Linux 0.11
调试介绍
Linux 0.11-调试 Linux 最早期的代码-36
启动跟踪
BIOS 加载
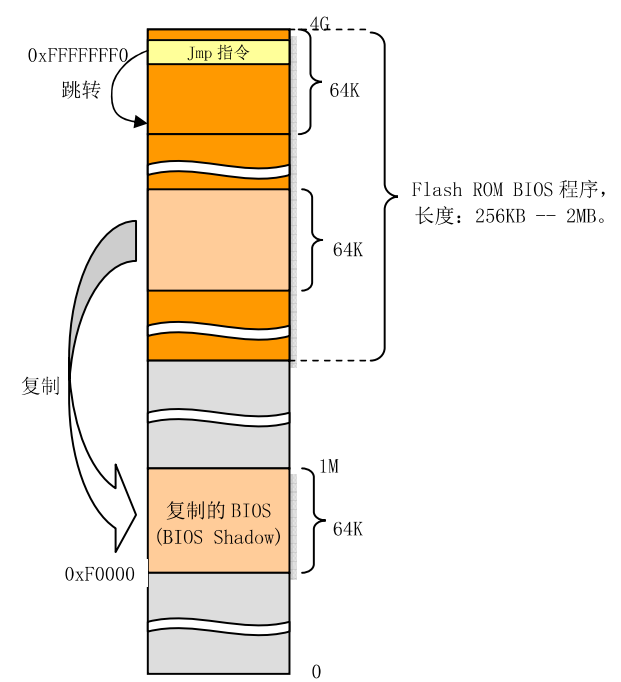
电脑启动,CPU指向0xFFFFFFF0处,这里正好是系统ROM BIOS存放的地址。即开始执行BIOS指令。为了保持向下兼容,就会把与原PC兼容的BIOS代码和数据复制到低端1M末端的64K处。最后BIOS会把操作系统引导程序加载到内存0x7c00处。如下图:
bootsect.s
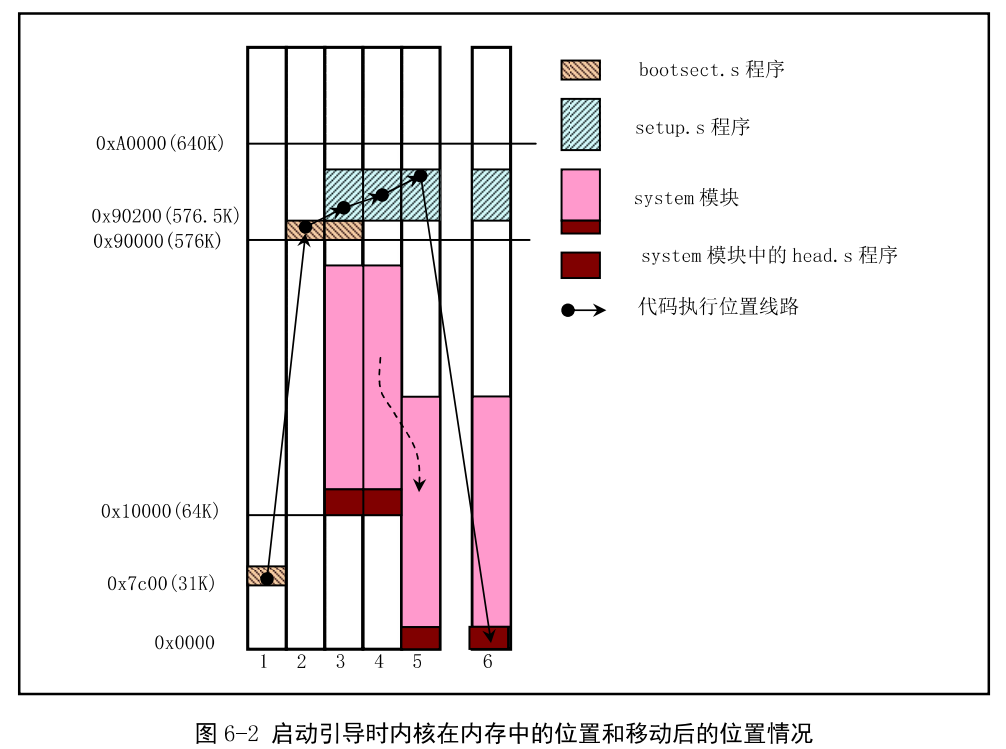
bootsect.s 把自己移动到内存0x90000(576KB)处,并把启动设备中后2KB字节代码(setup.s)读入到内存0x90200处,并把内核其它部分(system模块)读入到0x10000(64KB)处。
setup.s
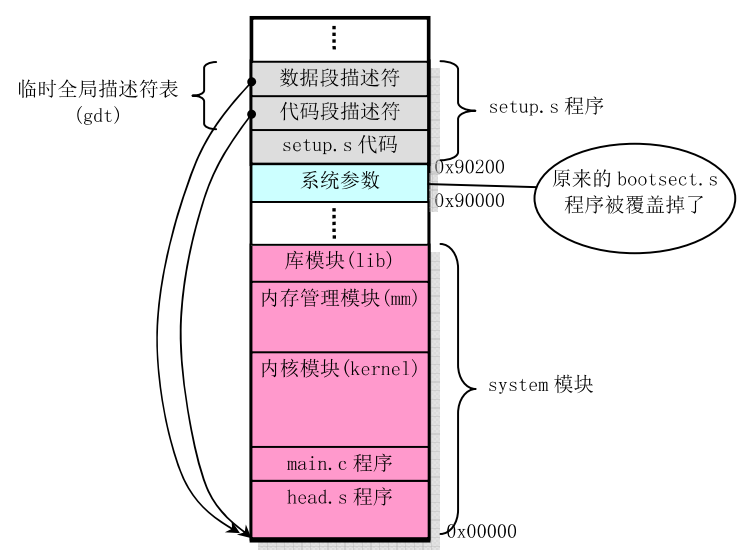
setup.s把system模块移动到内存0处。最后会调用system模块。其内存如下:
head.s
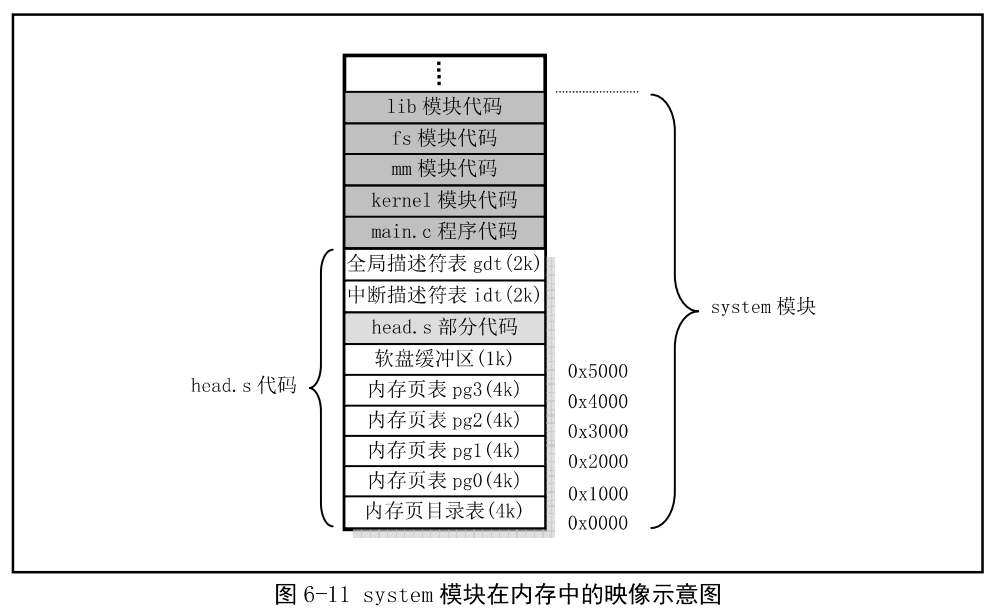
head.s位于system模块的开头处,setup.s把控制权交给head.s后,head.s程序执行结束后,其内存如下:
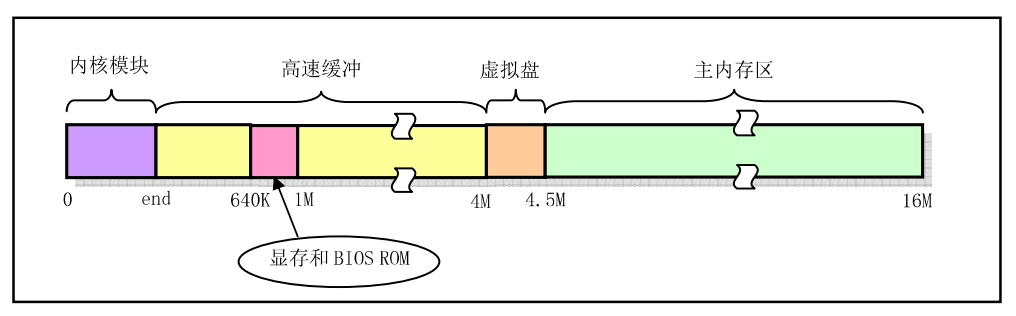
高速缓冲部分还要扣除被显存和ROM BIOS占用的部分,其用于磁盘等块设备临时存放数据的地方,在buffer_init函数中初始化。主内存区由内存管理模块mm通过分页机制进行管理分配。
高速缓冲区初始化代码,由buffer_head结构体形成链表进行管理,每个buffer_head大小为1K。
struct buffer_head {
char * b_data; /* pointer to data block (1024 bytes) */
unsigned long b_blocknr; /* block number */
unsigned short b_dev; /* device (0 = free) */
unsigned char b_uptodate;
unsigned char b_dirt; /* 0-clean,1-dirty */
unsigned char b_count; /* users using this block */
unsigned char b_lock; /* 0 - ok, 1 -locked */
struct task_struct * b_wait;
struct buffer_head * b_prev;
struct buffer_head * b_next;
struct buffer_head * b_prev_free;
