Pandas教程之二十九: 使用 Pandas 处理日期和时间
Python | 使用 Pandas 处理日期和时间
在处理数据时,遇到时间序列数据是很常见的。在处理时间序列数据时,Pandas 是一个非常有用的工具。
Pandas提供了一组不同的工具,我们可以使用这些工具对日期时间数据执行所有必要的任务。让我们尝试通过下面讨论的示例来理解。
在 Pandas 中使用日期
Python 的 DateTime 模块中的日期类处理公历中的日期。它接受三个整数参数:年、月和日。
- Python3
| from datetime import date
d= date(2000,9,17)
print(d)
print(type(d)) |
输出:
2000-09-17
<class 'datetime.date'>
提取年、月、日
从 Timestamp 对象中检索年、月、日部分。
- Python3
| import pandas as pd
# Creating a Timestamp object timestamp = pd.Timestamp('2023-10-04 15:30:00')
# Extracting the year from the Timestamp year = timestamp.year
# Printing the extracted year print(year)
# Extracting the month from the Timestamp month = timestamp.month
# Printing the extracted month print(month)
# Extracting the day from the Timestamp day = timestamp.day
# Printing the extracted day print(day) |
输出:
2023
10
4
工作日和季度
确定与时间戳相关的星期几和季度。
- Python3
| # Extracting the hour from the Timestamp hour = timestamp.hour
# Printing the extracted hour print(hour)
# Extracting the minute from the Timestamp minute = timestamp.minute
# Printing the extracted minute print(minute) # Extracting the weekday from the Timestamp weekday = timestamp.weekday()
# Printing the extracted weekday print(weekday)
# Extracting the quarter from the Timestamp quarter = timestamp.quarter
# Printing the extracted quarter print(quarter) |
输出:
15 30 2 4
在 Pandas 中使用时间
DateTime 模块中的另一个类称为 time,它返回一个 DateTime 对象并接受整数参数,时间间隔最高达微秒:
- Python3
| from datetime import time
t = time(12,50,12,40)
print(t)
print(type(t)) |
输出:
12:50:12.000040
<class ‘datetime.time’> 复制代码
时间段和日期偏移
创建自定义时间段和日期偏移,以实现灵活的日期操作。
- Python3
| # Creating a time period object time_period = pd.Period('2023-10-04', freq='M')
# Extracting the year from the time period year = time_period.year
# Printing the extracted year print(year)
# Extracting the month from the time period month = time_period.month
# Printing the extracted month print(month)
# Extracting the quarter from the time period quarter = time_period.quarter
# Printing the extracted quarter print(quarter)
# Creating a date offset object date_offset = pd.DateOffset(years=2, months=3, days=10)
# Adding the date offset to a Timestamp new_timestamp = timestamp + date_offset
# Printing the new Timestamp print(new_timestamp) |
输出:
2023
10
4
2026-01-14 15:30:00
处理时区
时区在日期和时间数据中起着至关重要的作用。Pandas 提供了有效处理时区的机制:
- UTC 和时区转换:在 UTC(协调世界时)和当地时区之间转换。
- 时区感知数据操作:使用时区感知数据,确保准确的日期和时间解释。
- 自定义时区设置:为数据分析和可视化指定自定义时区设置。
- Python3
| import pandas as pd
