设计模式(15)组合模式
一、介绍:
1、定义:组合多个对象形成树形结构以表示“整体-部分”的关系的层次结构。组合模式对叶子节点和容器节点的处理具有一致性,又称为整体-部分模式。
2、优缺点:
优点:
(1)高层模块调用简单:组合模式使得客户端代码可以一致地处理单个对象和组合对象,无须关心自己处理的是单个对象,还是组合对象,这简化了客户端代码。
(2)节点自由增加:更容易在组合体内加入新的对象,客户端不会因为加入了新的对象而更改源代码。
缺点:
(1)在使用组合模式时,其叶子和树枝的声明都是实现类,而不是接口,违反了依赖倒置原则。
(2)设计较复杂,客户端需要花更多时间理清类之间的层次关系。
(3)不容易限制容器中的构件。
3、组成:
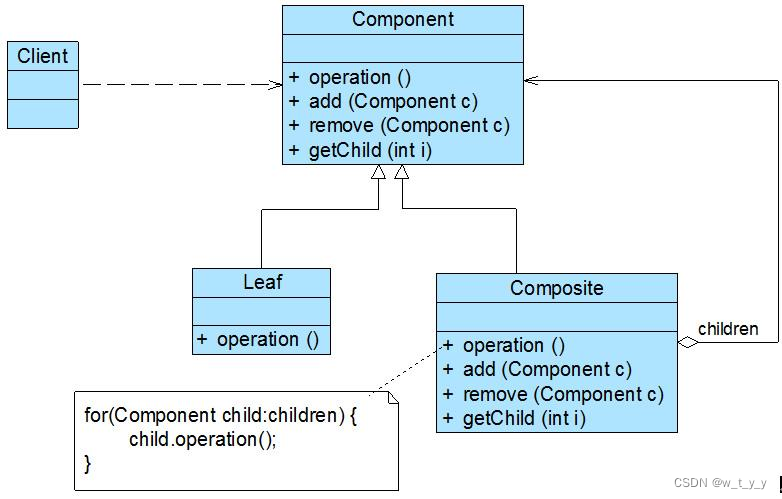

(1)抽象构件(Component)角色:它的主要作用是为树叶构件和树枝构件声明公共接口,并实现它们的默认行为。在透明式的组合模式中抽象构件还声明访问和管理子类的接口;在安全式的组合模式中不声明访问和管理子类的接口,管理工作由树枝构件完成。(总的抽象类或接口,定义一些通用的方法,比如新增、删除)。
(2)树枝构件(Composite)角色 / 中间构件:是组合中的分支节点对象,它有子节点,用于继承和实现抽象构件。它的主要作用是存储和管理子部件,通常包含 Add()、Remove()、GetChild() 等方法。
(3)树叶构件(Leaf)角色:是组合中的叶节点对象,它没有子节点,用于继承或实现抽象构件。
// 定义抽象构件
public abstract class Component {
protected String name;
public Component(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract void add(Component component);
public abstract void remove(Component component);
public abstract void display();
}
// 定义叶子构件
public class Leaf extends Component {
public Leaf(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
System.out.println("Cannot add to a leaf");
}
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
System.out.println("Cannot remove from a leaf");
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println("Leaf: " + name);
}
}
// 定义容器构件
public class Composite extends Component {
private List<Component> children = new ArrayList<>();
public Composite(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
children.add(component);
}
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
children.remove(component);
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println("Composite: " + name);
for (Component component : children) {
component.display();
}
}
}
// 客户端代码
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Component root = new Composite("root");
Component leaf1 = new Leaf("leaf1");
Component leaf2 = new Leaf("leaf2");
Component composite1 = new Composite("composite1");
Component leaf3 = new Leaf("leaf3");
Component composite2 = new Composite("composite2");
root.add(leaf1);
root.add(leaf2);
root.add(composite1);
composite1.add(leaf3);
composite1.add(composite2);
root.display();
}
}4、应用场景:部分、整体场景,如树形菜单,文件、文件夹的管理。
二、demo:
1、菜单:
(1)数据库model
public class MenuDTO {
private String menuName;
private String menuCode;
private String parentMenuCode;
public MenuDTO(String menuName,String menuCode,String parentMenuCode){
this.menuCode = menuCode;
this.menuName = menuName;
