代码随想录-基础篇
数组
二分法
-
[left,right] 左闭右闭
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> /*左闭右闭需要注意的问题 1. 总的搜索区间[0,numsize] binary_search(0, 4-1, arr, 2); 注意这里的4-1 2.while (left < right)循环条件没有等号 3. 区间左移右移时: right和left都不包含边界 */ int binary_search(int left, int right, int *arr, int target) { int middle = (left + right) / 2; while (left <= right) { middle = (left + right) / 2; if (*(arr + middle) < target) left = middle + 1; // 注意这里是+1,不包括right,因为if条件中判断已经说*(arr + middle) != target else if (*(arr + middle) > target) right = middle - 1; else return middle; } return -1; } int main() { int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4}; int pos = binary_search(0, 4 - 1, arr, 2); // 注意这里是左闭右闭 [] printf("%d\n", pos); return 0; }
-
-
[left,right)
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> /*左闭右开需要注意的问题 1. 总的搜索区间[0,numsize] binary_search(0, 4, arr, 2); 注意这里的4 2.while (left < right)循环条件没有等号 3. 区间左移时: right = middle; // 不包含右边界 */ int binary_search(int left, int right, int *arr, int target) { int middle = (left + right) / 2; while (left < right) { middle = (left + right) / 2; if (*(arr + middle) < target) left = middle + 1; // 包含左边界 else if (*(arr + middle) > target) right = middle; // 不包含右边界 else return middle; } return -1; } int main() { int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4}; int pos = binary_search(0, 4, arr, 2); // 注意这里是左闭右闭 [) printf("%d\n", pos); return 0; }
-
移除元素
-
暴力解法(O(n^2))
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> int removeElement(int *nums, int numsSize, int val) { for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) { if (*(nums + i) == val) { int j = i; while (j < numsSize - 1) { *(nums + j) = *(nums + j + 1); j++; } numsSize--; --i; // 万一遇到两个连续相等的val,需要在原来的位置再比较一下 } } return numsSize; } int main() { int arr[] = {0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 0, 4, 2}; int numsSize = removeElement(arr, 8, 2); printf("%d\n", numsSize); for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) printf("%d,", arr[i]); return 0; }
-
-
双指针解法(O(n))
-
思路:在一个数组上定义两个指针,一个是指向“新”数组的指针,一个是指向“旧”数组的指针。
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <math.h> int removeElement(int *nums, int numsSize, int val) { // 双指针解法 int *pNew = nums, *pOld = nums; int numNew = 0; while (pOld != (nums + numsSize)) { if (*pOld != val) { numNew++; *pNew++ = *pOld++; } else pOld++; } return numNew; } int main() { int arr[] = {0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 0, 4, 2}; int numsSize = removeElement(arr, 8, 2); printf("%d\n", numsSize); for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) printf("%d,", arr[i]); return 0; }
-
有序数组的平方
-
先平方在冒泡排序
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // 给你一个按 非递减顺序 排序的整数数组 nums,返回 每个数字的平方 组成的新数组,要求也按 非递减顺序 排序。 /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ int *sortedSquares(int *nums, int numsSize, int *returnSize) { int *array = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * numsSize); for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) array[i] = nums[i] * nums[i]; for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < numsSize - i - 1; j++) { if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) { int tmp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[j + 1]; nums[j + 1] = tmp; } } } *returnSize = numsSize; return array; } main() { int nums[] = {-7, -3, 2, 3, 11}; int numsSize = 0; sortedSquares(nums, 5, &numsSize); for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) { printf("%d ", nums[i]); } putchar('\n'); return 0; }
-
-
双指针法
-
首先原数组是递增排列,其中可能具有负数。而平方最大的值只可能出现在左右两边。所以,使用两个指针分别从前和从后向中间扫描,找到最大的值放到新数组的后面(新的数组是从后往前依次存放)
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // 给你一个按 非递减顺序 排序的整数数组 nums,返回 每个数字的平方 组成的新数组,要求也按 非递减顺序 排序。 /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ int *sortedSquares(int *nums, int numsSize, int *returnSize) { int head = 0, tail = numsSize - 1, newI = numsSize - 1; int *array = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * numsSize); while (newI >= 0) { if (nums[head] * nums[head] > nums[tail] * nums[tail]) // 找到最大的放 { array[newI] = nums[head] * nums[head]; head++; newI--; } else { array[newI] = nums[tail] * nums[tail]; tail--; newI--; } } *returnSize = numsSize; return array; } main() { int nums[] = {-7, -3, 2, 3, 11}; int numsSize = 0; int *array = sortedSquares(nums, 5, &numsSize); for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) { printf("%d ", array[i]); } putchar('\n'); return 0; }
-
长度最小的子数组

-
注意子数组:
-
子数组 是数组中连续的 非空 元素序列。
-
当不是子数组,只选取数组的元素即可,首先需要明白的是选择的一定较大的数,可以使用贪心法,利用冒泡排序。 ==== Error
-
int minSubArrayLen(int target, int *nums, int numsSize) { int j = 0, sum = 0, count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) { for (j = 0; j < numsSize - i - 1; j++) { if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) { int tmp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[j + 1]; nums[j + 1] = tmp; } } sum += nums[j]; count++; printf("j = %d,nums[j] = %d, sum = %d,\n", j, nums[j], sum); if (sum >= target) return count; } return 0; } main() { int nums[] = {12, 28, 83, 4, 25, 26, 25, 2, 25, 25, 25, 12}; int numsSize = 0; int min = minSubArrayLen(213, nums, sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0])); printf("%d,\n", min); putchar('\n'); return 0; }
-
-
-
-
暴力法O(n^2)
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int minSubArrayLen(int target, int *nums, int numsSize) { int min = numsSize, flag = 0; for (int num = 1; num <= numsSize; num++) // 遍历可能的元素数量 { for (int begins = 0; begins < numsSize; begins++) // 遍历可能的元素起点 { int sum = 0, count = 0, begin = begins; while (count != num && begin < numsSize) // 从该起点开始计算序列之和 { sum += nums[begin++]; count++; if (sum >= target && min > count) { min = count; flag = 1; } } } } if (flag) return min; return 0; } main() { int nums[] = {2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3}; int numsSize = 0; int min = minSubArrayLen(7, nums, sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0])); printf("%d,\n", min); putchar('\n'); return 0; }
-
-
双指针法
-
首先定义两个指针,都是从0开始,这两个指针包围的范围就是,首先是尾指针先移动,直到找到大于sum的集合,然后开始循环头指针,找到满足要求最小的集合元素。
-
int minSubArrayLen(int target, int *nums, int numsSize) { int headP = 0, tailP = 0, sum = 0, min = target, flag = 0; for (; tailP < numsSize; tailP++) { sum += nums[tailP]; while (sum >= target) { int tmp = tailP - headP + 1; flag = 1; if (tmp < min) min = tmp; sum -= nums[headP++]; } } if (flag) return min; return 0; }
-
链表
反转链表
头插法
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
};
struct ListNode *reverseList(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode *head1 = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head1->next = NULL;
struct ListNode *p1 = head;
if (head == NULL) // 空链表
return head;
struct ListNode *p2;
while (p1)
{
// 拿到一个新元素p1 使用头插法
p2 = p1->next;
p1->next = head1->next;
head1->next = p1;
p1 = p2;
}
}
双指针法

struct ListNode *reverseList(struct ListNode *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return head;
// 双指针法
struct ListNode *pre = NULL, *cur =head , *tmp;
while (cur)
{
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
head = pre;
return head;
}
递归法
由双指针->递归
struct ListNode *reverse(struct ListNode *pre, struct ListNode *cur)
{
if (cur == NULL)
return pre;
struct ListNode *tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
return reverse(cur, tmp); // 这里为什么return
}
struct ListNode *reverseList(struct ListNode *head)
{
return reverse(NULL, head);
}
两两交换链表中的结点

