【LeetCode每日一题合集】2023.10.16-2023.10.22(只出现一次的数字Ⅲ)
文章目录
- 260. 只出现一次的数字 III⭐(异或)🐂
- 2652. 倍数求和
- 解法1——枚举模拟
- 解法2—— O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)容斥原理
- 相似题目——1201. 丑数 III(二分查找+容斥原理)
- 2530. 执行 K 次操作后的最大分数
- 解法1——贪心+优先队列
- 解法2—— O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)空间原地堆化
- 1726. 同积元组(哈希表+组合数学)
- 2525. 根据规则将箱子分类(按题意模拟,分类讨论)
- 2316. 统计无向图中无法互相到达点对数
- 解法1——并查集
- 解法2——dfs求连通块大小
- 1402. 做菜顺序
- 解法1——动态规划
- 解法2——贪心⭐
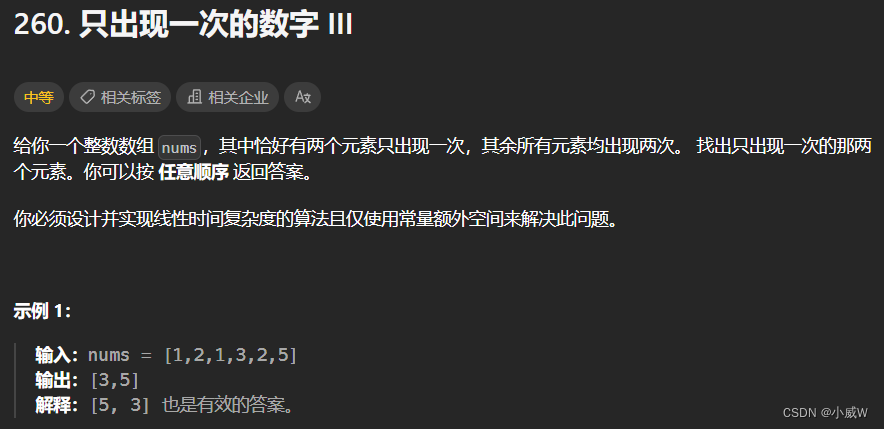
260. 只出现一次的数字 III⭐(异或)🐂
https://leetcode.cn/problems/single-number-iii/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-10-16
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10^4
-2^31 <= nums[i] <= 2^31 - 1
除两个只出现一次的整数外,nums 中的其他数字都出现两次
类似分治的思想。
先将数组全部异或,得出的结果是两个只出现一次数字的异或结果。
其中一定有1,因为这两个数字不同。
取出其最低位的1作为判断标准对原数组分组(实际上任意位的1都可以),分成的两组分别包括这两个只出现一次的数字。
这样就把问题转换成了两个 136. 只出现一次的数字
class Solution {
public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int xor = 0;
for (int num: nums) xor ^= num;
int mask = xor & (-xor); // 获取最低位的1
int[] ans = new int[2];
for (int num: nums) {
if ((num & mask) == 0) ans[0] ^= num;
else ans[1] ^= num;
}
return ans;
}
}
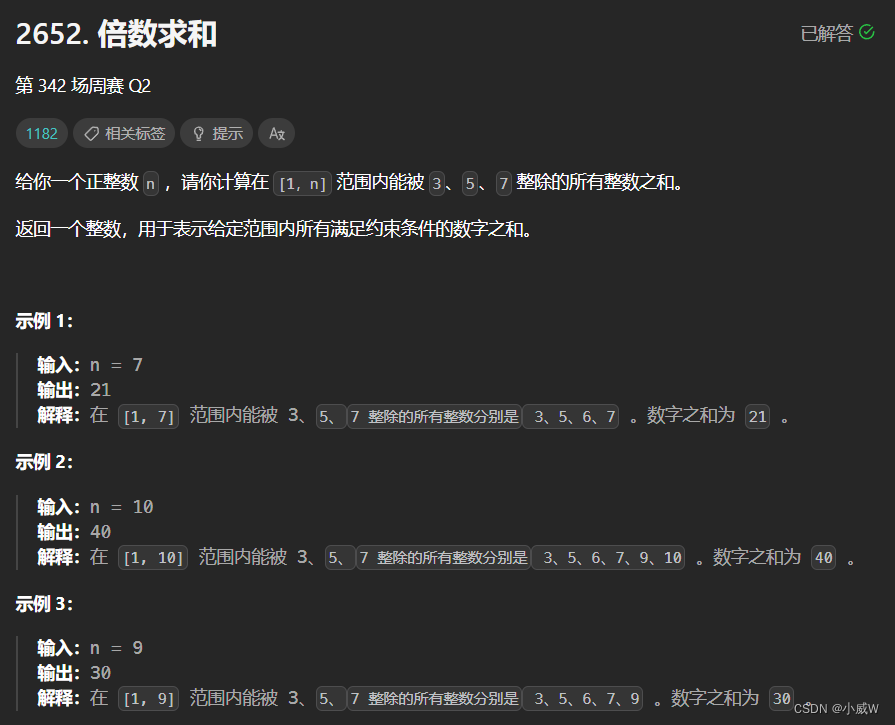
2652. 倍数求和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-multiples/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-10-17
提示:
1 <= n <= 10^3
解法1——枚举模拟
class Solution {
public int sumOfMultiples(int n) {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (i % 3 == 0 || i % 5 == 0 || i % 7 == 0) ans += i;
}
return ans;
}
}
解法2—— O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)容斥原理
class Solution {
int n;
public int sumOfMultiples(int n) {
this.n = n;
