异常语法详解
异常语法详解
- 一:异常的分类:
- 二:异常的处理
- 1:异常的抛出:throw
- 2:异常的声明:throws
- 3:try-catch捕获并处理异常
- 三:finally关键字
- 四:自定义异常类:
一:异常的分类:
1:编译时异常:在程序编译期间发生的异常,称为编译时异常,也称受查异常。
2:运行时异常:在程序执行期间发生的异常,称为运行时异常,也称非受查异常。RunTimeException以及子类构成的异常,都称为运行时异常。
编译时出现的语法错误,不能称为异常。比如拼写错误关键字。
二:异常的处理
1:异常的抛出:throw
在Java中,使用throw将异常抛出,将错误信息告知给调用者。
注意:
1:throw 必须写在方法的内部
2:抛出的对象必须是Exception或者是Exception的子类对象
3:如果抛出的是RunTimeException,或者是RunTimeException的子类,则可以不处理,直接交给JVM来处理
4:异常一旦抛出,其后的代码就不会再执行 。
举例说明:
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array){
if(array==null){
throw new NullPointerException();//throw关键字来抛出运行时异常
System.out.println("异常");//异常抛出,该句代码不会再执行
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//此时fun()的调用者main()对异常也没有处理,将交给JVM来处理
int[] array=null;
fun(array);
}
}
5:如果抛出的是编译时异常,用户必须处理,否则无法通过编译。
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
if(array==null){
throw new CloneNotSupportedException();//受查异常,必须处理,但可以通过throws关键字声明,交给调用者处理
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
int[] array=null;
fun(array);//该调用者main()也没有处理,但也通过throws声明了,此时将交给JVM来处理
}
}
2:异常的声明:throws
处在方法声明时的参数列表之后,当方法中抛出已换成那个时,用户不想处理该异常,就可以通过throws将异常抛给方法的调用者来处理。
当前方法不处理,交给该方法的调用者来处异常
注意:
1:throws必须跟在方法的参数列表之后
2:声明的异常必须是Exception,或者是Exception的子类;
3:方法的内部如果出现了多个异常,throws之后必须跟多个异常类型,之间用逗号隔开,如果抛出的多个异常类型具有父子关系,直接声明父类即可。
4:调用声明抛出异常的方法时,调用者必须对该异常进行处理,或者继续使用Throws抛出。
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
if(array==null){
throw new CloneNotSupportedException();//受查异常,必须处理,但可以通过throws关键字声明,交给调用者处理
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException{