双指针法
直接交换数值(测试可以通过,但是交换的是值,应该交换物理节点)
#include <stdio.h>
struct ListNode *swapPairs(struct ListNode *head)
{
// 遇到空结点
if (!head)
return head;
// 遇到只有一个结点
if (!head->next)
return head;
// 双指针法
struct ListNode *pre = head, *cur = head->next;
int tmp;
while (cur != NULL)
{
// 交换两个头结点的值
tmp = pre->val;
pre->val = cur->val;
cur->val = tmp;
// 两个指针向后移动
pre = cur->next;
if (pre)
cur = pre->next;
else
cur = NULL;
}
return head;
}
真正交换物理节点:
需要仔细考虑,两两交换之后,这前后两个组合如何保存的问题

#include <stdio.h>
// #include <stdlib.h>
struct ListNode *swapPairs(struct ListNode *head)
{
// 遇到空结点
if (!head)
return head;
// 遇到只有一个结点
if (!head->next)
return head;
// 双指针法
struct ListNode *pre = head, *cur = head->next, *tmp;
int flag = 0;
head = head->next; // head指向第二个节点
struct ListNode *p1 = NULL;
while (cur != NULL)
{
// 交换两个头结点的值
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre->next = tmp;
// 两个指针向后移动
if (p1 != NULL)
{
p1->next = cur;
p1 = pre;
}
else
{
p1 = pre;
}
pre = pre->next;
if (pre)
cur = pre->next;
else
cur = NULL;
}
return head;
}
通过引入头结点

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct ListNode LL;
struct ListNode *swapPairs(struct ListNode *head)
{
// 遇到空结点
if (!head)
return head;
// 遇到只有一个结点
if (!head->next)
return head;
// 双指针法
struct ListNode *pre = head, *cur = head->next, *dumpHead = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(LL));
dumpHead->next = head;
struct ListNode *p1 = dumpHead, *tmp = NULL;
while (cur != NULL)
{
p1->next = cur;
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre->next = tmp;
p1 = pre;
pre = pre->next;
if (pre)
cur = pre->next;
else
cur = NULL;
}
head = dumpHead->next;
free(dumpHead);
return head;
}
删除第n个元素
-
先统计指针长度,然后在从头遍历,删除元素
-
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> typedef struct ListNode LL; struct ListNode *removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode *head, int n) { if (!head) return head; // 删除倒数第n个节点 // 创建头节点 struct ListNode *dumpyhead = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(LL)); dumpyhead->next = head; int len = 0; struct ListNode *p = dumpyhead->next; while (p) { len++; p = p->next; } // 需要删除第len-n+1 int deleteNum = len - n + 1; p = dumpyhead; struct ListNode *p2 = p->next; while (--deleteNum) { p = p2; p2 = p2->next; } p->next = p2->next; if (p2 == head) head = NULL; free(p2); return head; }
-
快慢指针
-
定义快指针fast和慢指针slow,先让快指针移动n步,再移动慢指针。直到快指针到达空。这样慢指针就指向要删除的倒数第n个节点了
- 原理:固定快慢指针的间隔为n,然后两个同时移动,快的到达末尾了,慢就指向要删除的指针了
-
因为在链表中删除节点,需要直到要删除节点的前一个结点。所以,需要快指针先移动n+1步
-
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> typedef struct ListNode LL; struct ListNode *removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode *head, int n) { if (!head) return head; // 删除倒数第n个节点 // 创建头节点 struct ListNode *dumpyhead = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(LL)); dumpyhead->next = head; struct ListNode *fast, *slow; fast = dumpyhead; slow = dumpyhead; n++; while (fast != NULL) { if (n <= 0) slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; n--; } struct ListNode *tmp = slow->next; if (slow->next == head) head = NULL; slow->next = slow->next->next; free(tmp); return head; }
-
判断链表中是否有环并且环的位置

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
};
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode *fast = head; // 每次走两步
struct ListNode *slow = head; // 每次走一步
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow)
{
// 此时说明链表中有环
struct ListNode *index1 = fast;
struct ListNode *index2 = slow;
while (index1 != index2)
{
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index1; // 返回环开始的位置
}
}
return false;
}
哈希表
哈希问题的三个结构
-
set
-
map
-
数组
想到哈希解法的条件反射
- 判断一个数在一个集合中是否出现,
有效的字母异位词

-
暴力法
-
/* s中的所有字符都可以在t最终找到 t中的所有字母都可以在s中找到 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> bool Anagram(char *s, char *t) { int flag; char *p; while (*s != '\0') { flag = 0; p = t; while (*p != '\0') { if (*p == *s) { flag = 1; break; } p++; } if (!flag) // flag!=1 // 在t中没有找到*s的 break; s++; } if (*s == '\0') return true; else return false; } bool isAnagram(char *s, char *t) { return Anagram(s, t) && Anagram(t, s); }
-
-
哈希表法
-
字母全都是小写字母
// 使用数组作为hash , 数组中的26个元素分别对应,26个小写字母。= bool isAnagram(char *s, char *t) { // a -》 97 // 下标为0表示a出现的次数 int hash_letter[26] = {0}; while (*s != '\0') hash_letter[*s++ - 'a']++; while (*t != '\0') hash_letter[*t++ - 'a']--; for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) if (hash_letter[i] != 0) return false; return true; }
-
两个数组的交集

-
哈希表
-
/* 通过自己构造的数组:建立一个哈希表 */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef struct Leecodes { int data; int count1; int count2; } Leecode; /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ int *intersection(int *nums1, int nums1Size, int *nums2, int nums2Size, int *returnSize) { int count = nums1Size + nums2Size; Leecode *p = (Leecode *)malloc(sizeof(Leecode) * count); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { p[i].data = -1; p[i].count1 = -1; p[i].count2 = -1; } for (int i = 0; i < nums1Size; i++) { int j = 0; while (j < count) { if (nums1[i] == p[j].data) // 这个数在p[j]中已经存在 { p[j].count1++; break; } else if (p[j].data == -1) // 这个数在p[j]中不存在 { p[j].data = nums1[i]; p[j].count1 = 1; break; } j++; } } for (int i = 0; i < nums2Size; i++) { int j = 0; while (j < count) { if (nums2[i] == p[j].data) // 这个数在p[j]中已经存在 { p[j].count2++; break; } else if (p[j].data == -1) // 这个数在p[j]中不存在 { p[j].data = nums2[i]; p[j].count2 = 1; break; } j++; } } *returnSize = 0; int *res = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * count); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (p[i].count1 != -1 && p[i].count2 != -1) { res[*returnSize] = p[i].data; (*returnSize)++; } } return res; }
-
-
使用STL中的
unorder_set-
class Solution { public: vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { unordered_set<int> result_set; // 存放结果,之所以用set是为了给结果集去重 unordered_set<int> nums_set(nums1.begin(), nums1.end()); for (int num : nums2) { // 发现nums2的元素 在nums_set里又出现过 if (nums_set.find(num) != nums_set.end()) { result_set.insert(num); } } return vector<int>(result_set.begin(), result_set.end()); } }; -

-
两数之和

-
暴力解法
-
class Solution { public: vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { //vector类型为长度可变的数组,更灵活。需要#include<vector> vector<int> a; for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++) { for(int j =i+1;j<nums.size();j++) { if(nums[i]+nums[j] == target) { //在a的最后添加元素 a.push_back(i); a.push_back(j); break; } } } return a; } };
-
哈希法
将已经遍历的元素全部存入unordered_multimap中,每遍历一个元素,就查找target-元素是否存在于已经遍历的元素中。如存在则返回
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
/*
1. 三个map之间的区别
2. map类的find的原理
3. map类的迭代器
4. map类的插入方法
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
/*
key:元素
value: 下标
遍历每个元素并存入map中,以元素值作为key,以下标作为value
然后在遍历的同时看map中的key是否存在target-当前元素
*/
unordered_multimap<int, int> res;
unordered_multimap<int, int>::iterator it;
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size();i++)
{
// unordered_multimap的find方法,是根据key查找的,如果找不到就返回end()
if((it=res.find(target-nums[i]))!=res.end()) // 已经遍历的元素中存在target-nums[i]
{
result.push_back(it->second); // map类型的迭代器的方法 key:first() value:second()
result.push_back(i);
break;
}
res.insert({nums[i], i}); // unordered_multimap没有下标操作。 需要{}
}
return result;
}
};
四数相加
暴力解法

