2025-03-21 Unity 序列化 —— 自定义2进制序列化
文章目录
- 前言
- 1 项目结构
- 1.1 整体
- 1.2 代码
- 2 实现
- 2.1 Processor
- 2.1.1 BaseType
- 2.1.2 CollectionType
- 2.1.3 CustomType
- 2.2 ByteFormatter
- 2.3 ByteHelper
- 3 使用
前言
BinaryFormatter 类可以将 C# 类对象快速转换为字节数组数据。
在网络开发时,不会使用 BinaryFormatter 进行数据序列化和反序列化。因为客户端和服务端的开发语言多数情况下不同,BinaryFormatter 序列化的数据无法兼容其它语言。
因此,需要自定义序列化方式。
BinaryFormatter 参考链接:2023-05-27 Unity 2进制4——类对象的序列化与反序列化_unity 二进制序列化-CSDN博客。
- 项目链接:https://github.com/zheliku/ByteHelper。
- Unity 版本:6000.0.42f1。
1 项目结构
1.1 整体
- Scenes(示例场景)
- Scripts(脚本)
- ByteHelper(工具脚本)
- Test(测试脚本)
1.2 代码
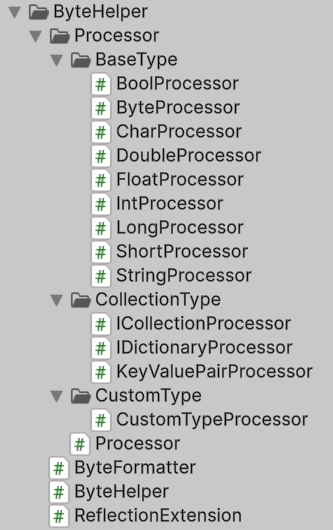
- Processor(存放对应类型的 Processor)
- BaseType(基本类型的 Processor)
- CollectionType(集合类型的 Processor)
- CustomType(自定义类型的 Processor)
- Processor.cs(抽象基类,用于处理对象和字节数组之间的转换)
- ByteFormatter.cs(存储所有 Processor,并依据类型进行 Write 与 Read)
- ByteHelper.cs(封装序列化 API)
- ReflectionExtension.cs(反射方法拓展)
2 实现
2.1 Processor
一个 Processor 用于处理一种类型的序列化,其包含以下 3 种方法:
-
GetBytesLength
获取对象在字节数组中占用的字节数。
-
Write
将对象写入 bytes 数组。
-
Read
从 bytes 数组中读取对象。
// 抽象类 Processor,用于处理对象和字节数组之间的转换
public abstract class Processor
{
public abstract int GetBytesLength(object value);
public abstract int Write(byte[] bytes, object value, int index);
public abstract int Read(byte[] bytes, int index, out object value);
}
使用泛型版本标识每个 Processor 处理的类型:
public abstract class Processor<TValue> : Processor
{
public abstract int GetBytesLength(TValue value);
public abstract int Write(byte[] bytes, TValue value, int index);
public abstract int Read(byte[] bytes, int index, out TValue value);