return s(3) + s(5) + s(7) - s(15) - s(21) - s(35) + s(105);
}
// 计算从x~(n/x)x,共n/x项
public int s(int x) {
return n / x * (x + n / x * x) / 2;
}
}
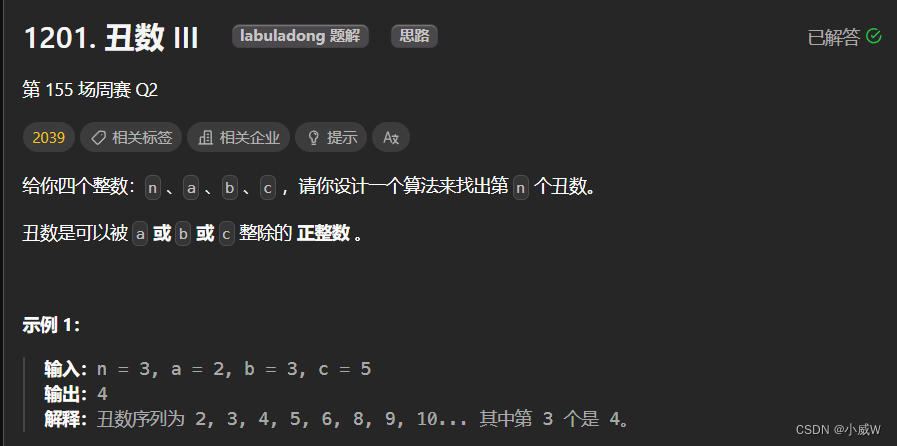
相似题目——1201. 丑数 III(二分查找+容斥原理)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/ugly-number-iii/description/
提示:
1 <= n, a, b, c <= 10^9
1 <= a * b * c <= 10^18
本题结果在 [1, 2 * 10^9] 的范围内
为什么会想到二分?
因为直接求答案不好求,但是我们可以判断1~x的范围内是否有n个丑数。
class Solution {
public int nthUglyNumber(int n, int a, int b, int c) {
long x = lcm(a, b), y = lcm(b, c), z = lcm(a, c), q = lcm(x, y);
long l = 1, r = (long)2e9;
while (l < r) {
long mid = l + r >> 1;
long aa = mid / a, bb = mid / b, cc = mid / c, xx = mid / x, yy = mid / y, zz = mid / z, qq = mid / q;
long s = aa + bb + cc - xx - yy - zz + qq;
if (s < n) l = mid + 1;
else r = mid;
}
return (int)l;
}
public long gcd(long a, long b) {
return b == 0? a: gcd(b, a % b);
}
public long lcm(long a, long b) {
return a / gcd(a, b) * b;
}
}
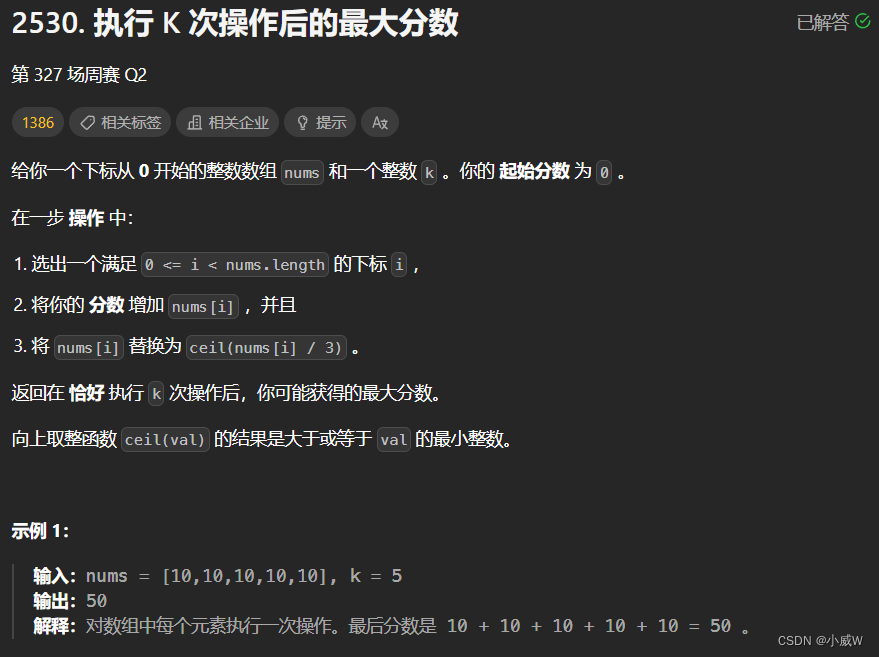
2530. 执行 K 次操作后的最大分数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximal-score-after-applying-k-operations/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-10-18
提示:
1 <= nums.length, k <= 10^5
1 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
解法1——贪心+优先队列
每次增加最大的数字即可。
class Solution {
public long maxKelements(int[] nums, int k) {
long ans = 0;
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a);
for (int num: nums) pq.offer(num);
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
int c = pq.poll();
ans += c;
pq.offer((c + 2) / 3);
}
return ans;
}
}
解法2—— O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)空间原地堆化