int[] array=null;
fun(array);//该调用者main()也没有处理,但也通过throws声明了,此时将交给JVM来处理
}
}
3:try-catch捕获并处理异常
throws并没有对异常进行真正的处理,而是将异常报告给抛出异常方法的调用者,由调用者来处理,如果想要对异常进行处理,就需要try-catch。
注意:
1:try块内抛出异常位置后的代码即将不会被执行;
2:如果抛出的异常与catch时的异常不匹配,即异常不会被成功捕获,也不会被处理,继续往外抛,直到JVM来处理
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array){
try{
System.out.println(array[10]);//抛出的是数组越界异常
System.out.println(10/0);//抛出的是算数异常
}catch (ArithmeticException e){//没有处理数组越界异常,将交给该方法的调用者来处理
//但该方法的调用者main()并没有处理,将交给JVM来处理
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("算数异常");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={1,2,3,4};
fun(array);
}
}
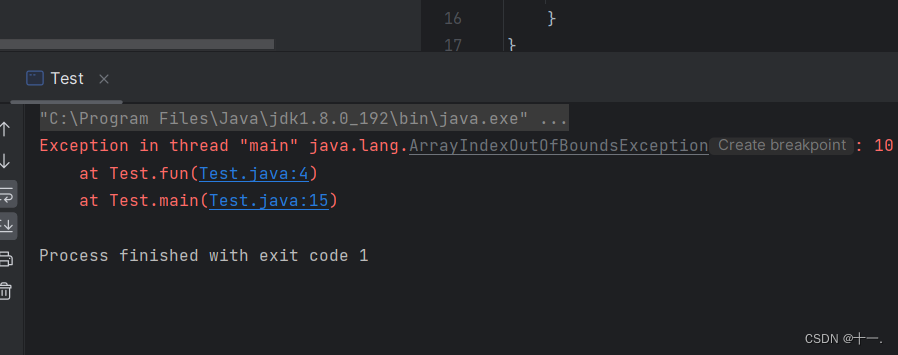
3:try中可能存在多个不同的异常对象,则必须通过多个catch来捕获异常
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array){
try{
System.out.println(array[10]);//抛出的是数组越界异常
System.out.println(10/0);//抛出的是算数异常
}catch (ArithmeticException e){//没有处理数组越界异常,将交给该方法的调用者来处理
//但该方法的调用者main()并没有处理,将交给JVM来处理
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("算数异常");
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("数组越界异常");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={1,2,3,4};
fun(array);
}
}
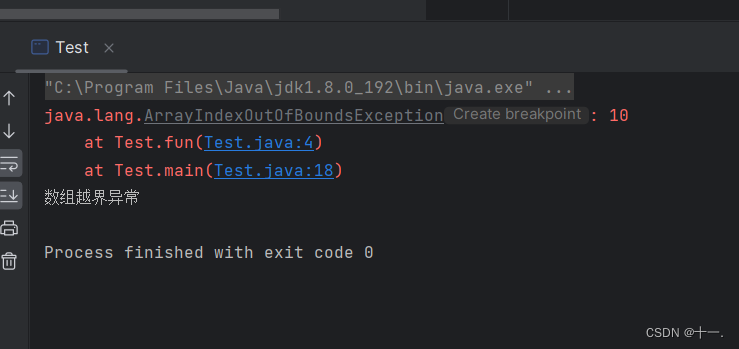
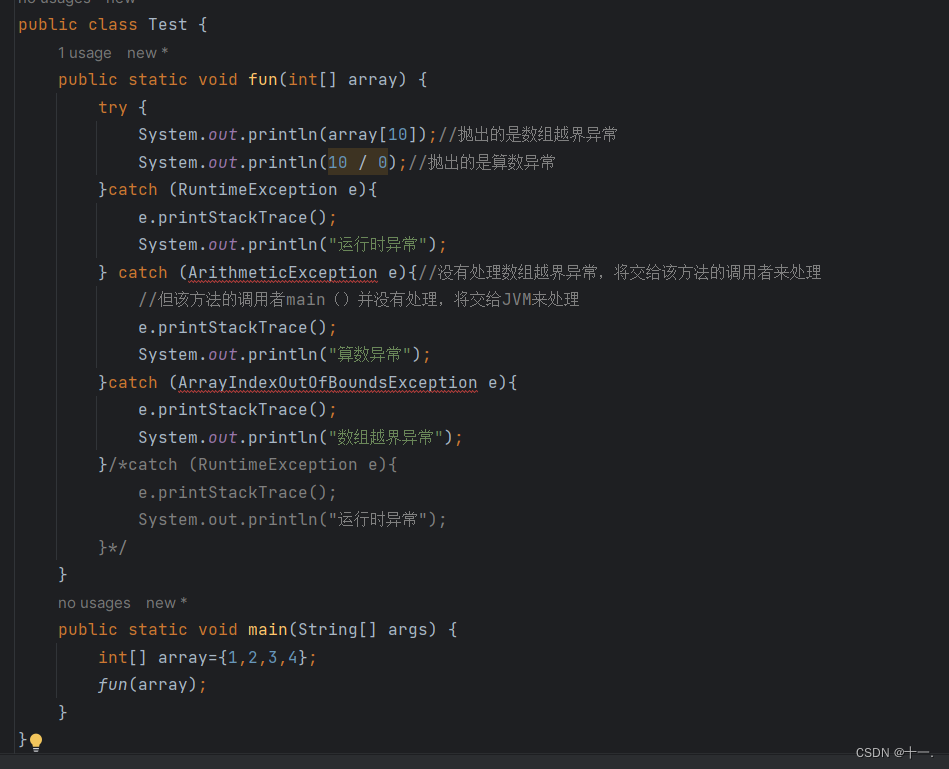
4:如果多个异常具有父子类关系,一定子类异常在前catch,父类异常在后catch ,否则语法错误。
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array) {
try {
System.out.println(array[10]);//抛出的是数组越界异常
System.out.println(10 / 0);//抛出的是算数异常
}/*catch (RuntimeException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("运行时异常");
}*/ catch (ArithmeticException e){//没有处理数组越界异常,将交给该方法的调用者来处理