-
class Solution { public: int fourSumCount(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, vector<int>& nums3, vector<int>& nums4) { // 暴力解法 int zreo_count = 0; for(int n1:nums1){ for(int n2:nums2){ for(int n3:nums3){ for(int n4:nums4){ if(n1+n2+n3+n4==0) zreo_count++; } } } } return zreo_count; } };
哈希解法
-
分别求出前两个数组和后两个数组,得到两个数组。然后可以利用两数之和的哈希法进行求解
-
利用数组的解法(其实这样是不合适的)
-
class Solution { public: int fourSumCount(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, vector<int>& nums3, vector<int>& nums4) { // 暴力解法 int zreo_count = 0; vector<int> add1; vector<int> add2; for(int n1:nums1) for(int n2:nums2) add1.push_back(n1 + n2); for(int n1:nums3) for(int n2:nums4) add2.push_back(n1 + n2); for(int n1:add1) { for(int n2:add2 ) { if(n2==-n1) zreo_count++; } } return zreo_count; } };
-
-
三数之和

暴力解法
-
注意这刚开始插入的选择的multiset而不是vector,因为{1,2,3}和{3,2,1}在vector<vector>属于不同的元素,所以在使用find中会被认为是不同的元素,而multiset不同
-
multiset<multiset<int>> mul{{1,2,3}}; multiset<int> a{2,1, 3}; cout << (find(mul.begin(), mul.end(), a)==mul.end() )<< endl; // 0 找到vector<vector<int>> vec{{1,2,3}}; vector<int> b{2,1, 3}; cout << (find(vec.begin(), vec.end(), b)==vec.end() )<< endl; // 1 没有找到
-
-
嵌套的容器的复制,不能直接使用容器的构造函数配合begin()和end()迭代器范围进行
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
multiset<multiset<int>> res;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size();i++)
for (int j = 0; j < nums.size();j++)
for (int k = 0; k < nums.size();k++)
{
multiset<int> tmp{};
tmp.insert(nums[i]);
tmp.insert(nums[j]);
tmp.insert(nums[k]);
if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]==0 && i!=j&&i!=k&&j!=k&&find(res.begin(),res.end(),tmp)==res.end())
res.insert(tmp);
}
vector<vector<int>> ve;
for (const auto& innerSet : res) {
std::vector<int> tempVec(innerSet.begin(), innerSet.end());
ve.push_back(tempVec);
}
return ve;
}
};
哈希法
可以排序的原因是,只需要返回元素值即可,不用返回下标
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
// 找出a + b + c = 0
// a = nums[i], b = nums[j], c = -(a + b)
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// 排序之后如果第一个元素已经大于零,那么不可能凑成三元组
if (nums[i] > 0) {
break;
}
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) { //三元组元素a去重
continue;
}
unordered_set<int> set;
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.size(); j++) {
if (j > i + 2
&& nums[j] == nums[j-1]
&& nums[j-1] == nums[j-2]) { // 三元组元素b去重
continue;
}
int c = 0 - (nums[i] + nums[j]);
if (set.find(c) != set.end()) {
result.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], c});
set.erase(c);// 三元组元素c去重
} else {
set.insert(nums[j]);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
双指针法
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
// 找出a + b + c = 0
// a = nums[i], b = nums[left], c = nums[right]
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// 排序之后如果第一个元素已经大于零,那么无论如何组合都不可能凑成三元组,直接返回结果就可以了
if (nums[i] > 0) {
return result;
}
// 错误去重a方法,将会漏掉-1,-1,2 这种情况
/*
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
continue;
}
*/
// 正确去重a方法
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
while (right > left) {
// 去重复逻辑如果放在这里,0,0,0 的情况,可能直接导致 right<=left 了,从而漏掉了 0,0,0 这种三元组
/*
while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
*/
if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0) right--; // 和有点大
else if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < 0) left++;// 和有点小
else {
result.push_back(vector<int>{nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]});
// 去重逻辑应该放在找到一个三元组之后,对b 和 c去重
while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
// 找到答案时,双指针同时收缩
right--;
left++;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
四数之和
暴力法
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
multiset<multiset<int>> res;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size();i++)
for (int j = 0; j < nums.size();j++)
for (int k = 0; k < nums.size();k++)
for (int v = 0; v < nums.size();v++)
{
multiset<int> tmp{};
tmp.insert(nums[i]);
tmp.insert(nums[j]);
tmp.insert(nums[k]);
tmp.insert(nums[v]);
if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]+nums[v]==target&&i!=j&&i!=k&&j!=k&&k!=v &&j!=v&&i!=v&&find(res.begin(),res.end(),tmp)==res.end())
res.insert(tmp);
}
vector<vector<int>> ve;
for (const auto& innerSet : res) {
std::vector<int> tempVec(innerSet.begin(), innerSet.end());
ve.push_back(tempVec);
}
return ve;
}
};
哈希法
-

-
class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { vector<vector<int>> result; sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); for (int k = 0; k < nums.size(); k++) { // 剪枝处理 if (nums[k] > target && nums[k] >= 0) { // 注意这里不能只有nums[k] > target因为还可能是负数,三数之和那道题是要求所求之和为0 break; // 这里使用break,统一通过最后的return返回 } // 对nums[k]去重 if (k > 0 && nums[k] == nums[k - 1]) { continue; } for (int i = k + 1; i < nums.size(); i++) { // 2级剪枝处理 if (nums[k] + nums[i] > target && nums[k] + nums[i] >= 0) { break; } // 对nums[i]去重 if (i > k + 1 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) { continue; } int left = i + 1; int right = nums.size() - 1; while (right > left) { // nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > target 会溢出 if ((long) nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > target) { right--; // nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < target 会溢出 } else if ((long) nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] < target) { left++; } else { result.push_back(vector<int>{nums[k], nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]}); // 对nums[left]和nums[right]去重 while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--; while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++; // 找到答案时,双指针同时收缩 right--; left++; } } } } return result; } };
字符串

反转字符串1
双指针法
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
class Solution {
public:
void reverseString(vector<char>& s) {
vector<char>::iterator t1 = s.begin();
vector<char>::iterator t2 = s.end()-1;
while(t1!=t2)
{
char tmp;
tmp = *t1;
*t1 = *t2;
*t2 = tmp;
t1++;
t2--;
}
}
};
不知道上面这道题有问题,本地测试没问题,在Leecode测试报错
class Solution {
public:
void reverseString(vector<char>& s) {
int begin = 0, end = s.size() - 1;
while(begin<end)
{
char tmp = s[begin];
s[begin] = s[end];
s[end] = tmp;
begin++;
end--;
}
}
};
反转字符串2

思路:i += 2*k;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
void reverseBetween(string &s,int left,int right)
{
while(left<right)
{
int tmp = s[left];
s[left] = s[right];
s[right] = tmp;
right--;
left++;
}
}
string reverseStr(string s, int k) {
int i = 0;
while(i<s.size())
{
reverseBetween(s, i, i + k - 1);
i += 2*k;
if(s.size()-i < k) //如果剩余字符少于 k 个,则将剩余字符全部反转。
{
reverseBetween(s, i, s.size() - 1);
break;
}
else if(s.size()-i>=k && s.size()-i <2*k) // 如果剩余字符小于 2k 但大于或等于 k 个,则反转前 k 个字符,其余字符保持原样。
{
reverseBetween(s, i, i+k-1);
break;
}
}
return s;
}
};
反转字符串中的单词