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximal-score-after-applying-k-operations/solutions/2487446/o1-kong-jian-zuo-fa-pythonjavacgojsrust-ztx6f/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-10-18
原地堆化,把 nums 数组当成一个堆。
从 h.length / 2 - 1 开始倒序下沉。
class Solution {
public long maxKelements(int[] nums, int k) {
heapify(nums);
long ans = 0;
while (k-- > 0) {
ans += nums[0];
nums[0] = (nums[0] + 2) / 3;
sink(nums, 0); // 下沉
}
return ans;
}
// 保证h[0]>=max(h[2*i+1],h[2*i+2])
public void heapify(int[] h) {
for (int i = h.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
sink(h, i);
}
}
public void sink(int[] h, int i) {
int n = h.length;
while (2 * i + 1 < n) {
// 挑选左右儿子中更大的和i交换
int j = 2 * i + 1; // i的左儿子
if (j + 1 < n && h[j + 1] > h[j]) j++;
if (h[j] <= h[i]) break; // 停止下沉
swap(h, i, j);
i = j;
}
}
public void swap(int[] h, int i, int j) {
int tmp = h[i];
h[i] = h[j];
h[j] = tmp;
}
}
1726. 同积元组(哈希表+组合数学)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/tuple-with-same-product/description/
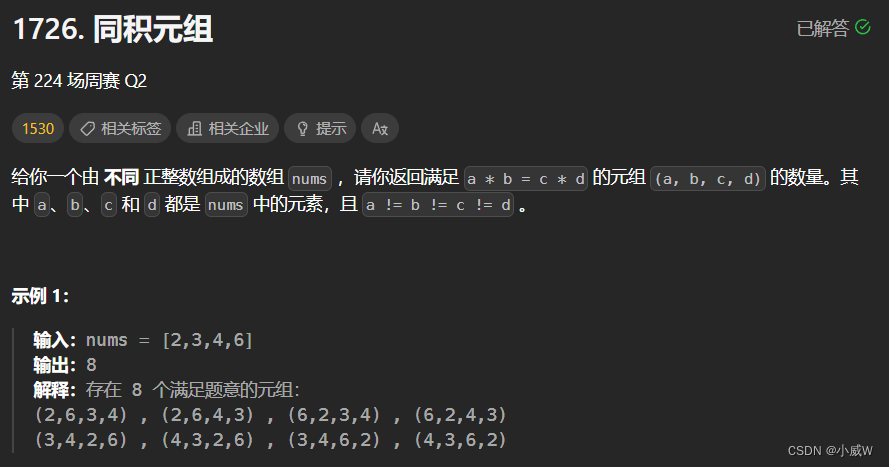
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000
1 <= nums[i] <= 10^4
nums 中的所有元素 互不相同
计算出数组中所有两两组合的乘积的各个数量。
那么各个成绩的组合数就是
C
x
2
=
x
∗
(
x
−
1
)
C_x^2=x*(x-1)
Cx2=x∗(x−1),即任选两组。每种组合4个数字可以任意排位置,最后结果*4。
class Solution {
public int tupleSameProduct(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, ans = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
cnt.merge(nums[i] * nums[j], 1, Integer::sum);
}
}
for (int v: cnt.values()) {
if (v > 1) ans += v * (v - 1);
}
return ans * 4;
}
}
2525. 根据规则将箱子分类(按题意模拟,分类讨论)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/categorize-box-according-to-criteria/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-10-20