struct buffer_head * b_next_free;
};
// fs/buffer.c
// end 为内核模块结束地址
struct buffer_head * start_buffer = (struct buffer_head *) &end;
void buffer_init(long buffer_end)
{
struct buffer_head * h = start_buffer;
void * b;
int i;
// 640K ~ 1M 为显示区域和BIOS区域(1M末端处,大小为64K)
if (buffer_end == 1<<20)
b = (void *) (640*1024);
else
b = (void *) buffer_end;
while ( (b -= BLOCK_SIZE) >= ((void *) (h+1)) ) {
h->b_dev = 0;
h->b_dirt = 0;
h->b_count = 0;
h->b_lock = 0;
h->b_uptodate = 0;
h->b_wait = NULL;
h->b_next = NULL;
h->b_prev = NULL;
h->b_data = (char *) b;
h->b_prev_free = h-1;
h->b_next_free = h+1;
h++;
NR_BUFFERS++;
if (b == (void *) 0x100000)
b = (void *) 0xA0000;
}
h--;
free_list = start_buffer;
free_list->b_prev_free = h;
h->b_next_free = free_list;
for (i=0;i<NR_HASH;i++)
hash_table[i]=NULL;
} 内存管理初始化代码,mem_map进行管理内存是否有使用。每个字符管理4K大小内存。
// mm/memory.c
static unsigned char mem_map [ PAGING_PAGES ] = {0,};
void mem_init(long start_mem, long end_mem)
{
int i;
HIGH_MEMORY = end_mem;
for (i=0 ; i<PAGING_PAGES ; i++)
mem_map[i] = USED;
i = MAP_NR(start_mem);
end_mem -= start_mem;
end_mem >>= 12;
while (end_mem-->0)
mem_map[i++]=0;
}
head.s最后会调用main.c中的main()函数。
main
void main(void) /* This really IS void, no error here. */