# Creating a Timestamp object with a specific time zone timestamp = pd.Timestamp('2023-10-04 15:30:00', tz='America/New_York')
# Printing the Timestamp with its time zone print(timestamp)
# Converting the Timestamp to UTC utc_timestamp = timestamp.utcfromtz('America/New_York')
# Printing the UTC timestamp print(utc_timestamp)
# Converting the UTC timestamp back to the original time zone original_timestamp = utc_timestamp.tz_localize('America/New_York')
# Printing the original timestamp print(original_timestamp)
# Creating a DatetimeIndex with a specific time zone datetime_index = pd.DatetimeIndex(['2023-10-04', '2023-10-11', '2023-10-18'], tz='Asia/Shanghai')
# Printing the DatetimeIndex with its time zone print(datetime_index)
# Converting the DatetimeIndex to UTC utc_datetime_index = datetime_index.utcfromtz('Asia/Shanghai')
# Printing the UTC DatetimeIndex print(utc_datetime_index)
# Converting the UTC DatetimeIndex back to the original time zone original_datetime_index = utc_datetime_index.tz_localize( 'Asia/Shanghai')
# Printing the original DatetimeIndex print(original_datetime_index) |
输出:
Original Timestamp: 2023-10-04 15:30:00-04:00
UTC Timestamp: 2023-10-04 19:30:00+00:00
Original Timestamp (Back to America/New_York): 2023-10-04 15:30:00-04:00
Original DatetimeIndex: DatetimeIndex(['2023-10-04 00:00:00+08:00', '2023-10-11 00:00:00+08:00',
'2023-10-18 00:00:00+08:00'],
dtype='datetime64[ns, Asia/Shanghai]', freq=None)
UTC DatetimeIndex: DatetimeIndex(['2023-10-03 16:00:00+00:00', '2023-10-10 16:00:00+00:00',
'2023-10-17 16:00:00+00:00'],
dtype='datetime64[ns, UTC]', freq=None)
Original DatetimeIndex (Back to Asia/Shanghai): DatetimeIndex(['2023-10-04 00:00:00+08:00', '2023-10-11 00:00:00+08:00',
'2023-10-18 00:00:00+08:00'],
dtype='datetime64[ns, Asia/Shanghai]', freq=None)
在 Pandas 中使用日期和时间
Pandas 提供了方便的方法从 Timestamp 对象中提取特定的日期和时间部分。这些方法包括:
步骤 1:创建日期数据框
- Python3
| import pandas as pd
# Create dates dataframe with frequency data = pd.date_range('1/1/2011', periods = 10, freq ='H')
data |
输出:
DatetimeIndex(['2011-01-01 00:00:00', '2011-01-01 01:00:00',
'2011-01-01 02:00:00', '2011-01-01 03:00:00',
'2011-01-01 04:00:00', '2011-01-01 05:00:00',
'2011-01-01 06:00:00', '2011-01-01 07:00:00',
'2011-01-01 08:00:00', '2011-01-01 09:00:00'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='H')
步骤 2:创建日期范围并显示基本特征
- Python3
| # Create date and time with dataframe data = pd.date_range('1/1/2011', periods = 10, freq ='H')
x = pd.datetime.now() x.month, x.year |
输出:
(9, 2018)
日期时间特征可分为两类。第一类是某个时期内的时间点,第二类是自某个特定时期以来经过的时间。这些特征对于理解数据中的模式非常有用。
步骤 3:将给定日期划分为特征 -
pandas.Series.dt.year返回日期时间的年份。pandas.Series.dt.month 返回日期时间的月份。pandas.Series.dt.day 返回日期时间的日期。pandas.Series.dt.hour 返回日期时间的小时。pandas.Series.dt.minute 返回日期时间的分钟。
将日期和时间分解为单独的特征
- Python3
| # Create date and time with dataframe rng = pd.DataFrame() rng['date'] = pd.date_range('1/1/2011', periods = 72, freq ='H')