-
常规做法
-
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class Solution { public: string reverseWords(string s) { string::iterator sEnd = s.end() - 1; string result; while (sEnd != s.begin()) { while (*sEnd == ' ' && sEnd != s.begin()) // 找到第一个不是空格的字符 sEnd--; string::iterator tmp1 = sEnd; // 指向有字符的位置 while (*sEnd != ' ' && sEnd != s.begin()) // 找到第一个是空格的字符 sEnd--; // 最终指向有空格的位置 if (sEnd != s.begin()) // 对于中间的字符 result.append(sEnd + 1, tmp1 + 1); else // 对于开头字符 result.append(sEnd, tmp1 + 1); while (*sEnd == ' ' && sEnd != s.begin()) //" hello world! "开头的空格 sEnd--; // 加入分隔符空格 if (sEnd != s.begin()) result.append(" "); else if (sEnd == s.begin()&& *sEnd != ' ' && *(sEnd+1)==' ') //"a hello world! "结尾的空格 { result.append(" "); result.append(sEnd, sEnd + 1); } } return result; } };
-
-
假设空间复杂度为O(1)
-
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; /* 分为两步 第一步 先去掉空格(利用快慢指针) 第二步 再反转每个单词 先反转整个句子 再反转每个单词 */ class Solution { public: void reverseWord(string& s,int left,int right) { while (left < right) { char tmp = s[left]; s[left] = s[right]; s[right] = tmp; right--; left++; } } string reverseWords(string s) { // 1. 首先利用快慢指针去除空格。 int fast = 0, slow = 0; for (; fast < s.size(); fast++) { if (s[fast] != ' ') { s[slow++] = s[fast]; } else if (s[fast] == ' ' && (fast + 1) < s.size() && s[fast + 1] != ' ' && slow != 0) { s[slow++] = s[fast]; } } s.resize(slow); // 2.反转整个句子 reverseWord(s,0,s.size()-1); //3. 反转句子中的每个单词 int end = 0,begin=0; while (end < s.size()) { if (s[end] == ' ') { reverseWord(s,begin,end-1); begin = end + 1; end++; } else { end++; } if (end == s.size()) reverseWord(s, begin, end - 1); } cout << s.size() << endl; return s; } }; int main() { string s = "the blue a"; Solution sol; string s1 = sol.reverseWords(s); cout << s1 << "_________" << endl; return 0; }
KMP
BP算法
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int BP(char str[], char pattern[])
{
int i = 0, j = 0,tmp=0;
for (; str[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
tmp = i;
for (j=0; pattern[j]!='\0' &&str[i] != '\0'; j++)
{
if (pattern[j] != str[i])
{
i = tmp;
break;
}
else if (pattern[j+1] == '\0')
{
return i-j;
}
i++;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
char str[] = "123456", pattern[] = "34";
int pos = BP(str,pattern);
return 0;
}
KMP
- 前置表
- 前缀
- 包含首字母不包含尾字母的子串
- 后缀
- 包含尾字母不包含首字母的子串
- next数组
只直到一个即可
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 构建next数组
void getNext(char *pattern, int *next)
{
int lenStr = strlen(pattern);
int j = -1, i = 0;
next[0] = -1;
while (i < lenStr)
{
if (j == -1 || pattern[i] == pattern[j])
{
i++;
j++;
next[i] = j;
}
else
{
j = next[j];
}
}
}
// 使用KMP算法进行字符串匹配
int kmpMatch(char *text, char *pattern)
{
int textLength = strlen(text);
int patternLength = strlen(pattern);
int next[patternLength];
getNext(pattern, next);
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < textLength && j < patternLength)
{
if (j == -1 || text[i] == pattern[j])
{
i++;
j++;
// if (j == patternLength)
// {
// printf("position %d find\n", i - j);
// j = next[j];
// }
}
else
{
j = next[j];
}
}
if (j == patternLength)
return i - j;
else
return -1;
}
int main()
{
char text[] = "ABABDABACDABABCABAB";
char pattern[] = "ABABCABAB"; // -1
int pos = kmpMatch(text, pattern); // 使用KMP算法进行字符串匹配
printf("%d\n", pos);
return 0;
}
找到所有匹配的字串的位置
// 构建next数组
void getNext(char *pattern, int *next)
{
int lenStr = strlen(pattern);
int j = -1, i = 0;
next[0] = -1;
while (i < lenStr)
{
if (j == -1 || pattern[i] == pattern[j])
{
i++;
j++;
next[i] = j;
}
else
{
j = next[j];
}
}
}
// 使用KMP算法进行字符串匹配
int kmpMatch(char *text, char *pattern, int *allSonStr)
{
int textLength = strlen(text);
int patternLength = strlen(pattern);
int next[patternLength];
getNext(pattern, next);
int k = 0;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < textLength && j < patternLength)
{
if (j == -1 || text[i] == pattern[j])
{
i++;
j++;
if (j == patternLength)
{
allSonStr[k++] = i - j;
j = next[j];
}
}
else
{
j = next[j];
}
}
if (k != 0)
return k;
else
return 0;
}
重复的子字符串

