LeetCode热题100(三十四) —— 23.合并K个升序链表
- 题目描述
- 代码实现
- 思路一:选择排序(199ms)
- 思路二:归并排序(2ms)
- 思路解析
- 你好,我是杨十一,一名热爱健身的程序员
- 在Coding的征程中,不断探索与成长
- LeetCode热题100——刷题记录(不定期更新)
此系列文章用于记录我在学习 LeetCode热题100 过程中的总结和收获
愿与诸君共同探讨,在代码世界里携手共进,攻克难题,提升自我
题目描述
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
提示:
k == lists.length
0 <= k <= 10^4
0 <= lists[i].length <= 500
-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4
lists[i] 按 升序 排列
lists[i].length 的总和不超过 10^4
代码实现
思路一:选择排序(199ms)
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode newTail = newHead;
while (true) {
int index = -1;
int minVal = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {
if (lists[i] != null && lists[i].val < minVal) {
index = i;
minVal = lists[i].val;
}
}
if (index == -1) break;
newTail .next = lists[index];
newTail = newTail .next;
lists[index] = lists[index].next;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}
思路二:归并排序(2ms)
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) return null;
if (lists.length == 1) return lists[0];
int currentLength = lists.length;
while (currentLength != 1) {
int i = 0;
while (i < currentLength / 2) {
lists[i] = merge(lists[i * 2], lists[i * 2 + 1]);
if (i > 0) {
lists[i * 2] = null;
lists[i * 2 + 1] = null;
}
i++;
}
if (currentLength % 2 == 1) {
lists[i] = lists[currentLength - 1];
currentLength = currentLength / 2 + 1;
} else {
currentLength = currentLength / 2;
}
}
return lists[0];
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode nodeA, ListNode nodeB) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode newTail = newHead;
while (nodeA != null && nodeB != null) {
if (nodeA.val < nodeB.val) {
newTail.next = nodeA;
nodeA = nodeA.next;
} else {
newTail.next = nodeB;
nodeB = nodeB.next;
}
newTail = newTail.next;
}
if (nodeA == null) newTail.next = nodeB;
if (nodeB == null) newTail.next = nodeA;
return newHead.next;
}
}
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
思路解析
- 输入:链表头节点的数组
ListNode[] lists - 输出:合并后的有序链表头节点
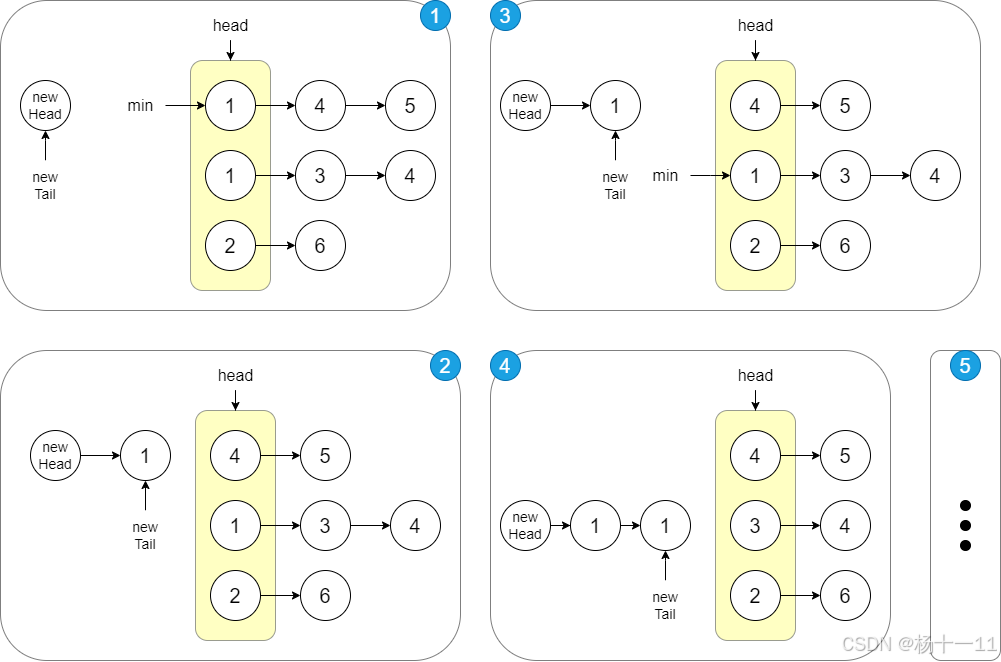
ListNode newHead - 思路一:选择排序
- 遍历所有链表的头节点,将其中最小的添加至有序的
newHead链表中 - 被选中节点的下一个节点作为该链表新的头节点
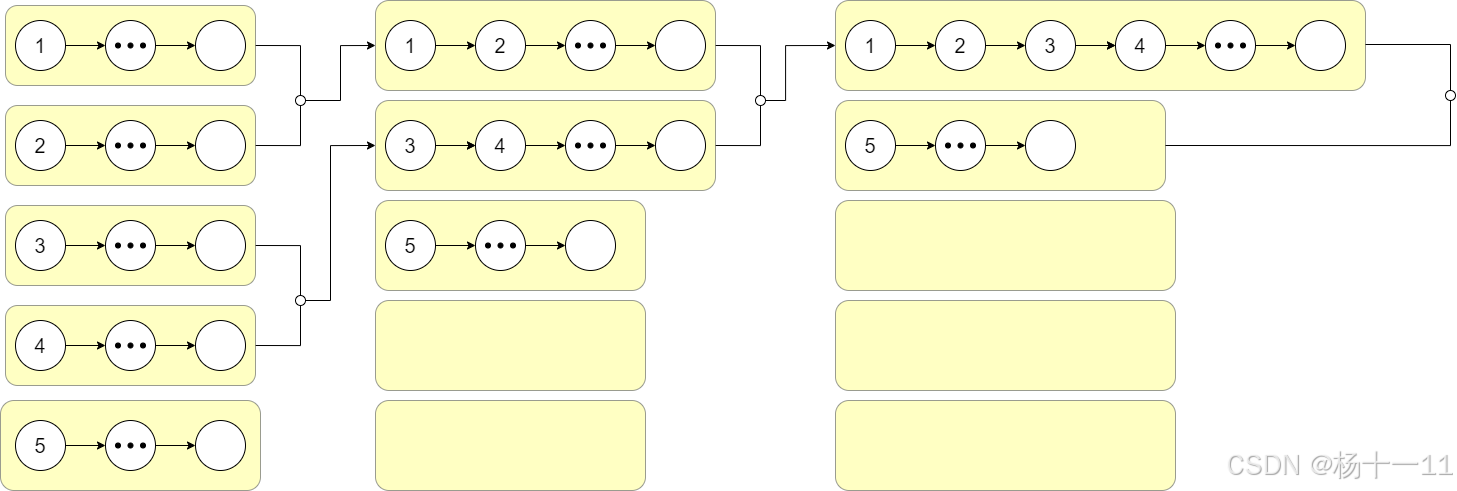
- 思路二:归并排序
- 两两链表进行合并,参考LeetCode热题100(二十七)链表 —— 合并两个有序链表
- 将合并后的结果保存在原数组中,需注意:
- 合并过程中当链表数量为奇数时,最后单个的链表添加至数组末尾
- 你好,我是杨十一,一名热爱健身的程序员
- 在Coding的征程中,不断探索与成长
- LeetCode热题100——刷题记录(不定期更新)
此系列文章用于记录我在学习 LeetCode热题100 过程中的总结和收获
愿与诸君共同探讨,在代码世界里携手共进,攻克难题,提升自我