public override int GetBytesLength(object value)
{
return GetBytesLength((TValue) value);
}
public override int Write(byte[] bytes, object value, int index)
{
return Write(bytes, (TValue) value, index);
}
public override int Read(byte[] bytes, int index, out object value)
{
int result = Read(bytes, index, out TValue typedValue);
value = typedValue;
return result;
}
}
2.1.1 BaseType
以 int、string 类型为例:
IntProcessor
-
GetBytesLength
int 类型使用 4 个子节存储,可直接返回 4,也可使用
sizeof(int)。 -
Write
直接转换为子节,写入 bytes 中的 index 位置。返回值为写入后下一处的位置。
-
Read
直接将 bytes 中 index 位置的数据读取。返回值为读取后下一处的位置。
public class IntProcessor : Processor<int>
{
public override int GetBytesLength(int value)
{
return sizeof(int);
}
public override int Write(byte[] bytes, int value, int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index);
return index + sizeof(int);
}
public override int Read(byte[] bytes, int index, out int value)
{
value = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, index);
return index + sizeof(int);
}
}
StringProcessor
string 类型长度可变,因此需要先写入长度(int 类型),再写入内容。
- GetBytesLength:int 长度 + 字符串长度。
- Write:先写入长度,后写入内容。
- Read:先读取长度,后读取内容。
public class StringProcessor : Processor<string>
{
public override int GetBytesLength(string value)
{
return sizeof(int) + value.Length;
}
public override int Write(byte[] bytes, string value, int index)
{
BitConverter.GetBytes(value.Length).CopyTo(bytes, index);
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(value).CopyTo(bytes, index + sizeof(int));
return index + sizeof(int) + value.Length;
