C/C++ 堆和优先队列
一.堆和优先队列
在计算机中一颗完全二叉树可以用一个数组来进行表示:
 堆:结构讲解
堆:结构讲解
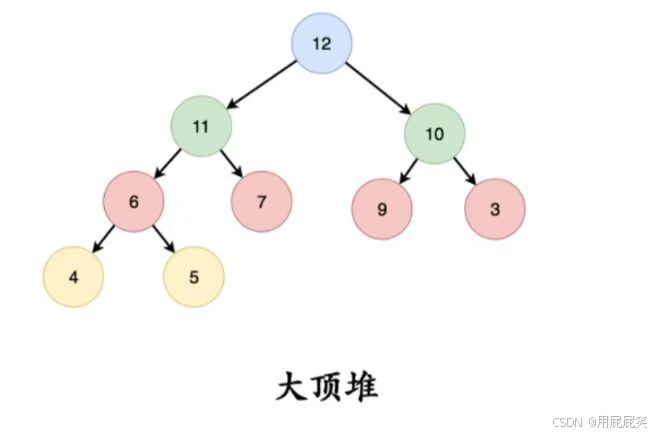
如果完全二叉树中的根节点存储的值为当前树中所有值的最大值,在任意一个三元组(父节点,左子树,右子树),父节点的值永远是最大的,就叫大顶堆/大根堆;
反之,就叫做小根堆/小顶堆.
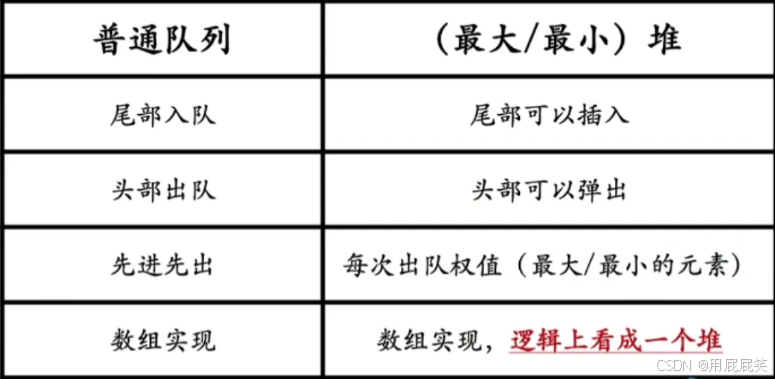
堆:优先队列
代码演示:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define ROOT 1
#define cmp >
#define FATHER(i) ((i)/2)
#define LEFT(i) ((i) * 2)
#define RIGHT(i) ((i) * 2 + 1)
typedef struct PriorityQueue {
int* data, *__data;
int size, n;
} PriorityQueue;
PriorityQueue* initPQ(int size) {
PriorityQueue* p = (PriorityQueue*)malloc(sizeof(PriorityQueue));
p->__data = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
p->data = p->__data - 1;
p->size = size;
p->n = 0;
return p;
}
int empty(PriorityQueue* p) {
return p->n == 0;
}
int full(PriorityQueue* p) {
return p->n == p->size;
}
int top(PriorityQueue* p) {
return p->data[1];
}
void up_update(int* data, int i) {
while (i > ROOT && data[i] cmp data[FATHER(i)]) {
swap(data[i], data[FATHER(i)]);
i = FATHER(i);
}
return;
}
void down_update(int* data, int i, int n) {
int ind;
while (LEFT(i) <= n && data[i] cmp data[FATHER(i)]) {
ind = i;
if (data[LEFT(i)] cmp data[ind]) ind = LEFT(i);
if (RIGHT(i) <= n &&data[RIGHT(i)] cmp data[ind]) ind = RIGHT(i);
if (ind == i) break;
swap(data[i], data[ind]);
i = ind;
}
return;
}
int push(PriorityQueue* p, int x) {
if (full(p)) return 0;
p->n += 1;
p->data[p->n] = x;
up_update(p->data, p->n);
return 1;
}
int pop(PriorityQueue* p) {
if (empty(p)) return 0;
p->data[ROOT] = p->data[p->n];
p->n -= 1;
down_update(p->data, ROOT, p->n);
return 1;
}
void clearPQ(PriorityQueue* p) {
if (p == NULL) return;
free(p->__data);
free(p->data);
free(p);
return;
}
void output(PriorityQueue* p) {
printf("PQ(%d) : ", p->n);
for (int i = 1; i <= p->n; i++) {
printf("%d ", p->data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return ;
}
int main() {
#define MAX_OP 100
int op, x;
PriorityQueue* p = initPQ(MAX_OP);
while (~scanf("%d", &op)) {
if (op == 1) {
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("insert %d to priority_queue : \n", x);
push(p, x);
output(p);
}
else {
printf("top : %d\n", top(p));
pop(p);
output(p);
}
}
clearPQ(p);
return 0;
}二.堆排序与线性建堆法
堆排序 口决:
1.将堆顶元素与堆尾元素交换;
2.将此操作看做是堆顶元素弹出操作;
3.按照头部弹出以后的策略调整堆;
普通建堆: 向上调整
依次把每个元素插入到堆中, 比较低效;
线性建堆: 向下调整
从后向前依次扫描拥有子节点的节点,然后对该节点三元组进行向下调整, 比较高效;
时间复杂度O(n);
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define ROOT 1
#define cmp >
#define FATHER(i) ((i)/2)
#define LEFT(i) ((i) * 2)
#define RIGHT(i) ((i) * 2 + 1)
#define TEST(func, arr, n) {\
printf("TEST: %s\n", #func);\
int *temp = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); \
memcpy(temp, arr, sizeof(int) * n); \
long long b = clock(); \
func(temp, n); \
long long e = clock(); \
if(check(temp, n)) { \
printf("OK\t"); \
} else { \
printf("FAIL\t"); \
} \
printf("%lld ms\n", 1000 * (e - b) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC); \
free(temp); \
}
int* getRandData(int n) {
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) arr[i] = rand() % 100000;
return arr;
}
bool check(int* arr, int n) {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[i - 1]) return false;
//printf("%d " ,arr[i]);
}
return true;
}
inline void up_updata(int* data, int i) {
while (i > 1 && data[i] cmp data[FATHER(i)]) {
swap(data[i], data[FATHER(i)]);
i = FATHER(i);
}
}
inline void down_updata(int* data, int i, int n) {
while (LEFT(i) <= n) {
int ind = i, l = LEFT(i), r = RIGHT(i);
if (data[l] cmp data[ind]) ind = l;
if (r <= n && data[r] cmp data[ind]) ind = r;
if (ind == i) return;
swap(data[ind], data[i]);