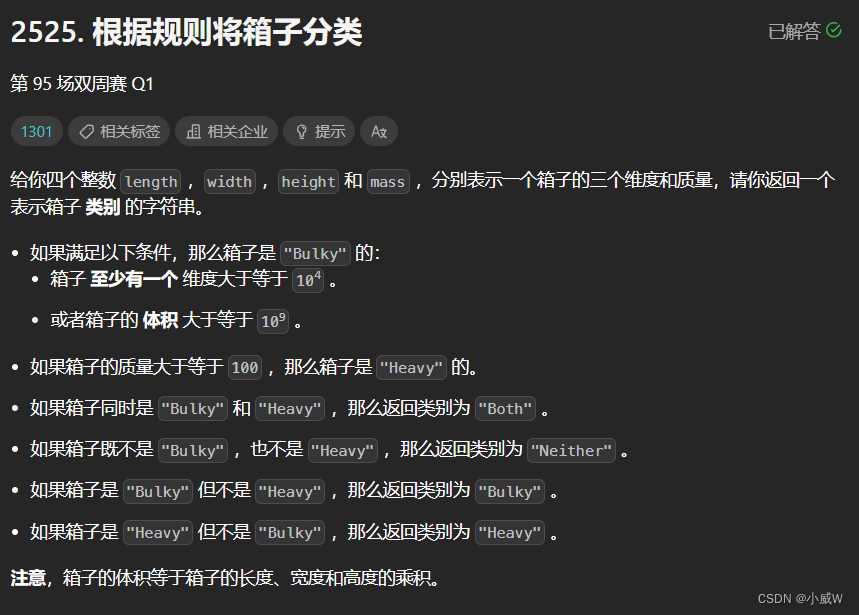
提示:
1 <= length, width, height <= 10^5
1 <= mass <= 10^3
class Solution {
public String categorizeBox(int length, int width, int height, int mass) {
boolean bulky = false, heavy = false;
if (length >= 10000 || width >= 10000 || height >= 10000 || mass >= 10000 || (long)length * width * height >= 1000000000) bulky = true;
if (mass >= 100) heavy = true;
if (bulky && heavy) return "Both";
if (!bulky && !heavy) return "Neither";
if (bulky) return "Bulky";
return "Heavy";
}
}
2316. 统计无向图中无法互相到达点对数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-unreachable-pairs-of-nodes-in-an-undirected-graph/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-10-21
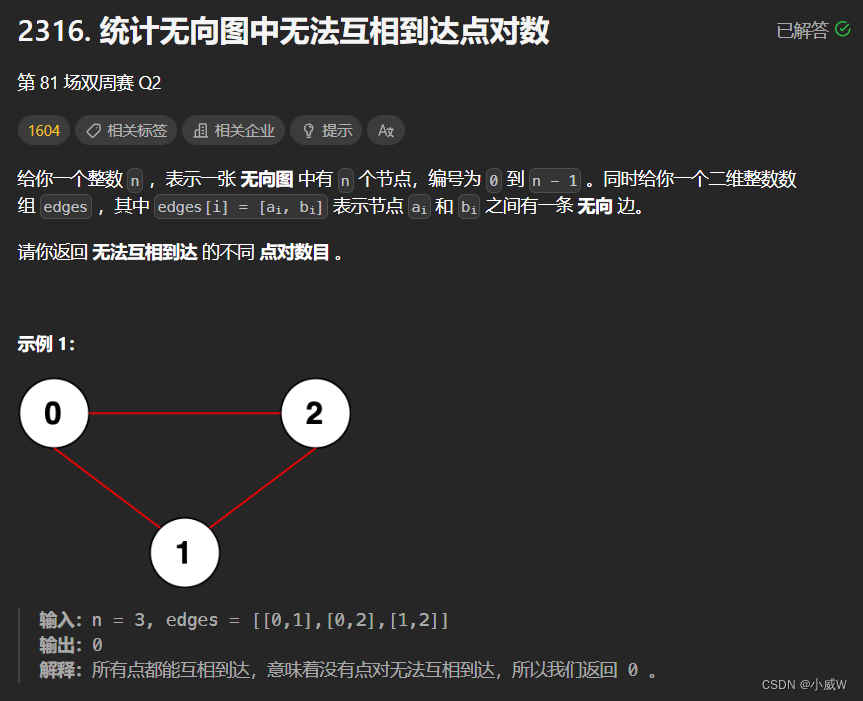
提示:
1 <= n <= 10^5
0 <= edges.length <= 2 * 10^5
edges[i].length == 2
0 <= ai, bi < n
ai != bi
不会有重复边。
解法1——并查集
关于并查集可见:【算法基础:数据结构】2.3 并查集
并查集得出各个联通集合中元素的数量,不同集合中的元素都可以两两组合。
class Solution {
public long countPairs(int n, int[][] edges) {
long ans = 0;
// 并查集
int[] p = new int[n];
Arrays.setAll(p, e -> e);
for (int[] e: edges) {
if (p[e[0]] != p[e[1]]) p[find(p, e[0])] = find(p, e[1]);
}
// 记录每个集合中的元素个数
Map<Integer, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cnt.merge(find(p, i), 1, Integer::sum);
}
for (int v: cnt.values()) {
ans += (long)v * (n - v); // 和其它所有集合的一一对应
}
return ans / 2; // 结果除以2去掉重复计算的
}
public int find(int[]p, int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p, p[x]);
return p[x];
}
}
解法2——dfs求连通块大小
class Solution {
public long countPairs(int n, int[][] edges) {
long ans = 0, total = 0;
List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[n];