//但该方法的调用者main()并没有处理,将交给JVM来处理
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("算数异常");
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("数组越界异常");
}catch (RuntimeException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("运行时异常");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={1,2,3,4};
fun(array);
}
}
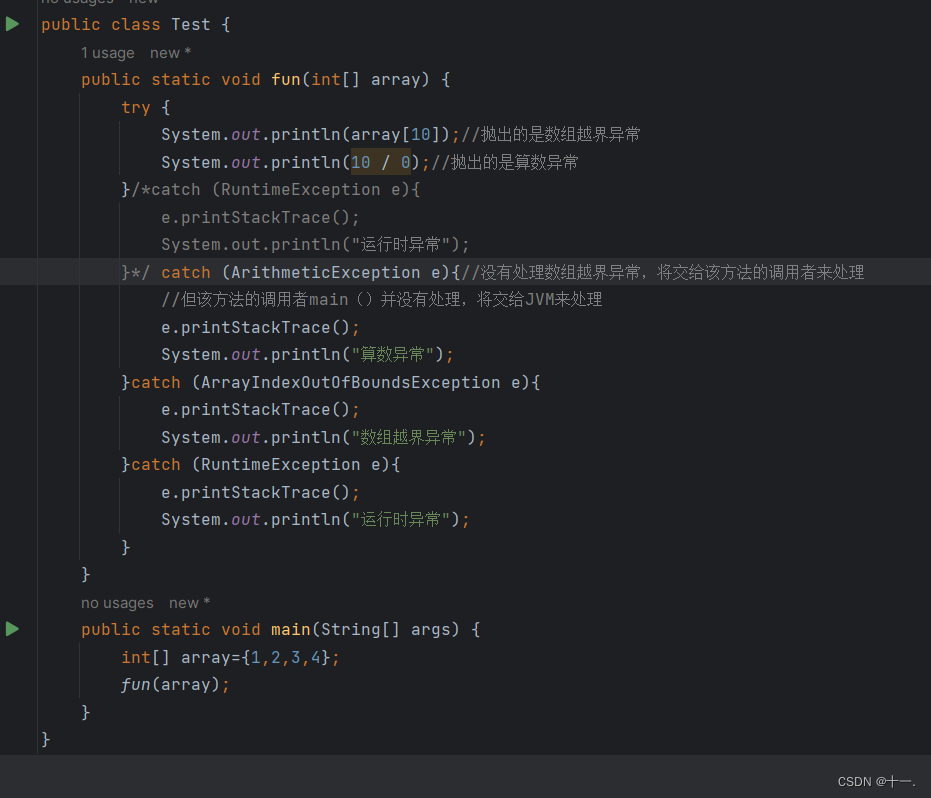
下面是错误代码:
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array) {
try {
System.out.println(array[10]);//抛出的是数组越界异常
System.out.println(10 / 0);//抛出的是算数异常
}catch (RuntimeException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("运行时异常");
} catch (ArithmeticException e){//没有处理数组越界异常,将交给该方法的调用者来处理
//但该方法的调用者main()并没有处理,将交给JVM来处理
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("算数异常");
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("数组越界异常");
}/*catch (RuntimeException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("运行时异常");
}*/
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={1,2,3,4};
fun(array);
}
}
三:finally关键字
在程序中有些特定的代码,不论程序是否发生异常,都需要被执行,比如程序中打开的资源:网站连接,数据库连接 ,IO流等,在程序正常或者异常退出时,必须对资源进行回收,此时必须使用finally来对资源进行回收。
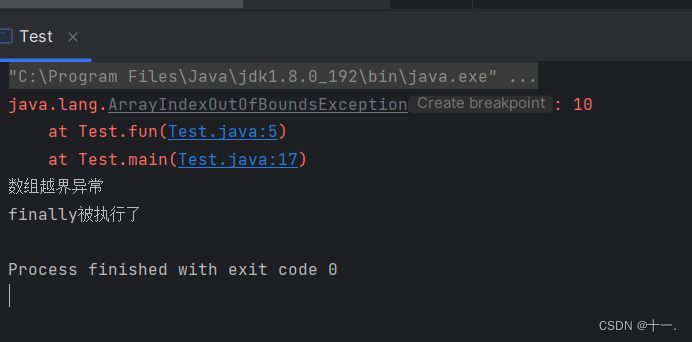
1:有异常出现时:finally会被执行
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array){
try{
System.out.println(array[10]);//存在数组越界异常
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("数组越界异常");
}finally{
System.out.println("finally被执行了");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={1,2,3,4,5};
fun(array);
}
}
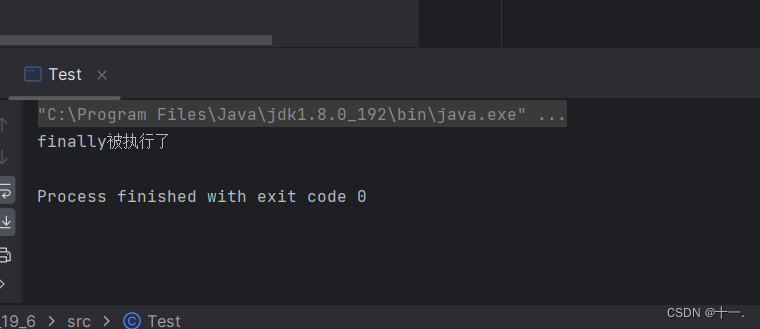
 2:当没有异常时,finally还会被执行
