Netty网络编程
入门案例
1、服务器端代码
public class HelloServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、启动器,负责装配netty组件,启动服务器
new ServerBootstrap()
// 2、创建 NioEventLoopGroup,可以简单理解为 线程池 + Selector
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
// 3、选择服务器的 ServerSocketChannel 实现
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
// 4、child 负责处理读写,该方法决定了 child 执行哪些操作
// ChannelInitializer 处理器(仅执行一次)
// 它的作用是待客户端SocketChannel建立连接后,执行initChannel以便添加更多的处理器
.childHandler(
//channel 代表和客户端进行数据读写的通道,InitiaLizer 初始化,负责添加别的handler
new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel nioSocketChannel) throws Exception {
// 5、SocketChannel的处理器,使用StringDecoder解码,ByteBuf=>String
nioSocketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
// 6、SocketChannel的业务处理,使用上一个处理器的处理结果
//SimpleChannelInboundHandler 自定义的handler
nioSocketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>() {
@Override//读事件
protected void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, String s) throws Exception {
//打印上一步转换好的字符串
System.out.println(s);
}
});
}
// 7、ServerSocketChannel绑定8080端口
}).bind(8080);
}
}2、客户端代码
public class HelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Bootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
// 选择客户 Socket 实现类,NioSocketChannel 表示基于 NIO 的客户端实现
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
// ChannelInitializer 处理器(仅执行一次)
// 它的作用是待客户端SocketChannel建立连接后,执行initChannel以便添加更多的处理器
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
// 消息会经过通道 handler 处理,这里是将 String => ByteBuf 编码发出
channel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
// 指定要连接的服务器和端口
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080))
// Netty 中很多方法都是异步的,如 connect
// 这时需要使用 sync 方法等待 connect 建立连接完毕
.sync()
// 获取 channel 对象,它即为通道抽象,可以进行数据读写操作
