详细手把手教会二叉树链式结构【数据结构】
文章目录
- 二叉树链式结构的实现
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 层序遍历
- 树节点个数
- 树的深度
- 第K层节点个数
- 查找二叉树中的元素
二叉树链式结构的实现
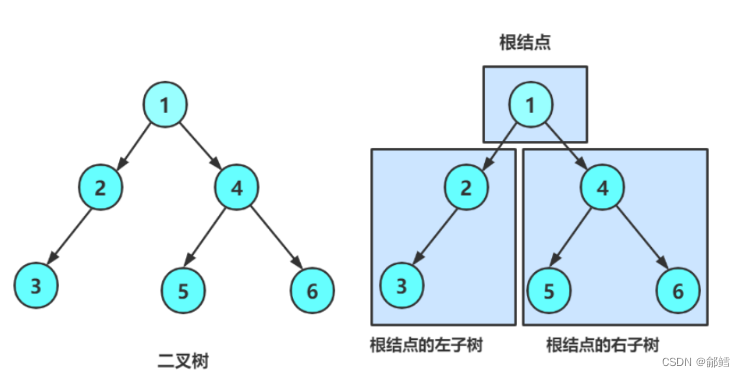
typedef int BinartTreeType;
typedef struct BinarytTreeNode
{
BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据
struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子
struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子
}BTNode;
前序遍历
访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前
简单来说就是 根节点 左子树 右子树
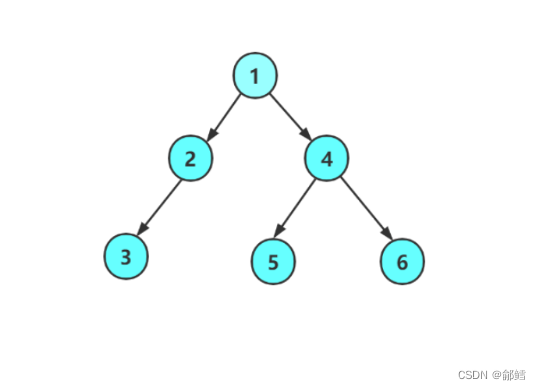
1 2 3 NULL NULL NULL 4 5 NULL NULL 6 NULL NULL
BTNode* CreateTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left= node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
//node3->right = node7;
return node1;
}
void PreOreder(BTNode* root) //根 左子树 右子树
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOreder(root->left);
PreOreder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreateTree();
PreOreder(root);
return 0;
}
从根节点1开始遍历 , 遍历完1这个根节点 ,然后去遍历1这个根节点的左子树(2) ,遍历到节点2时 , 但是节点 2 又被分成根节点 (2)、左子树(3) 、右子树(NULL) 。遍历到节点3时 ,节点3又被分成根节点 (3)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,对于节点3而言 ,3的左子树(NULL)走完 ,就走节点3的右子树(NULL) , 3这一整棵树作为2的左子树 ,2的左子树走完了 ,就走2的右子树(NULL) , 2的整棵树作为1的左子树, ,2这一整棵树走完了, 就走到1的右子树4 ,但是节点 4 又被分成根节点 (4)、左子树(5) 、右子树(6) ,然后走到4的左子树5 ,但是节点 5 又被分成根节点 (5)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,5的整棵树作为4的左子树, ,5这一整棵树走完了,就来到了4的右子树(6),但是节点 6又被分成根节点 (6)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL), 4的左子树,右子树都遍历完了 ,4的这一整棵树也遍历完了,4这一整棵树是作为1的右子树 ,
前序遍历就是将每一个节点不断拆分成 根,左子树 ,右子树的一个过程
前序遍历递归展开图,以左子树为例,右子树并未画出

中序遍历
访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)
简单来说就是 左子树 根节点 右子树
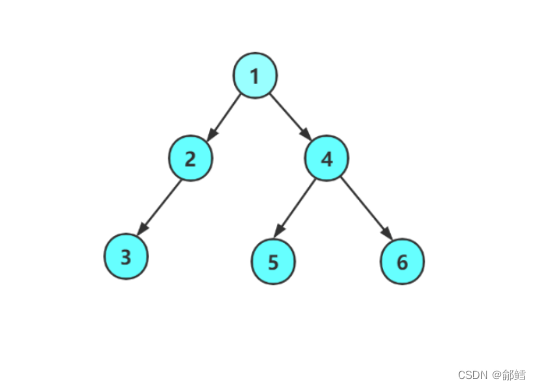
NULL 3 NULL 2 NULL 1 NULL 5 NULL 4 NULL 6 NULL