i = ind;
}
return;
}
void normal_heap_build(int* data, int n) {
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
up_updata(data, i);
}
return;
}
void linear_heap_build(int* data, int n) {
for (int i = n / 2; i >= 1; i--) {
down_updata(data, i, n);
}
return;
}
void heap_sort(int* data, int n) {
for (int i = n; i >= 2; i--) {
swap(data[1], data[i]);
down_updata(data, 1, i - 1);
}
return;
}
void normal_heap(int* arr, int n) {
int* data = arr - 1;
normal_heap_build(data, n);
heap_sort(data, n);
return;
}
void linear_heap(int* arr, int n) {
int* data = arr - 1;
linear_heap_build(data, n);
heap_sort(data, n);
return;
}
int main() {
srand(time(0));
#define MAX_N 10000000
int* arr = getRandData(MAX_N);
TEST(normal_heap, arr, MAX_N);
TEST(linear_heap, arr, MAX_N);
}三.用堆优化哈夫曼编码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node {
char ch;
int freq;
Node* lchild, * rchild;
}Node;
typedef struct Heap {
Node** data, **__data;
int n, size;
}Heap;
Heap* getNewHeap(int size) {
Heap* h = (Heap*)malloc(sizeof(Heap));
h->__data = (Node**)malloc(sizeof(Node*));
h->data = h->__data - 1;
h->n = 0;
h->size = size;
return h;
}
int fullHeap(Heap* h) {
return h->n == h->size;
}
int cmpHeap(Heap* h, int i, int j) {
return h->data[i]->freq < h->data[j]->freq;
}
void up_maintain(Heap* h, int i) {
while (i > 1 && cmpHeap(h, i, i /2)) {
swap(h->data[i], h->data[i / 2]);
i = i / 2;
}
return;
}
void down_maintain(Heap* h, int i) {
while (i * 2 <= h->n) {
int ind = i, l = i * 2, r = i * 2 + 1;
if (cmpHeap(h, l, ind)) ind = l;
if (r <= h->n && cmpHeap(h, r, ind)) ind = r;
if (ind = i) return;
swap(h->data[i], h->data[ind]);
i = ind;
}
return;
}
int pushHeap(Heap* h, Node* n) {
if (fullHeap(h)) return 0;
h->n += 1;
h->data[h->n] = n;
up_maintain(h, h->n);
return 1;
}
int emptyHeap(Heap* h) {
return h->n == 0;
}
Node* topHeap(Heap* h) {
if (emptyHeap(h)) return NULL;
return h->data[1];
}
int popHeap(Heap* h) {
if (emptyHeap(h)) return 0;
h->data[1] = h->data[h->n];
h->n -= 1;
down_maintain(h, h->n);
return 1;
}
void clearHeap(Heap* h) {
if (h == NULL) return;
free(h->__data);
free(h);
return;
}
Node* getNewNode(int freq, char ch) {
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->ch = ch;
p->freq = freq;
p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;
return p;
}
void clear(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
clear(root->lchild);
clear(root->rchild);
free(root);
root = NULL;
return;
}
void swap_node(Node** node_arr, int i, int j) {
Node* temp = node_arr[i];
node_arr[i] = node_arr[j];
node_arr[j] = temp;
}
int find_min_node(Node** node_arr, int n) {
int ind = 0;//假设最小值的下标是0
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (node_arr[ind]->freq > node_arr[j]->freq) ind = j;
}
return ind;
}
Node* buildHuffmanTree(Node** node_arr, int n) {
/*for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%c %d\n", node_arr[i]->ch, node_arr[i]->freq);
}*/
Heap* h = getNewHeap(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) pushHeap(h, node_arr[i]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
Node* node1 = topHeap(h);
popHeap(h);
Node* node2 = topHeap(h);
popHeap(h);
Node* node3 = getNewNode(node1->freq + node2->freq, 0);
node3->lchild = node1;
node3->rchild = node2;
pushHeap(h, node3);
}//进行n - 1次的合并
Node* ret = topHeap(h);
clearHeap(h);
return ret;
}
#define MAX_CHAR_NUM 128
char* char_code[MAX_CHAR_NUM] = { 0 };
void extractHuffmanCode(Node* root, char buff[], int k) {//k表示前缀的长度
buff[k] = 0;
if (root == NULL) return;
if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL) {