}
public override int Read(byte[] bytes, int index, out string value)
{
int length = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, index);
value = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes, index + sizeof(int), length);
return index + sizeof(int) + length;
}
}
2.1.2 CollectionType
以 ICollectionProcessor 为例,泛型集合类型需要记录集合本身的 Type 与元素的 Type,因此 ICollectionProcessor 具有 2 个泛型参数。
-
GetBytesLength
集合长度可变,因此也先写入长度,后顺序写入集合元素。
-
Write
先写入长度,后顺序写入集合元素。
使用
ByteFormatter.Write方法,依据元素类型,自动调用对应的 Processor 写入内容。 -
Read
先读取长度,后顺序读取集合元素。
使用
ByteFormatter.Read方法,依据元素类型,自动调用对应的 Processor 读取内容。
public class ICollectionProcessor<TCollection, TValue> : Processor<TCollection> where TCollection : ICollection<TValue>
{
public override int GetBytesLength(TCollection value)
{
var length = sizeof(int);
foreach (var item in value)
{
length += ByteFormatter.GetBytesLength(item);
}
return length;
}
public override int Write(byte[] bytes, TCollection value, int index)
{
int count = value.Count;
// 写长度
BitConverter.GetBytes(count).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(int); // 留 1 个 int 位置用于写长度
// 写内容
foreach (var item in value)
{
index = ByteFormatter.Write(bytes, item, index);
}
return index;
}
public override int Read(byte[] bytes, int index, out TCollection value)
{
// 1. 读取长度(元素数量)
int length = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
// 2. 读取内容
value = (TCollection) Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(TCollection));
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