2:当没有异常时,finally还会被执行
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array){
try{
// System.out.println(array[10]);//存在数组越界异常
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("数组越界异常");
}finally{
System.out.println("finally被执行了");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={1,2,3,4,5};
fun(array);
}
}
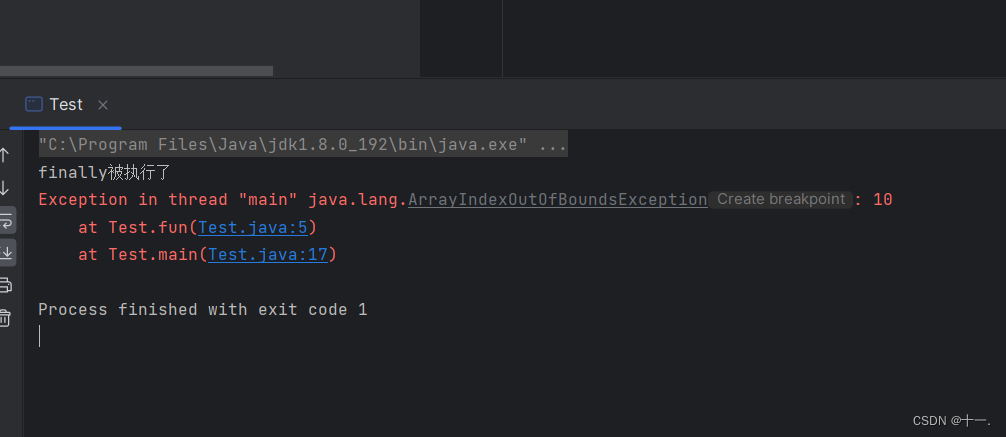
 3:异常没有被成功捕获,finally还是会被执行
3:异常没有被成功捕获,finally还是会被执行
public class Test {
public static void fun(int[] array){
try{
System.out.println(array[10]);//存在数组越界异常
}catch(ArithmeticException e){//捕获算数异常
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("算数异常");
}finally{
System.out.println("finally被执行了");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={1,2,3,4,5};
fun(array);
}
}
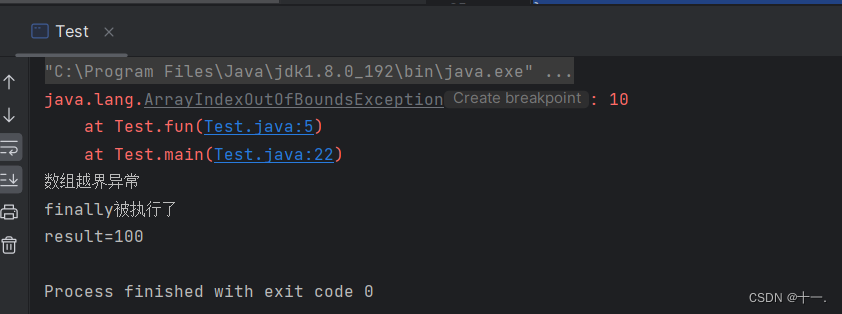
finally执行时机: finally一定会被执行,无论程序是否异常,finally执行的时机是方法返回之前(try或者catch中如果有return,会在这个return 之前执行finally),如果finally中也存在return语句,那么只会执行finally中的return,而不会执行try中的return。
public class Test {
public static int fun(int[] array){
try{
System.out.println(array[10]);//存在数组越界异常
return 10;
}catch(ArithmeticException e){//捕获算数异常
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("算数异常");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("数组越界异常");
return 20;
} finally{
System.out.println("finally被执行了");
return 100;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array={1,2,3,4,5};
int result=fun(array);
System.out.println("result="+result);
}
}
 【异常处理流程总结】
【异常处理流程总结】
1:程序先执行 try 中的代码
2:如果 try 中的代码出现异常, 就会结束 try 中的代码, 看和 catch 中的异常类型是否匹配.
3:如果找到匹配的异常类型, 就会执行 catch 中的代码