//printf("%c : %s\n", root->ch, buff);
char_code[root->ch] = _strdup(buff);//将buff拷贝一份赋值给字符指针
return;
}
buff[k] = '0';
extractHuffmanCode(root->lchild, buff, k + 1);
buff[k] = '1';
extractHuffmanCode(root->rchild, buff, k + 1);
return;
}
int main() {
int n, freq;
char s[10];
scanf("%d", &n);
Node** node_arr = (Node**)malloc(n * sizeof(Node*));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%s%d", s, &freq);
node_arr[i] = getNewNode(freq, s[0]);
}
Node* root = buildHuffmanTree(node_arr, n);
char buff[1000];
extractHuffmanCode(root, buff, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CHAR_NUM ; i++ ) {
if (char_code[i] == NULL) continue;
printf("%c : %s\n", i, char_code[i]);
}
clear(root);
return 0;
}习题
703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class KthLargest {
public:
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int k, tot;
set<PII> s;
KthLargest(int k, vector<int>& nums) {
this->k = k;
for(auto x : nums) {
add(x);
}
return ;
}
int add(int val) {
if(s.size() < k || val >s.begin()->first) {
s.insert(PII(val, tot++));
}
if(s.size() > k) {
s.erase(s.begin());
}
return s.begin()->first;
}
};
295. 数据流的中位数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class MedianFinder {
public:
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
int tot;
set<PII> s1, s2;
MedianFinder() {
tot = 0;
}
void addNum(int num) {
if(s1.size() == 0 || num < -s1.begin()->first) {
s1.insert(PII(-num,tot++));
} else {
s2.insert(PII(num,tot++));
}
int n1 = (s1.size() + s2.size() + 1) / 2;
if(n1 == s1.size()) return;
if(n1 > s1.size()) {
s1.insert(PII(-s2.begin()->first,tot++));
s2.erase(s2.begin());
} else {
s2.insert(PII(-s1.begin()->first,tot++));
s1.erase(s1.begin());
}
}
double findMedian() {
if((s1.size() + s2.size()) % 2) {
return (double)-s1.begin()->first;
} else {
return (s2.begin()->first-s1.begin()->first) / 2.0;
}
}
};
/**
* Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MedianFinder* obj = new MedianFinder();
* obj->addNum(num);
* double param_2 = obj->findMedian();
*/23. 合并 K 个升序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
int tot = 0, n = lists.size();
set<PII> s;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(lists[i]) s.insert(PII(lists[i]->val,i));
}
ListNode new_head, *p = &new_head, *q;
new_head.next = nullptr;
while(s.size()) {
PII a = *s.begin();
s.erase(s.begin());
q = lists[a.second];
lists[a.second] = lists[a.second]->next;
p->next = q;
q->next = nullptr;
p = q;
if(lists[a.second]) {
s.insert(PII(lists[a.second]->val, a.second));
}
}
return new_head.next;
}
};264. 丑数 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
set<long long> s;
s.insert(1);
long long ans = 0, flag = 0;
while(n--) {
ans = *s.begin();
s.erase(s.begin());
if(ans % 5 == 0) flag = 2;
else if(ans % 3 == 0) flag = 1;
else flag = 0;
switch(flag) {
case 0: s.insert(ans * 2);
case 1: s.insert(ans * 3);
case 2: s.insert(ans * 5);
}
}
return ans;
}
};序列M小和 - 题目 - Online Judge
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int main() {
int n, m, t = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
set<PII> s;
s.insert(PII(0, t++));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int i1 = i % 2, i2 = 1 - i1;
vector<int> temp;
for (auto x : s){
temp.push_back(x.first);
}
s.clear();
for (int j = 0, a; j < m; j++) {
cin >> a;
for (auto x : temp) {
if (s.size() < m || s.begin()->first < x - a) {
s.insert(PII(x - a, t++));
}
if (s.size() > m) s.erase(s.begin());
}
}
}
int flag = 0;
for (auto iter = s.rbegin(); iter != s.rend(); iter++) {
if (flag) cout << " ";
cout << -iter->first;
flag = 1;
}
return 0;
}