文献阅读 250104-Overconfidence in climate overshoot
Overconfidence in climate overshoot
来自 <Overconfidence in climate overshoot | Nature>
对气候超调的过度自信
## Key Pts:
- 全球减排努力仍不足以实现《巴黎协定》的温度目标,这意味着需要探究将温度降低至安全水平前暂时超过目标全球变暖限制的超调路径。Although the idealized situation is that allow tem to reach a dangerous peak and deline after that, but the world experience climate overshoot is dirffernet. We need to make a systematic estimation.
- Three type of pathways:
- PD(Peak and Decline pathway): pathway that aim to reduce all GHGs and to realize net-negative CO2 emission
- PD-OS: pathway that set a safe tem. Limit (s.a. 1.5degrees), allow it to be exceeded with high likelihood over the near term in the conviction that warming can be reversed again at a later stage.
- PD-EP (Enhanced Protection pathway) : Stringent and rapid GHG emission reduction as much and as early as possible, achieving net-zero CO2 emissions as soon as possible while minimizing residual emissions, and achieving sustainable levels of net-negative CO2 emissions thereafter in order to potentially reach net-zero or net-negative GHGs.
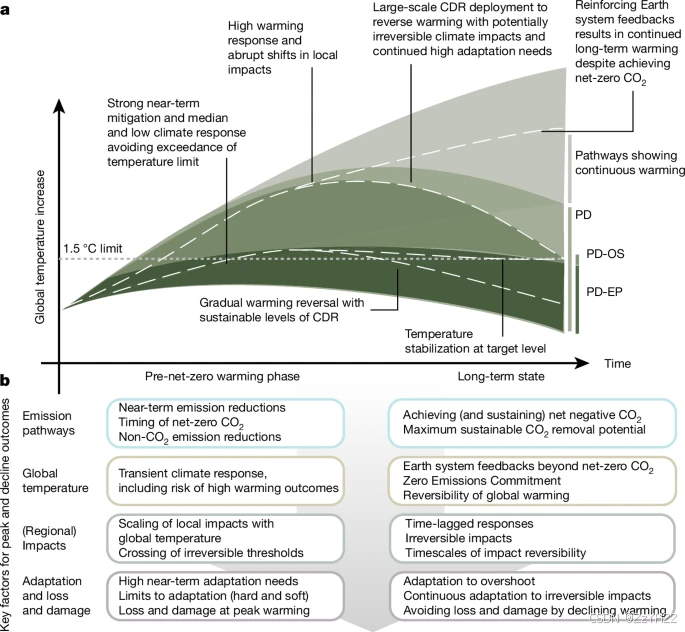
- Uncertain climate response and reversal
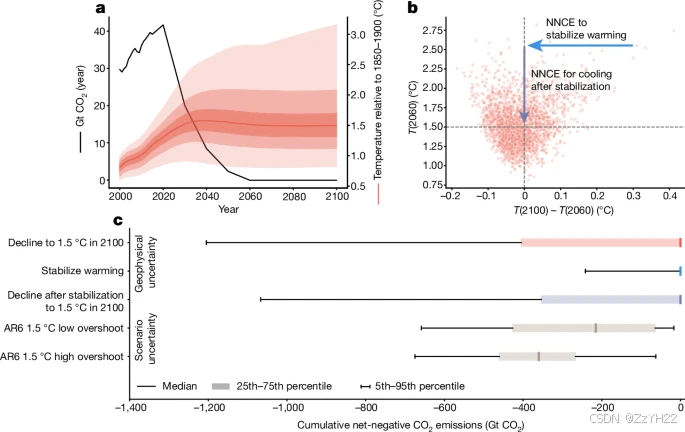
net-negative CO2 emissions (NNCE)
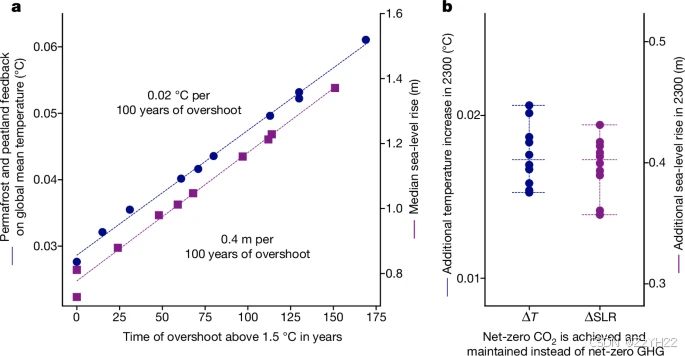
峰值变暖取决于全球二氧化碳净零排放之前的累积二氧化碳排放量和非二氧化碳温室气体减排的严格程度。
对NNCE的大多数估计与峰值和下降路径中变暖的长期逆转一致,侧重于中值变暖结果。然而,为了全面评估超调风险和逆转变暖的NNCE要求,还必须考虑气候反应的不确定性。这些因素包括变暖阶段的不确定性(例如,由于放大变暖反馈而导致的高变暖结果)和长期状态的不确定性(二氧化碳净零排放后持续变暖的可能性以及气候系统对NNCE的响应)。
- Regional climate change reversibility
carbon dioxide removal (CDR)
超调路径的主张是,如果全球变暖从长远来看回到某一水平(即1.5 °C)以下,那么无法将变暖保持在理想的温度极限以下是可以接受的。
Even if global warming is stabilized at a certain level without overshoot, the climate system continues to change as its components keep adjusting and equilibrate30, with implications for regional climate patterns. The question then becomes what additional imprints on regional climate may originate directly from the overshoot.
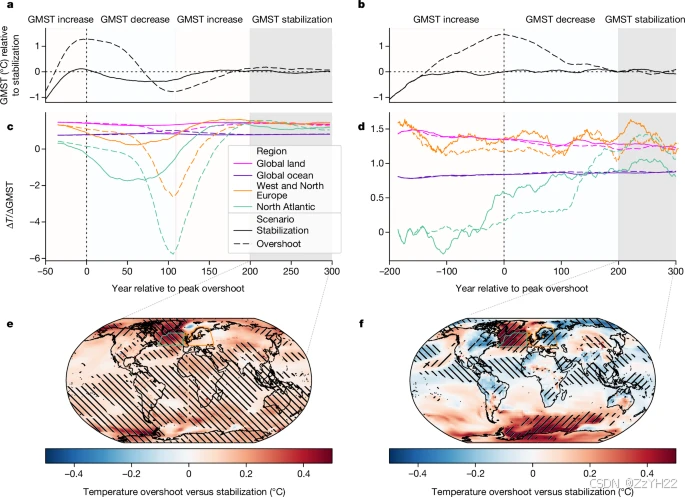
在 NorESM2-LM 模型中,观察到区域温度尺度与超冲下的北大西洋和邻近欧洲陆地区域的全球平均地表空气温度 (GMST) 变化发生逆转,导致暂时的区域降温和随后的区域恢复和变暖.
- Time-lagged and irreversible impacts
For a range of climate impacts, there is no expectation of immediate reversibility after an overshoot. This includes changes in the deep ocean, marine biogeochemistry and species abundance, land-based biomes, carbon stocks and crop yields, but also biodiversity on land36. An overshoot will also increase the probability of triggering potential Earth system tipping elements. Sea levels will continue to rise for centuries to millennia even if long-term temperatures decline.