.channel()
// 写入消并清空缓冲区,向客户端发送数据
.writeAndFlush("hello world");
}
}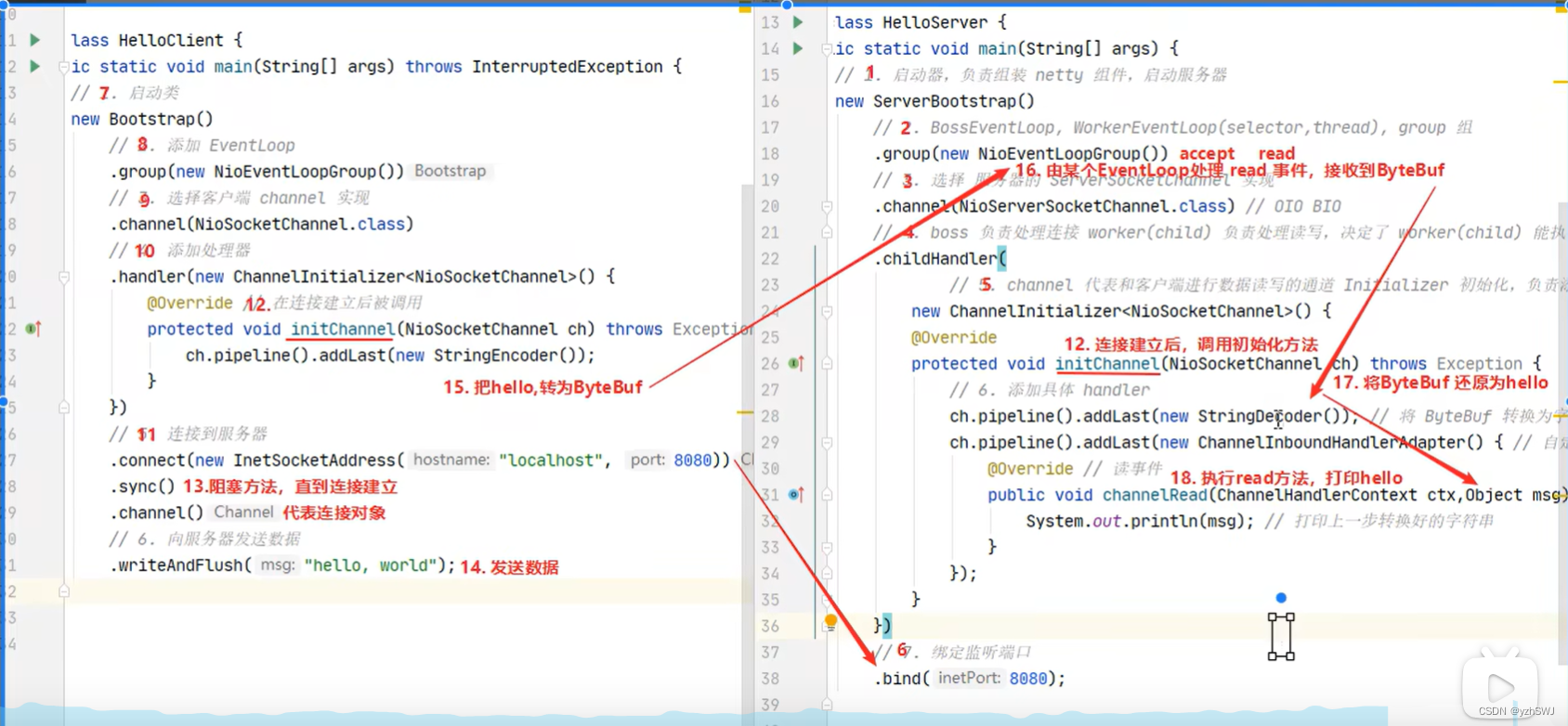
组件解释
- channel 可以理解为数据的通道
- msg 理解为流动的数据,最开始输入是 ByteBuf,但经过 pipeline 中的各个 handler 加工,会变成其它类型对象,最后输出又变成 ByteBuf
- handler 可以理解为数据的处理工序
- 工序有多道,合在一起就是 pipeline(传递途径),pipeline 负责发布事件(读、读取完成…)传播给每个 handler, handler 对自己感兴趣的事件进行处理(重写了相应事件处理方法)
- pipeline 中有多个 handler,处理时会依次调用其中的 handler
- handler 分 Inbound 和 Outbound 两类
- Inbound 入站
- Outbound 出站
- 工序有多道,合在一起就是 pipeline(传递途径),pipeline 负责发布事件(读、读取完成…)传播给每个 handler, handler 对自己感兴趣的事件进行处理(重写了相应事件处理方法)
- eventLoop 可以理解为处理数据的工人
- eventLoop 可以管理多个 channel 的 io 操作,并且一旦 eventLoop 负责了某个 channel,就会将其与channel进行绑定,以后该 channel 中的 io 操作都由该 eventLoop 负责
- eventLoop 既可以执行 io 操作,也可以进行任务处理,每个 eventLoop 有自己的任务队列,队列里可以堆放多个 channel 的待处理任务,任务分为普通任务、定时任务
- eventLoop 按照 pipeline 顺序,依次按照 handler 的规划(代码)处理数据,可以为每个 handler 指定不同的 eventLoop
三、组件
1、EventLoop
事件循环对象 EventLoop
EventLoop 本质是一个单线程执行器(同时维护了一个 Selector),里面有 run 方法处理一个或多个 Channel 上源源不断的 io 事件
它的继承关系如下
- 继承自 j.u.c.ScheduledExecutorService 因此包含了线程池中所有的方法
- 继承自 netty 自己的 OrderedEventExecutor
- 提供了 boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread) 方法判断一个线程是否属于此 EventLoop
- 提供了 EventLoopGroup parent() 方法来看看自己属于哪个 EventLoopGroup
事件循环组 EventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup 是一组 EventLoop,Channel 一般会调用 EventLoopGroup 的 register 方法来绑定其中一个 EventLoop,后续这个 Channel 上的 io 事件都由此 EventLoop 来处理(保证了 io 事件处理时的线程安全)
- 继承自 netty 自己的 EventExecutorGroup
- 实现了 Iterable 接口提供遍历 EventLoop 的能力
- 另有 next 方法获取集合中下一个 EventLoop
处理普通与定时任务
public class TestEventLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建拥有两个EventLoop的NioEventLoopGroup,对应两个线程
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2);
// 通过next方法可以获得下一个 EventLoop
System.out.println(group.next());
