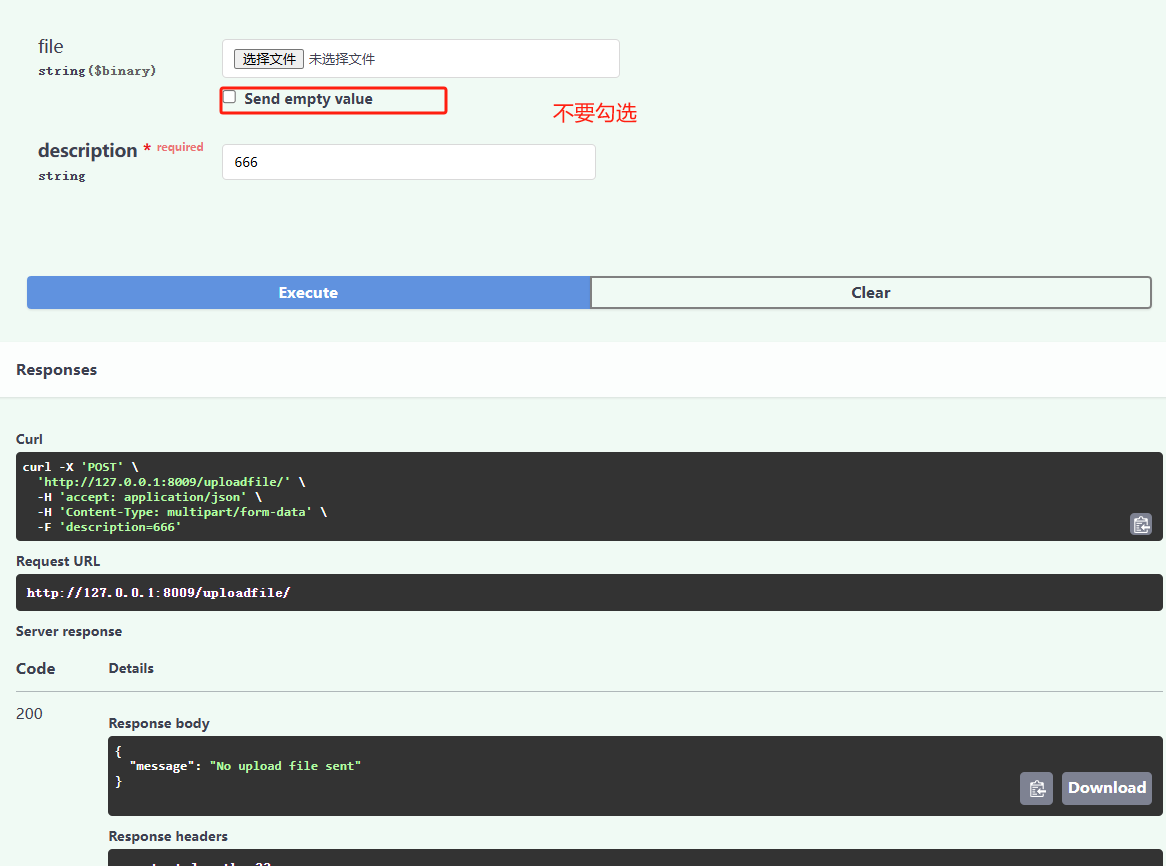
在这个例子中,file 是一个可选的文件上传参数。如果用户没有上传文件,FastAPI 会自动将 file 设置为 None。
这里必须得有个能上传的参数,不然会报错;
三、结合表单和文件上传
在大多数应用场景中,我们可能需要同时处理表单字段和文件上传。FastAPI 允许开发者在同一个路径操作中声明多个 Form 和 File 参数。下面作者将给出一个完整的Demo,各位可以在其上进行修改测试;
from fastapi import FastAPI, File, Form, UploadFile, HTTPException
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
import uvicorn
import logging
# 配置日志记录
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/upload/")
async def upload_file_and_form(
file: UploadFile = File(None), # 可选文件上传
token: str = Form(...), # 必填表单字段
username: str = Form(min_length=4), # 表单字段,最小长度为4
password: str = Form(min_length=6) # 表单字段,最小长度为6
):
"""
处理文件和表单字段上传请求,返回文件名和表单字段值
"""
# 检查文件是否为空
if file is None or file.filename == "":
return JSONResponse(content={"message": "No upload file sent"}, status_code=200)
try:
# 读取文件内容
contents = await file.read()
# 统计文件内容的字节数
content_bytes = len(contents)
# 尝试解码文件内容为字符串,并统计字符数
try:
content_chars = len(contents.decode('utf-8'))
except UnicodeDecodeError:
content_chars = None