index = ByteFormatter.Read(bytes, index, typeof(TValue), out var item);
value.Add((TValue) item);
}
return index;
}
}
2.1.3 CustomType
自定义类型默认序列化所有的字段,且需要添加 [ByteSerializable] 特性。
-
GetBytesLength
长度可变,因此也先写入长度,后顺序写入字段。
-
Write
先写入长度,后使用反射获取所有字段信息,依次写入字段内容。
反射方法
value.GetFieldValues()在 ReflectionExtension.cs 中封装,默认获取所有字段的值。使用
ByteFormatter.Write方法,依据字段类型,自动调用对应的 Processor 写入。 -
Read
先读取长度,后使用反射获取所有字段信息,依次读取字段内容。
反射方法
obj.GetFieldInfos()在 ReflectionExtension.cs 中封装,默认获取所有字段的信息。使用
ByteFormatter.Read方法,依据字段类型,自动调用对应的 Processor 读取。考虑到值类型,在读取时需要装箱,否则反射赋值时,会将内容赋值给 fieldInfo.SetValue 方法中的临时变量。
public class CustomTypeProcessor<TValue> : Processor<TValue>
{
public override int GetBytesLength(TValue value)
{
return sizeof(int) + value.GetFieldValues().Sum(v => ByteFormatter.GetBytesLength(v));
}
public override int Write(byte[] bytes, TValue value, int index)
{
// 先写长度,以便读取
BitConverter.GetBytes(GetBytesLength(value)).CopyTo(bytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
var fieldValues = value.GetFieldValues();
foreach (var fieldValue in fieldValues)
{
index = ByteFormatter.Write(bytes, fieldValue, index);
}
return index;
}
public override int Read(byte[] bytes, int index, out TValue value)
{
var obj = (object) Activator.CreateInstance<TValue>(); // 装箱,以防 TValue 为值类型
index += sizeof(int);
var fieldInfos = obj.GetFieldInfos();
foreach (var fieldInfo in fieldInfos)
{
index = ByteFormatter.Read(bytes, index, fieldInfo.FieldType, out var v);
fieldInfo.SetValue(obj, v);
}
value = (TValue) obj; // 拆箱,还原 value
return index;
}
