简单模拟 Spring 创建的动态代理类(解释一种@Transactional事务失效的场景)
模拟 Spring 创建的动态代理类
本文主要目的是从父类和子类继承的角度去分析为什么在 @Service 标注的业务类中使用 this 调用方法会造成事务失效。解释在这种情况下 this 为什么是原始类对象而不是代理类对象。
问题描述
在 @Service 标注的业务类中,如果调用本类中的方法,那么会造成事务失效。原因是因为事务的功能是 @Transactional 注解通过 AOP 切面的方式对原始类进行的增强,因此事务功能是代理类对象中的方法才具备的。
现在问题来了,在 CGLib 的动态代理模式中,代理类(假设为 UserServiceImplProxy)是继承了 UserServiceImpl,也就是说代理类是原始类的子类,而通过 Spring 容器的 getBean 方法获取到的也是代理类对象,那么在主方法中调用 userServiceImplProxy.transactionFailTest() 方法,那问题似乎变成了在父类中使用 this 关键字时,this 代表的是子类对象还是父类对象?
先说结论,this 代表的对象是不确定的。
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl;
public void transactionFailTest() {
System.out.println("this=" + this);
System.out.println("this.getClass()=" + this.getClass());
System.out.println("this.getClass().getSuperclass() = " + this.getClass().getSuperclass());
// 重点是探究this对象到底是什么?为什么this不是代理类对象
this.transactionTest();
}
public void transactionSuccessTest() {
// 调用代理类中的方法
userServiceImpl.transactionTest();
}
@Transactional
public void transactionTest() {
userMapper.updatePasswordById(1L, "111111");
// if (true) {
// throw new RuntimeException("故意制造异常");
// }
userMapper.updatePasswordById(2L, "222222");
}
}
继承关系中的方法调用
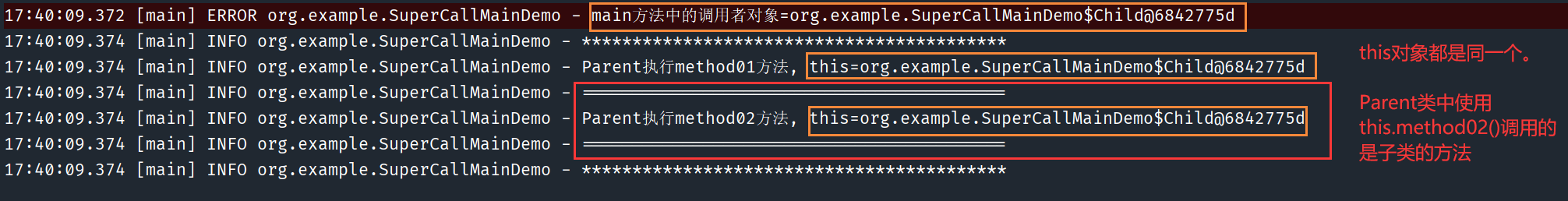
在下面的测试案例中,同样是在父类 Parent 中的方法中使用 this 关键字,而实际调用的是子类 Child 中的方法。这是因为 main 方法中方法的调用者就是一个 Child 对象,所以无论是 Parent 类还是 Child 类中的 this,都是指向该调用对象的地址。
/**
* 通过super调用父类方法
*/
@Slf4j
public class SuperCallMainDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent = new Child();
log.error("main方法中的调用者对象={}", parent);
parent.method01();
}
static class Child extends Parent {
@Override
public void method01() {
log.info("******************************************");
super.method01();
log.info("******************************************");
}
@Override
public void method02() {
log.info("==========================================");
super.method02();
log.info("==========================================");
}
}
static class Parent {
public void method01() {
log.info("Parent执行method01方法, this={}", this);
this.method02();
}
public void method02() {
log.info("Parent执行method02方法, this={}", this);
}
}
}
在继承中使用反射进行方法调用(模拟动态代理类逻辑)
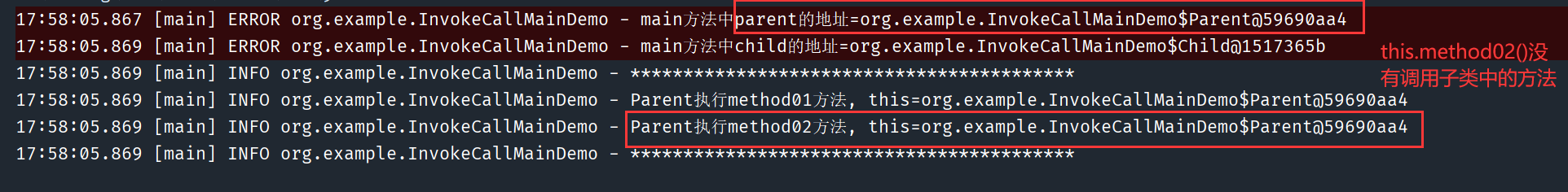
在下面的测试案例中,和 Spring 通过 CGLIB 动态代理生成的动态代理类的原理相同。虽然代理类是子类,但由于是动态生成的,所以没有办法通过 super 关键字来直接调用父类中的同名方法,因此即使拦截到父类中的方法 m1、m2,也还是需要通过 invoke 反射的方式进行调用。因此 this 关键字指向的是 invoke 方法传递过去的父类对象。
/**
* 通过反射调用父类方法
*/
@Slf4j
public class InvokeCallMainDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent = new Parent();
log.error("main方法中parent的地址={}", parent);
Parent child = new Child(parent, Parent.class);
log.error("main方法中child的地址={}", child);
child.method01();
}
static class Child extends Parent {
Parent target;
Class<?> clazz;
Method m1;
Method m2;
@SneakyThrows
public Child(Parent target, Class<?> clazz) {
this.target = target;
this.clazz = clazz;
// 这里模拟代理类拦截父类的所有方法
m1 = clazz.getMethod("method01");
m2 = clazz.getMethod("method02");
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void method01() {
log.info("******************************************");
// 实际上这里的方法是被拦截下来的
m1.invoke(target);
log.info("******************************************");
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void method02() {
log.info("==========================================");
m2.invoke(target);
log.info("==========================================");
}
}
static class Parent {
public void method01() {
log.info("Parent执行method01方法, this={}", this);
this.method02();
}
public void method02() {
log.info("Parent执行method02方法, this={}", this);
}
}
}
总结
- 无论是那种调用方式,
this都表示实际调用的那个对象,不会因为使用super关键字而被更改。 - 在反射调用方式中,通过
method.invoke(target)进行调用方法时,传递的对象就是 target,因此this表示的就是 target 对象。(动态代理类只能选择这种方式) - Spring 中的代理类会保存原始类对象,通过反射的方式去调用原始类中的方法。这里通过模拟的方式实际上代理类中除了继承隐式地保存一个原始类对象之外,还显式地保存了一个原始类对象,因为 super 并不能够和 this 一样可以独立作为一个对象引用来使用。
