LeetCode刷题——贪心法(C/C++)
这里写目录标题
- [中等]买卖股票的最佳时机 II
- [中等]移掉k位数字
- [中等]跳跃游戏
- [中等]跳跃游戏 II
- [中等]加油站
- [中等]划分字母区间
- [中等]无重叠区间
- [中等]用最少数量的箭引爆气球
[中等]买卖股票的最佳时机 II
- 原题链接
- 题解
最简单的思路,效率不高,只要明天的股价大于今天的,就把这个差值算上,(因为允许你当天卖当天买)只要有正的差额,都不放过。(现实中炒股也这么美好就好了)
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int maxn = 0;
for(int i=0;i<prices.size()-1;i++){
if(prices[i]<prices[i+1]) maxn += prices[i+1]-prices[i];
}
return maxn;
}
};
[中等]移掉k位数字
- 原题链接
- 题解
主要思路就是在入栈的时候,如果当前元素比栈顶元素小,并且还没有删到k个数,就将栈顶元素出栈,这题的判断条件很繁杂,前导0我就判断了两次,先是在字符入栈的时候就判断一次,最后转化成字符串输出时又要再算一次
在思路正确的情况下,最后一个用例一直过不去,超时,然后就想到问问chatgpt,最后他帮我优化了代码的效率,主要卡在两个问题上:
①substr()的效率很低,循环使用时间复杂度很高,我原先是循环使用substr在输出前删除前导0,比较傻的做法。
while(answer.size()>0 && answer[0] == '0'){
answer = answer.substr(1,answer.size()-1);
}
②原先出栈转字符串的操作也是类似用字符串循环拼接的思路,说明字符串拼接或者剪切本身复杂度是比较高的,最好是不要循环使用
//出栈转化结果
string answer = "";
while (ans.size() > 0) {
answer = ans.top() + answer;
ans.pop();
}
最后是修改后正确通过的代码
class Solution {
public:
string removeKdigits(string num, int k) {
if (num.size() == k) return "0";
int m = k;
stack<char> ans;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num.size() && m != 0; i++) {
while (m > 0 && ans.size() > 0 && ans.top() > num[i]){
ans.pop();
m--;
}
if (num[i] != '0' || ans.size() > 0) {
ans.push(num[i]);
}
}
while(i<num.size()) ans.push(num[i++]);
while((m--)>0 && ans.size()>0) ans.pop();
//出栈转化结果
string answer(ans.size(), ' ');
int j = ans.size() - 1;
while (!ans.empty()) {
answer[j--] = ans.top();
ans.pop();
}
//再次删除前导0
int index = 0;
while (index < answer.size() && answer[index] == '0') {
index++;
}
if(answer.size() == 0) return "0";
return answer.substr(index == answer.size() ? index - 1 : index, answer.size());
}
};
ps:ChatGPT关于优化这个算法给出的建议

[中等]跳跃游戏
- 原题链接
- 题解
int flag[30100];
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 1) return true;
if(nums.size() == 0) return false;
for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++){
flag[i] = 0;
}
flag[0] = 1;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size()-1;i++){
if(flag[i] == 1){
for(int j=1;j<=nums[i];j++){
if(i+j == nums.size()-1) return true;
flag[i+j] = 1;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
[中等]跳跃游戏 II
- 原题链接
- 题解
基本跟上一题差不多,记得初始化的时候,flag[]里面,除了第一个元素是0,他本身可以0步到达自己,其他都是int的最大值,用于后面的min函数比较,每一次循环就将当前位置能达到的所有下标的值进行一个比较,如果当前位置值+1,比原先记录到达当前下标需要的最小步数小,则更新。
int flag [10001];
class Solution {
public:
int jump(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return 0;
for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++){
flag[i] = INT_MAX;
}
flag[0] = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size()-1;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=nums[i] && i+j<nums.size();j++){
flag[i+j] = min(flag[i] + 1,flag[i+j]);
}
}
return flag[nums.size()-1];
}
};
[中等]加油站
- 原题链接
- 题解
当j走到一个位置无法前进的时候,说明i~j中间都是无法作为起点的,对i~j中间任意一点k,若以k作为起点,那么出发时的汽油储量只有gas[k],而从k之前的点i走过来,汽油储量应该>=gas[k](能够顺利走到k点,到的时候汽油起码是0),所以下一层循环可以直接从j+1开始考虑作为起点。
class Solution {
public:
int canCompleteCircuit(vector<int>& gas, vector<int>& cost) {
int gasCount;