}
2.2 ByteFormatter
管理所有类型的 Processor,使用字典存储预置基础类型:
public class ByteFormatter
{
// 定义字典,用于存储预置类型的处理器
public static readonly Dictionary<Type, object> PRIMITIVE_PROCESSORS = new Dictionary<Type, object>()
{
{ typeof(int), new IntProcessor() },
{ typeof(short), new ShortProcessor() },
{ typeof(long), new LongProcessor() },
{ typeof(float), new FloatProcessor() },
{ typeof(double), new DoubleProcessor() },
{ typeof(bool), new BoolProcessor() },
{ typeof(char), new CharProcessor() },
{ typeof(byte), new ByteProcessor() },
{ typeof(string), new StringProcessor() },
};
...
}
依据传入类型,提供对应的 Processor,若不存在则创建。
- 在预置类型的字典中,直接读取
public class ByteFormatter
{
// 根据类型获取对应的处理器
public static Processor<T> GetProcessor<T>()
{
return (Processor<T>) GetProcessor(typeof(T));
}
public static Processor GetProcessor(Type type)
{
// 在预置类型的字典中,直接读取
if (PRIMITIVE_PROCESSORS.TryGetValue(type, out object value))
{
return (Processor) value;
}
}
}
-
优先处理字典类型,并且先处理 KeyValuePair。
若字典中存在,则直接读取,否则创建 Processor 添加到字典中再返回。
// 如果类型是 KeyValuePair,则使用 KeyValuePairProcessor
if (type.IsGenericType && type.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(KeyValuePair<,>))
{
var processorType = typeof(KeyValuePairProcessor<,>).MakeGenericType(type.GetGenericArguments());
var processor = (Processor) Activator.CreateInstance(processorType);
PRIMITIVE_PROCESSORS.Add(type, processor); // 添加到字典中
return processor;
}
// 如果类型是字典,则使用 IDictionaryProcessor
if (type.IsAssignableToGenericInterface(typeof(IDictionary<,>)))
{