this.parentMenuCode = parentMenuCode;
}
/**省略所有set、get芳芳*/
}
抽象构件Component
public abstract class MenuComponent extends MenuDTO {
MenuComponent(String menuName, String menuCode,String parentMenuCode) {
super(menuName, menuCode,parentMenuCode);
}
void addMenu(MenuComponent component){}
void removeMenu(MenuComponent component){}
}
(2)树枝构件(Composite):
public class MenuVO extends MenuComponent {
private List<MenuComponent> children = new ArrayList<>();
MenuVO(String menuName, String menuCode,String parentMenuCode) {
super(menuName, menuCode,parentMenuCode);
}
@Override
void addMenu(MenuComponent component) {
children.add(component);
}
@Override
void removeMenu(MenuComponent component) {
}
}
(3)树叶
public class MenuLeaf extends MenuComponent {
MenuLeaf(String menuName, String menuCode,String parentMenuCode) {
super(menuName, menuCode,parentMenuCode);
}
@Override
void addMenu(MenuComponent component) {
super.addMenu(component);
}
@Override
void removeMenu(MenuComponent component) {
super.removeMenu(component);
}
}客户端:
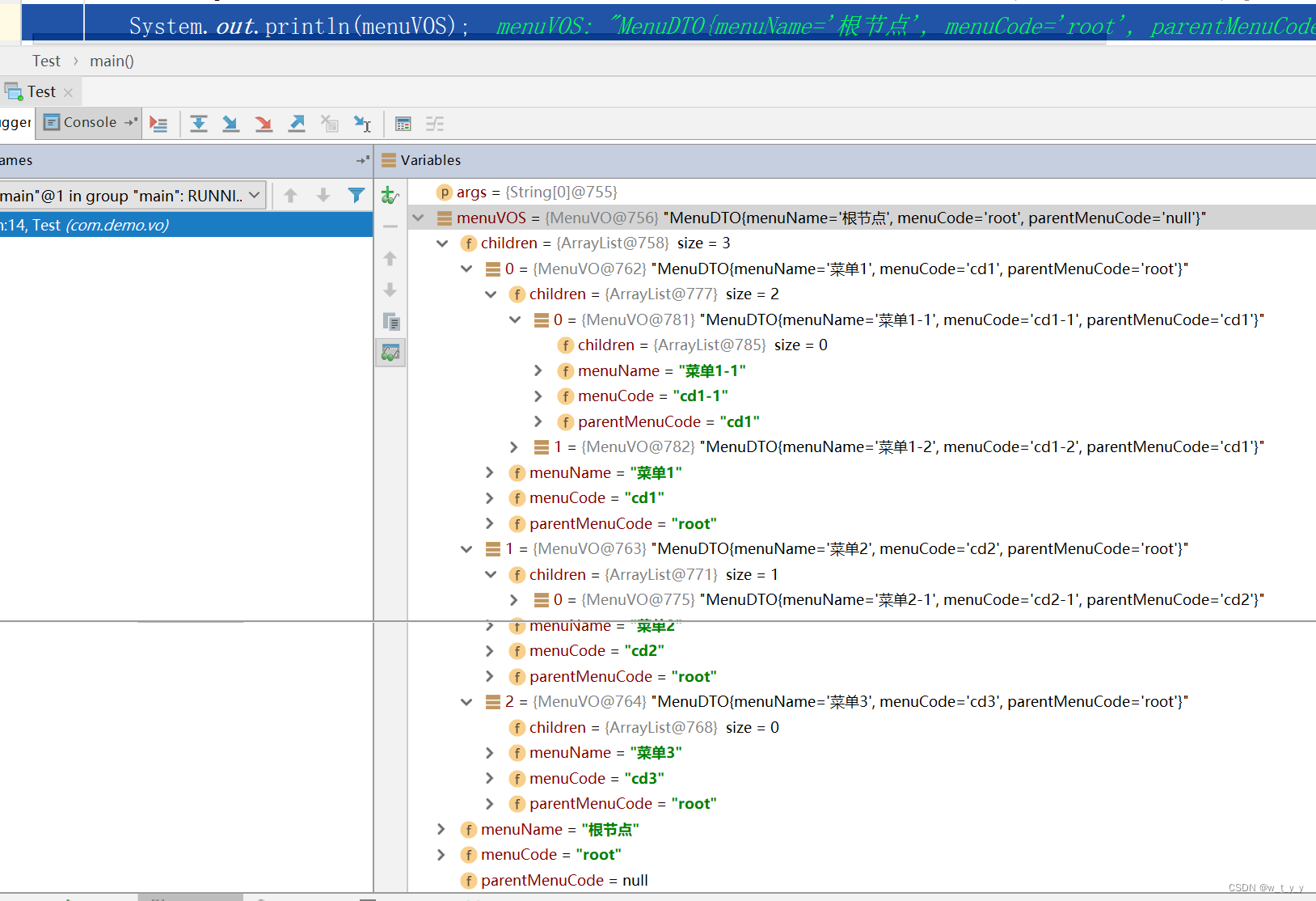
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
MenuComponent menuVOS = listMenus();
System.out.println(menuVOS);
}
public static MenuComponent listMenus(){
//模拟数据库查询,查询所有一级菜单(menu_type = 1)、二级菜单(menu_type = 2)
List<MenuDTO> firstMenus = new ArrayList<>();
MenuDTO menuDTO = new MenuDTO("菜单1","cd1","root");
firstMenus.add(menuDTO);
menuDTO = new MenuDTO("菜单2","cd2","root");
firstMenus.add(menuDTO);
menuDTO = new MenuDTO("菜单3","cd3","root");
firstMenus.add(menuDTO);
List<MenuDTO> secondMenus = new ArrayList<>();
menuDTO = new MenuDTO("菜单1-1","cd1-1","cd1");
secondMenus.add(menuDTO);
menuDTO = new MenuDTO("菜单1-2","cd1-2","cd1");
secondMenus.add(menuDTO);
menuDTO = new MenuDTO("菜单2-1","cd2-1","cd2");
secondMenus.add(menuDTO);
Map<String, List<MenuDTO>> childMenuMap = secondMenus.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(MenuDTO::getParentMenuCode));
/**实现
* 根节点
* 菜单1 菜单2 菜单3
*菜单1-1 菜单1-2 菜单2-1
* */
//1、定义根节点
MenuComponent root = new MenuVO("根节点","root",null);
//2、处理菜单层级
for(MenuDTO firstMenu : firstMenus){
//二级菜单
MenuComponent firstMenuVO = new MenuVO(firstMenu.getMenuName(),firstMenu.getMenuCode(),firstMenu.getParentMenuCode());
//三级菜单
List<MenuDTO> secondMenuVOs = childMenuMap.get(firstMenu.getMenuCode());
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(secondMenuVOs)){
for(MenuDTO secondMenu : secondMenuVOs){
