idea-java项目中的全部接口提取
方法类型一 value和method
涉及
@RequestMapping({“/api/rest”})
@RequestMapping(
value = {“/internal/v1/machine/delete”},
method = {RequestMethod.DELETE}
)
这种提取
示例代码如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping({"/api/rest"})
public class ModelManageApi {
@Autowired
private ModelMachineService modelMachineService;
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/internal/v1/machine/addModel"},
method = {RequestMethod.POST}
)
@ResponseBody
public void addModelMachine(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody ModelMachineDto modelMachineDto) throws Exception {
List<ModelMachinePO> modelMachines = new ArrayList();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(modelMachineDto.getCreateTime())) {
throw new RuntimeException("Request createDate can not be null");
} else if (null != modelMachineDto.getSns() && modelMachineDto.getSns().size() != 0) {
List<String> sns = modelMachineDto.getSns();
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date createtime = format.parse(modelMachineDto.getCreateTime().trim());
for(int i = 0; i < sns.size(); ++i) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty((CharSequence)sns.get(i))) {
throw new RuntimeException("Request SN can not be null");
}
ModelMachinePO modelMachinePO = new ModelMachinePO();
modelMachinePO.setCreateTime(createtime);
modelMachinePO.setSn((String)sns.get(i));
modelMachinePO.setMachineType(MachineType.PROTOTYPE.getValue());
modelMachines.add(modelMachinePO);
}
this.modelMachineService.addModelMachine(modelMachines);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Request SN can not be null");
}
}
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/internal/v1/machine/delete"},
method = {RequestMethod.DELETE}
)
@ResponseBody
public void removeModelMachine(@RequestBody ModelMachineDto modelMachineDto) throws Exception {
if (null != modelMachineDto.getSns() && modelMachineDto.getSns().size() != 0) {
this.modelMachineService.removeModelMachine(modelMachineDto.getSns());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Request fail because sn is null");
}
}
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/internal/{version}/device/deliveryInfo"},
method = {RequestMethod.GET}
)
@ResponseBody
public DeliveryInfo getDeliveryInfo(String sn) throws Exception {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(sn)) {
this.logger.error("sn is empty");
return null;
} else {
DeliveryInfo result = this.modelMachineService.getSnRecordBySn(sn);
this.logger.debug("getDeliveryInfo by {} return {} ", sn, result);
return result;
}
}
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/internal/{version}/device/checkDeviceIsModel"},
method = {RequestMethod.GET}
)
public String checkDeviceIsModel(String deviceSn) {
return StringUtils.isEmpty(deviceSn) ? "false" : String.valueOf(this.modelMachineService.checkNemoIsModelMachine(deviceSn));
}
}
目标获得其中的接口,类似如下
/api/rest/internal/v1/machine/addModel
/api/rest/internal/v1/machine/delete
/api/rest/internal/{version}/device/deliveryInfo
/api/rest/internal/{version}/device/checkDeviceIsModel
首先我写了一段代码
java1.py
import re
import os
def extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory):
# 定义用于匹配 @RequestMapping 注解值的正则表达式
pattern = re.compile(r'@RequestMapping\s*\(\s*value\s*=\s*.*\s*method*.*}')
# 存储所有接口路径及其所在文件的列表
endpoints = []
# 遍历指定目录下的所有文件
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith(".java"):
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
# 使用正则表达式匹配 @RequestMapping 注解的值,并将结果存储到 endpoints 列表中
matches = pattern.findall(content)
for match in matches:
endpoints.append((file_path, match)) # 存储文件路径和匹配到的接口路径
return endpoints
# 调用函数并输出结果
directory = r"C:\Users\qiezi\Desktop\java-jiekou"
endpoints = extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory)
print("All endpoints found in Java files:")
for file_path, endpoint in endpoints:
print(f"Endpoint '{endpoint}' found in file: {file_path}")
可获得分支接口(除了根路径接口)

这个当前目录和子目录都可以获得,但是没达到我们的目的就是获得全部接口(也就是拼接好的接口)
java3.py
import re
import os
def extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory):
# 定义用于匹配类级和方法级的 @RequestMapping 注解的正则表达式
class_pattern = re.compile(r'@RequestMapping\s*\(\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*\)')
method_pattern = re.compile(
r'@RequestMapping\s*\(\s*value\s*=\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*,\s*method\s*=\s*{\s*([^}]*)\s*}\s*\)')
# 存储所有接口路径及其所在文件的列表
endpoints = []
# 遍历指定目录下的所有文件
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith(".java"):
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
# 提取类级别的路径
class_match = class_pattern.search(content)
base_path = class_match.group(1) if class_match else ''
# 使用正则表达式匹配方法级别的 @RequestMapping 注解的值,并将结果存储到 endpoints 列表中
method_matches = method_pattern.findall(content)
for match in method_matches:
endpoint_path = base_path + match[0]
methods = match[1].replace('RequestMethod.', '').replace(' ', '').split(',')
endpoints.append((file_path, endpoint_path, methods)) # 存储文件路径、完整接口路径和请求方法
return endpoints
# 调用函数并输出结果
directory = r"H:\\WEB-INF\classes"
endpoints = extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory)
print("All endpoints found in Java files:")
for file_path, endpoint, methods in endpoints:
methods_str = ', '.join(methods)
print(f"Endpoint '{endpoint}' with methods [{methods_str}] found in file: {file_path}")
这个写的方式是
提取类级别的 @RequestMapping 注解路径。
提取方法级别的 @RequestMapping 注解路径和请求方法。
拼接类级别和方法级别的路径。
效果
可以看到成功输出,接下来写成输出到某个文件中
import re
import os
def extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory):
# 定义用于匹配类级和方法级的 @RequestMapping 注解的正则表达式
class_pattern = re.compile(r'@RequestMapping\s*\(\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*\)')
method_pattern = re.compile(
r'@RequestMapping\s*\(\s*value\s*=\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*,\s*method\s*=\s*{\s*([^}]*)\s*}\s*\)')
# 存储所有接口路径及其所在文件的列表
endpoints = []
# 遍历指定目录下的所有文件
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith(".java"):
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
# 提取类级别的路径
class_match = class_pattern.search(content)
base_path = class_match.group(1) if class_match else ''
# 使用正则表达式匹配方法级别的 @RequestMapping 注解的值,并将结果存储到 endpoints 列表中
method_matches = method_pattern.findall(content)
for match in method_matches:
endpoint_path = base_path + match[0]
methods = match[1].replace('RequestMethod.', '').replace(' ', '').split(',')
endpoints.append((file_path, endpoint_path, methods)) # 存储文件路径、完整接口路径和请求方法
return endpoints
# 调用函数并输出结果
directory = r"H:\WEB-INF\classes"
endpoints = extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory)
output_file = "endpoints_output.txt"
with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("All endpoints found in Java files:\n")
for file_path, endpoint, methods in endpoints:
methods_str = ', '.join(methods)
f.write(f"Endpoint '{endpoint}' with methods [{methods_str}] found in file: {file_path}\n")
print(f"Results have been written to {output_file}")
# Print results to console
print("All endpoints found in Java files:")
for file_path, endpoint, methods in endpoints:
methods_str = ', '.join(methods)
print(f"Endpoint '{endpoint}' with methods [{methods_str}] found in file: {file_path}")
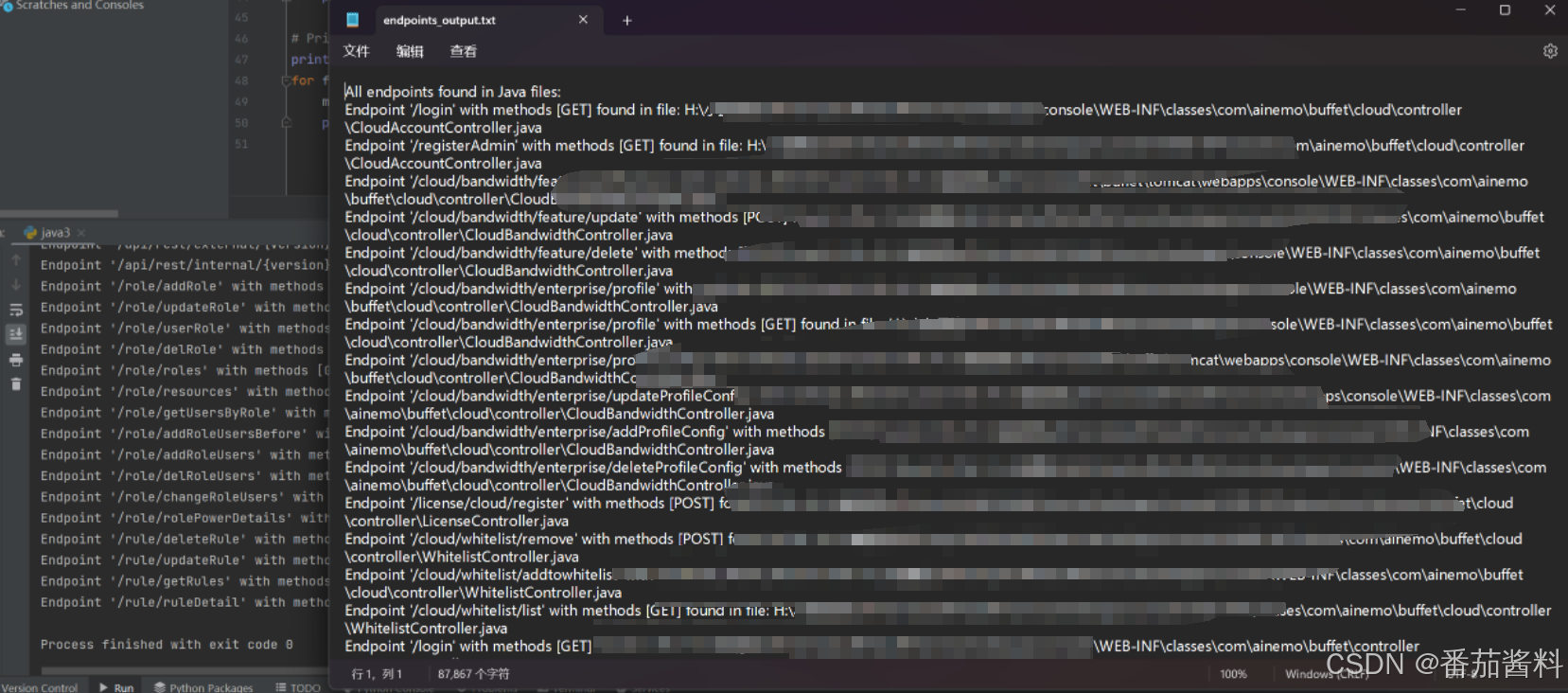
可以看到输出成功
那么接下来把url提取出来输出到单个文件url.txt中
java4.py
import re
import os
def extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory):
# 定义用于匹配类级和方法级的 @RequestMapping 注解的正则表达式
class_pattern = re.compile(r'@RequestMapping\s*\(\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*\)')
method_pattern = re.compile(
r'@RequestMapping\s*\(\s*value\s*=\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*,\s*method\s*=\s*{\s*([^}]*)\s*}\s*\)')
# 存储所有接口路径及其所在文件的列表
endpoints = []
# 遍历指定目录下的所有文件
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith(".java"):
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
# 提取类级别的路径
class_match = class_pattern.search(content)
base_path = class_match.group(1) if class_match else ''
# 使用正则表达式匹配方法级别的 @RequestMapping 注解的值,并将结果存储到 endpoints 列表中
method_matches = method_pattern.findall(content)
for match in method_matches:
endpoint_path = base_path + match[0]
methods = match[1].replace('RequestMethod.', '').replace(' ', '').split(',')
endpoints.append((file_path, endpoint_path, methods)) # 存储文件路径、完整接口路径和请求方法
return endpoints
# 调用函数并输出结果
directory = r"H:\WEB-INF\classes"
endpoints = extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory)
# 将结果写入 endpoints_output.txt
endpoints_output_file = "endpoints_output.txt"
with open(endpoints_output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("All endpoints found in Java files:\n")
for file_path, endpoint, methods in endpoints:
methods_str = ', '.join(methods)
f.write(f"Endpoint '{endpoint}' with methods [{methods_str}] found in file: {file_path}\n")
print(f"Results have been written to {endpoints_output_file}")
# 将结果写入 url.txt
url_output_file = "url.txt"
with open(url_output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for _, endpoint, _ in endpoints:
f.write(f"{endpoint}\n")
print(f"URLs have been written to {url_output_file}")
# Print results to console
print("All endpoints found in Java files:")
for file_path, endpoint, methods in endpoints:
methods_str = ', '.join(methods)
print(f"Endpoint '{endpoint}' with methods [{methods_str}] found in file: {file_path}")
方法类型二 正常的@Requestmapping,@Postmapping,@Getmapping
java6.py