var processorType = typeof(IDictionaryProcessor<,,>).MakeGenericType(type, type.GetGenericArguments()[0], type.GetGenericArguments()[1]);
var processor = (Processor) Activator.CreateInstance(processorType);
PRIMITIVE_PROCESSORS.Add(type, processor); // 添加到字典中
return processor;
}
-
对于集合类型与用户自定义类型,同理。
对于用户自定义类型,需要继承
[ByteSerializable]特性。也可以根据需要自定义其他方式。
// 如果是集合类型,则使用 ICollectionProcessor
if (type.IsAssignableToGenericInterface(typeof(ICollection<>)))
{
var processorType = typeof(ICollectionProcessor<,>).MakeGenericType(type, type.GetGenericArguments()[0]);
var processor = (Processor) Activator.CreateInstance(processorType);
PRIMITIVE_PROCESSORS.Add(type, processor); // 添加到字典中
return processor;
}
// 如果拥有 ByteSerializableAttribute 特性,则使用 CustomTypeProcessor
if (type.HasAttribute<ByteSerializableAttribute>())
{
var processorType = typeof(CustomTypeProcessor<>).MakeGenericType(type);
var processor = (Processor) Activator.CreateInstance(processorType);
PRIMITIVE_PROCESSORS.Add(type, processor); // 添加到字典中
return processor;
}
提供 Write 和 Read 方法,依据参数类型,自动获取对应 Processor 处理。
public static int Write<T>(byte[] bytes, T value, int index)
{
return GetProcessor<T>().Write(bytes, value, index);
}
public static int Write(byte[] bytes, object value, int index)
{
return GetProcessor(value.GetType()).Write(bytes, value, index);
}
public static int Read<T>(byte[] bytes, int index, out T value)
{
return GetProcessor<T>().Read(bytes, index, out value);
}
public static int Read(byte[] bytes, int index, Type type, out object value)
{
return GetProcessor(type).Read(bytes, index, out value);
}