MenuComponent secondMenuVO = new MenuVO(secondMenu.getMenuName(),secondMenu.getMenuCode(),secondMenu.getParentMenuCode());
firstMenuVO.addMenu(secondMenuVO);
}
}
root.addMenu(firstMenuVO);
}
return root;
}
}运行main方法
2、文件夹:
(1)抽象构件Component
public abstract class FileComponent {
//文件名称
protected String name;
//文件的层级 1 一级目录 2 二级目录 ...
protected Integer level;
//文件的类型 1 文件夹 2文件
protected Integer type;
//添加子文件/文件夹
public abstract void add(FileComponent fileComponent);
//移除子文件/文件夹
public abstract void remove(FileComponent fileComponent);
//获取指定的子文件/文件夹
public abstract FileComponent getChild(int index);
//打印子 子文件/子文件夹 名称的方法
public abstract void print();
}
(2)树枝构件(Composite)
public class FileFolder extends FileComponent{
//文件夹可以有多个子文件夹或者子文件
private List<FileComponent> fileComponentList;
public FileFolder(String name, Integer level, Integer type) {
this.name = name;
this.level = level;
this.type = type;
this.fileComponentList = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Override
public void add(FileComponent fileComponent) {
fileComponentList.add(fileComponent);
}
@Override
public void remove(FileComponent fileComponent) {
fileComponentList.remove(fileComponent);
}
@Override
public FileComponent getChild(int index) {
return fileComponentList.get(index);
}
@Override
public void print() {
//打印菜单名称
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
System.out.print("\t");
}
System.out.println(name);
//打印子菜单或者子菜单项名称
for (FileComponent component : fileComponentList) {
component.print();
}
}
}
(3)树叶构件(Leaf)
public class FileItem extends FileComponent{
public FileItem(String name, Integer level, Integer type) {
this.name = name;
this.level = level;
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public void add(FileComponent fileComponent) {
}
@Override
public void remove(FileComponent fileComponent) {
}
@Override
public FileComponent getChild(int index) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void print() {
//打印文件的名称
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
System.out.print("\t");
}
System.out.println(name);
}
}
客户端:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义根目录
FileComponent rootComponent = new FileFolder("我是根目录",1,1);
//定义二级文件夹
FileComponent secondLevelComponent = new FileFolder("我是二级目录",2,1);
//定义文件
FileComponent file = new FileItem("我是文件",3,2);
//向根目录添加二级目录
rootComponent.add(secondLevelComponent);
//向二级目录添加文件
secondLevelComponent.add(file);
//打印
rootComponent.print();
}
}
