共享模型之不可变
前言
该文章后续还需要进行修改!!
不可变的解释是对象属性不可以更改。
在多线程下,格式转化使用SimpleDateFormat可能会报错。这是因为线程之间互相影响导致。
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
Date parse = simpleDateFormat.parse("2003-6-03");
System.out.println(parse);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}多线程下安全格式转化
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
TemporalAccessor parse = dateTimeFormatter.parse("2003-06-03");
System.out.println(parse);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}不可变类的设计
以String为例
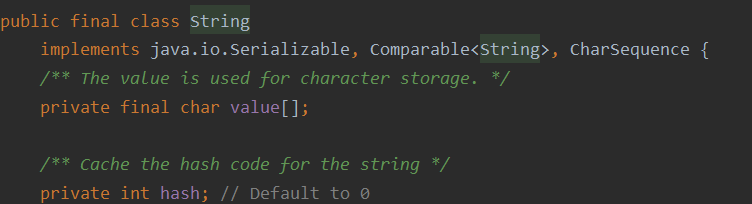
值使用char数组存储。hash是用来存储哈希值,第一次调用hashCode时存储在hash中做缓存。
- 属性使用final保证属性是只读,不可以发生更改
- 类使用final保证方法不能被覆盖,避免子类破坏不可变性
保护性拷贝
public String(char value[]) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
}这是String类中的构造方法。对于char数组,如果value引用参数地址的话,当外部char数组发生改变时,String对象中的值也跟着改变。因此要拷贝出一样的char数组让value来引用拷贝出来的地址。
类似于String类容易频繁创建对象,这时通常会用享元模式来减少对象的创建。JDK使用了享元模式的源码解析
DIY一个连接池
连接池作用是可以避免在高并发的情况下反复建立连接浪费系统性能,实现连接复用。基于享元模式实现的。
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
pool pool = new pool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
Connection connect = pool.getConnect();
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
pool.freeConnect(connect);
}).start();
}
}
}
public class pool {
//连接池大小
private final int poolSize;
//连接对象数组
private Connection[] connections;
//连接对象状态 0表示空闲。1是繁忙
private AtomicIntegerArray states;
public pool(int poolSize) {
this.poolSize = poolSize;
this.connections = new Connection[poolSize];
this.states = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[poolSize]);
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
connections[i] = new MyConnect("nameIs"+i);
}
}
//获取连接
public Connection getConnect(){
while (true){
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
if (states.get(i)==0){
if (states.compareAndSet(i,0,1)){
System.out.println("获取连接"+connections[i]);
return connections[i];
}
}
}
//如果没有空闲连接
synchronized (this){
try {
System.out.println("没有空闲连接");
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//释放连接
public void freeConnect(Connection connection){
//判断传过来的连接是否是连接池中的。
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
if (connections[i]==connection){
//因为只有一个线程拿到该连接,因此不会发生线程安全问题,直接使用set即可
states.set(i,0);
System.out.println("释放连接:"+connection);
synchronized (this){
this.notifyAll();
}
break;
}
}
}
}获取连接MyConnect{name='nameIs0'}
获取连接MyConnect{name='nameIs1'}
没有空闲连接
获取连接MyConnect{name='nameIs2'}
没有空闲连接
释放连接:MyConnect{name='nameIs0'}
获取连接MyConnect{name='nameIs0'}
没有空闲连接
释放连接:MyConnect{name='nameIs2'}
获取连接MyConnect{name='nameIs2'}
释放连接:MyConnect{name='nameIs0'}
释放连接:MyConnect{name='nameIs2'}
释放连接:MyConnect{name='nameIs1'}