节点 1被分成根节点 (1)、左子树(2) 、右子树(4) ,先遍历1的左子树2,遇到节点2不能直接访问,得继续拆分 , 节点 2被分成根节点 (2)、左子树(3) 、右子树(NULL) ,遇到节点3,节点3又被分成根节点 (3)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,那什么样的情况,能直接访问左子树? 遇到空树就可以直接访问,因为空树不能再被拆分,是最小规模的子问题 。 所以第一个访问的是节点3的左子树(NULL) ,再到根节点(3) ,再到3的右子树(NULL) 。3的整棵树作为2的左子树, ,3这一整棵树走完了。2的左子树访问完了 ,就可以访问根节点2了 ,然后到2的右子树(NULL),2的整棵树作为1的左子树, ,2这一整棵树走完了 ,就可以访问根节点1了 ,然后到1的右子树(4) ,遇到节点4不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 4 又被分成根节点 (4)、左子树(5) 、右子树(6),遇到节点5不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 5 又被分成根节点 (5)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,然后访问5的左子树(NULL) ,、5(根节点)、5的右子树(NULL),5这一整棵树走完了。4的左子树访问完了 ,就可以访问根节点4了 ,然后到4的右子树(6),遇到节点6不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 6又被分成根节点 (6)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,然后访问6的左子树(NULL) ,、6(根节点)、6的右子树(NULL),6这一整棵树走完了,4的右子树访问完了 , 4这一整棵树作为1的右子树也访问完了
中序遍历访问的第一个一定是NULL ,因为任何一个节点都可以被视作根节点 ,有些书上中序遍历访问的第一个不是NULL ,是因为书上省略了
BTNode* CreateTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left= node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
//node3->right = node7;
return node1;
}
void PreOreder(BTNode* root) //根 左子树 右子树
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOreder(root->left);
PreOreder(root->right);
}
void InOreder(BTNode* root) //中序遍历 左子树 根 右子树
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOreder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOreder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreateTree();
/* PreOreder(root);*/
InOreder(root);
PostOreder(root);
return 0;
}
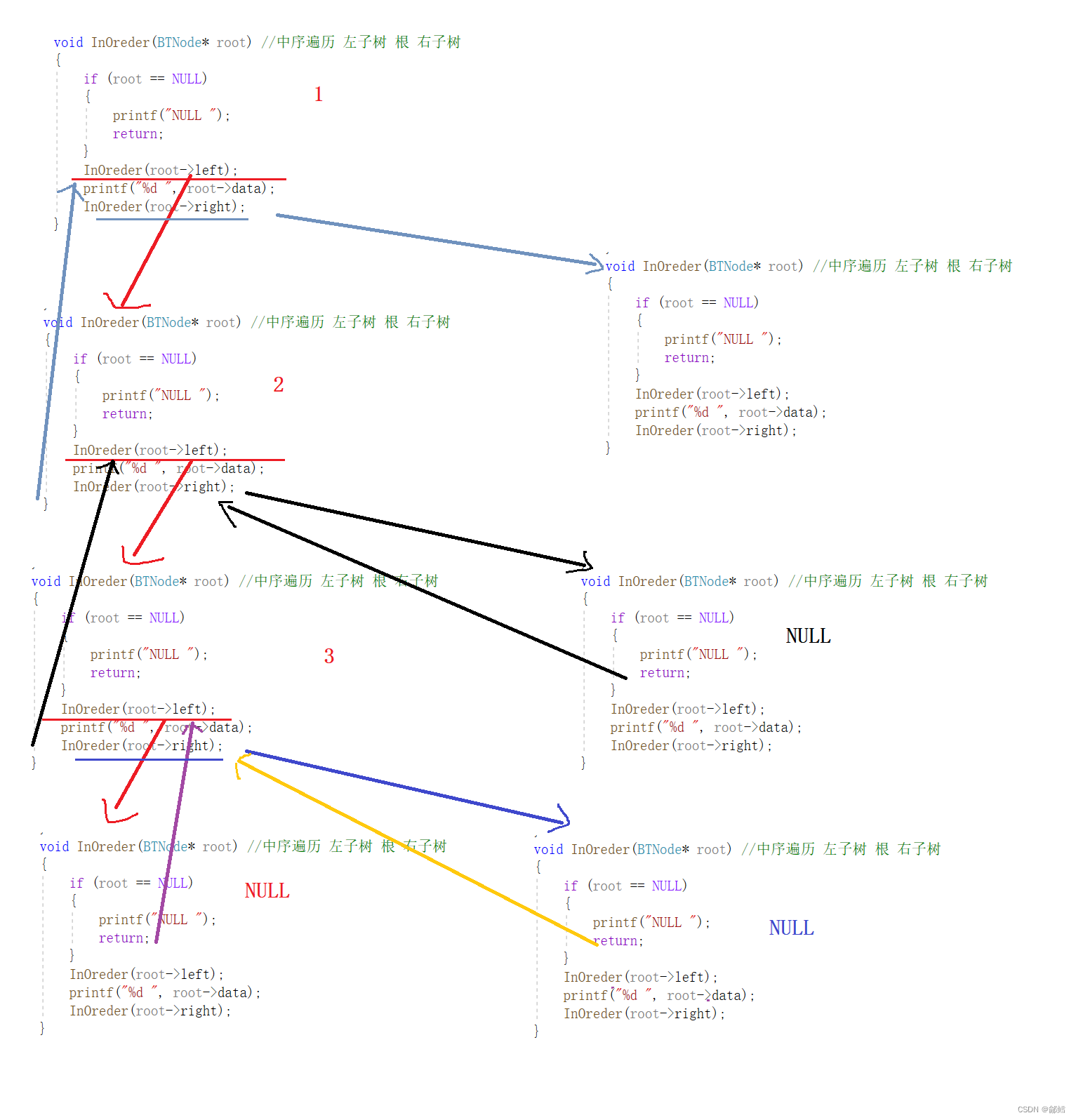
中序遍历递归展开图,以左子树为例,右子树并未画出
后序遍历
访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后
简单来说就是 左子树 右子树 根
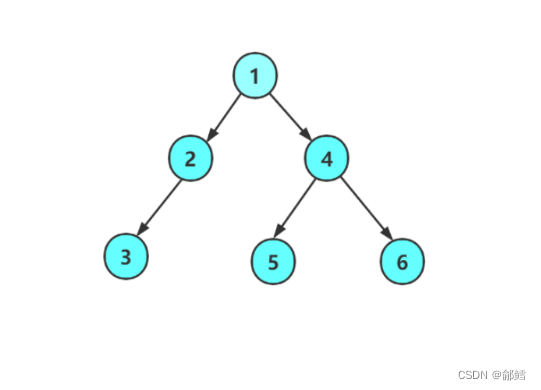
NULL NULL 3 NULL 2 NULL NULL 5 NULL NULL 6 4 1
遇到节点1不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点1又被分成根节点 (1)、左子树(2) 、右子树(4) ,遇到节点2不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 2被分成根节点 (2)、左子树(3) 、右子树(NULL) ,遇到节点3不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点3又被分成根节点 (3)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL), 先访问3的左子树(NULL) ,再访问3的右子树(NULL) ,然后才到根节点(3),3这一整棵树走完了。2的左子树访问完了 ,再访问2的右子树(NULL)了,然后才到根节点(2)。