{ /* The startup routine assumes (well, ...) this */
/*
* Interrupts are still disabled. Do necessary setups, then
* enable them
*/
ROOT_DEV = ORIG_ROOT_DEV;
drive_info = DRIVE_INFO;
memory_end = (1<<20) + (EXT_MEM_K<<10);
memory_end &= 0xfffff000;
if (memory_end > 16*1024*1024)
memory_end = 16*1024*1024;
if (memory_end > 12*1024*1024)
buffer_memory_end = 4*1024*1024;
else if (memory_end > 6*1024*1024)
buffer_memory_end = 2*1024*1024;
else
buffer_memory_end = 1*1024*1024;
main_memory_start = buffer_memory_end;
#ifdef RAMDISK
main_memory_start += rd_init(main_memory_start, RAMDISK*1024);
#endif
mem_init(main_memory_start,memory_end);
trap_init();
blk_dev_init();
chr_dev_init();
tty_init();
time_init();
sched_init();
buffer_init(buffer_memory_end);
hd_init();
floppy_init();
sti();
move_to_user_mode();
if (!fork()) { /* we count on this going ok */
init();
}
/*
* NOTE!! For any other task 'pause()' would mean we have to get a
* signal to awaken, but task0 is the sole exception (see 'schedule()')
* as task 0 gets activated at every idle moment (when no other tasks
* can run). For task0 'pause()' just means we go check if some other
* task can run, and if not we return here.
*/
for(;;) pause();
}fork
