037、目标检测-SSD实现
之——简单实现
目录
之——简单实现
杂谈
正文
1.类别预测层
2.边界框预测
3.多尺度输出联结做预测(提高预测效率)
4.多尺度实现
5.基本网络块
6.完整模型
杂谈
原理查看:037、目标检测-算法速览-CSDN博客
正文
1.类别预测层
类别预测的实现,锚框类别数num_classes+1背景:

该图层使用填充为1的3×3的卷积层。此卷积层的输入和输出的宽度和高度保持不变,只是改变了通道数:
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from d2l import torch as d2l
def cls_predictor(num_inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
return nn.Conv2d(num_inputs, num_anchors * (num_classes + 1),
kernel_size=3, padding=1)2.边界框预测
把边界框也看做一个预测问题,要预测的值就是两个坐标四个值,所以输出通道为4*num_anchors:
def bbox_predictor(num_inputs, num_anchors):
return nn.Conv2d(num_inputs, num_anchors * 4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)3.多尺度输出联结做预测(提高预测效率)
单发多框检测使用多尺度特征图来生成锚框并预测其类别和偏移量。 在不同的尺度下,特征图的形状或以同一单元为中心的锚框的数量可能会有所不同。 因此,不同尺度下预测输出的形状可能会有所不同。
def forward(x, block):
return block(x)
Y1 = forward(torch.zeros((2, 8, 20, 20)), cls_predictor(8, 5, 10))
Y2 = forward(torch.zeros((2, 16, 10, 10)), cls_predictor(16, 3, 10))
Y1.shape, Y2.shape![]()
通道维包含中心相同的锚框的预测结果。我们首先将通道维移到最后一维。 因为不同尺度下批量大小仍保持不变,我们可以将预测结果转成二维的(批量大小,高×宽×通道数)的格式,以方便之后在维度1上的连结 :
def flatten_pred(pred):
return torch.flatten(pred.permute(0, 2, 3, 1), start_dim=1)
def concat_preds(preds):
return torch.cat([flatten_pred(p) for p in preds], dim=1)
4.多尺度实现
为了在多个尺度下检测目标,我们在下面定义了高和宽减半块down_sample_blk,该模块将输入特征图的高度和宽度减半。
def down_sample_blk(in_channels, out_channels):
blk = []
for _ in range(2):
blk.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1))
blk.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels))
blk.append(nn.ReLU())
in_channels = out_channels
blk.append(nn.MaxPool2d(2))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)跟当时VGG的实现极其类似,效果:
forward(torch.zeros((2, 3, 20, 20)), down_sample_blk(3, 10)).shape
5.基本网络块
基本网络块用于从输入图像中抽取特征。 为了计算简洁,我们构造了一个小的基础网络,该网络串联3个高和宽减半块,并逐步将通道数翻倍。 给定输入图像的形状为256×256,此基本网络块输出的特征图形状为32×32:
def base_net():
blk = []
num_filters = [3, 16, 32, 64]
for i in range(len(num_filters) - 1):
blk.append(down_sample_blk(num_filters[i], num_filters[i+1]))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
forward(torch.zeros((2, 3, 256, 256)), base_net()).shape6.完整模型
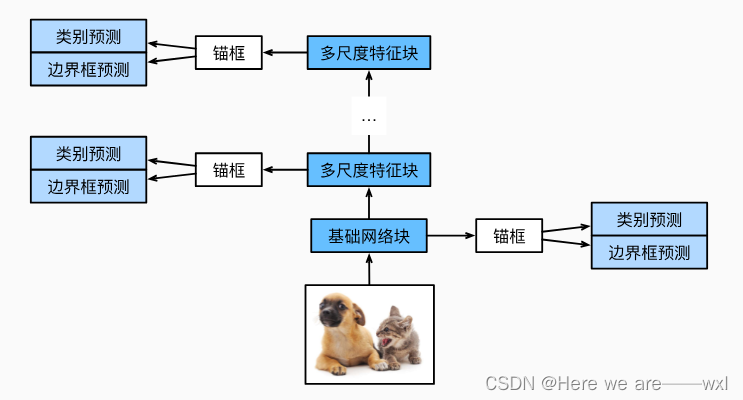
完整的单发多框检测模型由五个模块组成。每个块生成的特征图既用于生成锚框,又用于预测这些锚框的类别和偏移量。在这五个模块中,第一个是基本网络块,第二个到第四个是高和宽减半块,最后一个模块使用全局最大池化将高度和宽度都降到1。
def get_blk(i):
if i == 0:
blk = base_net()
elif i == 1:
blk = down_sample_blk(64, 128)
elif i == 4:
blk = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1,1))
else:
blk = down_sample_blk(128, 128)
return blk 每个块的前向传播:为每个块定义前向传播。与图像分类任务不同,此处的输出包括:CNN特征图Y;在当前尺度下根据Y生成的锚框;预测的这些锚框的类别和偏移量(基于Y):
def blk_forward(X, blk, size, ratio, cls_predictor, bbox_predictor):
Y = blk(X)
anchors = d2l.multibox_prior(Y, sizes=size, ratios=ratio)
cls_preds = cls_predictor(Y)
bbox_preds = bbox_predictor(Y)
return (Y, anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds) 一个较接近顶部的多尺度特征块是用于检测较大目标的,因此需要生成更大的锚框。 在上面的前向传播中,在每个多尺度特征块上,我们通过调用的multibox_prior函数的sizes参数传递两个比例值的列表。
sizes = [[0.2, 0.272], [0.37, 0.447], [0.54, 0.619], [0.71, 0.79],
[0.88, 0.961]]
ratios = [[1, 2, 0.5]] * 5
num_anchors = len(sizes[0]) + len(ratios[0]) - 1汇总:
class TinySSD(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, **kwargs):
super(TinySSD, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_classes = num_classes
idx_to_in_channels = [64, 128, 128, 128, 128]
for i in range(5):
# 即赋值语句self.blk_i=get_blk(i)
setattr(self, f'blk_{i}', get_blk(i))
setattr(self, f'cls_{i}', cls_predictor(idx_to_in_channels[i],
num_anchors, num_classes))
setattr(self, f'bbox_{i}', bbox_predictor(idx_to_in_channels[i],
num_anchors))
def forward(self, X):
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = [None] * 5, [None] * 5, [None] * 5
for i in range(5):
# getattr(self,'blk_%d'%i)即访问self.blk_i
X, anchors[i], cls_preds[i], bbox_preds[i] = blk_forward(
X, getattr(self, f'blk_{i}'), sizes[i], ratios[i],
getattr(self, f'cls_{i}'), getattr(self, f'bbox_{i}'))
anchors = torch.cat(anchors, dim=1)
cls_preds = concat_preds(cls_preds)
cls_preds = cls_preds.reshape(
cls_preds.shape[0], -1, self.num_classes + 1)
bbox_preds = concat_preds(bbox_preds)
return anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds训练:
batch_size = 32
train_iter, _ = d2l.load_data_bananas(batch_size)
device, net = d2l.try_gpu(), TinySSD(num_classes=1)
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.2, weight_decay=5e-4)
#损失函数和评价函数
cls_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
bbox_loss = nn.L1Loss(reduction='none')
def calc_loss(cls_preds, cls_labels, bbox_preds, bbox_labels, bbox_masks):
batch_size, num_classes = cls_preds.shape[0], cls_preds.shape[2]
cls = cls_loss(cls_preds.reshape(-1, num_classes),
cls_labels.reshape(-1)).reshape(batch_size, -1).mean(dim=1)
bbox = bbox_loss(bbox_preds * bbox_masks,
bbox_labels * bbox_masks).mean(dim=1)
return cls + bbox
def cls_eval(cls_preds, cls_labels):
# 由于类别预测结果放在最后一维,argmax需要指定最后一维。
return float((cls_preds.argmax(dim=-1).type(
cls_labels.dtype) == cls_labels).sum())
def bbox_eval(bbox_preds, bbox_labels, bbox_masks):
return float((torch.abs((bbox_labels - bbox_preds) * bbox_masks)).sum())
#训练
num_epochs, timer = 20, d2l.Timer()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs],
legend=['class error', 'bbox mae'])
net = net.to(device)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 训练精确度的和,训练精确度的和中的示例数
# 绝对误差的和,绝对误差的和中的示例数
metric = d2l.Accumulator(4)
net.train()
for features, target in train_iter:
timer.start()
trainer.zero_grad()
X, Y = features.to(device), target.to(device)
# 生成多尺度的锚框,为每个锚框预测类别和偏移量
anchors, cls_preds, bbox_preds = net(X)
# 为每个锚框标注类别和偏移量
bbox_labels, bbox_masks, cls_labels = d2l.multibox_target(anchors, Y)
# 根据类别和偏移量的预测和标注值计算损失函数
l = calc_loss(cls_preds, cls_labels, bbox_preds, bbox_labels,
bbox_masks)
l.mean().backward()
trainer.step()
metric.add(cls_eval(cls_preds, cls_labels), cls_labels.numel(),
bbox_eval(bbox_preds, bbox_labels, bbox_masks),
bbox_labels.numel())
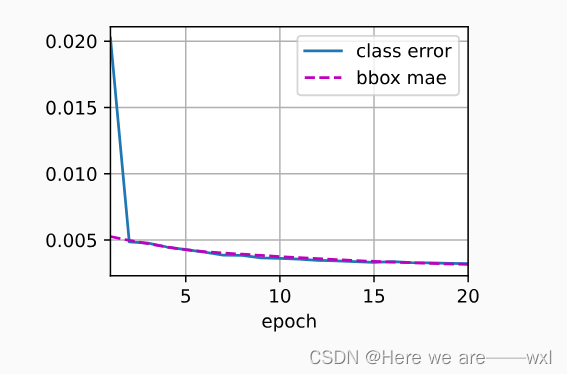
cls_err, bbox_mae = 1 - metric[0] / metric[1], metric[2] / metric[3]
animator.add(epoch + 1, (cls_err, bbox_mae))
print(f'class err {cls_err:.2e}, bbox mae {bbox_mae:.2e}')
print(f'{len(train_iter.dataset) / timer.stop():.1f} examples/sec on '
f'{str(device)}')结果: