1 阻塞IO
进程1
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char buf[128] = {0};
int a,b;
int fd = open("/dev/myled0",O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("打开设备文件失败\n");
exit(-1);
}
while(1)
{
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("buf:%s\n",buf);
}
}
进程2
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char buf[128] = "hello world";
int a,b;
int fd = open("/dev/myled0",O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("打开设备文件失败\n");
exit(-1);
}
write(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));
}
驱动程序
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
int major;
char kbuf[128] = {0};
unsigned int *vir_rcc;
struct class *cls;
struct device *dev;
//定义等待队列
wait_queue_head_t wq_head;
unsigned int condition=0;
int mycdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
return 0;
}
ssize_t mycdev_read(struct file *file, char *ubuf, size_t size,loff_t *lof)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
if(file->f_flags&O_NONBLOCK)//用户程序以非阻塞读写数据
{}
else{
wait_event_interruptible(wq_head,condition);//判断condition的值,为假则进程休眠
}
//将获取到的硬件数据拷贝到用户
int ret = copy_to_user(ubuf,kbuf,size);
if(ret)
{
printk("copy_to_user filed\n");
return -EIO;
}
condition = 0; //表示下一次数据没有准备就绪
return 0;
}
ssize_t mycdev_write(struct file *file, const char *ubuf, size_t size,loff_t *lof)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
int ret;
ret = copy_from_user(kbuf,ubuf,size);
if (ret)
{
printk("copy_from_user filed\n");
return -EIO;
}
condition = 1;//表示硬件数据就绪
wake_up_interruptible(&wq_head);//唤醒休眠的进程
return 0;
}
int mycdev_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
return 0;
}
//定义操作方法结构体变量并赋值
struct file_operations fops={
.open = mycdev_open,
.read = mycdev_read,
.write = mycdev_write,
.release = mycdev_close,
};
static int __init mycdev_init(void)
{
//初始化等待队列
init_waitqueue_head(&wq_head);
//字符设备驱动
major = register_chrdev(0,"mychrdev",&fops);
if(major < 0)
{
printk("字符设备驱动注册失败\n");
return major;
}
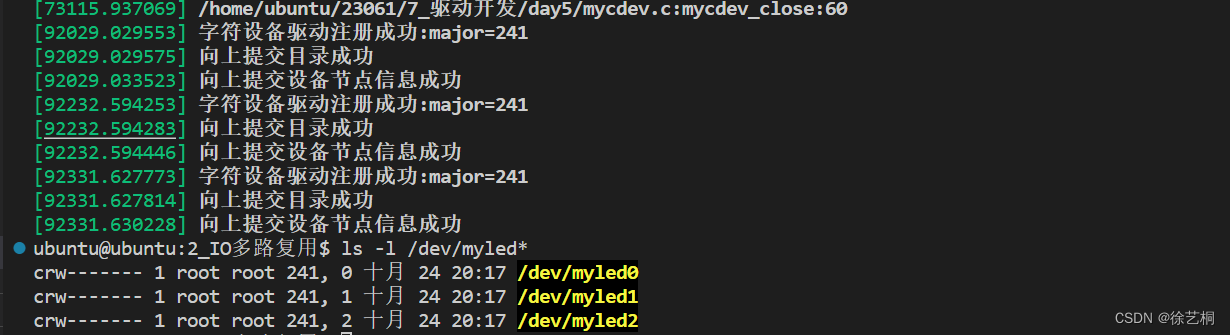
printk("字符设备驱动注册成功:major=%d\n",major);
//向上提交目录 class_create
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE,"mychrdev");
if(IS_ERR(cls))
{
printk("向上提交目录失败\n");
return -PTR_ERR(cls);
}
printk("向上提交目录成功\n");
//向上提交设备节点信息 device_create
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
dev = device_create(cls,NULL,MKDEV(major,i),NULL,"myled%d",i);
if(IS_ERR(dev))
{
printk("向上提交设备节点失败\n");
return -PTR_ERR(dev);
}
}
printk("向上提交设备节点信息成功\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit mycdev_exit(void)
{
//1.销毁设备节点信息
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,i));
}
//2.销毁目录
class_destroy(cls);
//3.注销字符设备驱动
unregister_chrdev(major,"mychrdev");
}
module_init(mycdev_init);
module_exit(mycdev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile
modname ?= demo
arch ?= arm
ifeq ($(arch),arm) #通过命令行传过来的架构决定怎么编译
#KERBELDIR保存开发板内核源码路径
KERNELDIR := /home/ubuntu/FSMP1A/linux-stm32mp-5.10.61-stm32mp-r2-r0/linux-5.10.61
else
#保存UBUNTU内核源码路径
KERNELDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
endif
#PWD保存当前内核模块的路径
PWD := $(shell pwd)
all:
#make modules是模块化编译命令
#make -C $(KERNLEDIR) 执行make之前先切换到KERNELDIR对应的路径
#M=$(PWD)表示进行模块化编译的路径是PWD保存的路径
make -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
#编译清除
make -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) clean
#将obj-m保存的文件单独链接为内核模块
obj-m := $(modname).o
效果演示
2 IO多路复用
驱动程序
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
int major;
char kbuf[128] = {0};
unsigned int *vir_rcc;
struct class *cls;
struct device *dev;
//定义等待队列
wait_queue_head_t wq_head;
unsigned int condition=0;
int mycdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
return 0;
}
ssize_t mycdev_read(struct file *file, char *ubuf, size_t size,loff_t *lof)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
if(file->f_flags&O_NONBLOCK)//用户程序以非阻塞读写数据
{}
else{
// wait_event_interruptible(wq_head,condition);//判断condition的值,为假则进程休眠
}
//将获取到的硬件数据拷贝到用户
int ret = copy_to_user(ubuf,kbuf,size);
if(ret)
{
printk("copy_to_user filed\n");
return -EIO;
}
condition = 0; //表示下一次数据没有准备就绪
return 0;
}
__poll_t mycdev_poll(struct file *file, struct poll_table_struct *wait)
{
__poll_t mask = 0;
// 向上提交等待队列队头
poll_wait(file, &wq_head, wait);
// 根据数据是否就绪给定一个合适的返回值
if (condition)
mask = POLLIN;
return mask;
}
ssize_t mycdev_write(struct file *file, const char *ubuf, size_t size,loff_t *lof)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
int ret = copy_from_user(kbuf,ubuf,size);
if (ret)
{
printk("copy_from_user filed\n");
return -EIO;
}
condition = 1;//表示硬件数据就绪
wake_up_interruptible(&wq_head);//唤醒休眠的进程
return 0;
}
int mycdev_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
return 0;
}
//定义操作方法结构体变量并赋值
struct file_operations fops={
.open = mycdev_open,
.read = mycdev_read,
.write = mycdev_write,
.poll = mycdev_poll,
.release = mycdev_close,
};
static int __init mycdev_init(void)
{
//初始化等待队列
init_waitqueue_head(&wq_head);
//字符设备驱动
major = register_chrdev(0,"mychrdev",&fops);
if(major < 0)
{
printk("字符设备驱动注册失败\n");
return major;
}
printk("字符设备驱动注册成功:major=%d\n",major);
//向上提交目录 class_create
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE,"mychrdev");
if(IS_ERR(cls))
{
printk("向上提交目录失败\n");
return -PTR_ERR(cls);
}
printk("向上提交目录成功\n");
//向上提交设备节点信息 device_create
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
dev = device_create(cls,NULL,MKDEV(major,i),NULL,"myled%d",i);
if(IS_ERR(dev))
{
printk("向上提交设备节点失败\n");
return -PTR_ERR(dev);
}
}
printk("向上提交设备节点信息成功\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit mycdev_exit(void)
{
//1.销毁设备节点信息
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
device_destroy(cls,MKDEV(major,i));
}
//2.销毁目录
class_destroy(cls);
//3.注销字符设备驱动
unregister_chrdev(major,"mychrdev");
}
module_init(mycdev_init);
module_exit(mycdev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
进程1:监听多个事件
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char buf[128] = {0};
int fd1,fd2;
fd1 = open("/dev/input/mouse0",O_RDWR);
if(fd1 < 0)
{
printf("打开鼠标设备失败\n");
return -1;
}
fd2 = open("/dev/myled0",O_RDWR);
if(fd2 < 0)
{
printf("打开设备失败\n");
return -1;
}
// 定义读事件集合
fd_set readfds;
while(1)
{
// 清空集合
FD_ZERO(&readfds);
// 将要监听的事件添加进集合
FD_SET(fd1, &readfds);
FD_SET(fd2, &readfds);
// 阻塞监听事件
int ret;
ret = select(fd2 + 1, &readfds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if(ret < 0)
{
printf("select 调用失败\n");
return -1;
}
// 判断事件是否发生
if(FD_ISSET(fd1, &readfds));
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(fd1, buf, sizeof(buf));
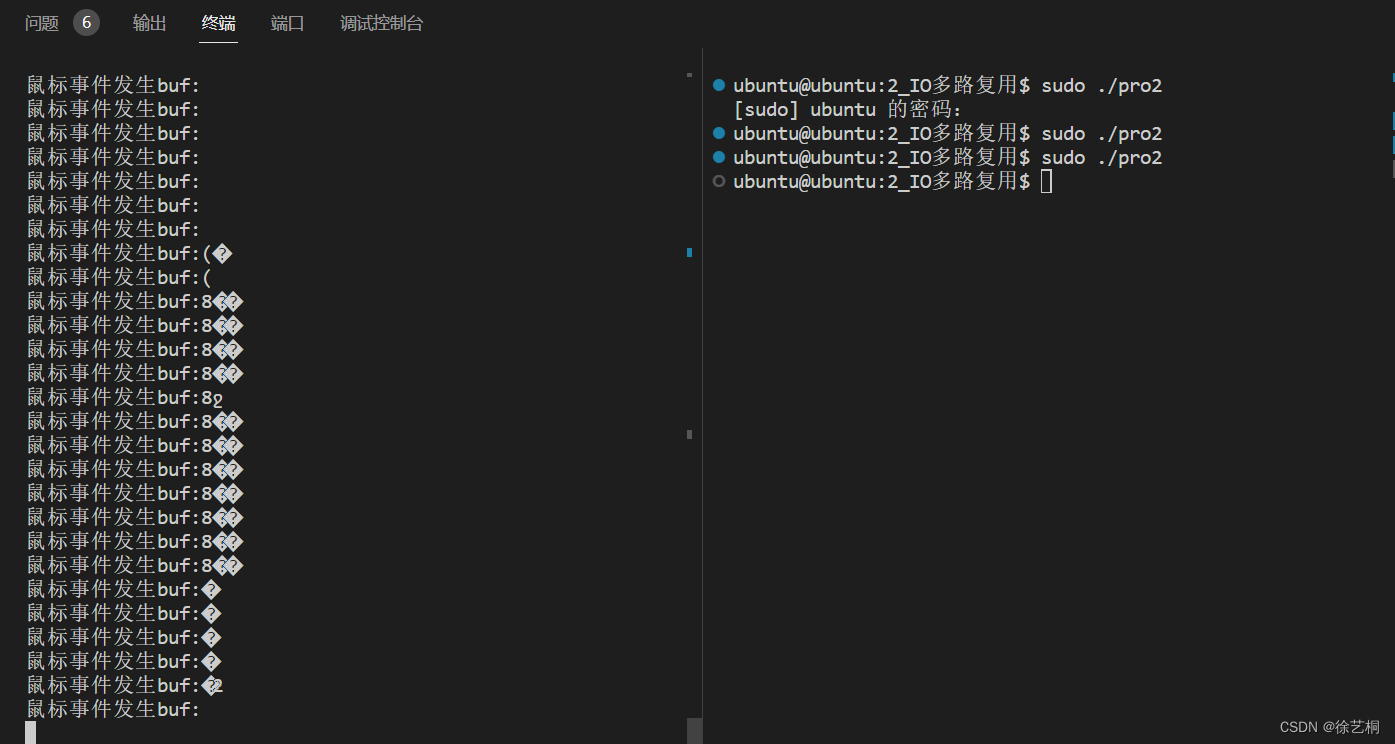
printf("鼠标事件发生buf:%s\n", buf);
}
if(FD_ISSET(fd2, &readfds))
{
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
read(fd2,buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("事件发生buf:%s\n",buf);
}
}
// 关闭文件描述符
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
return 0;
}
进程2:模拟自定义事件就绪
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char buf[128] = "hello world";
int a,b;
int fd = open("/dev/myled0",O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("打开设备文件失败\n");
exit(-1);
}
write(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));
}
效果演示