2.3 ByteHelper
封装序列化方法。
public class ByteHelper
{
public const string EXTENSION = ".bytes";
public static string BinarySavePath { get; set; } = Application.persistentDataPath + "/Binary";
public static byte[] Serialize<TData>(TData data)
{
var processor = ByteFormatter.GetProcessor<TData>();
var bytes = new byte[processor.GetBytesLength(data)];
processor.Write(bytes, data, 0);
return bytes;
}
public static TData Deserialize<TData>(byte[] bytes)
{
ByteFormatter.Read<TData>(bytes, 0, out var value);
return value;
}
public static void SaveBytes<TData>(string filePath, TData data, string extension = EXTENSION)
{
string fullPath = Path.Combine(BinarySavePath, filePath);
fullPath = Path.ChangeExtension(fullPath, EXTENSION);
var directory = Path.GetDirectoryName(fullPath);
if (directory != null && !Directory.Exists(directory))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(directory);
}
byte[] bytes = Serialize(data);
File.WriteAllBytes(fullPath, bytes);
#if UNITY_EDITOR
UnityEditor.AssetDatabase.Refresh();
#endif
}
public static TData LoadBytes<TData>(string filePath, string extension = ByteHelper.EXTENSION)
{
string fullPath = Path.Combine(BinarySavePath, filePath);
fullPath = Path.ChangeExtension(fullPath, EXTENSION);
if (!File.Exists(fullPath))
{ // 不存在文件,则警告,并返回默认值
Debug.LogWarning($"ByteHelper: Can't find path \"{fullPath}\"");
return default(TData);
}
byte[] bytes = File.ReadAllBytes(fullPath);
return Deserialize<TData>(bytes);
}
}
3 使用
以 CustomType 为例,打开 CustomType 场景,点击 “TestScript” 物体,右侧编辑你想要的数据。
