MySQL存储过程和存储函数_mysql 存储过 call proc_stat_data(3,null)
2)很难调试存储过程。只有少数数据库管理系统允许调试存储过程。不幸的是,MySQL不提供调试存储过程的功能。
1.2 数据准备
- 创建数据库:
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8;
use test;
这里记得设置编码!
- 创建测试表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `class`;
CREATE TABLE `class` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO\_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO\_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `class`(`id`,`name`) values
(1,'Java'),
(2,'UI'),
(3,'产品');
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO\_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`class\_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO\_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/\*Data for the table `student` \*/
insert into `student`(`id`,`name`,`class\_id`) values
(1,'张三',1),
(2,'李四',1),
(3,'王五',2),
(4,'赵刘',1),
(5,'钱七',3);
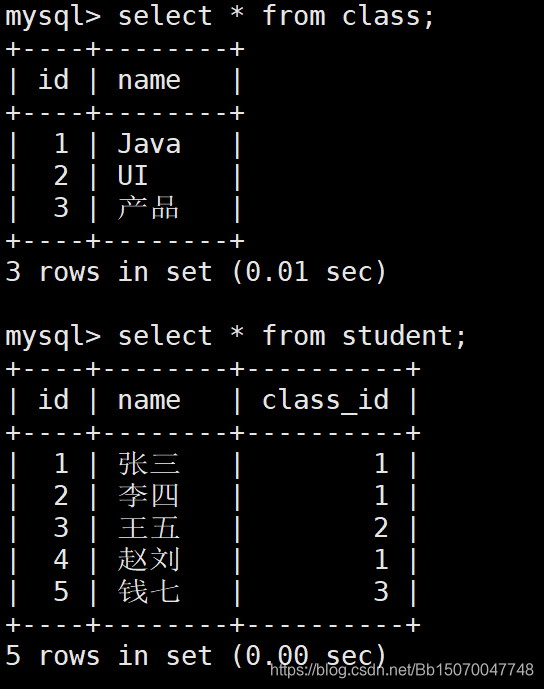
- 查询数据:
select \* from class;
select \* from student;
1.3 存储过程的使用
- 语法
CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_name ([parameters[,...]])
begin
-- SQL语句
end ;
- 示例
create procedure test1()
begin
select 'Hello';
end;
- 调用存储过程
call test1();

- 查看存储过程
-- 查看db01数据库中的所有存储过程
select name from mysql.proc where db='test';
-- 查看存储过程的状态信息
show procedure status;
-- 查看存储过程的创建语句
show create procedure test1;
- 删除存储过程
drop procedure test1;
1.2 存储过程的语法
1.2.1 变量
- declare:声明变量
CREATE PROCEDURE test2 ()
begin
declare num int default 0; -- 声明变量,赋默认值为0
select num+10;
end ;
call test2(); -- 调用存储过程

- set:赋值操作
CREATE PROCEDURE test3 ()
begin
declare num int default 0;
set num =20; -- 给num变量赋值
select num;
end ;
call test3();

- into:赋值
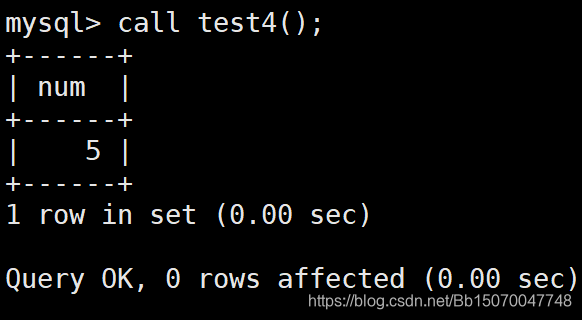
CREATE PROCEDURE test4 ()
begin
declare num int default 0;
select count(1) into num from student;
select num;
end ;
call test4();
1.2.2 if语句
- 需求:根据class_id判断是Java还是UI还是产品
CREATE PROCEDURE test5 ()
begin
declare id int default 1;
declare class_name varchar(30);
if id=1 then
set class_name='哇塞,Java大佬!';
elseif id=2 then
set class_name='原来是UI的啊';
else
set class_name='不用想了,肯定是产品小样';
end if;
select class_name;
end ;
call test5();