import re
import os
def extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory):
# 定义用于匹配类级和方法级的 @RequestMapping 注解的正则表达式
class_pattern = re.compile(r'@RequestMapping\s*\(\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*\)')
request_mapping_pattern = re.compile(r'@RequestMapping\s*\(\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*\)')
get_mapping_pattern = re.compile(r'@GetMapping\s*\(\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*\)')
post_mapping_pattern = re.compile(r'@PostMapping\s*\(\s*{\s*"([^"]*)"\s*}\s*\)')
# 存储所有接口路径及其所在文件的列表
endpoints = []
# 遍历指定目录下的所有文件
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
if file.endswith(".java"):
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
# 提取类级别的路径
class_match = class_pattern.search(content)
base_path = class_match.group(1) if class_match else ''
print(f"Base path: {base_path}")
# 使用正则表达式匹配 @RequestMapping 注解的值,并将结果拼接为完整的接口路径
request_mapping_matches = request_mapping_pattern.finditer(content)
first_match = True
for request_mapping_match in request_mapping_matches:
if first_match:
first_match = False
continue # 跳过第一个匹配项
method_path = request_mapping_match.group(1)
full_endpoint = base_path + method_path
print(f"Full endpoint: {full_endpoint}")
endpoints.append(full_endpoint) # 存储完整接口路径
# 使用正则表达式匹配 @GetMapping 注解的值,并将结果拼接为完整的接口路径
get_mapping_matches = get_mapping_pattern.finditer(content)
for get_mapping_match in get_mapping_matches:
method_path = get_mapping_match.group(1)
full_endpoint = base_path + method_path
print(f"Full endpoint: {full_endpoint}")
endpoints.append(full_endpoint) # 存储完整接口路径
# 使用正则表达式匹配 @PostMapping 注解的值,并将结果拼接为完整的接口路径
post_mapping_matches = post_mapping_pattern.finditer(content)
for post_mapping_match in post_mapping_matches:
method_path = post_mapping_match.group(1)
full_endpoint = base_path + method_path
print(f"Full endpoint: {full_endpoint}")
endpoints.append(full_endpoint) # 存储完整接口路径
return endpoints
# 调用函数并输出结果
directory = r"C:\Users\qiezi\Desktop\java-jiekou" # 将路径替换为你的目录路径
endpoints = extract_endpoints_from_java_files(directory)
# 将结果写入 url.txt
url_output_file = "url.txt"
with open(url_output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for endpoint in endpoints:
f.write(f"{endpoint}\n")
print(f"URLs have been written to {url_output_file}")
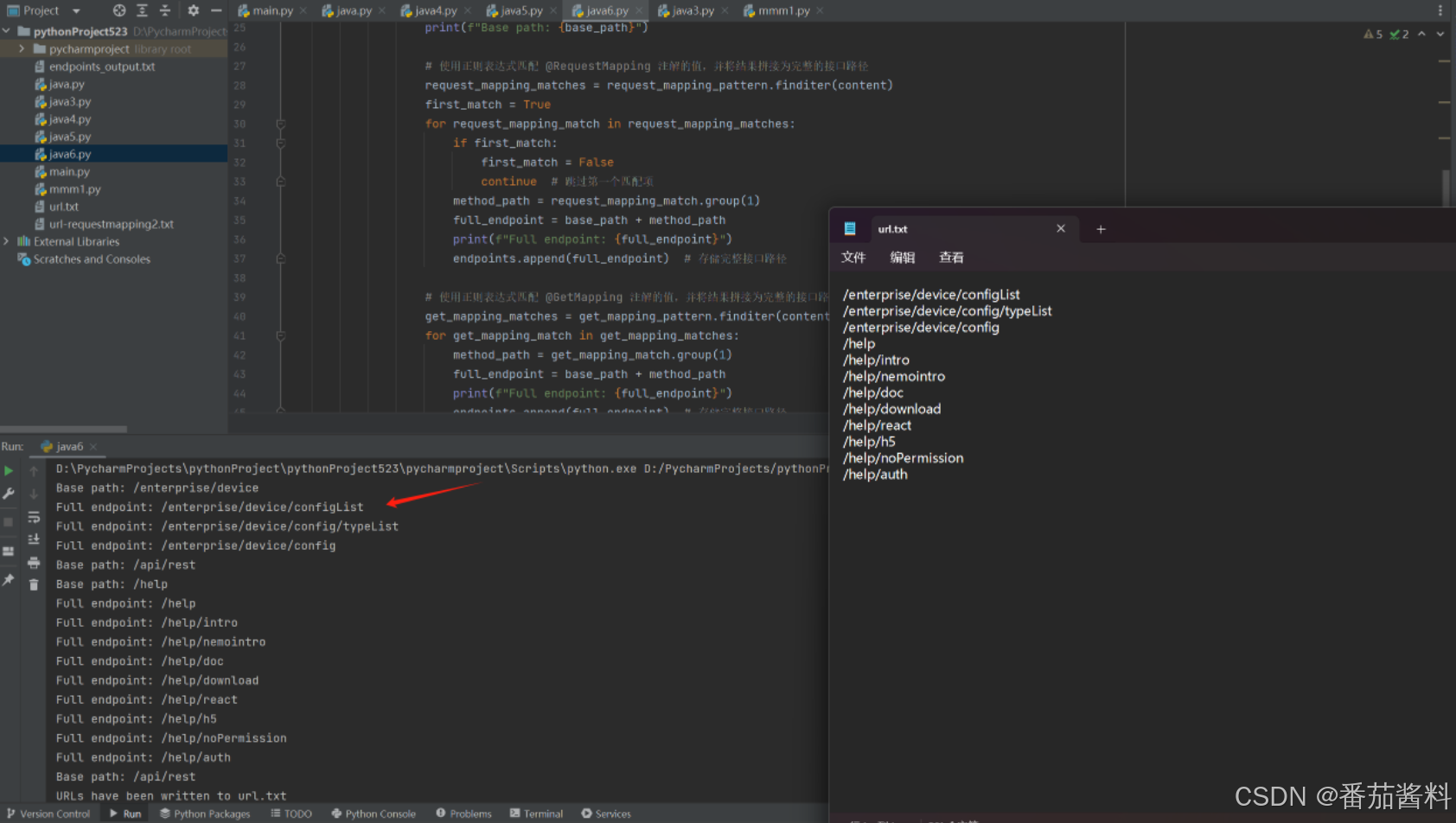
很全面,以后直接使用就可以了