2的整棵树作为1的左子树, ,2这一整棵树走完了 ,就走到节点1,但是遇到节点1不能直接访问,然后走到1的右子树(4),但是遇到节点4不能直接访问 得继续拆分,节点 4 又被分成根节点 (4)、左子树(5) 、右子树(6),来到4的左子树节点5,还是不能直接访问 ,得继续拆分,节点 5 又被分成根节点 (5)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,先访问5的左子树(NULL) ,再访问5的右子树(NULL) ,然后才到根节点(5),5这一整棵树走完了。4的左子树访问完了 ,再访问4的右子树(6)了,遇到节点6不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 6又被分成根节点 (6)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL),先访问6的左子树(NULL) ,再访问6的右子树(NULL),然后才到根节点(6),6的整棵树作为4的右子树, ,6这一整棵树走完了 ,就走到节点4, 4的整棵树作为1的右子树, ,4这一整棵树走完了 ,就走到节点1
BTNode* CreateTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left= node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
//node3->right = node7;
return node1;
}
void PreOreder(BTNode* root) //根 左子树 右子树
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOreder(root->left);
PreOreder(root->right);
}
void InOreder(BTNode* root) //中序遍历 左子树 根 右子树
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOreder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOreder(root->right);
}
PostOreder(BTNode* root) // 后序遍历 左子树 右子树 根
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOreder(root->left);
PostOreder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreateTree();
/* PreOreder(root);*/
InOreder(root);
PostOreder(root);
return 0;
}
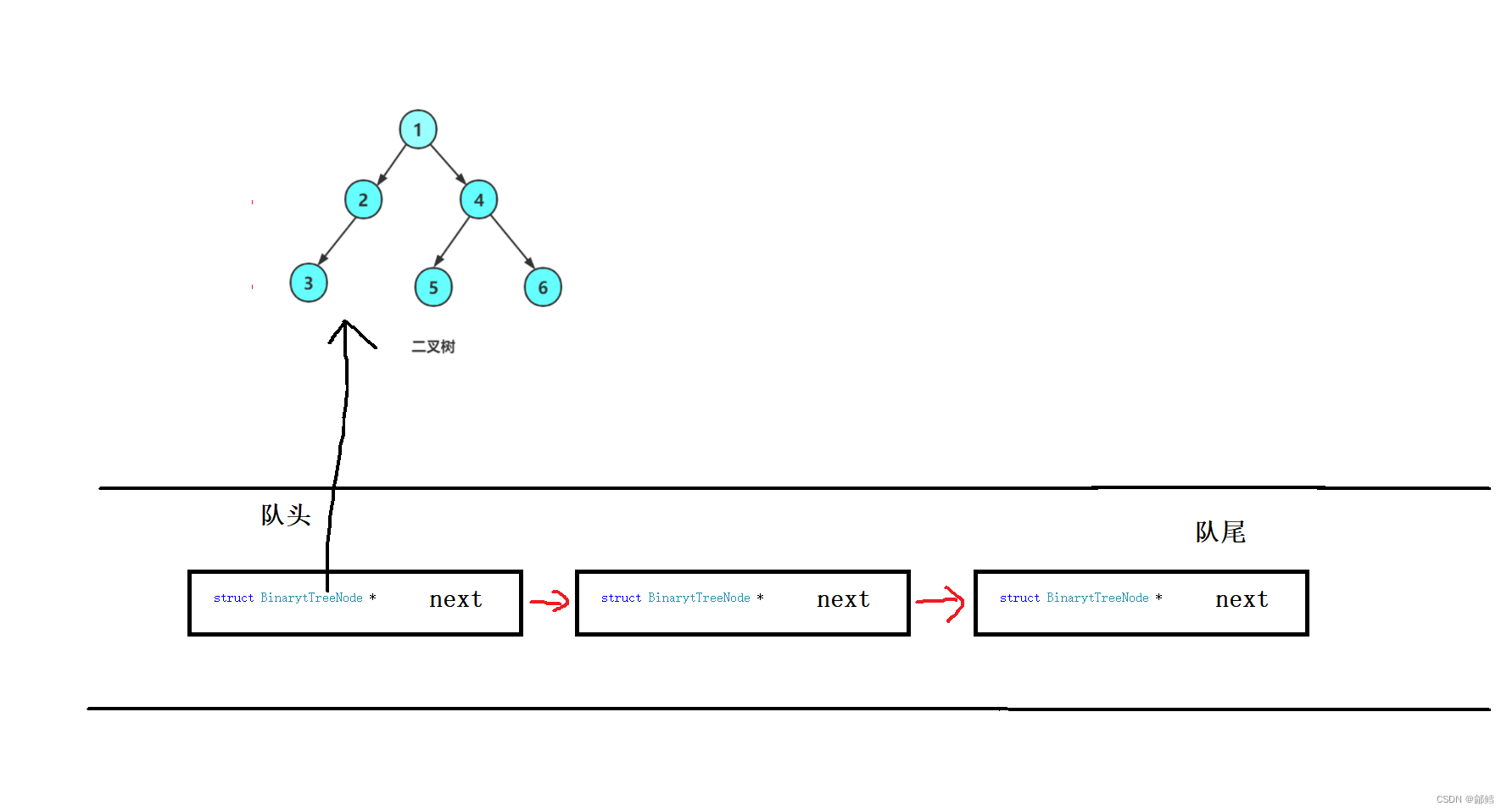
层序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6
层序遍历使用队列先进先出的特性,二叉树的上一层 出队,二叉树的下一层入队
根节点1入队 ,然后1节点出队 ,再把1节点的左孩子2 、右孩子4入队 , 再2节点出队 ,2的左孩子3入队 ,2的右孩子空树 ,空树就不入队了 ,4出队 ,4的左孩子5入队 ,右孩子6入队 ,
最后3出队 ,左右孩子都是空树就不入队了,5出队 ,左右孩子都是空树就不入队了,6出队 ,左右孩子都是空树就不入队了, 当所有节点出队也就结束了
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root) //层序遍历
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
//遍历
//不是空树
if (root)
QueuePush(&q ,root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q) )
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ",front->data);
if (front->left)//不是空树 入队
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right) //不是空树 入队
