Vue(四)
1.Vuex
1.1 Vuex是什么
Vuex 是一个插件,可以帮我们管理 Vue 通用的数据。例如:购物车数据、个人信息数据。
1.2 vuex的使用
1.安装 vuex
安装 vuex 与 vue-router 类似,vuex 是一个独立存在的插件,如果脚手架初始化没有选 vuex,就需要额外安装。
yarn add vuex@3 或者 npm i vuex@32.新建store/index.js专门存放vuex
为了维护项目目录的整洁,在 src 目录下新建一个 store 目录其下放置一个 index.js 文件。 和 router/index.js 类似。
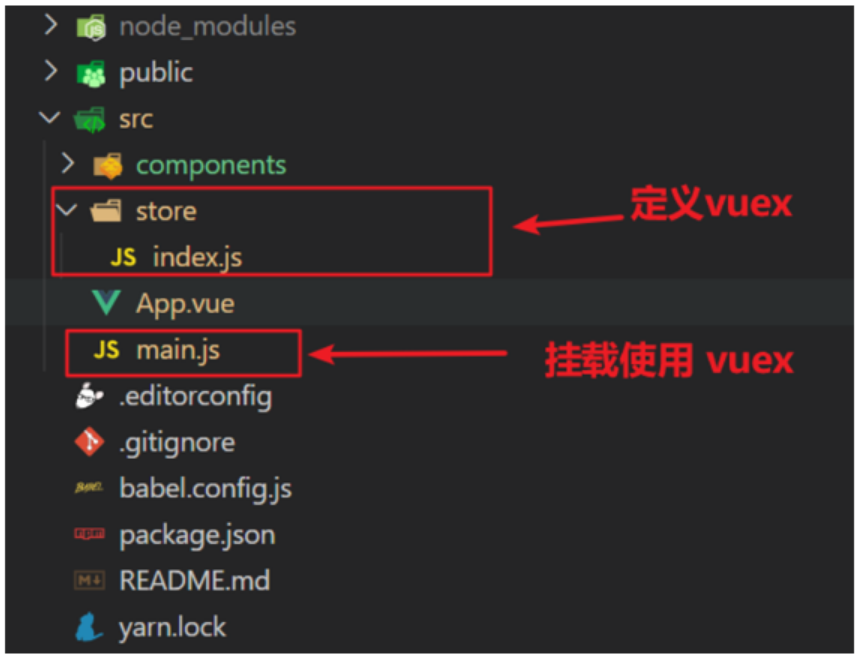
3.在store/index.js里创建仓库
// 导入 vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// vuex也是vue的插件, 需要use一下, 进行插件的安装初始化
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库 store
const store = new Vuex.Store()
// 导出仓库
export default store4.在main.js中导入挂载到Vue实例上
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')5.测试打印Vuex
created(){
console.log(this.$store)
}1.3 state
共享的数据都统一放到了 Store 中的 state 里存储。如果我们想要访问Vuex中的数据,只需访问 state 就可以了。
// 创建仓库 store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// state 状态, 即数据, 类似于vue组件中的data,
// 区别:
// 1.data 是组件自己的数据,
// 2.state 中的数据整个vue项目的组件都能访问到
state: {
count: 101
}
})通过$store访问
//模板中访问
<h1>state的数据 - {{ $store.state.count }}</h1>
//组件逻辑中访问
<h1>state的数据 - {{ count }}</h1>
computed: { //把state中数据,定义在组件内的计算属性中
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
//js文件中访问
import store from "@/store"
console.log(store.state.count)1.4 mapState
上述获取state中的值是有些麻烦的,Vuex提供了辅助函数mapState来简化访问。mapState的作用是帮助我们把store中的数据映射到组件的计算属性中。
1.导入mapState
import { mapState } from 'vuex'2.利用展开运算符将导出的状态映射给计算属性
computed: {
...mapState(['state属性名'])
}1.5 mutations
mutations是一个对象,对象中存放了同步修改state的方法。需要注意的是,提交的参数只能是一个,如果有多个参数要传,可以传递一个对象。
下面是通过mutations修改state数据的步骤。
1.定义mutations
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
// 定义mutations
mutations: {
// 方法里参数 第一个参数是当前store的state属性
// payload 载荷 运输参数 调用mutaiions的时候 可以传递参数 传递载荷
addCount (state, count) {
state.count = count
}
},
})2.使用mutations修改state
this.$store.commit('mutations中的方法名字', 参数)1.6 mapMutations
mapMutations和mapState很像,是用来帮助我们把mutations中的方法映射到组件的methods中。
//导入mapMutations
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapMutations(['addCount'])
}//具体使用
<button @click="addCount">值+1</button>1.7 actions
state是存放数据的,mutations是同步更新数据,actions则负责进行异步操作。
//actions的定义
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
changeCount (state, newCount) {
state.count = newCount
}
}
actions: {
setAsyncCount (context, num) {
// 一秒后, 给一个数, 去修改 num
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCount', num)
}, 1000)
}
},
})//组件中通过dispatch调用
setAsyncCount () {
this.$store.dispatch('setAsyncCount', 666)
}1.8 mapActions
mapActions 是把位于 actions中的方法提取了出来,映射到组件methods中。
//导入mapActions
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapActions(['changeCountAction'])
}//具体使用
<button @click="changeCountAction(200)">+异步</button>1.9 getters
有时我们还需要从state中筛选出符合条件的一些数据,这些数据是依赖state的,此时会用到getters。例如,state中定义了list,为1-10的数组。
组件中,需要显示所有大于5的数据,正常的方式,是需要list在组件中进行再一步的处理,但是getters可以帮助我们实现它。