# 检查文件类型
if file.content_type.startswith("image/"):
file_content_info = "Binary image content"
elif content_chars is not None:
file_content_info = contents.decode('utf-8')
else:
file_content_info = "Binary content"
# 返回文件和表单字段的详细信息
return {
"token": token,
"username": username,
"password": password,
"filename": file.filename,
"content_type": file.content_type,
"size_in_bytes": content_bytes,
"size_in_chars": content_chars,
"file_content_info": file_content_info
}
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error processing file: {e}")
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail="Error processing file")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用 uvicorn 运行 FastAPI 应用
uvicorn.run(app, host='127.0.0.1', port=8009)
代码逻辑很简单,作者就不解释了,有问题可自行GPT;
在这个例子中,我们同时处理了文件上传和表单字段 token。FastAPI 会自动解析这些数据,并将其作为函数参数传递。
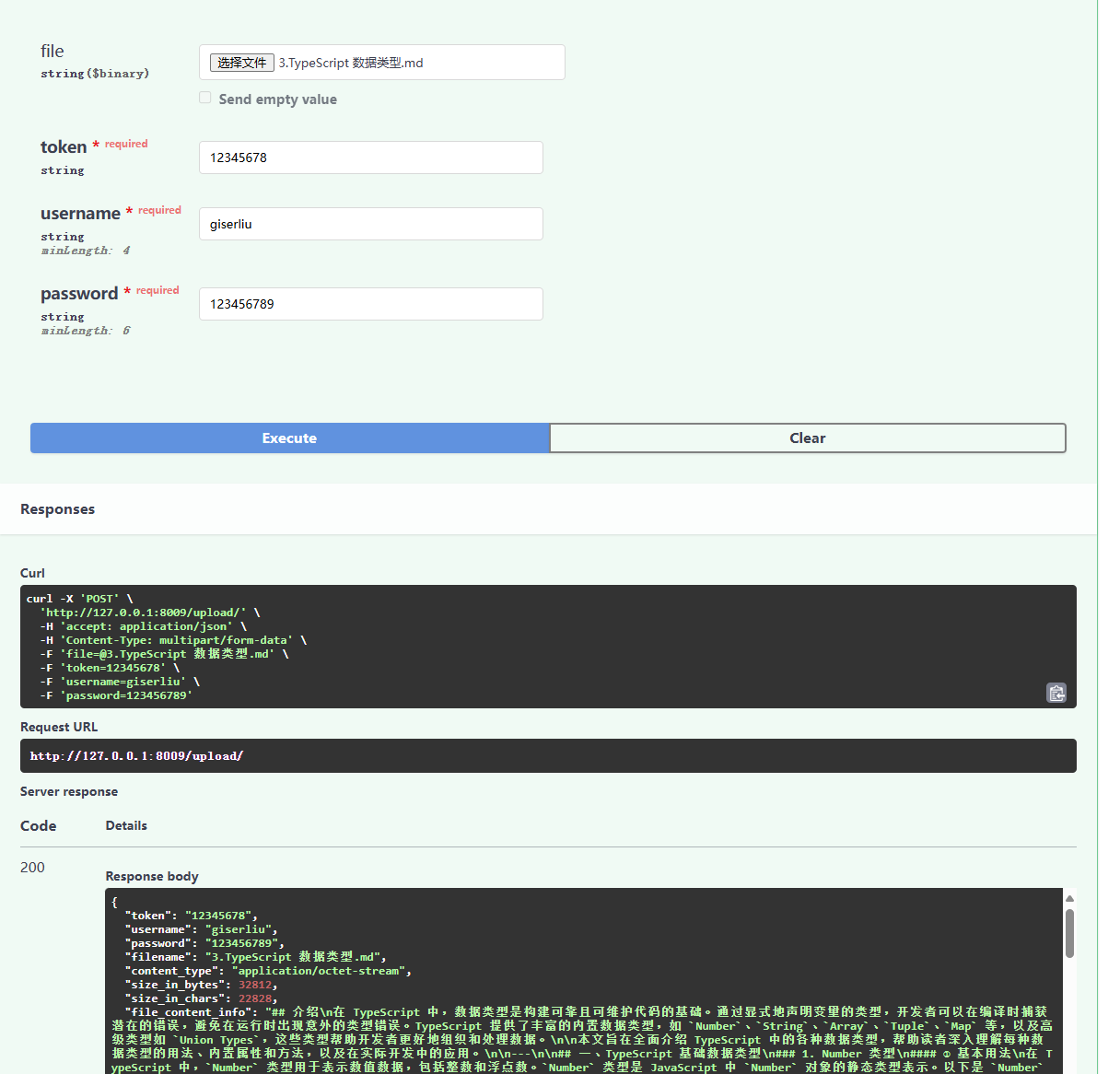
测试通过,没什么问题!😊
在全栈开发中,这些基础API很容易掌握,我们需要重点记忆的是业务流程,熟悉了业务流程,经过两个项目的实践,便很容易开发后端接口!😎
OK,今天就学习到这!👌
相关链接
- 项目地址:FastAPI-CookBook
- 相关文档:专栏地址
- 作者主页:GISer Liu-CSDN博客

如果觉得我的文章对您有帮助,三连+关注便是对我创作的最大鼓励!或者一个star🌟也可以😂.