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestory(&q);
}
树节点个数
采用分治方法
分治法的设计思想是:将一个难以直接解决的大问题,分割成一些规模较小的相同问题,以便各个击破,分而治之。
分治策略是:对于一个规模为n的问题,若该问题可以容易地解决(比如说规模n较小)则直接解决,否则将其分解为k个规模较小的子问题,这些子问题互相独立且与原问题形式相同,递归地解这些子问题,然后将各子问题的解合并得到原问题的解。这种算法设计策略叫做分治法。
typedef int BinartTreeType;
typedef struct BinarytTreeNode
{
BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据
struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子
struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BinartTreeType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
//扩容成功
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreateTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
//node3->right = node7;
return node1;
}
//int TreeSize(BTNode* root, int* psize)
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// return;
// (*psize)++;
// TreeSize(root->left, psize);
// TreeSize(root->right, psize);
//}
int TreeSize(BTNode* root) //分治思想
{
return root == NULL ? 0 :
TreeSize(root->left )
+TreeSize(root->right)
+ 1; // +1 是加上自己
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreateTree();
printf("%d ", TreeSize(root));
return 0;
}
树的深度
采用分治思想 ,求出最长的那一条
当前树的高度 = 左右子树高度大的+1
typedef int BinartTreeType;
typedef struct BinarytTreeNode
{
BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据
struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子
struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BinartTreeType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
//扩容成功
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreateTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
//node3->right = node7;
return node1;
}
//int TreeHight(BTNode* root) //求整棵树的高度
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// return 0;
// }
// return TreeHight(root->left) > TreeHight(root->right)
// ? TreeHight(root->left) + 1: TreeHight(root->right) + 1;
//}
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if( root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight
? leftHeight + 1
: rightHeight + 1;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreateTree();
printf("%d ", TreeHeight(root));
return 0;
}
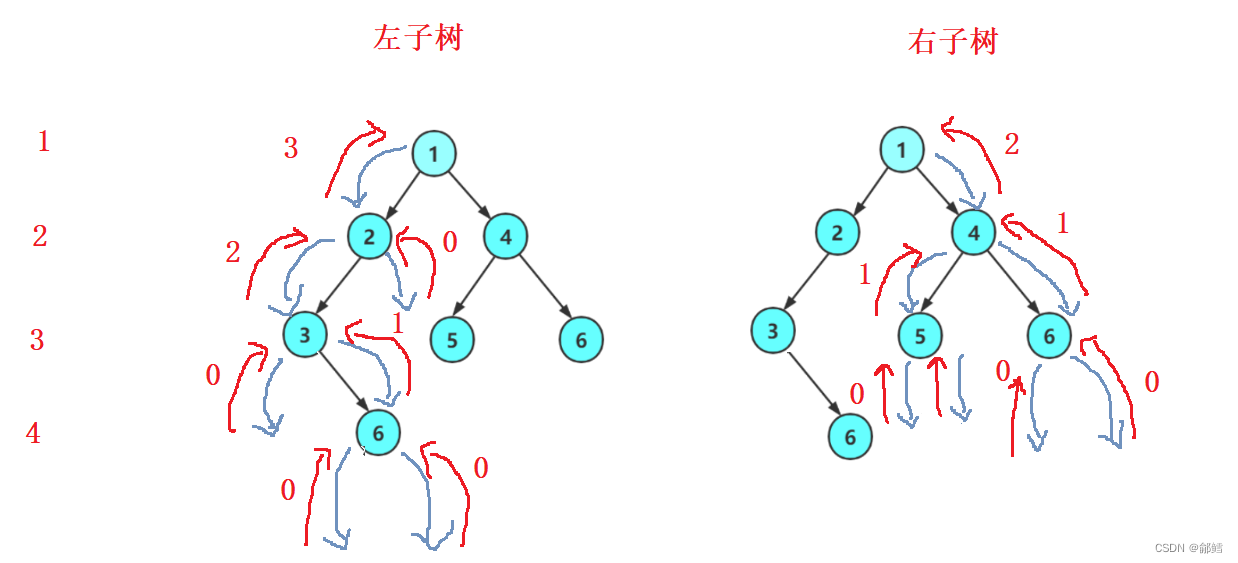
第K层节点个数
根的第K层节点个数 = 左子树的第K-1层个数 + 右子树的第K-1 层个数
typedef int BinartTreeType;
typedef struct BinarytTreeNode
{
BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据
struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子
struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BinartTreeType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
//扩容成功
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreateTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
node3->right = node7;
return node1;
}
int TreeKlevel(BTNode* root,int k) //第K层节点个数
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1) // 隐含root != NULL , 此时是第K层
return 1;
//左子树 K-1 个数 + 右子树K-1 个数
int leftKlevel = TreeKlevel(root->left, k - 1);
int rightKlevel = TreeKlevel(root->right, k - 1);
return leftKlevel + rightKlevel;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreateTree();
int k = 3;
printf("%d ", TreeKlevel(root,k));
return 0;
}
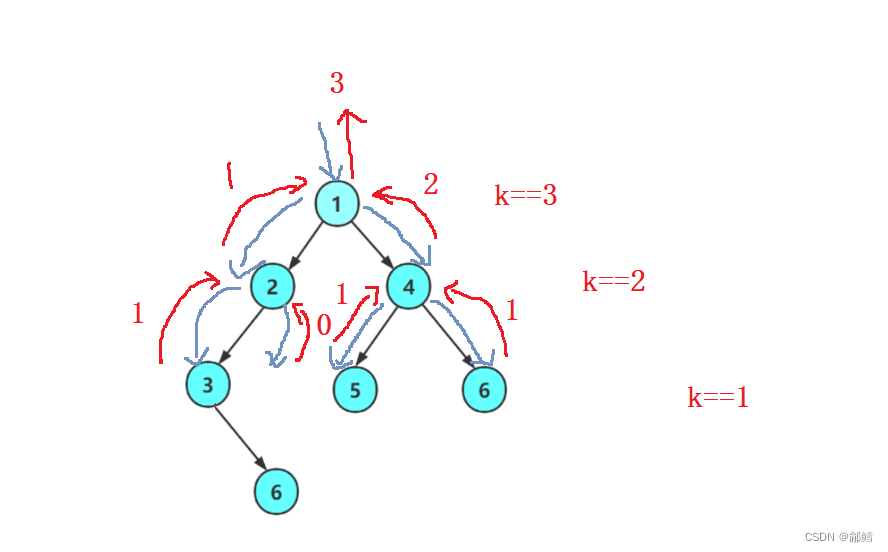
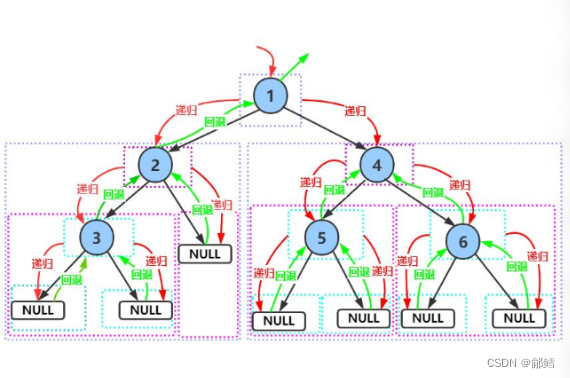
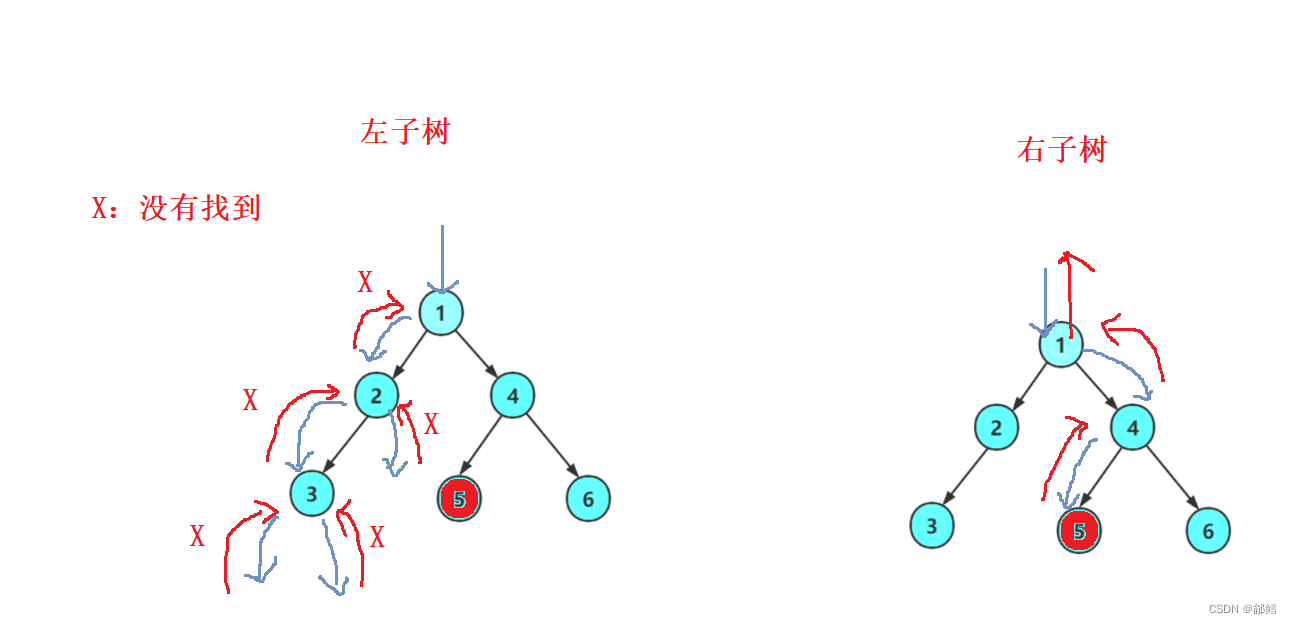
查找二叉树中的元素
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root , BinartTreeType x )//查找二叉树中的元素
{
//左子树 右子树 根
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
//保存
BTNode* lret = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
if (lret)
return lret;
//保存
BTNode* rret = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
if (rret)
return rret;
//没有找到
return NULL;
}
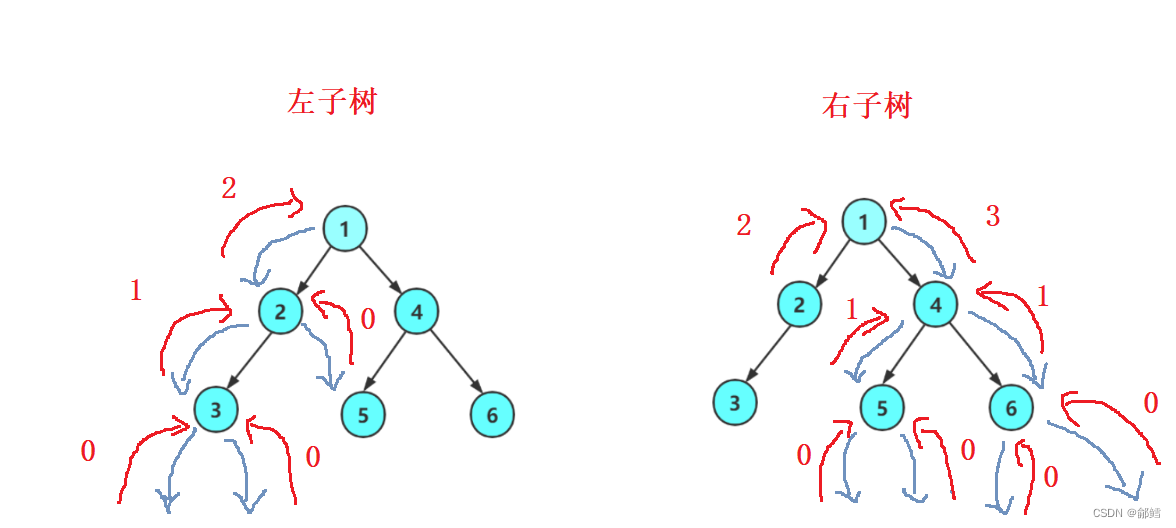
递归展开图:

完整代码
Test.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include"Queue.h"
typedef int BinartTreeType;
typedef struct BinarytTreeNode
{
BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据
struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子
struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BinartTreeType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