暴力法
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
string repeadString(string s, int count)
{
string tmp(s);
for (int i = 0; i < count-1; i++)
s.append(tmp);
return s;
}
bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string s) {
string res;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
string tmp(s, 0, i+1);
if (s.size() / tmp.size() > 1)
{
res = repeadString(tmp, s.size() / tmp.size());
if (s == res)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
```
移动匹配
思路:
class Solution {
public:
bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string s) {
string tmp(s);
s += s;
s.erase(s.begin());
s.erase(s.end()-1);
if (s.find(tmp) != std::string::npos)
return true;
return false;
}
};
栈与队列
用栈实现队列

#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
/*
两个栈实现一个队列的算法: in,out
进队时: 将out中的都出栈,并入栈到in中,然后将入栈元素入栈到in中
出队时: 将in中的都出栈,并入栈到out中,然后将out中元素出栈
*/
class MyQueue {
public:
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) { //进入队列
while (!out.empty()) // 首先将out的
{
in.push(out.top());
out.pop();
}
in.push(x);
}
int pop() {// 出队
while (!in.empty())
{
out.push(in.top());
in.pop();
}
int tmp = out.top();
out.pop();
return tmp;
}
int peek() {
while (!in.empty())
{
out.push(in.top());
in.pop();
}
return out.top();
}
bool empty() {
return in.empty() && out.empty();
}
private:
stack<int> in;
stack<int> out;
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
用队列实现栈

- 用两个队列实现一个栈(同上)
- 用一个队列实现栈
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
/*
实现思路:只用一个队列实现栈
出栈:处队size-1个并将这size-1个元素入队
进栈:直接入队即可
*/
class MyStack {
public:
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
q.push(x);
}
int pop() {
int size = q.size() - 1;
while (size > 0)
{
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
size--;
}
int tmp = q.front();
q.pop();
return tmp;
}
int top() {
int size = q.size() - 1;
while (size > 0)
{
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
size--;
}
int tmp = q.front();
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
return tmp;
}
bool empty() {
return q.empty();
}
private:
queue<int> q;
};
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = new MyStack();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
有效的括号

#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<char> sa;
for (char ch : s)
{
if (ch == '[' || ch == '{' || ch == '(')
sa.push(ch);
else if (ch == ']' )
{
char tmp = sa.top();
sa.pop();
if (tmp != '[')
return false;
}
else if ( ch == '}' )
{
char tmp = sa.top();
sa.pop();
if (tmp != '{')
return false;
}
else if ( ch == ')')
{
char tmp = sa.top();
sa.pop();
if (tmp != '(')
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项

暴力匹配
class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string s) {
for (int i = 0; i < s.size()-1; i++)
{
if (s[i] == s[i + 1])
{
s.erase(i, 2);
i = -1;
}
}
return s;
}
};
使用栈

#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string s) {
stack<char> sa;
for (char ch : s)
{
if (sa.empty() || sa.top() != ch) // 栈为空或者顶部元素与ch不相等
sa.push(ch);
else if(sa.top() == ch)
sa.pop();
}
string res = "";
while (!sa.empty())
{
res.insert(res.begin(), sa.top());
sa.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
逆波兰式表达式求值

#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<string> sa;
int result = 0;
int num1 = 0, num2 = 0;
/*
思路分析: 依次扫描字符串,
只要不是算术符号就入栈
如果是算术符号就出栈两个数字,进行运算
*/
for (string ch : tokens)
{
if (ch == "/")
{
num1 = stoi(sa.top());
sa.pop();
num2 = stoi(sa.top());
sa.pop();
result = (num2 / num1);
sa.push(to_string(result));
}
else if (ch == "*")
{
num1 = stoi(sa.top());
sa.pop();
num2 = stoi(sa.top());
sa.pop();
result = (num1 * num2);
sa.push(to_string(result));
}
else if (ch == "+")
{
num1 = stoi(sa.top());
sa.pop();
num2 = stoi(sa.top());
sa.pop();
result = (num1 + num2);
sa.push(to_string(result));
}
else if (ch == "-")
{
num1 = stoi(sa.top());
sa.pop();
num2 = stoi(sa.top());
sa.pop();
result = (num2 - num1);
sa.push(to_string(result));
}
else
sa.push(ch);
}
cout << "result= " << result << endl;
return result;
}
};
void main()
{
Solution s1;
//vector<string> tokens = { "2","1","+","3","*" };
vector<string> tokens = { "10","6","9","3","+","-11","*","/","*","17","+","5","+" };
s1.evalRPN(tokens);
}
滑动窗口最大值

暴力法
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
vector<int> res;
vector<int>::iterator iter;
for (iter=nums.begin();(iter+k)<nums.end();iter++)
{
vector<int>::iterator max = max_element(iter,iter+k);
res.push_back(*max);
}
vector<int>::iterator max = max_element(iter, iter + k);
res.push_back(*max);
return res;
}
};
单调队列

#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class MyQueue { //单调队列(从大到小)
public:
deque<int> que; // 使用deque来实现单调队列
// 这样就保持了队列里的数值是单调从大到小的了。
void push(int value)
{
while (!que.empty() && value > que.back()) // 队列前面的元素必须比即将加入的元素要打
que.pop_back();
que.push_back(value);
}
// 每次弹出的时候,比较当前要弹出的数值是否等于队列出口元素的数值,如果相等则弹出。
// 同时pop之前判断队列当前是否为空。
void pop(int value) {
if (!que.empty() && value == que.front())
que.pop_front();
}
// 查询当前队列里的最大值 直接返回队列前端也就是front就可以了。
int get_max() {
return que.front();
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
MyQueue que;
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { // 先将前k的元素放进队列
que.push(nums[i]);
}
result.push_back(que.get_max()); // result 记录前k的元素的最大值
for (int i = k; i < nums.size(); i++) {
que.pop(nums[i - k]); // 滑动窗口移除最前面元素
que.push(nums[i]); // 滑动窗口前加入最后面的元素
result.push_back(que.get_max()); // 记录对应的最大值
}
return result;
}
};
前k个高频元素

- 利用map集合
#include<iostream> #include<queue> #include<vector> #include<map> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; class Solution { public: vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) { map<int, int> result; vector<int> results; for (int elem : nums) { if (result.find(elem) == result.end()) result.insert(make_pair(elem, 1)); else { result[elem]++; } } for (pair<int, int> pa : result) { if (pa.second >= k) results.push_back( pa.first); } return results; } };
二叉树
理论基础
-
满二叉树
-
完全二叉树
-
二叉树搜索树
-
平衡二叉搜索树(元素是有序的)
- map
- set
- multimap
- multiset
-
存储方式
-
链式存储(常用)
-
线式存储
-
二叉树的遍历
-
深度优先搜索
-

- 前序遍历(迭代,递归)
- 中序遍历(迭代,递归)
- 后序遍历(迭代,递归)
-
广度优先搜索
- 层序遍历 (迭代)
-
-
递归函数如何写
-
确定函数的参数和返回值
-
确定终止条件
-
确定单层递归的逻辑
遍历
前序遍历

递归版本
class Solution {
private:
std::vector<int> res;
public:
std::vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root)
{
res.push_back(root->val);
preorderTraversal(root->left);
preorderTraversal(root->right);
}
return res;
}
};
- 每次线遍历一个元素之后先将
非递归版本
- 每次遍历之前先把其右孩子压栈,然后将其左孩子压栈

#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
class Solution {
private:
std::vector<int> res;
public:
std::vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
/*
每次遍历之前先把其右孩子压栈,然后将其左孩子压栈
*/
std::stack<TreeNode*> sta;
sta.push(root);
while (!sta.empty())
{
TreeNode* node = sta.top();
sta.pop();
if(node)
res.push_back(node->val);
else
continue;
sta.push(node->right);
sta.push(node->left);
}
return res;
}
};
``
## 中序遍历
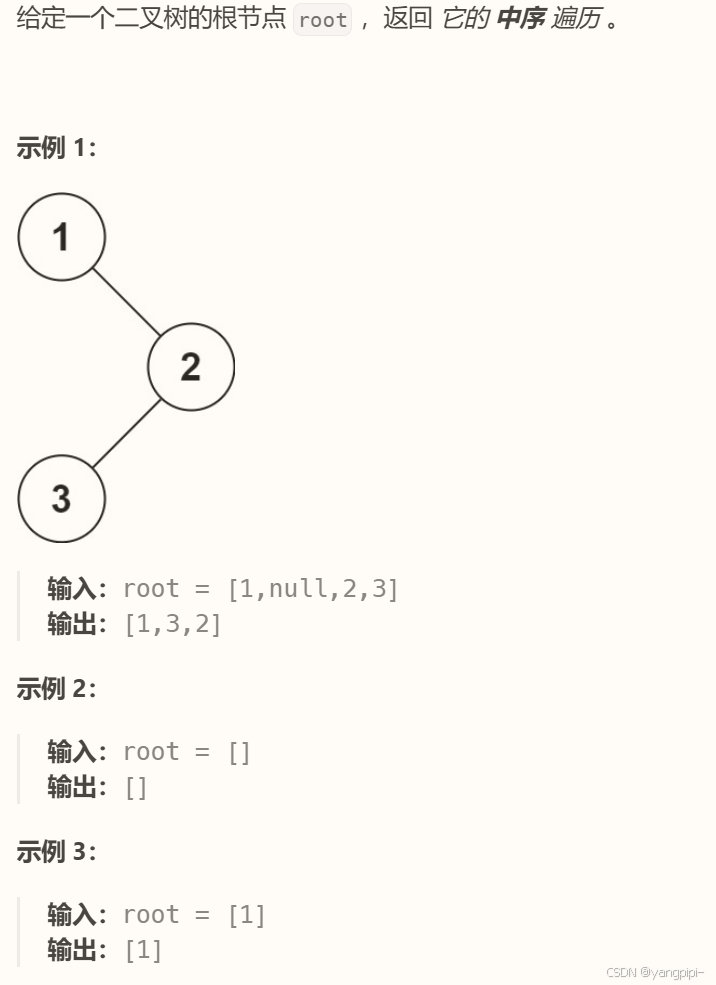
```cpp
class Solution {
private:
std::vector<int> res;
public:
std::vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root)
{
inorderTraversal(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
inorderTraversal(root->right);
}
return res;
}
};
中序遍历
递归版本
class Solution {
private:
std::vector<int> res;
public:
std::vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root)
{
inorderTraversal(root->left);
res.push_back(root->val);
inorderTraversal(root->right);
}
return res;
}
};
非递归版本
- 遍历的顺序和处理的顺序不一样
- 思路:需要一个栈和指针。首先是一直入栈(将左孩子入栈),直到遇NULL为止,然后弹栈,然后访问,然后将其右孩子入栈
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
};
class Solution {
private:
std::vector<int> res;
public:
std::vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
std::stack<TreeNode*> sta;
TreeNode* p = root;
while (p!=NULL || !sta.empty())
{
if (p)
{
sta.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
else
{
p = sta.top();
sta.pop();
res.push_back(p->val);
p = p->right;
}
}
return res;
}
};
后序遍历
递归版本

class Solution {
private:
std::vector<int> res;
public:
std::vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if (root)
{
postorderTraversal(root->left);
postorderTraversal(root->right);
res.push_back(root->val);
}
return res;
}
};
非递归版本(前序->后序)

#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
class Solution {
private:
std::vector<int> res;
public:
std::vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
/*
每次遍历之前先把其右孩子压栈,然后将其左孩子压栈
*/
std::stack<TreeNode*> sta;
sta.push(root);
while (!sta.empty())
{
TreeNode* node = sta.top();
sta.pop();
if (node)
res.push_back(node->val);
else
continue;
sta.push(node->left);
sta.push(node->right);
}
std::reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
层序遍历
- 注意这需要逐层输出,vector套着vector


#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<int> tmp;
int size = 0;
if (root != NULL)
tmp.push_back(root->val);
else
return res;
res.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
if (root->left != NULL)
que.push(root->left);
if (root->right != NULL)
que.push(root->right);
size = que.size();
while (!que.empty())
{
TreeNode* p = que.front();
que.pop();
tmp.push_back(p->val);
size--;
if (p->left != NULL)
que.push(p->left);
if (p->right != NULL)
que.push(p->right);
if (size == 0)
{
res.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
size = que.size();
}
}
return res;
}
};
int main()
{}
翻转二叉树