4:如果没有找到匹配的异常类型, 就会将异常向上传递到上层调用者.
5:无论是否找到匹配的异常类型, finally 中的代码都会被执行到(在该方法结束之前执行).
6:如果上层调用者也没有处理的了异常, 就继续向上传递
7:一直到 main 方法也没有合适的代码处理异常, 就会交给 JVM 来进行处理, 此时程序就会异常终止。
四:自定义异常类:
1:自定义异常类,然后继承来自Exception(默认是受查异常)或者来自RunTimeException(非受查异常)。
2:实现一个带String类型参数的构造方法,
参数含义:出现异常的原因
定义一个用户类,该用户有name,password两个成员变量:
public class Admin {
//定义一个用户类,该用户有name,password两个成员变量
public String name;
public String password;
public Admin(String name, String password) {
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
}
//登录方法
public void login(String name,String password) {
if (!(this.name.equals(name))) {
throw new NameException("用户名错误");
}
else if(!(this.password.equals(password))){
throw new PasswordException("密码错误");
}
else{
System.out.println("登录成功");
}
}
}
自定义 NameException 异常类,继承了RuntimeException:
public class NameException extends RuntimeException{
//自定义 NameException 异常类,继承了RuntimeException
public NameException() {
}
public NameException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
自定义PasswordException 异常类,继承了RuntimeException:
public class PasswordException extends RuntimeException{
//自定义PasswordException 异常类,继承了RuntimeException
public PasswordException() {
}
public PasswordException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
Test测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Admin admin=new Admin("Admin","123456");
try {
admin.login("admin","123456");
}catch (NameException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("用户名错误");
}catch (PasswordException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("密码错误");
}
}
}