1.2.3 传递参数
- 语法:
create procedure procedure_name([in/out/inout] 参数名 参数类型)
- in:该参数可以作为输入,也就是需要调用方传入值 , 默认
- out:该参数作为输出,也就是该参数可以作为返回值
- inout:既可以作为输入参数,也可以作为输出参数
1.2.3.1 in-输入参数
-- 定义一个输入参数
CREATE PROCEDURE test6 (in id int)
begin
declare class_name varchar(30);
if id=1 then
set class_name='哇塞,Java大佬!';
elseif id=2 then
set class_name='原来是UI的啊';
else
set class_name='不用想了,肯定是产品小样';
end if;
select class_name;
end ;
call test6(3);

1.2.3.2 out-输出参数
-- 定义一个输入参数和一个输出参数
CREATE PROCEDURE test7 (in id int,out class_name varchar(100))
begin
if id=1 then
set class_name='哇塞,Java大佬!';
elseif id=2 then
set class_name='原来是UI的啊';
else
set class_name='不用想了,肯定是产品小样';
end if;
end ;
call test7(1,@class\_name); -- 创建会话变量
select @class\_name; -- 引用会话变量

@xxx:代表定义一个会话变量,整个会话都可以使用,当会话关闭(连接断开)时销毁
@@xxx:代表定义一个系统变量,永久生效。
1.2.4 case语句
- 需求:传递一个月份值,返回所在的季节。
CREATE PROCEDURE test8 (in month int,out season varchar(10))
begin
case
when month >=1 and month<=3 then
set season='spring';
when month >=4 and month<=6 then
set season='summer';
when month >=7 and month<=9 then
set season='autumn';
when month >=10 and month<=12 then
set season='winter';
end case;
end ;
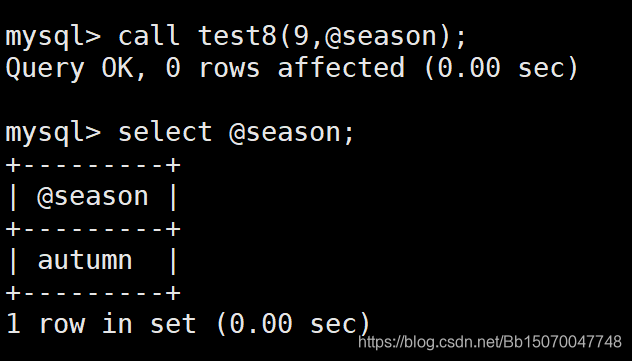
call test8(9,@season); -- 定义会话变量来接收test8存储过程返回的值
select @season;
1.3.5 while循环
- 需求:计算任意数的累加和
CREATE PROCEDURE test10 (in count int)
begin
declare total int default 0;
declare i int default 1;
while i<=count do
set total=total+i;
set i=i+1;
end while;
select total;
end ;
call test10(10);

1.3.6 repeat循环
- 需求:计算任意数的累加和
CREATE PROCEDURE test11 (count int) -- 默认是输入(in)参数
begin
declare total int default 0;
repeat
set total=total+count;
set count=count-1;
until count=0 -- 结束条件,注意不要打分号
end repeat;
select total;
end ;
call test11(10);

1.3.7 loop循环
- 需求:计算任意数的累加和
CREATE PROCEDURE test12 (count int) -- 默认是输入(in)参数
begin
declare total int default 0;
sum:loop -- 定义循环标识
set total=total+count;
set count=count-1;
if count < 1 then
leave sum; -- 跳出循环
end if;
end loop sum; -- 标识循环结束
select total;
end ;
call test12(10);