- 在遍历的过程中完成交换(只有非叶子节点才需要交换)
- 使用前序和后序遍历很合适,中序不方便。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root != NULL)
{
if (root->left != NULL || root->right != NULL)
{
TreeNode* tmp = root->left;
root->left = root->right;
root->right = tmp;
}
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
}
return root;
}
};
对称二叉树



class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
// 首先排除空节点的情况
if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false;
else if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false;
else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;
// 排除了空节点,再排除数值不相同的情况
else if (left->val != right->val) return false;
// 此时就是:左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况
// 此时才做递归,做下一层的判断
bool outside = compare(left->left, right->right); // 左子树:左、 右子树:右
bool inside = compare(left->right, right->left); // 左子树:右、 右子树:左
bool isSame = outside && inside; // 左子树:中、 右子树:中 (逻辑处理)
return isSame;
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return true;
return compare(root->left, root->right);
}
};
二叉树的最大深度

递归版本
-
深度
- 二叉树任意一个节点到根节点的距离
- 求深度用前序遍历
-
高度
- 二叉树任意一个节点到叶子节点距离
- 求高度用后序遍历
-
根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度
class Solution {
public:
// 这是一个求高度的代码:利用后序遍历
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
int left = maxDepth(root->left); // 左子树的高度
int right = maxDepth(root->right);//右子树的高度
return 1+(left > right ? left : right );
}
};
求二叉树的最小深度

-
易错点:深度是到叶子节点的距离(NULL不算叶子节点)

- NULL如果算叶子节点的话只需要把求最大深度的代码的大于号改为小于号即可
-
利用后序遍历求高度,此时的最小的高度就是最小深度
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int Left = minDepth(root->left) ; // 左子树的高度
int Right = minDepth(root->right);//右子树的高度
// NULL不算叶子节点
if (root->right != NULL && root->left == NULL)
return 1 + Right;
if (root->right == NULL && root->left != NULL)
return 1 + Left;
// 都不为空
int res = 1 + (Left > Right ? Right : Left);
return res;
}
};
完全二叉树节点的个数

使用层序遍历计算节点数量
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode*> sta;
int size = 0;
TreeNode* tmp = NULL;
if (root != NULL)
{
size++;
// cout << root->val << endl;
}
else
return 0;
if (root->left != NULL)
sta.push(root->left);
if (root->right != NULL)
sta.push(root->right);
while (!sta.empty())
{
tmp = sta.top();
sta.pop();
// cout << tmp->val << endl;
size++;
if (tmp->left != NULL)
sta.push(tmp->left);
if (tmp->right != NULL)
sta.push(tmp->right);
}
return size;
}
};
使用前序遍历计算节点数量
class Solution {
public:
Solution() :len(0) {}
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root != nullptr)
{
std::cout << root->val << std::endl;
this->len++;
countNodes(root->right);
countNodes(root->left);
}
return this->len;
}
private:
int len;
};
使用中序遍历计算节点数量
使用后序遍历计算节点数量
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (root != nullptr)
{
int lenRight = countNodes(root->right);
int lenLeft = countNodes(root->left);
return lenRight+ lenLeft+1;
}else
return 0;
}
};
使用满二叉树的节点计算公式
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root)
{
// 终止条件1
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
TreeNode* left = root->left;
TreeNode* right = root->right;
int leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0;
while (left)
{
left = left->left;
leftDepth++;
}
while (right)
{
right = right->right;
rightDepth++;
}
// 终止条件2
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) // 此子树是一个完全二叉树:2^n-1这是完全二叉树的节点总数计算公式
return pow(2, rightDepth+1) - 1;
// 计算总的节点数量
return countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right) +1;
}
};
平衡二叉树的判断
class Solution {
public:
int getHeight(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
int left = getHeight(root->left);
if (left == -1) // 左子树不是一个平衡二叉树
return -1;
int right = getHeight(root->right);
if (right == -1) // 右子树不是一个平衡二叉树
return -1;
int result;
if (abs(left - right > 1)) // 本节点所在的子树不是一棵平衡二叉树
result = -1;
else
result = (left > right ? left : right) + 1; // 求出本节点的高度
return result;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root)
{
return getHeight(root)==-1?false:true;
}
};
二叉树的所有路径

#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
// 前序遍历
std::vector<std::string> vec;
std::vector<int> path; // 经过的路径
std::vector<std::string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
/*
思路:此道题用到回溯的思想,回溯一般会和递归挂钩即栈
明显使用前序遍历
从上往下,
1. 遇到叶子时,此条路径结束,需要将其加入到容器中
2. 然后,需要把此叶子节点弹出,这里就是回溯。
*/
path.push_back(root->val);
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) // 到达叶子节点
{
std::string str;
for (std::vector<int>::iterator it = path.begin(); it != path.end(); it++)
{
if ((it + 1) == path.end())
str += std::to_string(*it);
else
str += std::to_string(*it) + "->";
}
vec.push_back(str);
return vec;
}
if (root->left != nullptr)
{
binaryTreePaths(root->left);
path.pop_back();// 左子树遍历完成,弹栈,回溯
}
if (root->right != nullptr)
{
binaryTreePaths(root->right);
path.pop_back(); // 回溯
}
}
};
左叶子之和

class Solution {
private:
int sumLeftLeaces;
public:
Solution() :sumLeftLeaces(0) {}
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
if (root != nullptr)
{
//前序遍历
if (root->left != nullptr)
this->sumLeftLeaces += root->left->val;
sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left);
sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
}
return this->sumLeftLeaces;
}
};
找树的左下角的值

- 注意不要搞混一个概念:题目要求的是最底层,不一定是左子树的上的节点,是最底层最靠近左边的节点

使用递归法
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth = INT_MIN;
int result;
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
if (depth > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = depth;
result = root->val;
}
return;
}
if (root->left) {
depth++;
traversal(root->left, depth);
depth--; // 回溯
}
if (root->right) {
depth++;
traversal(root->right, depth);
depth--; // 回溯
}
return;
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
traversal(root, 0);
return result;
}
};
层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
std::queue<TreeNode*> qu;
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return -1;
qu.push(root);
TreeNode* tmp;
while (!qu.empty())
{
tmp = qu.front();
if (qu.size() == 1 && tmp->right == nullptr && tmp->left== nullptr)
return tmp->val;
qu.pop();
if (tmp->right != nullptr)
qu.push(tmp->right);
if (tmp->left != nullptr)
qu.push(tmp->left);
}
return -1;
}
};
利用层序遍历,每次先将右孩子入队,再将左孩子入队。
路径之和



-
思路相同,代码不同
-
代码1
// 注意有返回值,应该返回每一次递归调用的返回值
class Solution {
public:
// 前序遍历
std::vector<int> path; // 经过的路径
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
/*
思路:此道题用到回溯的思想,回溯一般会和递归挂钩即栈
明显使用前序遍历
从上往下,
1. 遇到叶子时,此条路径结束,需要将其加入到容器中
2. 然后,需要把此叶子节点弹出,这里就是回溯。
*/
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
path.push_back(root->val);
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) // 到达叶子节点
{
int sum = 0;
for (std::vector<int>::iterator it = path.begin(); it != path.end(); it++)
sum += *it;
if (sum == targetSum)
return true;
}
if (root->left != nullptr)
{
bool ret = hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum);
if (ret) // 注意这里。不要忘记
return true;
path.pop_back();// 左子树遍历完成,弹栈,回溯
}
if (root->right != nullptr)
{
bool ret = hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum);
if (ret) // 注意这里。不要忘记
return true;
path.pop_back(); // 回溯
}
return false;
}
};
- 代码2
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == NULL)
return false;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && targetSum == 0)
return true;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && targetSum != 0)
return false;
if (root->left != NULL) {
targetSum -= root->left->val;
bool ret = hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum);
if (ret) {
return true;
}
else { // 回溯
targetSum += root->left->val;
}
}
if (root->right != NULL) {
targetSum -= root->right->val;
bool ret = hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum);
if (ret) {
return true;
}
else { // 回溯
targetSum += root->right->val;
}
}
return false;
}
};
从中序和后序序列中构造二叉树
构造二叉树的题目的遍历方式就是前序遍历