1.定义getters
getters: {
// getters函数的第一个参数是 state
// 必须要有返回值
filterList: state => state.list.filter(item => item > 5)
}2.使用getters
//原始方式-$store
<div>{{ $store.getters.filterList }}</div>
//辅助函数 - mapGetters
computed: {
...mapGetters(['filterList'])
}
<div>{{ filterList }}</div>1.10 Vuex的严格模式
我们需要明确,vuex 同样遵循单向数据流,组件中不能直接修改仓库的数据。
Vue默认不会监测是否是直接修改的仓库数据,因为监测需要成本。这种情况下就需要开启严格模式,让Vue帮我们检测。下述是开启严格模式的代码。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//开启严格模式
strict: true,
state: {
title: '仓库大标题',
count: 100
}
})2.module
如果把所有的状态都放在state中,当项目变得越来越大的时候,Vuex会变得越来越难以维护。由此,又有了Vuex的模块化。
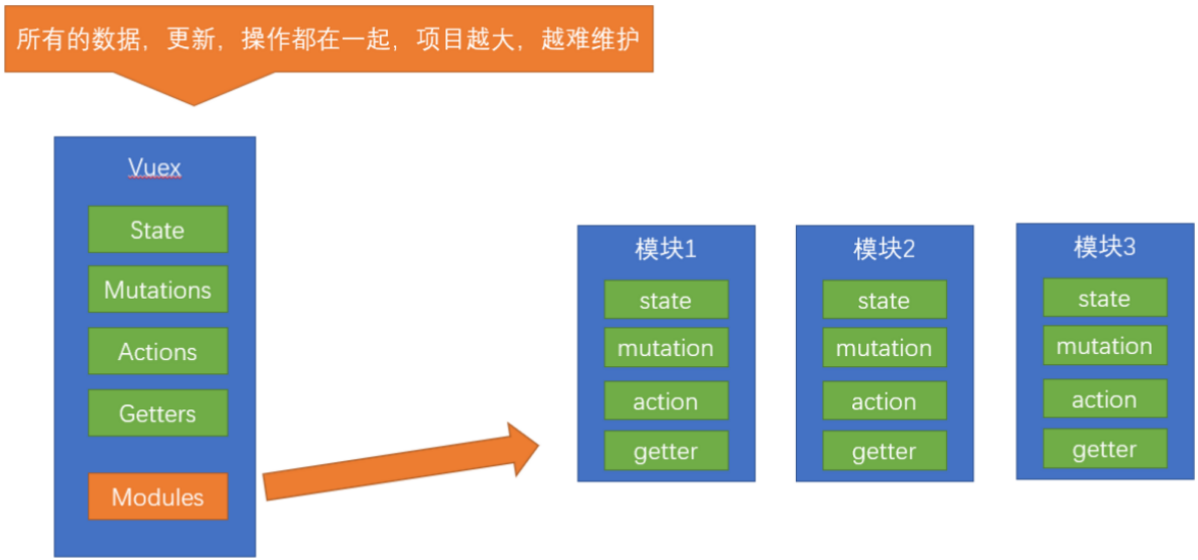
2.1 模块定义
定义两个模块 user 和 setting。
// user模块
const state = {
userInfo: {
name: 'zs',
age: 18
},
score: 80
}
const mutations = {
setUser (state, newUserInfo) {
state.userInfo = newUserInfo
}
}
const actions = {
setUserSecond (context, newUserInfo) {
// 将异步在action中进行封装
setTimeout(() => {
// 调用mutation context上下文,默认提交的就是自己模块的action和mutation
context.commit('setUser', newUserInfo)
}, 1000)
}
}
const getters = {
// 分模块后,state指代子模块的state
UpperCaseName (state) {
return state.userInfo.name.toUpperCase()
}
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
// setting模块
const state = {
theme: 'light', // 主题色
desc: '测试demo'
}
const mutations = {
setTheme (state, newTheme) {
state.theme = newTheme
}
}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}在store/index.js文件中的modules配置项中,注册这两个模块
import user from './modules/user'
import setting from './modules/setting'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
user,
setting
}
})2.2 获取模块的state
$store直接访问
$store.state.user.userInfo.name在mapState辅助函数访问
...mapState('user', ['userInfo']),
...mapState('setting', ['theme', 'desc']),2.3 获取模块内的getters
modules/user.js
const getters = {
// 分模块后,state指代子模块的state
UpperCaseName (state) {
return state.userInfo.name.toUpperCase()
}
}直接访问getters
<!-- 测试访问模块中的getters - 原生 -->
<div>{{ $store.getters['user/UpperCaseName'] }}</div>通过mapGetters访问
computed:{
...mapGetters('user', ['UpperCaseName'])
}2.4 获取模块内的mutations
modules/user.js
const mutations = {
setUser (state, newUserInfo) {
state.userInfo = newUserInfo
}
}modules/setting.js
const mutations = {
setTheme (state, newTheme) {
state.theme = newTheme
}
}Son1.vue
<button @click="updateUser">更新个人信息</button>
<button @click="updateTheme">更新主题色</button>
export default {
methods: {
updateUser () {
// $store.commit('模块名/mutation名', 额外传参)
this.$store.commit('user/setUser', {
name: 'xiaowang',
age: 25
})
},
updateTheme () {
this.$store.commit('setting/setTheme', 'pink')
}
}
}Son2.vue
<button @click="setUser({ name: 'xiaoli', age: 80 })">更新个人信息</button>
<button @click="setTheme('skyblue')">更新主题</button>
methods:{
// 分模块的映射
...mapMutations('setting', ['setTheme']),
...mapMutations('user', ['setUser']),
}2.5 获取模块内的actions