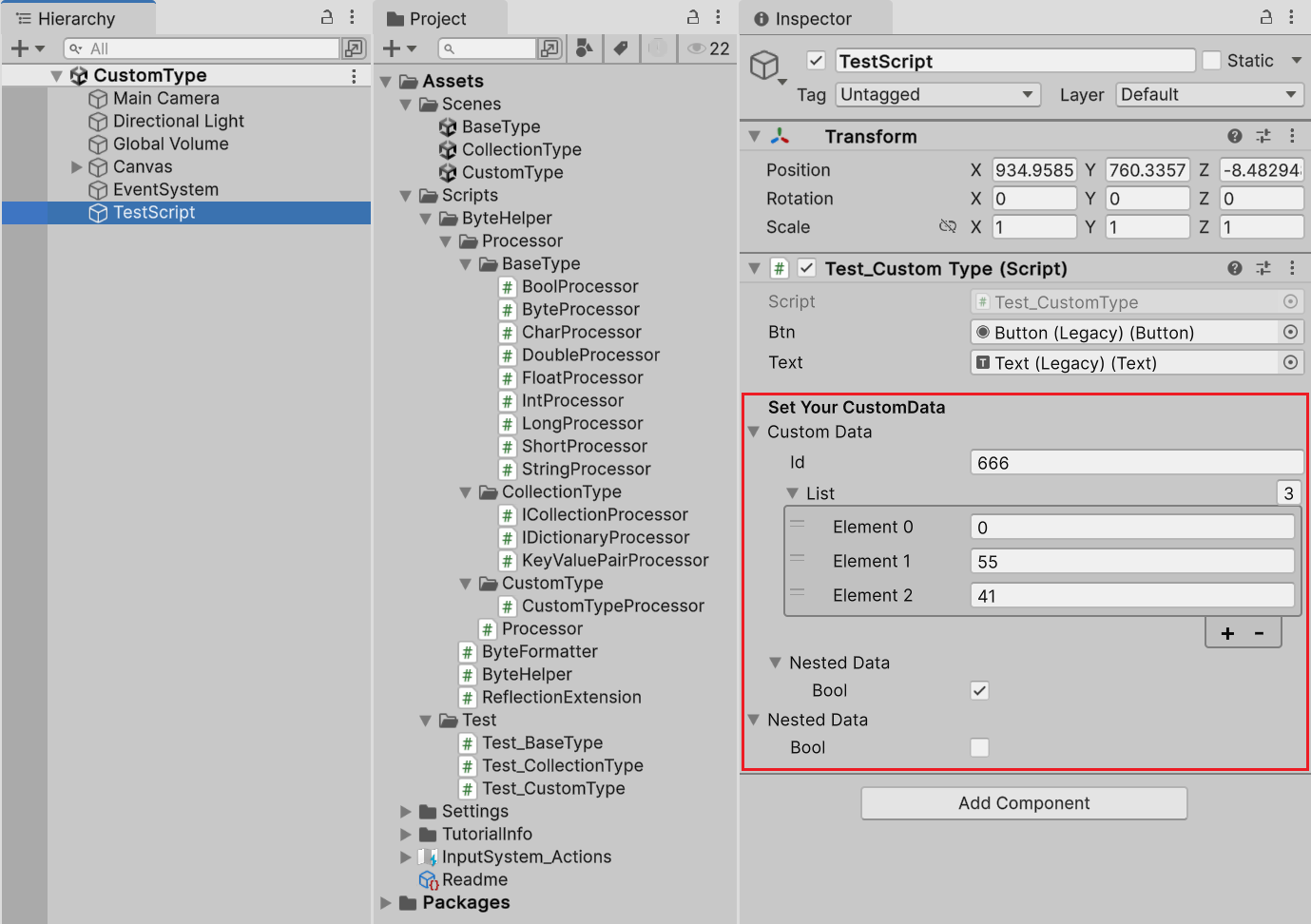
运行场景,会自动序列化数据,对应脚本如下:
[Serializable] [ByteSerializable]
public class CustomData
{
public int Id;
private string _name;
public List<int> List = new List<int>();
public NestedData NestedData; // Supports nested types
public string Name
{
get => _name;
set => _name = value;
}
public override string ToString() {...}
}
[Serializable] [ByteSerializable]
public struct NestedData
{
public bool Bool;
public override string ToString() {...}
}
public class Test_CustomType : MonoBehaviour
{
public Button Btn;
public Text Text;
[Header("Set Your CustomData")]
public CustomData CustomData;
public NestedData NestedData;
private void Start()
{
CustomData.Name = "zheliku"; // 设置私有字段
SerializeData();
Text.text = "Serialize Data Success!";
Btn.onClick.AddListener(OnClick);
}
// 序列化数据,保存到 CustomType 目录下。
private void SerializeData()
{
ByteHelper.SaveBytes($"CustomType/{nameof(CustomData)}", CustomData);
ByteHelper.SaveBytes($"CustomType/{nameof(NestedData)}", NestedData);
}
// 点击按钮时,显示反序列化数据
public void OnClick()
{
Text.text = "CustomData: " + ByteHelper.LoadBytes<CustomData>($"CustomType/{nameof(CustomData)}") + "\n\n" +
"NestedData: " + ByteHelper.LoadBytes<NestedData>($"CustomType/{nameof(NestedData)}");
}
}
点击按钮,即可显示反序列化数据:
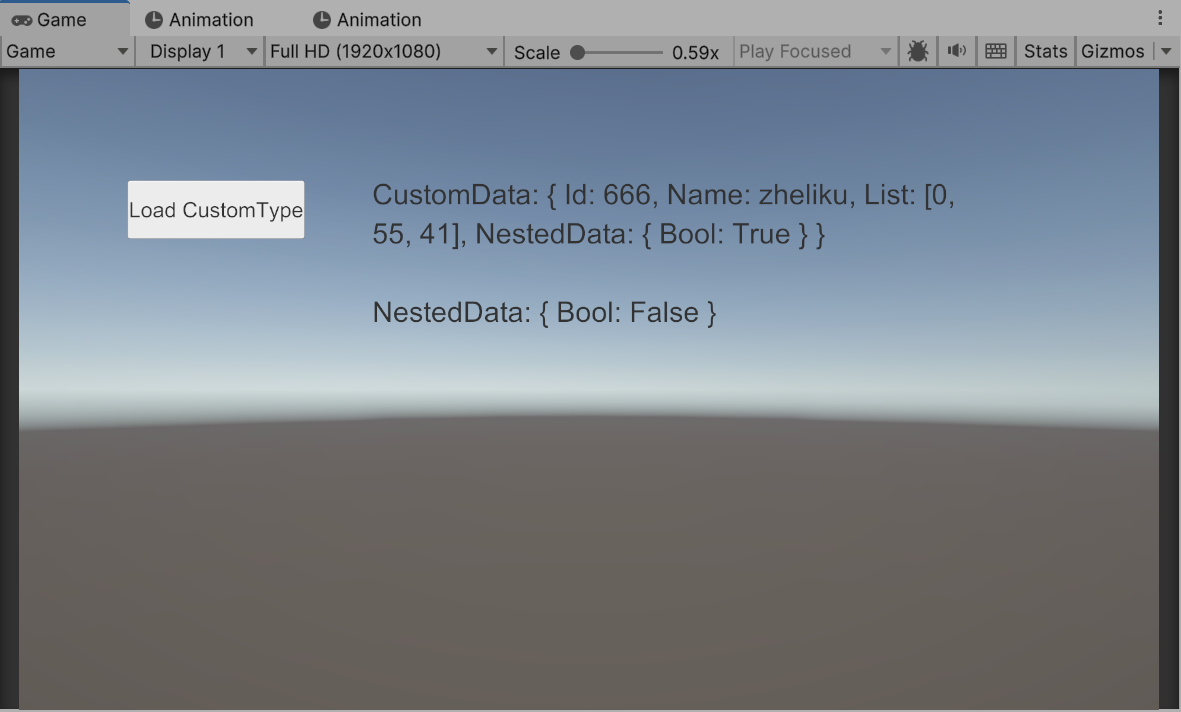
点击 “ByteHelper/Open Binary Folder” 可打开序列化数据存储目录。
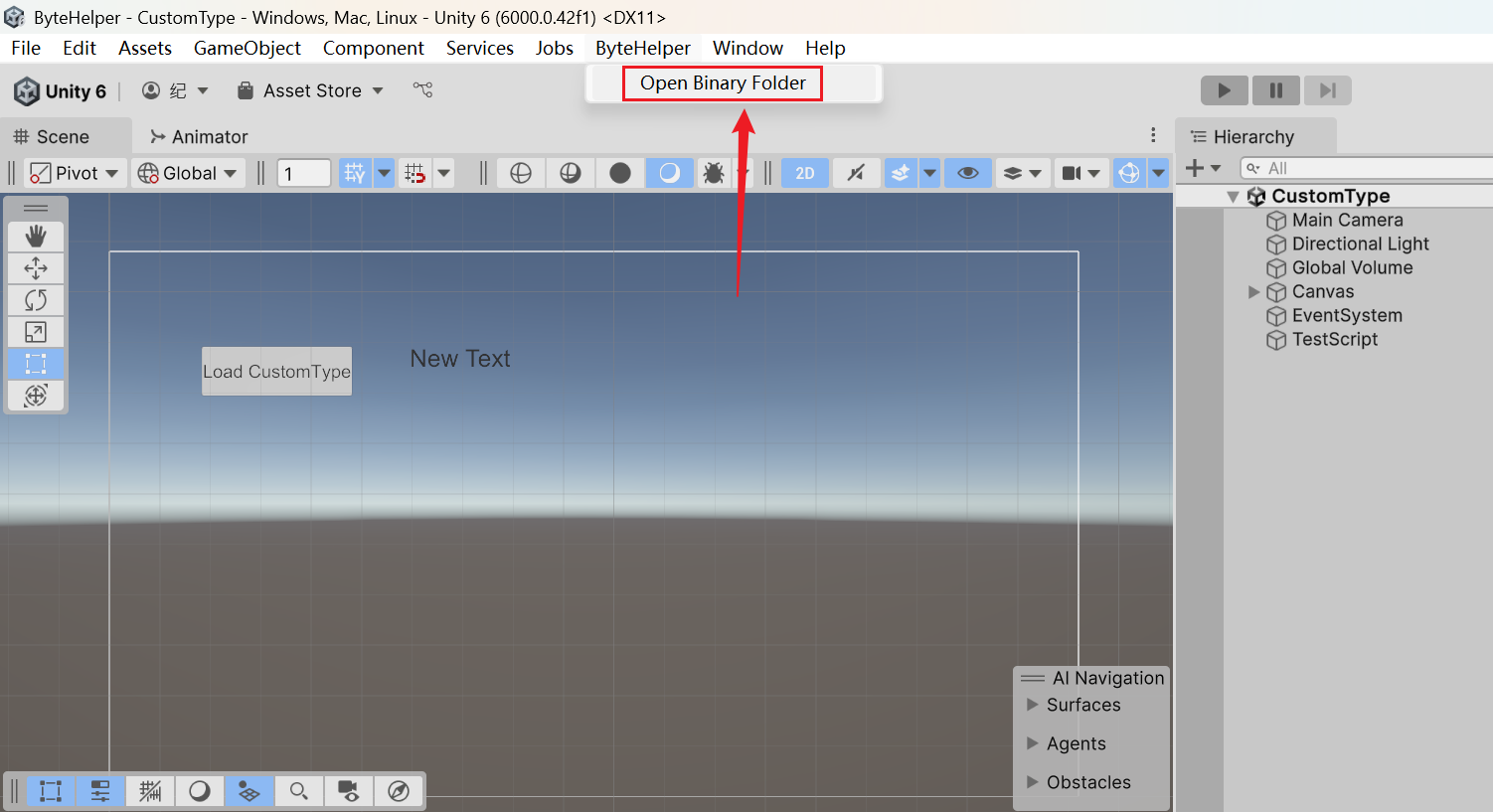
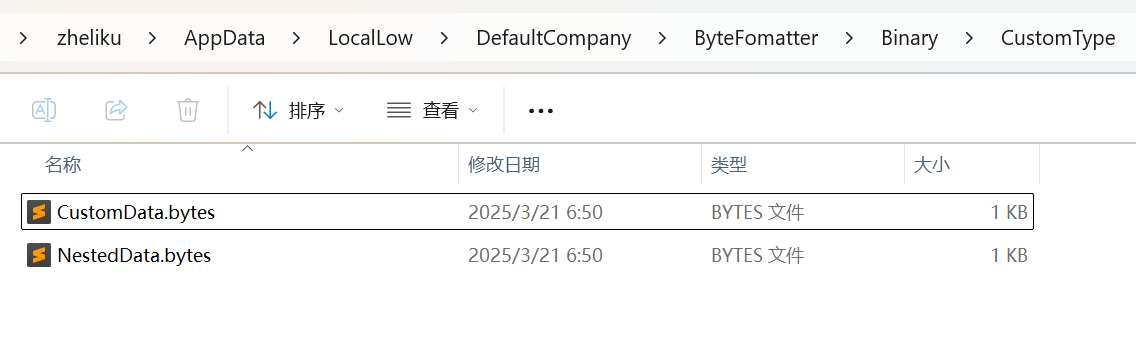
CustomType 保存在 “CustomType” 目录下。
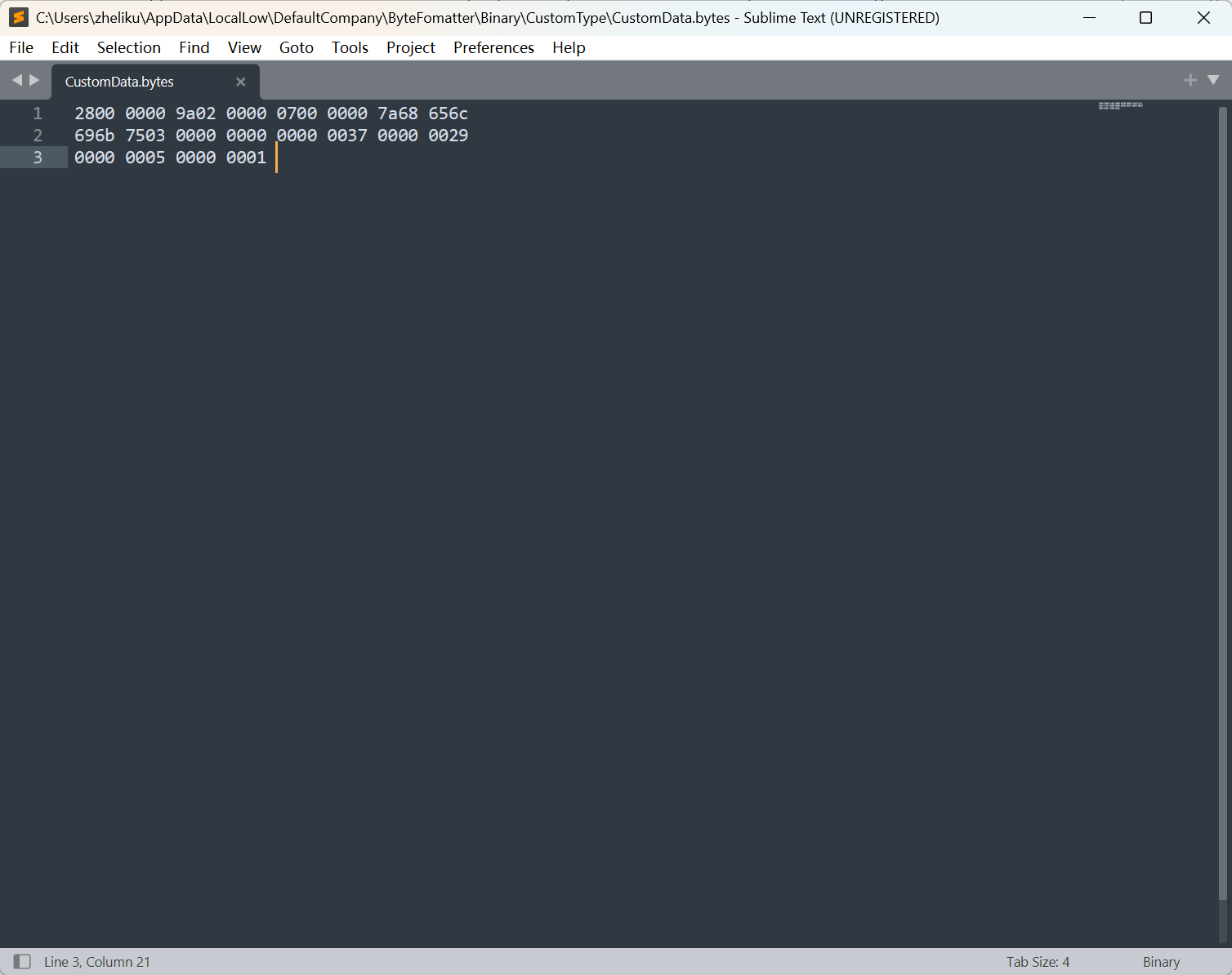
CustomData 的序列化内容如下:
根据需要可自行扩展 Processor。