//扩容成功
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreateTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
node3->right = node7;
return node1;
}
//void PreOreder(BTNode* root) //根 左子树 右子树
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// printf("NULL ");
// return;
// }
// printf("%d ", root->data);
// PreOreder(root->left);
// PreOreder(root->right);
//}
//void InOreder(BTNode* root) //中序遍历 左子树 根 右子树
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// printf("NULL ");
// return;
// }
// InOreder(root->left);
// printf("%d ", root->data);
// InOreder(root->right);
//}
//
//void PostOreder(BTNode* root) // 后序遍历 左子树 右子树 根
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// printf("NULL ");
// return;
// }
// PostOreder(root->left);
// PostOreder(root->right);
// printf("%d ", root->data);
//}
//int TreeSize(BTNode* root, int* psize)
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// return;
// (*psize)++;
// TreeSize(root->left, psize);
// TreeSize(root->right, psize);
//}
//
//int TreeSize(BTNode* root) //分治思想
//{
// return root == NULL ? 0 :
// TreeSize(root->left)
// + TreeSize(root->right)
// + 1; // +1 是加上自己
//
//}
//int TreeHight(BTNode* root) //求整棵树的高度
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// return 0;
// }
// return TreeHight(root->left) > TreeHight(root->right)
// ? TreeHight(root->left) + 1: TreeHight(root->right) + 1;
//}
//int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
//{
// if( root == NULL)
// return 0;
//
// int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
// int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
//
// return leftHeight > rightHeight
// ? leftHeight + 1
// : rightHeight + 1;
//
//}
//int TreeKlevel(BTNode* root,int k) //第K层节点个数
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// return 0;
// if (k == 1) // 隐含root != NULL , 此时是第K层
// return 1;
// //左子树 K-1 个数 + 右子树K-1 个数
// int leftKlevel = TreeKlevel(root->left, k - 1);