class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
/*
1. 后序数组为空,空节点
2. 后序数组最后一个元素为根节点
3. 在中序数组中找到根节点的位置作为切割点
4. 切中序数组
5. 切后序数组
6. 递归处理左区间和右区间
*/
//1. 后序数组为空,空节点
if (postorder.size() == 0)
return 0;
//2. 后序数组最后一个元素为根节点
int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size()-1];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode();
root->val = rootValue;
// 到达叶子节点
if (postorder.size() == 1)
return root;
//3. 在中序数组中找到根节点的位置作为切割点
int index = 0 ;
while (index < inorder.size())
{
if (inorder[index] == rootValue)
break;
index++;
}
// 4. 切中序数组 遵从左闭右开
vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin()+index);
vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + index+1, inorder.end());
// postorder 舍弃末尾元素,因为这个元素就是中间节点,已经用过了
// 5. 切后序数组 遵从左闭右开
// 5. 切后序数组 遵从左闭右开
postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);
vector<int> leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size());
//vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end());
vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size()+ rightInorder.size());
/*for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
leftInorder.push_back(inorder[i]);
for (int i = index+1; i < postorder.size(); i++)
rightInorder.push_back(inorder[i]);*/
//
//for (int i = 0; i < leftInorder.size(); i++)
// leftPostorder.push_back(postorder[i]);
//for (int i = leftInorder.size(); i < rightInorder.size(); i++)
// rightPostorder.push_back(postorder[i]);
///6. 递归处理左区间和右区间
root->left = buildTree(leftInorder, leftPostorder);
root->right = buildTree(rightInorder, rightPostorder);
return root;
}
};
最大二叉树


int max(vector<int>& nums)
{
int maxi = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[maxi] < nums[i])
maxi = i;
}
return maxi;
}
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
/*思路:
1. nums == NULL return NULL;
2. 找到最大值,构造根节点
3. 根据最大值点,分割左数组和右数组
4. 递归构造左子树和右子树
*/
// nums.size = 0
if (nums.size() == 0)
return NULL;
//2. 找到最大值,构造根节点
int maxi = max(nums);
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode();
root->val = nums[maxi];
if (nums.size() == 1)
return root;
//3. 根据最大值点,分割左数组和右数组
vector<int> leftNums(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + maxi);
vector<int> rightNums(nums.begin() + maxi+1, nums.end());
//4. 递归构造左子树和右子树
root->left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(leftNums);
root->right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(rightNums);
return root;
}
合并二叉树

class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
// 两个都采用前序遍历
if (root1 != NULL && root2 != NULL)
{
root1->val += root2->val;
if (root1->left == NULL && root2->left != NULL)
{
TreeNode* tmp = new TreeNode(0);
tmp->left = NULL;
tmp->right = NULL;
root1->left = tmp;
}
else if (root1->left != NULL && root2->left == NULL)
{
TreeNode* tmp = new TreeNode(0);
tmp->left = NULL;
tmp->right = NULL;
root2->left = tmp;
}
mergeTrees(root1->left, root2->left);
if (root1->right == NULL && root2->right != NULL)
{
TreeNode* tmp = new TreeNode(0);
tmp->left = NULL;
tmp->right = NULL;
root1->right = tmp;
}
else if (root1->right != NULL && root2->right == NULL)
{
TreeNode* tmp = new TreeNode(0);
tmp->left = NULL;
tmp->right = NULL;
root2->right = tmp;
}
mergeTrees(root1->right, root2->right);
}
return root1;
}
};

class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
// 两个都采用前序遍历
if (root1 == NULL) return root2;
if (root2 == NULL) return root1;
root1->val += root2->val;
root1->left = mergeTrees(root1->left, root2->left);
root1->right = mergeTrees(root1->right, root2->right);
return root1;
}
};
二叉搜索树中的搜索
- 注意二叉搜索树的特征

class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
// 这个为什么不行
/*if (root != NULL)
{
if (root->val == val)
return root;
searchBST(root->left, val);
searchBST(root->right, val);
}
return NULL;*/
if (root == NULL || root->val == val)
return root;
TreeNode* res = NULL;
if (val < root->val)
res = searchBST(root->left, val);
if (val > root->val)
res = searchBST(root->left, val);
return res;
}
};
验证二叉搜索树

- 直白的想法:中序得到遍历序列,判断这个序列是否是中序序列
class Solution {
public:
long long maxVal = LLONG_MIN;
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return true; // 注意空树也是BTS
// 判断左子树
bool left = isValidBST(root->left);
if (root->val > maxVal)
maxVal = root->val; // 如果是BTS则一定每次都会更换
else
return false;
// 判断右子树
bool right = isValidBST(root->right);
return left && right;
}
};

双指针优化
- 实际上就是保存前序节点的值
利用中序遍历BTS,得到的是一个递增序列的特点.
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* prev = nullptr; // 记录上一个访问的节点
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return true;
// 递归检查左子树
if (!isValidBST(root->left))
return false;
// 检查当前节点是否满足递增
if (prev != nullptr && root->val <= prev->val)
return false;
prev = root; // 更新上一个访问的节点
// 递归检查右子树
return isValidBST(root->right);
}
};
二叉搜索树中的最小绝对差


- 注意由于是二叉搜索树,暗含的意思的是最小值就是中序序列相邻元素的最小值
中序序列
- 思路1
// 得到其中序遍历序列,然后在序列中寻找,相邻元素的最小差值
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> vec;
void preVist(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
preVist(root->left);
vec.push_back(root->val);
preVist(root->right);
}
}
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root)
{
preVist(root);
int min = std::numeric_limits<int>::max();
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < vec.size(); i++)
{
if (abs(vec[i] - vec[i + 1]) < min)
min = abs(vec[i] - vec[i + 1]);
}
return min;
}
};
双指针优化
- 思路2
class Solution {
public:
int min = numeric_limits<int>::max();
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
getMinimumDifference(root->left);
if (prev != nullptr) // 注意这里的如何保存上一个节点的值
{
if (abs(prev->val - root->val) < min)
{
min = abs(prev->val - root->val);
}
}
prev = root;
getMinimumDifference(root->right);
}
return min;
}
};
二叉搜素树种的众数

//若是一棵普通的二叉树的思路
// 使用map,分别统计各个元素出现的次数
两阶段法
// 首先找到众数的个数
//然后依次计算每个元素出现的次数,次数等于众数个数的就是众数
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> res = {0};
TreeNode* pre = nullptr;
int count = 0;
int max = 0;
void findMax(TreeNode* root)
{//确定总数的最大值
if (root == nullptr)
return ;
findMode(root->left);
if (pre != nullptr)
{
if (pre->val == root->val)
{
count++;
}
else {
if (max < count)
max = count;
//count = 0;
count = 1; // 注意:这里是1 ,已经指向一个新的元素了
}
}
else {
count = 1; //注意:这里当pre为空时,root已经指向左下角的元素了。
}
pre = root;
findMode(root->right);
}
vector<int> findNum(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return res;
findNum(root->left);
if (pre != nullptr)
{
if (pre->val == root->val)
{
count++;
}
else {
if (max = count)
{
if(res[0] == 0)
res.clear();
res.push_back(pre->val);
}
}
}
pre = root;
findNum(root->right);
return res;
}
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root)
{
findMax(root);
findNum(root);
return res;
}
};
遍历1次
// 首先找到众数的个数
//然后依次计算每个元素出现的次数,次数等于众数个数的就是众数
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> res = {0};
TreeNode* pre = nullptr;
int count = 0;
int max = 0;
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return res;
findMode(root->left);
if (pre != nullptr)
{
if (pre->val == root->val)
{
count++;
}
else {
//count = 0;
count = 1; // 注意:这里是1 ,已经指向一个新的元素了
}
}
else {
count = 1; //注意:这里当pre为空时,root已经指向左下角的元素了。
}
pre = root;
//-----------------------------只需要依次遍历--------------------------------------
if (count == max)
res.push_back(pre->val);
if (count > max)
{
res.clear();
max = count;
res.push_back(pre->val);
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
findMode(root->right);
return res;
}
};
二叉树的最近公共祖先