System.out.println(group.next());
// 通过EventLoop执行普通任务
group.next().execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " hello");
});
// 通过EventLoop执行定时任务
group.next().scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " hello2");
}, 0, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 优雅地关闭
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}输出结果如下
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@7bb11784 io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop@33a10788
nioEventLoopGroup-2-1 hello
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 hello2
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 hello2
nioEventLoopGroup-2-2 hello2
关闭 EventLoopGroup
优雅关闭 shutdownGracefully 方法。该方法会首先切换 EventLoopGroup 到关闭状态从而拒绝新的任务的加入,然后在任务队列的任务都处理完成后,停止线程的运行。从而确保整体应用是在正常有序的状态下退出的
处理IO任务
服务器代码
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}客户端代码
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Channel channel = new Bootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080))
.sync()
.channel();
System.out.println(channel);
// 此处打断点调试,调用 channel.writeAndFlush(...);
System.in.read();
}
}分工
Bootstrap的group()方法可以传入两个EventLoopGroup参数,分别负责处理不同的事件
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
// 两个Group,第一个负责Accept连接事件,第二个负责读写事件
//默认可以不用传 第一个还是1 第二个是电脑核心线程*2
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(1), new NioEventLoopGroup(2))
...
}
} 多个客户端分别发送 hello 结果
nioEventLoopGroup-3-1 hello1
nioEventLoopGroup-3-2 hello2
nioEventLoopGroup-3-1 hello3
nioEventLoopGroup-3-2 hello4
nioEventLoopGroup-3-2 hello4
可以看出,一个EventLoop可以负责多个Channel,且EventLoop一旦与Channel绑定,则一直负责处理该Channel中的事件
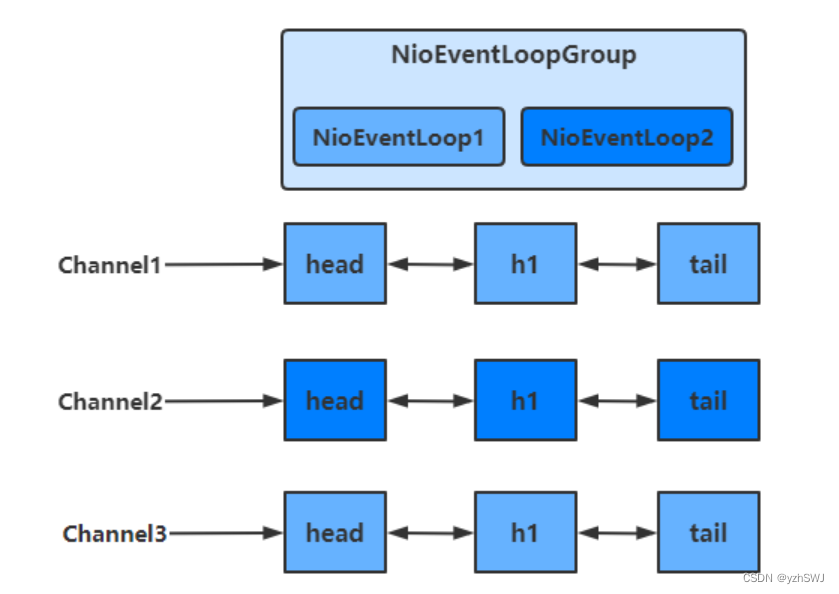
增加自定义EventLoopGroup
当有的任务需要较长的时间处理时,可以使用非NioEventLoopGroup,避免同一个NioEventLoop中的其他Channel在较长的时间内都无法得到处理