boolean[] st = new boolean[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<Integer>());
for (int[] e: edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1]);
g[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!st[i]) {
int cnt = dfs(g, st, i); // dfs计算连通块大小
ans += total * cnt;
total += cnt;
}
}
return ans;
}
public int dfs(List<Integer>[] g, boolean[] st, int x) {
int res = 1;
st[x] = true;
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (!st[y]) {
res += dfs(g, st, y);
}
}
return res;
}
}
1402. 做菜顺序
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reducing-dishes/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-10-22
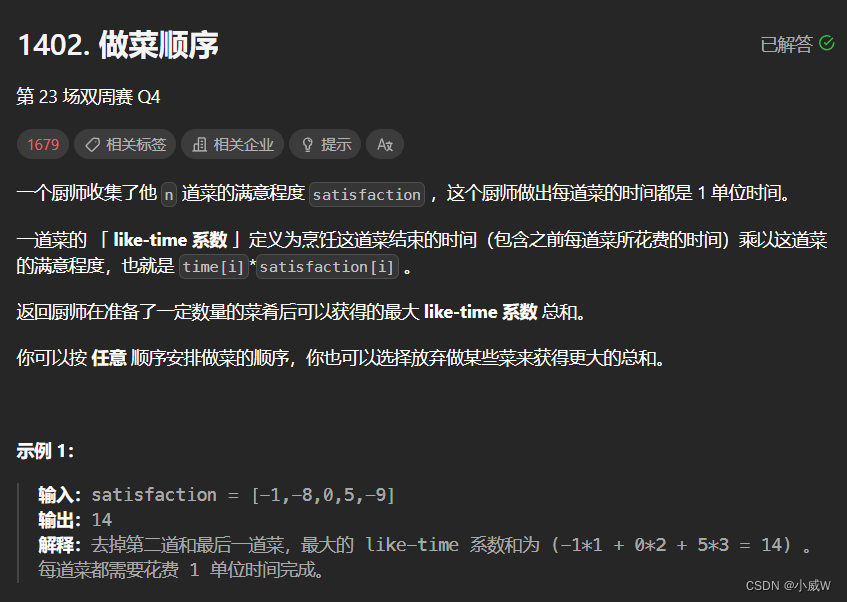
提示:
n == satisfaction.length
1 <= n <= 500
-1000 <= satisfaction[i] <= 1000
解法1——动态规划
dp[i][j] 表示前 i+1 个菜,选择 j 个时的值。
最后结果是前 n 个菜中,选择 0~n 个时的最大值。
class Solution {
public int maxSatisfaction(int[] satisfaction) {
int n = satisfaction.length;
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
Arrays.sort(satisfaction);
dp[0][1] = satisfaction[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i + 1; ++j) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + satisfaction[i] * j;
}
}
return Arrays.stream(dp[n - 1]).max().getAsInt();
}
}
解法2——贪心⭐
见:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reducing-dishes/solutions/198214/zuo-cai-shun-xu-by-leetcode-solution/?envType=daily-question&envId=2023-10-22
class Solution {
public int maxSatisfaction(int[] satisfaction) {
Arrays.sort(satisfaction);
int ans = 0, s = 0;
for (int i = satisfaction.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
s += satisfaction[i];
if (s <= 0) return ans;
ans += s;
}
return ans;
}
}