int n = gas.size();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int j = i;
gasCount = gas[i];
while (gasCount - cost[j] >= 0) {
if (gasCount + gas[(j+1)%n] - cost[j] >= 0) {
gasCount = gasCount + gas[(j+1)%n] - cost[j];
j = (j + 1) % n;
if(j==i) return i;
}
}
if(j < i) return -1;
i = j;
}
return -1;
}
};
以下代码就是暴力的思路,每次查找失败都是i++,导致时间复杂度过大,最后超时,有五个样例通不过,但是思路上是比较朴素能够想到的,上面那个正确的就可以基于这个思路得到。
class Solution {
public:
int canCompleteCircuit(vector<int>& gas, vector<int>& cost) {
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int gasCount = 0;
int n = gas.size();
while (i < n) {
gasCount += gas[j];
if (gasCount - cost[j % n] >= 0) {
gasCount -= cost[j % n];
j = (j + 1) % n;
if(j==i) return i;
}
else {
//重置起点
i++;
j = i;
gasCount = 0;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
[中等]划分字母区间
- 原题链接
- 题解
先开个int数组或者map记录一下字符串里面各个字母出现的次数,在循环的过程中,检查当前扫描到的字母出现的次数,如果和最大次数相同,说明当前段已经包含了这个字母的所有取值,kinds用于记录当前段中,出现次数已经达到最大的字母的数量,如果和map的大小相等,说明当前段所有字母都取到了最大数,则返回当前段长,并清空记录信息,继续向前循环。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> partitionLabels(string s) {
int count[26];
map<char,int> nowKinds;
int kinds = 0;
int length = 0;
vector<int> ans;
int n = s.size();
for(int i=0;i<26;i++){
count[i] = 0;
}
//记录各字母出现频次
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) count[s[i]-'a']++;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
nowKinds[s[i]]++;
if(nowKinds[s[i]] == count[s[i]-'a']) kinds++;
length++;
if(nowKinds.size() == kinds){
ans.push_back(length);
length = 0;
nowKinds.clear();
kinds = 0;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
[中等]无重叠区间
- 原题链接
- 题解
贪心的思路在于,对所有重叠的区间来说,只能取其中一个,其他都要放弃,在按右端点排序所有区间的条件下,尽可能选择右端点数字最小的,能够尽可能把右边空间空出去选择更多区间。
①将区间按右端点排序,然后从小到大循环,如果当前区间左端点大于等于上一次选择区间的右端点,则可以加入,并将pre更新为当前区间右端点,否则取出。
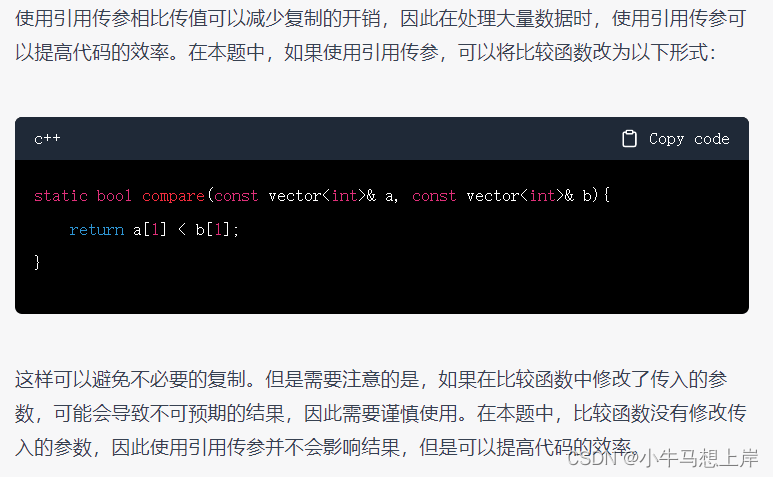
②有个坑就是样例通过之后还是显示超时,compare函数应该使用引用传参,这样会提高效率,原因chatpgt说的是能够减少复制开销
class Solution {
public:
int eraseOverlapIntervals(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {
if(intervals.empty()) return 0;
int n = intervals.size();
sort(intervals.begin(),intervals.end(),compare);
//记录上一个区间的右边界,最初始的为第一组数
int pre = 0;
int length = 0;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){
if(intervals[i][0] >= intervals[pre][1]){
pre = i;
}else{
length++;
}
}
return length;
}
static bool compare(vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b){
return a[1] < b[1];
}
};
[中等]用最少数量的箭引爆气球
- 原题链接
- 题解
其实就是判断重叠区间的问题,相比起上面那题无重叠区间,这里要判断的是如果区间有重叠区间就可以少射一支箭,箭数 = 区间总数-重叠次数,记住一个问题就是如果区间头尾相接,也算是能够一支箭射中两个。
class Solution {
public:
//重叠区间的问题,相当于选最少的点覆盖所有区间
int findMinArrowShots(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
if(points.empty()) return 0;
int n = points.size();
sort(points.begin(),points.end(),compare);
//记录上一个区间的右边界,最初始的为第一组数
int pre = 0;
int count = 0;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){
if(points[i][0] > points[pre][1]){
pre = i;
}else{
count++;
}
}
return n - count;
}
static bool compare(vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b){
return a[1] < b[1];
}
};