// int rightKlevel = TreeKlevel(root->right, k - 1);
// return leftKlevel + rightKlevel;
//
//}
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root , BinartTreeType x )//查找二叉树中的元素
{
//左子树 右子树 根
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
//保存
BTNode* lret = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
if (lret)
return lret;
//保存
BTNode* rret = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
if (rret)
return rret;
//没有找到
return NULL;
}
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root) //层序遍历
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
//遍历
//不是空树
if (root)
QueuePush(&q ,root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q) )
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ",front->data);
if (front->left)//不是空树 入队
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right) //不是空树 入队
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestory(&q);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreateTree();
/* PreOreder(root);*/
// InOreder(root);
// PostOreder(root);
//int size1 = 0;
//TreeSize(root, &size1);
//printf("%d ", size1);
//printf("%d ", TreeSize(root));
//printf("%d ", TreeHeight(root));
/*int k = 3;
printf("%d ", TreeKlevel(root,k));*/
/*printf("%p ", BinaryTreeFind(root, 2));*/
LevelOrder(root);
return 0;
}
Queue.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct BinarytTreeNode * QueueNodeTypeData;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QueueNodeTypeData data;
}QueueNodeType;
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNodeType * tail; // 队尾
QueueNodeType * head; //队头
int size;
} Queue; // 链式结构:表示队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq); // 初始化
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq); //队列的销毁
void QueuePush(Queue* pq , QueueNodeTypeData x ); // 队尾入队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq); //队头出队列
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);//获取队列中有效元素个数