Linux 系统中创建新进程使用 fork()系统调用。所有进程都是通过复制进程0而得到的,都是进程0的子进程。在创建新进程的过程中,系统首先在任务数组中找出一个还没有被任何进程使用的空项(task[NR_TASKS])。
然后系统为新建进程在主内存区中申请一页内存(4K大小)来存放其任务数据结构信息,并复制当前进程任务数据结构中的所有内容作为新进程任务数据结构的模板。
随后对复制的任务数据结构进行修改。设置初始运行时间片为15个系统滴答数(150ms)。接着根据当前进程设置任务状态段TSS中各寄存器的值。新建进程内核态堆栈指针tss.esp0被设置成新进程任务数据结构所在内存页面的顶端,而堆栈段tss.ss0被设置成内核数据段选择符。tss.ldt被设置为局部表描述符在GDT中的索引值。
此后系统设置新任务的代码和数据段基址、限长,并复制当前进程内存分页管理的页表。注意,此时系统并不为新的进程分配实际的物理内存页面,而是让它共享其父进程的内存页面。只有当父进程或新进程中任意一个有写内存操作时,系统才会为执行写操作的进程分配相关的独立使用的内存页面。
随后,如果父进程中有文件是打开的,则应将对应文件的打开次数增加1.接着在GDT中设置新任务的TSS和LDT描述符项,其中基地址信息指向新进程任务结构中的tss和ldt。最后再将新任务设置成可运行状态并返回新进程号。
fork() 函数在main.c中定义:
// init/main.c
static inline _syscall0(int,fork)
// include/unistd.h
#define _syscall0(type,name) \
type name(void) \
{ \
long __res; \
__asm__ volatile ("int $0x80" \
: "=a" (__res) \
: "0" (__NR_##name)); \
if (__res >= 0) \
return (type) __res; \
errno = -__res; \
return -1; \
}其展开后就是定义了fork函数为:
static inline int fork(void) \
{ \
long __res; \
__asm__ volatile ("int $0x80" \
: "=a" (__res) \
: "0" (__NR_fork)); \
if (__res >= 0) \
return (type) __res; \
errno = -__res; \
return -1; \
}
// include/unistd.h
#define __NR_fork 2即调用参数为0的系统调用。系统调用通过0x80陷入。在kernel/sched.c的sched_init函数中设置了中断0x80的处理函数为system_call(其代码在kernel/system_call.s中。)。
// kernel/sched.c
void sched_init(void)
{
// ...
