二叉树的右视图[中等]
优质博文:IT-BLOG-CN
一、题目
给定一个二叉树的 根节点root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
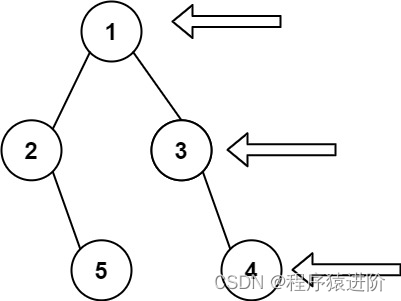
示例 1:
输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
示例 2:
输入: [1,null,3]
输出: [1,3]
示例 3:
输入: []
输出: []
二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[0,100]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
二、代码
由于树的形状无法提前知晓,不可能设计出优于O(n)的算法。因此,我们应该试着寻找线性时间解。带着这个想法,我们来考虑一些同等有效的方案。
【1】深度优先搜索: 我们对树进行深度优先搜索,在搜索过程中,我们总是先访问右子树。那么对于每一层来说,我们在这层见到的第一个结点一定是最右边的结点。这样一来,我们可以存储在每个深度访问的第一个结点,一旦我们知道了树的层数,就可以得到最终的结果数组。
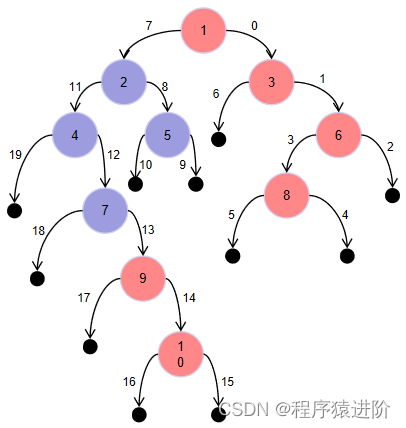
上图表示了问题的一个实例。红色结点自上而下组成答案,边缘以访问顺序标号。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, Integer> rightmostValueAtDepth = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
int max_depth = -1;
Deque<TreeNode> nodeStack = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Deque<Integer> depthStack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
nodeStack.push(root);
depthStack.push(0);
while (!nodeStack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeStack.pop();
int depth = depthStack.pop();
if (node != null) {
// 维护二叉树的最大深度
max_depth = Math.max(max_depth, depth);
// 如果不存在对应深度的节点我们才插入
if (!rightmostValueAtDepth.containsKey(depth)) {
rightmostValueAtDepth.put(depth, node.val);
}
nodeStack.push(node.left);
nodeStack.push(node.right);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
}
}
List<Integer> rightView = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int depth = 0; depth <= max_depth; depth++) {
rightView.add(rightmostValueAtDepth.get(depth));
}
return rightView;
}
}
时间复杂度: O(n)。深度优先搜索最多访问每个结点一次,因此是线性复杂度。
空间复杂度: O(n)。最坏情况下,栈内会包含接近树高度的结点数量,占用O(n)的空间。
【2】广度优先搜索: 我们可以对二叉树进行层次遍历,那么对于每层来说,最右边的结点一定是最后被遍历到的。二叉树的层次遍历可以用广度优先搜索实现。执行广度优先搜索,左结点排在右结点之前,这样,我们对每一层都从左到右访问。因此,只保留每个深度最后访问的结点,我们就可以在遍历完整棵树后得到每个深度最右的结点。除了将栈改成队列,并去除了rightmost_value_at_depth之前的检查外,算法没有别的改动。
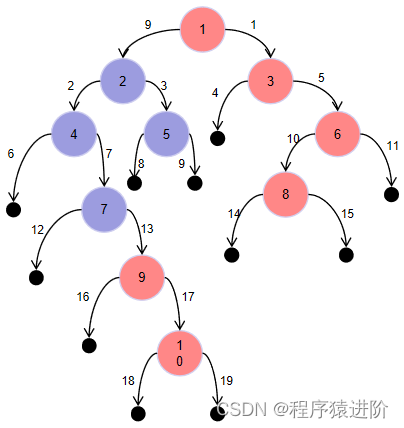
上图表示了同一个示例,红色结点自上而下组成答案,边缘以访问顺序标号。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
Map<Integer, Integer> rightmostValueAtDepth = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
int max_depth = -1;
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> depthQueue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
nodeQueue.add(root);
depthQueue.add(0);
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.remove();
int depth = depthQueue.remove();
if (node != null) {
// 维护二叉树的最大深度
max_depth = Math.max(max_depth, depth);
// 由于每一层最后一个访问到的节点才是我们要的答案,因此不断更新对应深度的信息即可
rightmostValueAtDepth.put(depth, node.val);
nodeQueue.add(node.left);
nodeQueue.add(node.right);
depthQueue.add(depth + 1);
depthQueue.add(depth + 1);
}
}
List<Integer> rightView = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int depth = 0; depth <= max_depth; depth++) {
rightView.add(rightmostValueAtDepth.get(depth));
}
return rightView;
}
}
时间复杂度: O(n)。每个节点最多进队列一次,出队列一次,因此广度优先搜索的复杂度为线性。
空间复杂度: O(n)。每个节点最多进队列一次,所以队列长度最大不不超过n,所以这里的空间代价为O(n)。