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 增加自定义的非NioEventLoopGroup 独立的EventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup();
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(1), new NioEventLoopGroup(2))
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
// 增加两个handler,第一个使用NioEventLoopGroup处理,第二个使用自定义EventLoopGroup处理
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("nioHandler",new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 将消息传给下一个handler
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
})
// 该handler绑定自定义的Group线程
.addLast(group, "myHandler", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}启动四个客户端发送数据
nioEventLoopGroup-4-1 hello1
defaultEventLoopGroup-2-1 hello1
nioEventLoopGroup-4-2 hello2
defaultEventLoopGroup-2-2 hello2
nioEventLoopGroup-4-1 hello3
defaultEventLoopGroup-2-3 hello3
nioEventLoopGroup-4-2 hello4
defaultEventLoopGroup-2-4 hello4
可以看出,客户端与服务器之间的事件,被nioEventLoopGroup和defaultEventLoopGroup分别处理
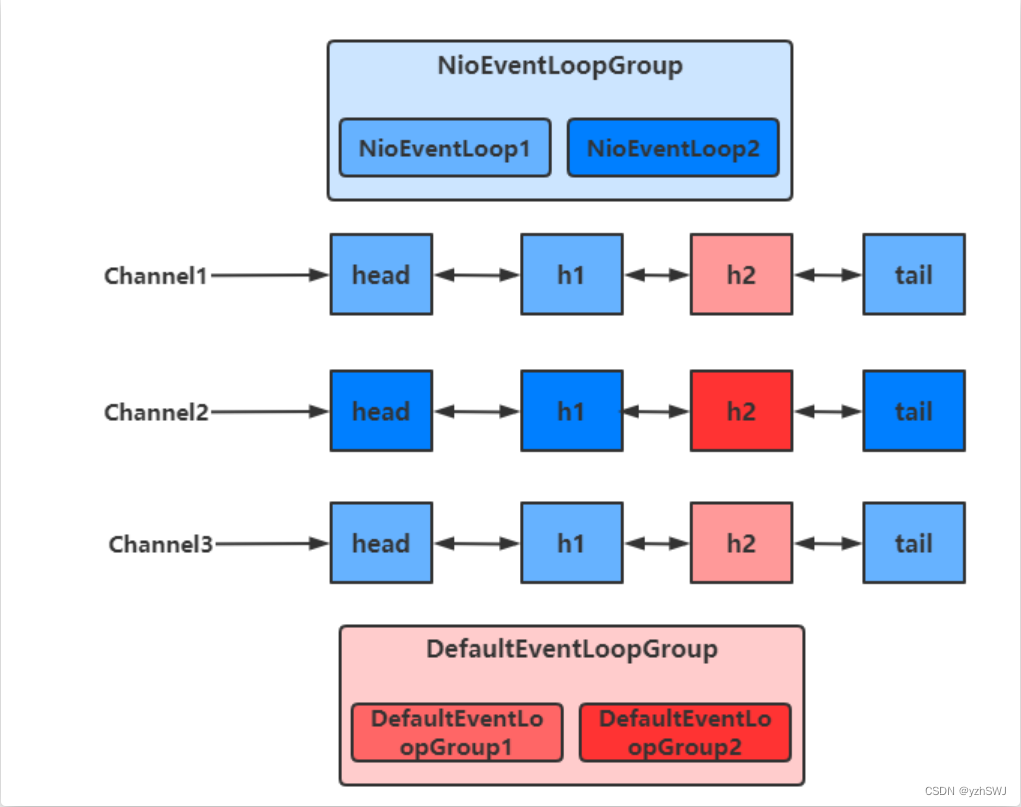
切换的实现
不同的EventLoopGroup切换的实现原理如下
由上面的图可以看出,当handler中绑定的Group不同时,需要切换Group来执行不同的任务
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {
final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);
// 获得下一个EventLoop, excutor 即为 EventLoopGroup
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
// 如果下一个EventLoop 在当前的 EventLoopGroup中
//当前header中的线程是否和EventLoop是同一线程
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
// 使用当前 EventLoopGroup 中的 EventLoop 来处理任务
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
} else {
// 否则让另一个 EventLoopGroup 中的 EventLoop 来创建任务并执行
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
});
}
}- 如果两个 handler 绑定的是同一个EventLoopGroup,那么就直接调用
- 否则,把要调用的代码封装为一个任务对象,由下一个 handler 的 EventLoopGroup 来调用