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq); // 判断队列是否为空
QueueNodeTypeData QueueFront(Queue* pq); //获取队列头部元素
QueueNodeTypeData QueueBack(Queue* pq); //获取队列尾部元素
Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq) //队列的销毁
{
assert(pq);
QueueNodeType * cur = pq->head;
//遍历
while (cur)
{
QueueNodeType* next = cur->next; //保存下一个节点的地址
free(cur); //释放当前节点
cur = next;
}
pq->tail = pq->head = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QueueNodeTypeData x) // 入队
{
assert(pq);
QueueNodeType* newnode =(QueueNodeType*) malloc( sizeof(QueueNodeType) );
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf(" malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//扩容成功
//第一次入队
if ( pq->head == NULL)
{
assert(pq->tail == NULL); //pq->head ==NULL , pq->tail != NULL ,就是出问题了
pq->tail = pq->head = newnode;
}
else //非第一次入队
{
pq->tail->next = newnode; // 类似尾插
pq->tail = newnode; // 更新tail 指针
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq) //队头出队列
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head != NULL);
//只有一个节点
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->tail); //出队
pq->tail = pq->head = NULL;
}
// 多个节点
else
{
QueueNodeType* next = pq->head->next; // 保存下一个节点的地址
free(pq->head); // 出队
pq->head = NULL;
pq->head = next; //更新pq->head ,往后走
}
pq->size--;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)//获取队列中有效元素个数
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
//bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) // 判断队列是否为空
//{
// assert(pq);
//
// if (pq->head == 0)
// {
// return true;
// }
// else
// {
// return false;
// }
//}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
QueueNodeTypeData QueueFront(Queue* pq) //获取队列头部元素
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); //防止队列为空
return pq->head->data;
}
QueueNodeTypeData QueueBack(Queue* pq) //获取队列尾部元素
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); //防止队列为空
return pq->tail->data;
}

如果你觉得这篇文章对你有帮助,不妨动动手指给点赞收藏加转发,给鄃鳕一个大大的关注
你们的每一次支持都将转化为我前进的动力!!!