set_system_gate(0x80,&system_call);
}system_call
# kernel/system_call.s
.globl system_call,sys_fork,timer_interrupt,sys_execve
.globl hd_interrupt,floppy_interrupt,parallel_interrupt
.globl device_not_available, coprocessor_error
.align 2
bad_sys_call:
movl $-1,%eax
iret
.align 2
reschedule:
pushl $ret_from_sys_call
jmp schedule
.align 2
system_call:
cmpl $nr_system_calls-1,%eax
ja bad_sys_call
push %ds
push %es
push %fs
pushl %edx
pushl %ecx # push %ebx,%ecx,%edx as parameters
pushl %ebx # to the system call
movl $0x10,%edx # set up ds,es to kernel space
mov %dx,%ds
mov %dx,%es
movl $0x17,%edx # fs points to local data space
mov %dx,%fs
call *sys_call_table(,%eax,4) # 调用地址sys_call_table + 4 * %eax
pushl %eax
movl current,%eax
cmpl $0,state(%eax) # state
jne reschedule
cmpl $0,counter(%eax) # counter
je reschedule
ret_from_sys_call:
movl current,%eax # task[0] cannot have signals
cmpl task,%eax
je 3f
cmpw $0x0f,CS(%esp) # was old code segment supervisor ?
jne 3f
cmpw $0x17,OLDSS(%esp) # was stack segment = 0x17 ?
jne 3f
movl signal(%eax),%ebx
movl blocked(%eax),%ecx
notl %ecx
andl %ebx,%ecx
bsfl %ecx,%ecx
je 3f
btrl %ecx,%ebx
movl %ebx,signal(%eax)
incl %ecx
pushl %ecx
call do_signal
popl %eax
3: popl %eax
popl %ebx
popl %ecx
popl %edx
pop %fs
pop %es
pop %ds
iret其会调用sys_call_table中预定义的函数,此处即为sys_fork。
// include/linux/sys.h
fn_ptr sys_call_table[] = { sys_setup, sys_exit, sys_fork, sys_read,
sys_write, sys_open, sys_close, sys_waitpid, sys_creat, sys_link,
sys_unlink, sys_execve, sys_chdir, sys_time, sys_mknod, sys_chmod,
sys_chown, sys_break, sys_stat, sys_lseek, sys_getpid, sys_mount,
sys_umount, sys_setuid, sys_getuid, sys_stime, sys_ptrace, sys_alarm,
sys_fstat, sys_pause, sys_utime, sys_stty, sys_gtty, sys_access,
sys_nice, sys_ftime, sys_sync, sys_kill, sys_rename, sys_mkdir,
sys_rmdir, sys_dup, sys_pipe, sys_times, sys_prof, sys_brk, sys_setgid,
sys_getgid, sys_signal, sys_geteuid, sys_getegid, sys_acct, sys_phys,
sys_lock, sys_ioctl, sys_fcntl, sys_mpx, sys_setpgid, sys_ulimit,
sys_uname, sys_umask, sys_chroot, sys_ustat, sys_dup2, sys_getppid,
sys_getpgrp, sys_setsid, sys_sigaction, sys_sgetmask, sys_ssetmask,
sys_setreuid,sys_setregid, sys_iam, sys_whoami };sys_fork
sys_fork 在 system_call.s中定义。
# kernel/system_call.s
.align 2
sys_fork:
call find_empty_process
testl %eax,%eax
js 1f
push %gs
pushl %esi
pushl %edi
pushl %ebp
pushl %eax
call copy_process
addl $20,%esp
1: retsys_fork 先调用find_empty_process函数找到空闲的进程(内核中定义了64个,NR_TASKS),其返回内部进程序列。然后调用copy_process函数
find_empty_process
为新进程取得不重复的进程号。函数返回在任务数组中的任务号。
// kernel/fork.c
int find_empty_process(void)
{
int i;
repeat:
if ((++last_pid)<0) last_pid=1;
for(i=0 ; i<NR_TASKS ; i++)
if (task[i] && task[i]->pid == last_pid) goto repeat;
for(i=1 ; i<NR_TASKS ; i++) // 任务0项,因为常驻,所以不使用
if (!task[i])
return i;
return -EAGAIN;
}copy_process
