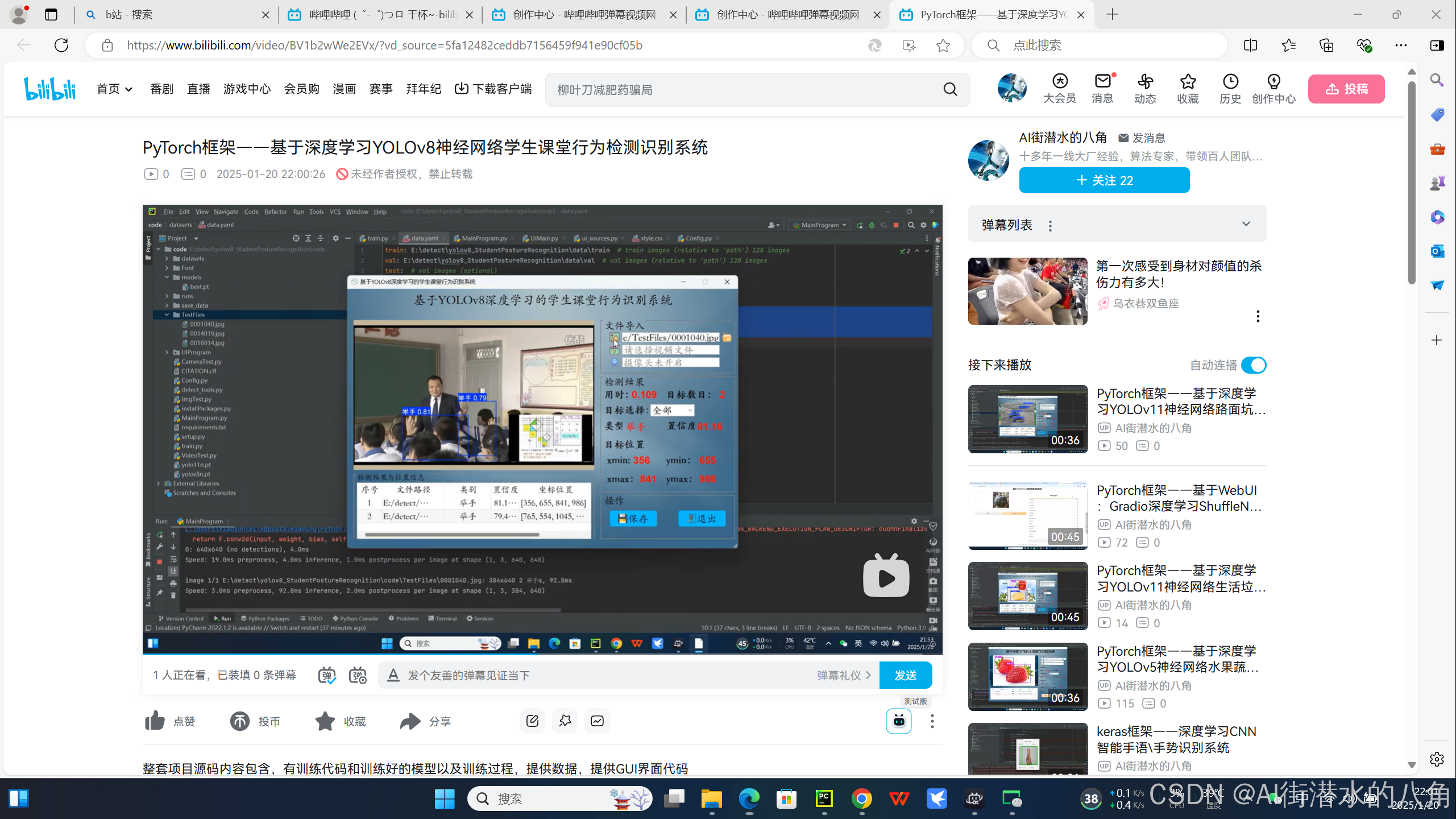
PyTorch框架——基于深度学习YOLOv8神经网络学生课堂行为检测识别系统
基于YOLOv8深度学习的学生课堂行为检测识别系统,其能识别三种学生课堂行为:names: ['举手', '读书', '写字']
具体图片见如下:

第一步:YOLOv8介绍
YOLOv8 是 ultralytics 公司在 2023 年 1月 10 号开源的 YOLOv5 的下一个重大更新版本,目前支持图像分类、物体检测和实例分割任务,在还没有开源时就收到了用户的广泛关注。
YOLOv8 算法的核心特性和改动可以归结为如下:
提供了一个全新的 SOTA 模型,包括 P5 640 和 P6 1280 分辨率的目标检测网络和基于 YOLACT 的实例分割模型。和 YOLOv5 一样,基于缩放系数也提供了 N/S/M/L/X 尺度的不同大小模型,用于满足不同场景需求
Backbone:
骨干网络和 Neck 部分可能参考了 YOLOv7 ELAN 设计思想,将 YOLOv5 的 C3 结构换成了梯度流更丰富的 C2f 结构,并对不同尺度模型调整了不同的通道数。
属于对模型结构精心微调,不再是无脑一套参数应用所有模型,大幅提升了模型性能。不过这个 C2f 模块中存在 Split 等操作对特定硬件部署没有之前那么友好了
Head: Head部分较yolov5而言有两大改进:1)换成了目前主流的解耦头结构(Decoupled-Head),将分类和检测头分离 2)同时也从 Anchor-Based 换成了 Anchor-Free
Loss :1) YOLOv8抛弃了以往的IOU匹配或者单边比例的分配方式,而是使用了Task-Aligned Assigner正负样本匹配方式。2)并引入了 Distribution Focal Loss(DFL)
Train:训练的数据增强部分引入了 YOLOX 中的最后 10 epoch 关闭 Mosiac 增强的操作,可以有效地提升精度
第二步:YOLOv8网络结构

第三步:代码展示
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
from pathlib import Path
from ultralytics.engine.model import Model
from ultralytics.models import yolo
from ultralytics.nn.tasks import ClassificationModel, DetectionModel, OBBModel, PoseModel, SegmentationModel, WorldModel
from ultralytics.utils import ROOT, yaml_load
class YOLO(Model):
"""YOLO (You Only Look Once) object detection model."""
def __init__(self, model="yolo11n.pt", task=None, verbose=False):
"""Initialize YOLO model, switching to YOLOWorld if model filename contains '-world'."""
path = Path(model)
if "-world" in path.stem and path.suffix in {".pt", ".yaml", ".yml"}: # if YOLOWorld PyTorch model
new_instance = YOLOWorld(path, verbose=verbose)
self.__class__ = type(new_instance)
self.__dict__ = new_instance.__dict__
else:
# Continue with default YOLO initialization
super().__init__(model=model, task=task, verbose=verbose)
@property
def task_map(self):
"""Map head to model, trainer, validator, and predictor classes."""
return {
"classify": {
"model": ClassificationModel,
"trainer": yolo.classify.ClassificationTrainer,
"validator": yolo.classify.ClassificationValidator,
"predictor": yolo.classify.ClassificationPredictor,
},
"detect": {
"model": DetectionModel,
"trainer": yolo.detect.DetectionTrainer,
"validator": yolo.detect.DetectionValidator,
"predictor": yolo.detect.DetectionPredictor,
},
"segment": {
"model": SegmentationModel,
"trainer": yolo.segment.SegmentationTrainer,
"validator": yolo.segment.SegmentationValidator,
"predictor": yolo.segment.SegmentationPredictor,
},
"pose": {
"model": PoseModel,
"trainer": yolo.pose.PoseTrainer,
"validator": yolo.pose.PoseValidator,
"predictor": yolo.pose.PosePredictor,
},
"obb": {
"model": OBBModel,
"trainer": yolo.obb.OBBTrainer,
"validator": yolo.obb.OBBValidator,
"predictor": yolo.obb.OBBPredictor,
},
}
class YOLOWorld(Model):
"""YOLO-World object detection model."""
def __init__(self, model="yolov8s-world.pt", verbose=False) -> None:
"""
Initialize YOLOv8-World model with a pre-trained model file.
Loads a YOLOv8-World model for object detection. If no custom class names are provided, it assigns default
COCO class names.
Args:
model (str | Path): Path to the pre-trained model file. Supports *.pt and *.yaml formats.
verbose (bool): If True, prints additional information during initialization.
"""
super().__init__(model=model, task="detect", verbose=verbose)
# Assign default COCO class names when there are no custom names
if not hasattr(self.model, "names"):
self.model.names = yaml_load(ROOT / "cfg/datasets/coco8.yaml").get("names")
@property
def task_map(self):
"""Map head to model, validator, and predictor classes."""
return {
"detect": {
"model": WorldModel,
"validator": yolo.detect.DetectionValidator,
"predictor": yolo.detect.DetectionPredictor,
"trainer": yolo.world.WorldTrainer,
}
}
def set_classes(self, classes):
"""
Set classes.
Args:
classes (List(str)): A list of categories i.e. ["person"].
"""
self.model.set_classes(classes)
# Remove background if it's given
background = " "
if background in classes:
classes.remove(background)
self.model.names = classes
# Reset method class names
# self.predictor = None # reset predictor otherwise old names remain
if self.predictor:
self.predictor.model.names = classes
第四步:统计训练过程的一些指标,相关指标都有

第五步:运行(支持图片、文件夹、摄像头和视频功能)




第六步:整个工程的内容
有训练代码和训练好的模型以及训练过程,提供数据,提供GUI界面代码

项目完整文件下载请见演示与介绍视频的简介处给出:➷➷➷
PyTorch框架——基于深度学习YOLOv8神经网络学生课堂行为检测识别系统_哔哩哔哩_bilibili