暴力法
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
// 如何得到所有叶子节点的从根到叶子的路径
/*
从上往下,
1. 遇到叶子时,此条路径结束,需要将其加入到容器中
2. 然后,需要把此叶子节点弹出,这里就是回溯。
*/
std::vector<TreeNode*> path; // 目前正在经过的路径。
std::map<TreeNode*, std::vector<TreeNode*>> leafPaths; //所有叶子节点路径
// 使用前向遍历
void getLeafsPath(TreeNode* root)
{
path.push_back(root);
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) // 到达叶子节点
{ // 将所在的路径添加到leafPaths中
leafPaths[root] = path;
}
// 左遍历
if (root->left != nullptr)
{
getLeafsPath(root->left);
path.pop_back();// 左子树遍历完成,弹栈,回溯
}
//右遍历
if (root->right != nullptr)
{
getLeafsPath(root->right);
path.pop_back(); // 回溯
}
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
getLeafsPath(root);
bool s1, s2;
int i1 = numeric_limits<int>::max(), i2 = numeric_limits<int>::max();
TreeNode* p1 = nullptr;
TreeNode* q1 = nullptr;
for (const auto pair : leafPaths)
{
//遍历每一天路径
// 当在同一条路径上时
s1 = false;
s2 = false;
for (int i = 0; i < pair.second.size(); i++)
{
if (pair.second[i]->val == p->val)
{
s1 = true;
i1 = i;
p1 = pair.first;
}
if (pair.second[i]->val == q->val)
{
s2 = true;
i2 = i;
q1 = pair.first;
}
if (s1 && s2)
{// 这里是为什么。。。。。。。。。。。。。
return i1 < i2 ? pair.second[i1] : pair.second[i2];
}
}
//当在不同路径上时
if (i1 != numeric_limits<int>::max() && i2 != numeric_limits<int>::max()) // 找到p和q所在的序列
{
std::vector<TreeNode*> v1 = leafPaths[p1];
std::vector<TreeNode*> v2 = leafPaths[q1];
for (; i1 >= 0 && i2 >= 0; i1--, i2--)
{
if (v1[i1]->val == v2[i2]->val)
return v1[i1];
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};
后序遍历+回溯
class Solution {
public:
// 要将找到的q或者p节点依次向上返回:所以需要采用后序遍历
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (root == nullptr) return root;
if (root == q || root == p) return root; // 向上返回
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if (left != nullptr && right != nullptr)
return root;
else if (left != nullptr && right == nullptr)
return left;
else if ((left == nullptr && right != nullptr))
return right;
else
return nullptr;
}
};
二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先

普通二叉树的方法
if (root == nullptr) return root;
if (root == q || root == p) return root; // 向上返回
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if (left != nullptr && right != nullptr)
return root;
else if (left != nullptr && right == nullptr)
return left;
else if ((left == nullptr && right != nullptr))
return right;
else
return nullptr;
前序遍历:利用搜索树的性质
class Solution {
public:
// 前序遍历:
/*
1. 若两个节点比root都小,则在左子树
2. 若两个节点比root都大,则在右子树
3. 若两个节点在root分叉,则是root
*/
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (root)
{
if (root->val > p->val && root->val > q->val)
root = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
if (root->val < p->val && root->val < q->val)
root = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if ((root->val < p->val && root->val > q->val) || (root->val > p->val && root->val < q->val))
return root;
}
return root;
}
};
二叉搜素树插入
差的
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* _root;
void insertNode(TreeNode* root,int val)
{
if (root)
{
if (root->val > val && root->left == nullptr)
{
TreeNode* tmp = new TreeNode(val);
tmp->left = nullptr;
tmp->right = nullptr;
root->left = tmp;
return ;
}
if (root->val > val && root->left != nullptr)
insertNode(root->left, val);
if (root->val < val && root->right == nullptr)
{
TreeNode* tmp = new TreeNode(val);
tmp->left = nullptr;
tmp->right = nullptr;
root->right = tmp;
return;
}
if (root->val < val && root->right != nullptr)
insertNode(root->right, val);
}
}
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
_root = root;
insertNode(root,val);
return _root;
}
};
标准
class Solution {
public:
// 插入节点的递归函数
void insertNode(TreeNode*& root, int val) {
if (!root) {
// 如果当前节点为空,则在此位置创建新节点
root = new TreeNode(val);
return;
}
if (val < root->val) {
// 如果插入值小于当前节点值,递归插入到左子树
insertNode(root->left, val);
} else if (val > root->val) {
// 如果插入值大于当前节点值,递归插入到右子树
insertNode(root->right, val);
}
// 如果相等则不做任何操作(假设不允许重复值)
}
// 插入节点的入口函数
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
insertNode(root, val);
return root;
}
};
简洁写法
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (root == nullptr)
{
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(val);
return node;
}
if (root->val < val)
{
root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left,val);
}
else if (root->val > val) {
root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val);
}
}
};
删除二叉搜索树的节点

习惯思路
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {
/* 利用后序遍历
1. 空树时
2. 叶子节点时
直接删除
3. 左子树为空
右子树直接替换本节点
4. 右子树为空
左子树直接替换本节点
5. 左右子树都不为空
左子树直接替换本节点,右子树查到左子树的最右下方
*/
if (root != nullptr)
{
root->left = deleteNode(root->left,key);
root->right = deleteNode(root->right,key);
if(root->val == key)
{
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) // 待删除节点为叶子
{
delete root;
root = nullptr;
return root;
}
else if (root->left == nullptr && root->right != nullptr)
{
TreeNode* ptmp = root->right;
delete root;
root = nullptr;
return ptmp;
}else if (root->left != nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
TreeNode* ptmp = root->left;
delete root;
root = nullptr;
return ptmp;
}
else { // 左右子树都存在:左子树直接替换本节点,右子树插到左子树的最右下方
TreeNode* pleft = root->left;
TreeNode* pright = root->right;
delete root;
root = nullptr;
// 找到左子树的最右下方
TreeNode* pre = pleft;
for (TreeNode* tmp = pleft->right; tmp != nullptr;)
{
pre = tmp;
tmp = tmp->right;
}
pre->right = pright;
return pleft;
}
}
}
return root;
}
};
修建二叉搜索树

class Solution {
public:
/*
本质上还是二叉搜索树指定节点的删除
*/
TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
if (root != nullptr)
{
root->left = trimBST(root->left,low,high);
root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high);
if(root->val < low || root->val>high)
{
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) // 待删除节点为叶子
{
delete root;
root = nullptr;
return root;
}
else if (root->left == nullptr && root->right != nullptr)
{
TreeNode* ptmp = root->right;
delete root;
root = nullptr;
return ptmp;
}else if (root->left != nullptr && root->right == nullptr)
{
TreeNode* ptmp = root->left;
delete root;
root = nullptr;
return ptmp;
}
else { // 左右子树都存在:左子树直接替换本节点,右子树插到左子树的最右下方
TreeNode* pleft = root->left;
TreeNode* pright = root->right;
delete root;
root = nullptr;
// 找到左子树的最右下方
TreeNode* pre = pleft;
for (TreeNode* tmp = pleft->right; tmp != nullptr;)
{
pre = tmp;
tmp = tmp->right;
}
pre->right = pright;
return pleft;
}
}
}
return root;
}
};
将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树

习惯思路
class Solution {
public:
/*
本质上还是二叉搜索树指定节点的删除
*/
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
TreeNode* root = nullptr;
if (nums.size()>0)
{
int mid = nums.size() / 2;
root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = nullptr;
root->right = nullptr;
vector<int> left(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + mid);
vector<int> right(nums.begin() + mid + 1, nums.end());
root->left = sortedArrayToBST(left);
root->right = sortedArrayToBST(right);
}
return root;
}
};
把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
右中左遍历
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
// 右中左:是从高到小遍历
if(root)
{
root->right = convertBST(root->right);
if (prev != nullptr)
{
root->val += prev->val;
}
prev = root;
root->left = convertBST(root->left);
}
return root;
}
};