1.3.8 游标
游标是用来存储查询结果集的数据类型,可以帮我们保存多条行记录结果,我们要做的操作就是读取游标中的数据获取每一行的数据。
- 声明游标
declare cursor_name cursor for statement;
- 打开游标
open cursor_name;
- 关闭游标
close cursor_name;
- 案例:
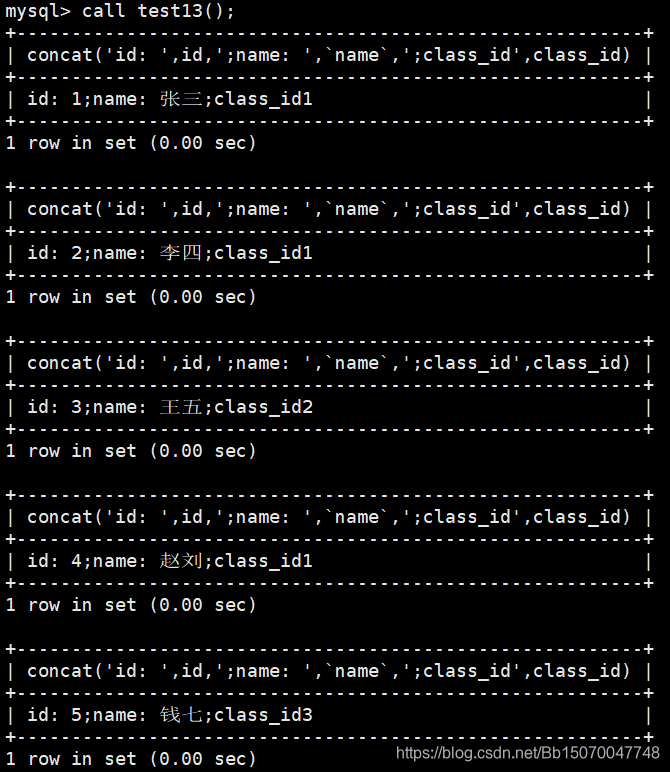
CREATE PROCEDURE test13 () -- 默认是输入(in)参数
begin
declare id int(11);
declare `name` varchar(20);
declare class_id int(11);
-- 定义游标结束标识符
declare has_data int default 1;
declare stu_result cursor for select \* from student;
-- 监测游标结束
declare exit handler for not FOUND set has_data=0;
-- 打开游标
open stu_result;
repeat
fetch stu_result into id,`name`,class_id;
select concat('id: ',id,';name: ',`name`,';class\_id',class_id);
until has_data=0 -- 退出条件,注意不要打分号
end repeat;
-- 关闭游标
close stu_result;
end ;
call test13();
1.3 存储过程和存储函数的区别
- 存储函数的限制比较多,例如不能用临时表,只能用表变量,而存储过程的限制较少,存储过程的实现功能要复杂些,而函数的实现功能针对性比较强。
- 返回值不同。存储函数必须有返回值,且仅返回一个结果值;存储过程可以没有返回值,但是能返回结果集(out,inout)。
- 调用时的不同。存储函数嵌入在SQL中使用,可以在select 存储函数名(变量值);存储过程通过call语句调用 call 存储过程名。
- 参数的不同。存储函数的参数类型类似于IN参数,没有类似于
OUT和INOUT的参数。存储过程的参数类型有三种,in、out和inout:- in:数据只是从外部传入内部使用(值传递),可以是数值也可以是变量
- out:只允许过程内部使用(不用外部数据),给外部使用的(引用传递:外部的数据会被先清空才会进入到内部),只能是变量
- inout:外部可以在内部使用,内部修改的也可以给外部使用,典型的引用 传递,只能传递变量。
1.3.1 临时表
临时表顾名思义就是临时要用创建的表,临时表的作用仅限于本次会话,等连接关闭后重新打开连接临时表将不存在
- 创建一张临时表:
create temporary table temp_table(
id int,
name varchar(10)
);
insert into temp_table values (1,'1');
select \* from temp_table ;
temporary:代表创建的表是一张临时表;
- 注意:临时表示查询不到的
show tables; -- 不会显示临时表的存在
- 测试存储过程创建临时表:
create procedure pro1()
begin
create temporary table temp_table(
id int
);
insert into temp_table values(1);
select \* from temp_table;
end;