# Print the dates in dd-mm-yy format rng[:5]
# Create features for year, month, day, hour, and minute rng['year'] = rng['date'].dt.year rng['month'] = rng['date'].dt.month rng['day'] = rng['date'].dt.day rng['hour'] = rng['date'].dt.hour rng['minute'] = rng['date'].dt.minute
# Print the dates divided into features rng.head(3) |
输出:
date year month day hour minute 0 2011-01-01 00:00:00 2011 1 1 0 0 1 2011-01-01 01:00:00 2011 1 1 1 0 2 2011-01-01 02:00:00 2011 1 1 2 0
步骤 4:要获取当前时间,使用 Timestamp.now(),然后将时间戳转换为日期时间并直接访问年、月或日。
- Python3
| # Input present datetime using Timestamp t = pandas.tslib.Timestamp.now() t |
输出:
Timestamp('2018-09-18 17:18:49.101496')
- Python3
| # Convert timestamp to datetime t.to_datetime() |
输出:
datetime.datetime(2018, 9, 18, 17, 18, 49, 101496)
步骤5:提取日期时间列的特定组成部分,如日期、时间、星期几,以供进一步分析。
- Python3
| # Directly access and print the features t.year t.month t.day t.hour t.minute t.second |
输出:
2018 8 25 15 53
探索 UFO 目击事件的历史
让我们在真实的数据集uforeports上分析这个问题。
- Python3
| import pandas as pd
url = 'http://bit.ly/uforeports'
# read csv file df = pd.read_csv(url) df.head() |
输出:
City Colors Reported Shape Reported State Time 0 Ithaca NaN TRIANGLE NY 6/1/1930 22:00 1 Willingboro NaN OTHER NJ 6/30/1930 20:00 2 Holyoke NaN OVAL CO 2/15/1931 14:00 3 Abilene NaN DISK KS 6/1/1931 13:00 4 New York Worlds Fair NaN LIGHT NY 4/18/1933 19:00
该代码用于将 Pandas DataFrame 中的一列时间值转换为日期时间格式。
- Python3
| # Convert the Time column to datetime format df['Time'] = pd.to_datetime(df.Time)
df.head() |
输出:
City Colors Reported Shape Reported State \
0 Ithaca NaN TRIANGLE NY
1 Willingboro NaN OTHER NJ
2 Holyoke NaN OVAL CO
3 Abilene NaN DISK KS
4 New York Worlds Fair NaN LIGHT NY
Time
0 1930-06-01 22:00:00
1 1930-06-30 20:00:00
2 1931-02-15 14:00:00
3 1931-06-01 13:00:00
4 1933-04-18 19:00:00
该代码用于显示 Pandas DataFrame 中每列的数据类型。
- Python3
| # shows the type of each column data df.dtypes |
输出:
City object Colors Reported object Shape Reported object State object Time datetime64[ns] dtype: object
该代码用于从 Pandas DataFrame 中的一列时间数据中提取小时详细信息。
- Python3
| # Get hour detail from time data df.Time.dt.hour.head() |
输出:
0 22 1 20 2 14 3 13 4 19 Name: Time, dtype: int64
该代码用于检索 Pandas DataFrame 中日期和时间数据列中的星期几名称。
- Python3
| # Get name of each date df.Time.dt.weekday_name.head() |
输出:
0 Sunday 1 Monday 2 Sunday 3 Monday 4 Tuesday Name: Time, dtype: object
该代码用于检索 Pandas DataFrame 中日期和时间数据列中每个日期的一年中的序数日。
- Python3
| # Get ordinal day of the year df.Time.dt.dayofyear.head() |
输出:
0 152 1 181 2 46 3 152 4 108 Name: Time, dtype: int64
创建可视化效果来探索一天中各个时段出现 UFO 的频率。
- Python3
|
输出:
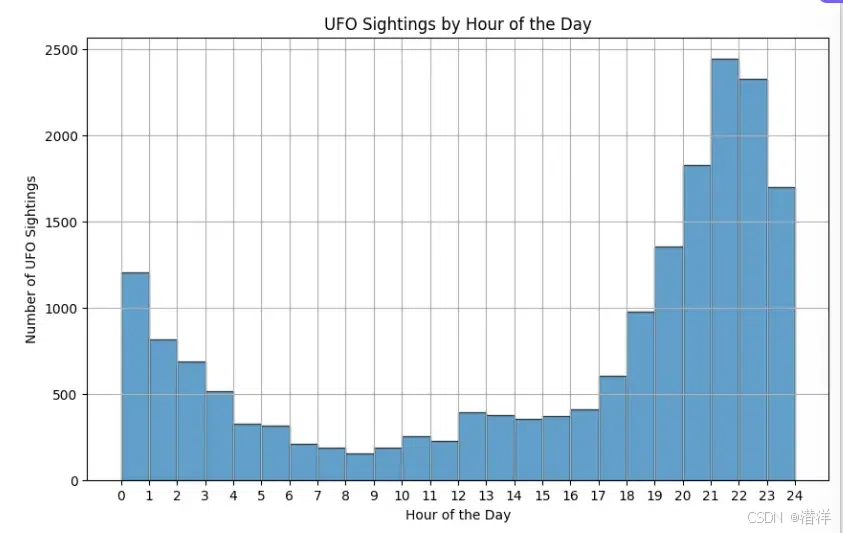
最后:
处理日期和时间数据是数据分析师和科学家的一项基本技能。Pandas 提供了一套全面的工具和技术,可有效处理日期和时间信息,从而实现对时间相关数据的深入分析。通过掌握这些技术,您可以从时间序列数据中获得有价值的见解,并在各个领域做出明智的决策。