用于创建并复制进程的代码段和数据段以及环境。在进程复制过程中,工作主要牵涉到进程数据结构中信息的设置。系统首先为新建进程在主内存区中申请一页内存来存放其任务数据结构信息,并复制当前进程任务数据结构中的所有内容作为新进程任务数据结构的模板。
// kernel/fork.c
int copy_process(int nr,long ebp,long edi,long esi,long gs,long none,
long ebx,long ecx,long edx,
long fs,long es,long ds,
long eip,long cs,long eflags,long esp,long ss)
{
struct task_struct *p;
int i;
struct file *f;
p = (struct task_struct *) get_free_page();
if (!p)
return -EAGAIN;
task[nr] = p;
// NOTE!: the following statement now work with gcc 4.3.2 now, and you
// must compile _THIS_ memcpy without no -O of gcc.#ifndef GCC4_3
*p = *current; /* NOTE! this doesn't copy the supervisor stack */
p->state = TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE;
p->pid = last_pid;
p->father = current->pid;
p->counter = p->priority;
p->signal = 0;
p->alarm = 0;
p->leader = 0; /* process leadership doesn't inherit */
p->utime = p->stime = 0;
p->cutime = p->cstime = 0;
p->start_time = jiffies;
p->tss.back_link = 0;
p->tss.esp0 = PAGE_SIZE + (long) p;
p->tss.ss0 = 0x10;
p->tss.eip = eip;
p->tss.eflags = eflags;
p->tss.eax = 0;
p->tss.ecx = ecx;
p->tss.edx = edx;
p->tss.ebx = ebx;
p->tss.esp = esp;
p->tss.ebp = ebp;
p->tss.esi = esi;
p->tss.edi = edi;
p->tss.es = es & 0xffff;
p->tss.cs = cs & 0xffff;
p->tss.ss = ss & 0xffff;
p->tss.ds = ds & 0xffff;
p->tss.fs = fs & 0xffff;
p->tss.gs = gs & 0xffff;
p->tss.ldt = _LDT(nr);
p->tss.trace_bitmap = 0x80000000;
if (last_task_used_math == current)
__asm__("clts ; fnsave %0"::"m" (p->tss.i387));
if (copy_mem(nr,p)) {
task[nr] = NULL;
free_page((long) p);
return -EAGAIN;
}
for (i=0; i<NR_OPEN;i++)
if ((f=p->filp[i]))
f->f_count++;
if (current->pwd)
current->pwd->i_count++;
if (current->root)
current->root->i_count++;
if (current->executable)
current->executable->i_count++;
set_tss_desc(gdt+(nr<<1)+FIRST_TSS_ENTRY,&(p->tss));
set_ldt_desc(gdt+(nr<<1)+FIRST_LDT_ENTRY,&(p->ldt));
p->state = TASK_RUNNING; /* do this last, just in case */
return last_pid;
}copy_mem
复制内存页表。参数nr是新任务号,p是新任务数据结构指针。该函数为新任务在线性地址空间中设置代码段和数据段基址、限长,并复制页表。由于Linux采用了写时复制技术,因此这里仅为新进程设置自己的页目录表项和页表项,而没有实际为新进程分配物理内存页面。此时新进程与其父进程共享所有内存页面。
int copy_mem(int nr,struct task_struct * p)
{
unsigned long old_data_base,new_data_base,data_limit;
unsigned long old_code_base,new_code_base,code_limit;
code_limit=get_limit(0x0f);
data_limit=get_limit(0x17);
old_code_base = get_base(current->ldt[1]);
old_data_base = get_base(current->ldt[2]);
if (old_data_base != old_code_base)
panic("We don't support separate I&D");
if (data_limit < code_limit)
panic("Bad data_limit");
new_data_base = new_code_base = nr * 0x4000000;
p->start_code = new_code_base;
set_base(p->ldt[1],new_code_base);
set_base(p->ldt[2],new_data_base);
if (copy_page_tables(old_data_base,new_data_base,data_limit)) {
printk("free_page_tables: from copy_mem\n");
free_page_tables(new_data_base,data_limit);
return -ENOMEM;
}
return 0;
}